中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 668-673.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2996
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
调控水通道蛋白表达延缓膝骨关节炎模型大鼠软骨退变
刘 欣1,颜飞华2,洪坤豪1
- 1广东省第二中医院骨伤一科,广东省广州市 510405;2喀什地区第一人民医院关节骨科,新疆维吾尔自治区喀什市 844000
Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis
Liu Xin1, Yan Feihua2, Hong Kunhao1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Guangdong Second Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, First People’s Hospital of Kashi, Kashi 844000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
水通道蛋白:是一种位于细胞膜上的蛋白质(内在膜蛋白),在细胞膜上组成“孔道”,可控制水在细胞的进出,就像是“细胞的水泵”一样。
p38 MAPK信号通路:p38 MAPK在正常软骨细胞生理及骨关节炎病理进程中起重要的调控作用。p38 MAPK可调控软骨细胞增殖、生存,调控细胞外基质代谢平衡,在基质金属蛋白酶、促炎症因子等导致的骨关节炎软骨退变病理进程中具有关键作用。
背景:下调水通道蛋白表达能延缓膝骨关节炎软骨退变,但其具体机制不明确。
目的:探讨p38 MAPK信号通路调控水通道蛋白表达对大鼠膝骨关节炎软骨退变的影响。
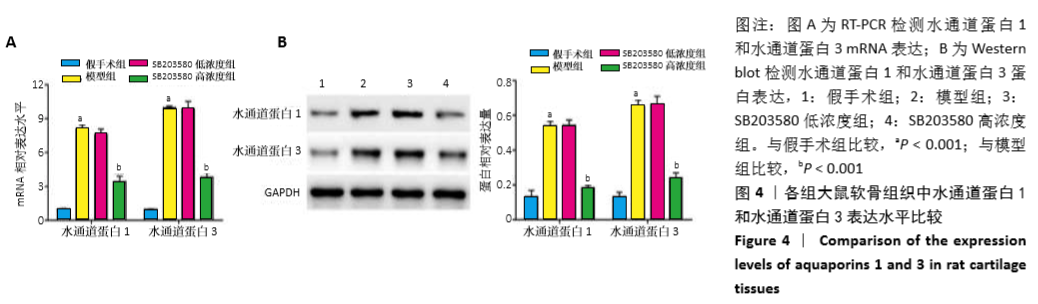
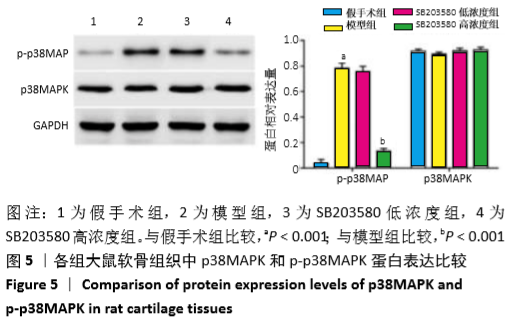
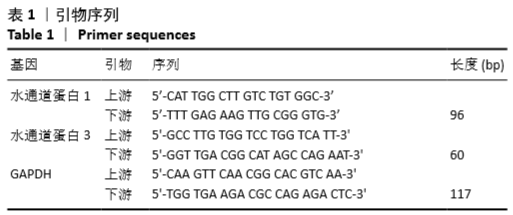
方法:60只SD大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组、SB203580低浓度组(7.5 mg/kg)和SB203580高浓度组(30 mg/kg),每组15只。除假手术组外其余3组均采用改良Hulth法构建大鼠膝骨关节炎模型;假手术组大鼠仅从右膝关节内侧打开关节腔,不破坏韧带和半月板,并保留关节软骨面。SB203580低、高浓度组大鼠于术后1周开始腹腔注射不同浓度p38 MAPK抑制剂SB203580进行干预;假手术组和模型组大鼠膝关节注射等体积生理盐水,1次/周,共8周。