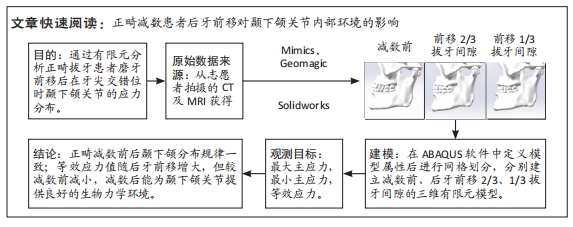
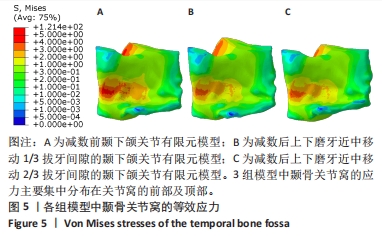
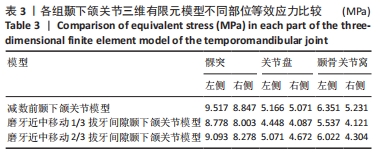
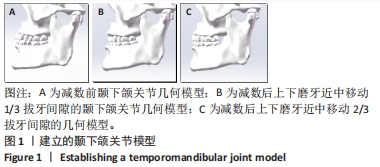
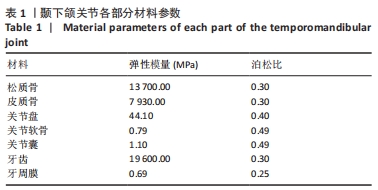
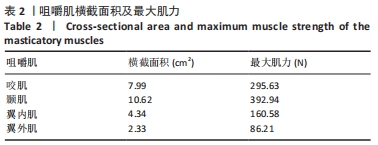
[1] 吕儒雅,尹艳娇,刘海霞,等.三维有限元分析成人安氏Ⅱ~1类患者单颌拔牙矫治后颞下颌关节的应力分布[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(36):5763-5768.
[2] 高博韬,刘奕.正畸联合多学科治疗颞下颌关节紊乱病的研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2023,16(4):398-401.
[3] 郑博文,刘奕.颞下颌关节紊乱病与错(牙合)畸形特征的关系[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2023,16(2):139-142.
[4] SHU J, ZHANG Y, LIU Z. Biomechanical comparison of temporomandibular joints after orthognathic surgery before and after design optimization. Med Eng Phys. 2019;68:11-16.
[5] SHAO B, TENG H, DONG S, et al. Finite element contact stress analysis of the temporomandibular joints of patients with temporomandibular disorders under mastication. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022;213:106526.
[6] 周勤,高洁,张旭,等.成人女性正畸治疗后鼻唇沟处软组织变化的三维定量研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2021,37(2):237-241.
[7] 宁振娟,吕康波,王琳丹.拔牙矫治成年女性错(牙合)畸形对其侧貌的影响[J].中国美容医学,2022,31(11):153-156.
[8] 聂丹丹. 拔牙与非拔牙矫治对成人安氏Ⅰ类牙性前突患者正貌的影响[D].芜湖:皖南医学院,2019.
[9] Kanavakis G, Mehta N. The role of occlusal curvatures and maxillary arch dimensions in patients with signs and symptoms of temporomandibular disorders. Angle Orthod. 2014;84(1):96-101.
[10] 刘吉玥,刘奕.咬合调整对颞下颌关节紊乱病的影响[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2023,16(2):147-151+155.
[11] 李小梅.颞下颌关节紊乱病与患者咬合关系及相关因素分析[D].广州:广州医科大学,2021.
[12] Cifter ED. Effects of Occlusal Plane Inclination on the Temporomandibular Joint Stress Distribution: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Int J Clin Pract. 2022;2022:2171049.
[13] LI A, CHONG DYR, SHAO B, et al. An Improved Finite Element Model of Temporomandibular Joint in Maxillofacial System: Experimental Validation. Ann Biomed Eng. 2023. doi: 10.1007/s10439-022-03124-7.
[14] GAO W, LU J, GAO X, et al. Biomechanical effects of joint disc perforation on the temporomandibular joint: a 3D finite element study. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):943.
[15] ZHENG F, ZHU Y, GONG Y, et al. Variation in stress distribution modified by mandibular material property: a 3D finite element analysis. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2023;229:107310.
[16] FENG Y, SHU J, LIU Y, et al. Biomechanical analysis of temporomandibular joints during mandibular protrusion and retraction motions: A 3d finite element simulation. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021;208:106299.
[17] SHU J, MA H, LIU Y, et al. In vivo biomechanical effects of maximal mouth opening on the temporomandibular joints and their relationship to morphology and kinematics. J Biomech. 2022;141:111175.
[18] 刘梦超,吴信雷,林崇翔,等.颞下颌关节骨骼肌肉系统三维有限元模型的构建[J].医用生物力学,2015,30(2):118-124.
[19] 李爽,张洪宇,易周,等.单、双侧第二磨牙正锁(牙合)与颞下颌关节退行性关节病的CBCT研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2023,39(6):774-778.
[20] 张红.牙尖交错位紧咬牙时颞下颌关节应力分布的三维有限元研究[D].南京:南京医科大学,2006.
[21] 郭宏,刘洪臣,张润荃,等.正常颞下颌关节应力分布的三维有限元研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2004,20(3):134-137.
[22] MORI H, HORIUCHI S, NISHIMURA S, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cartilaginous tissues in human temporomandibular joint during prolonged clenching. Arch Oral Biol. 2010;55(11):879-886.
[23] BARRIENTOS E, PELAYO F, TANAKA E, et al. Effects of loading direction in prolonged clenching on stress distribution in the temporomandibular joint. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;112:104029.
[24] KOOLSTRA JH, TANAKA E. Tensile stress patterns predicted in the articular disc of the human temporomandibular joint. J Anat. 2009;215(4):411-416.
[25] TANAKA E, HIROSE M, KOOLSTRA JH, et al. Modeling of the effect of friction in the temporomandibular joint on displacement of its disc during prolonged clenching. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;66(3):462-468.
[26] SAVOLDELLI C, BOUCHARD PO, LOUDAD R, et al. Stress distribution in the temporo-mandibular joint discs during jaw closing: a high-resolution three-dimensional finite-element model analysis. Surg Radiol Anat. 2012;34(5):405-413.
[27] HATTORI-HARA E, MITSUI SN, MORI H, et al. The influence of unilateral disc displacement on stress in the contralateral joint with a normally positioned disc in a human temporomandibular joint: an analytic approach using the finite element method. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014;42(8):2018-2024.
[28] SCAPINO RP, OBREZ A, GREISING D. Organization and function of the collagen fiber system in the human temporomandibular joint disk and its attachments. Cells Tissues Organs. 2006;182(3-4):201-225.
[29] SHU J, TENG H, SHAO B, et al. Biomechanical responses of temporomandibular joints during the lateral protrusions: A 3D finite element study. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020;195:105671.
[30] SHU J, MA H, JIA L, et al. Biomechanical behaviour of temporomandibular joints during opening and closing of the mouth: A 3D finite element analysis. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2020;36(8):e3373.
[31] 罗良语,刘钧.颞下颌关节动态三维有限元模型构建的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2022,38(8):715-717.
[32] KIM MR, GRABER TM, VIANA MA. Orthodontics and temporomandibular disorder: a meta-analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002;121(5):438-446.
[33] 石玲波,胡蓉,龙惠青,等.正畸减数治疗对成人颞下颌关节骨性结构的影响[J].中国药物与临床,2020,20(13):2109-2111.
[34] LAI L, HUANG C, ZHOU F, et al. Finite elements analysis of the temporomandibular joint disc in patients with intra-articular disorders. BMC Oral Health. 2020;20(1):93.
[35] KIJAK E, MARGIELEWICZ J, PIHUT M. Identification of Biomechanical Properties of Temporomandibular Discs. Pain Res Manag. 2020;2020:6032832.
[36] ZENO KG, MUSTAPHA S, AYOUB G, et al. Effect of force direction and tooth angulation during traction of palatally impacted canines: A finite element analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2020;157(3):377-384.
[37] KOOLSTRA JH, VAN EIJDEN TM. Consequences of viscoelastic behavior in the human temporomandibular joint disc. J Dent Res. 2007;86(12):1198-1202.
|