测量各组大鼠膝骨关节肿胀程度;苏木精-伊红染色观察大鼠软骨组织病理改变并进行Mankin′s评分;ELISA检测大鼠滑膜组织中白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和基质金属蛋白酶13表达水平;RT-PCR检测软骨组织中水通道蛋白1、水通道蛋白3 mRNA水平;Western blot检测软骨组织中水通道蛋白1、水通道蛋白3、cleaved-caspase-3、Bax、Bcl-2、p38MAPK和p-p38MAPK等蛋白表达水平。实验方案经广东省第二中医院动物实验伦理委员会批准(批准号为20180125004)。
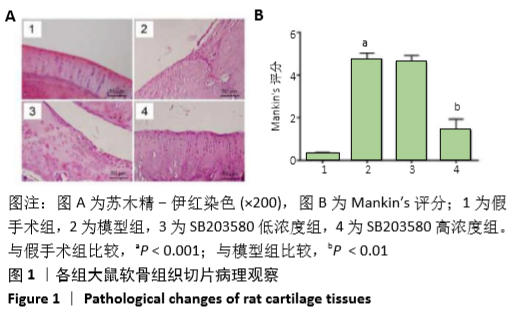
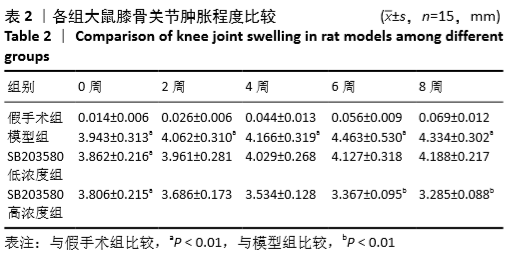
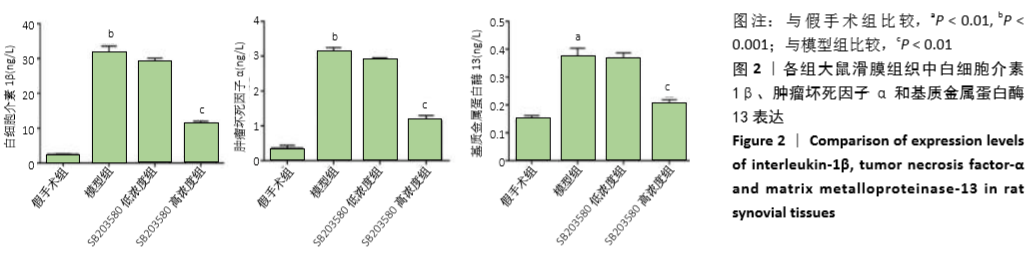
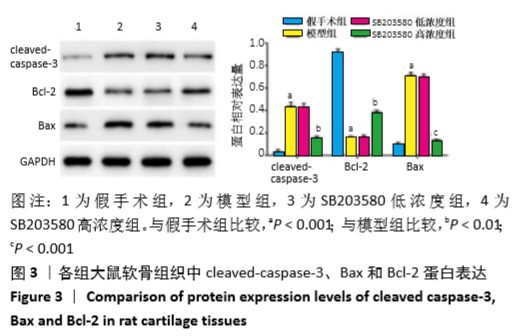
结果与结论:①与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠软骨组织损伤严重,Mankin′s评分及骨关节肿胀度显著增加(P < 0.05);滑膜组织中细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和基质金属蛋白酶13水平、软骨组织中cleaved-caspase-3、Bax和p-p38MAPK蛋白表达及水通道蛋白1、水通道蛋白3的mRNA和蛋白表达均显著上升(P < 0.05),而Bcl-2蛋白表达水平显著降低(P < 0.05);②与模型组比较,SB203580高浓度组大鼠软骨组织损伤得到明显改善,Mankin′s评分、骨关节肿胀度、滑膜组织中白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和基质金属蛋白酶13水平、软骨组织中cleaved-caspase-3、Bax和p-p38MAPK蛋白表达及水通道蛋白1、水通道蛋白3的mRNA和蛋白表达均显著降低(P < 0.05),而Bcl-2蛋白表达显著增加(P < 0.05);③SB203580低浓度组与模型组比较,相关指标差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④结果推测,阻断p38MAPK信号通路,可通过抑制水通道蛋白1和水通道蛋白3表达从而延缓膝骨关节炎关节软骨退变。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1418-3763 (刘欣)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: