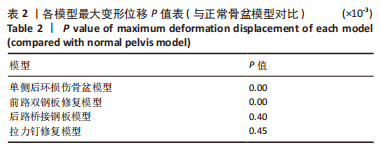
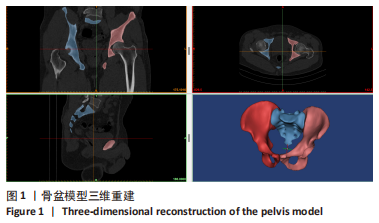
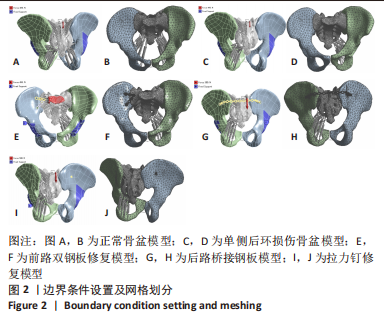
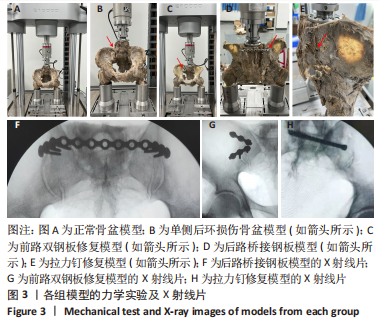
[1] TILE M, HELFET DL, KELLAMS JF. Fractures of the pelvis and acetabulum. 3rd Edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2003:131-167.
[2] 张少群,任茹霞,陈奕历,等.骶髂关节周围各韧带对骶髂关节稳定性的影响[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(5):500-506.
[3] 肖建德,王大平,陆伟,等.严重骨盆骨折的诊治[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006(1):31-33.
[4] 毕大卫,祖罡,韩雷,等.骨盆环不稳定性骨盆骨折的手术入路和内固定选择[J].中国骨伤,2017,30(3):213-216.
[5] 束晖,黄晓微.不同构型前路双钢板固定B、C型骶髂关节脱位的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(12):1810-1814.
[6] CHOY WS, KIM KJ, LEE SK, et al. Anterior pelvic plating and sacroiliac joint fixation in unstable pelvic ring injuries. Yonsei Med J. 2012;53(2): 422-426.
[7] 高加智,辛杰,王洪玉.不同桥接组合式内固定系统重建骨盆后环稳定性的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(4):342-348.
[8] METZ RM, BLEDSOE JG, MOED BR. Does posterior fixation of partially unstable open-book pelvic ring injuries decrease symphyseal plate failure? A biomechanical study. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32:18-24.
[9] QUEIPO-DE-LLANO A, PEREZ-BLANCA A, EZQUERRO F, et al. Simultaneous anterior and posterior compression of the pelvic ring with external fixation using a pre-tensed curved bar: A biomechanical study. Injury. 2013;44(12):1787-1792.
[10] 郑益钒,杨思宇,汪国栋,等.3D导航与C型臂X线机透视下经皮双节段长骶髂关节螺钉内固定治疗骨盆后环损伤的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2021,23(12):1037-1043.
[11] CAI L, ZHANG Y, ZHENG W, et al. A novel percutaneous crossed screws fixation in treatment of Day type II crescent fracture–dislocation: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Translat. 2020;20:37-46.
[12] VIGDORCHIK JM, JIN X, SETHI A, et al. A biomechanical study of standard posterior pelvic ring fixation versus a posterior pedicle screw construct. Injury. 2015;46(8):1491-1496.
[13] CAMINO WILLHUBER G, ZDERIC I, GRAS F, et al. Analysis of sacro-iliac joint screw fixation: does quality of reduction and screw orientation influence joint stability? A biomechanical study. Int Orthop. 2016;40(7): 1537-1543.
[14] LIU L, FAN S, CHEN Y, et al. Biomechanics of anterior ring internal fixation combined with sacroiliac screw fixation for Tile C3 pelvic fractures. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e915886.
[15] STUBY F M, DOEBELE S, AGARWAL Y, et al. Influence of flexible fixation for open book injury after pelvic trauma—a biomechanical study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2014;29(6):657-663.
[16] PATEL V, KOVALSKY D, MEYER SC, et al. Minimally invasive lateral transiliac sacroiliac joint fusion using 3D-printed triangular titanium implants. Medical Devices (Auckl). 2019;12:203-214.
[17] FREEMAN AL, BECHTOLD JE, POLLY DW. Biomechanical Stability of the Sacroiliac Joint with Differing Implant Configurations in a Synthetic Model. Int J Spine Surg. 2021;15(5):853-861.
[18] ZHANG L, PENG Y, DU C, et al. Biomechanical study of four kinds of percutaneous screw fixation in two types of unilateral sacroiliac joint dislocation: a finite element analysis. Injury. 2014;45(12):2055-2059.
[19] GONZÁLVEZ ÁL, REINA JM, LUIS PC, et al. Is cannulated-screw fixation an alternative to plate osteosynthesis in open book fractures? A biomechanical analysis. Injury. 2016;47:72-77.
[20] SHI D, WANG F, WANG D, et al. 3-D finite element analysis of the influence of synovial condition in sacroiliac joint on the load transmission in human pelvic system. Nat Rev Phys. 2014;36(6):745-753.
[21] HU P, WU T, WANG H, et al. Biomechanical comparison of three internal fixation techniques for stabilizing posterior pelvic ring disruption: a 3D finite element analysis. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(2):195-203.
[22] 胡畔. 三维有限元分析比较三种内固定物对骨盆后环损伤的治疗效果[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2017.
[23] YOON YC, MA DS, LEE SK, et al. Posterior pelvic ring injury of straddle fractures: Incidence, fixation methods, and clinical outcomes. Asian J Surg. 2021;44(1):59-65.
[24] 唐毓金,杨成亮,刘佳,等.骶髂关节脱位合并同侧骶骨翼骨折的手术方法及临床疗效评价[J].中华骨科杂志,2021,41(23):1692-1700.
[25] 高加智,王洪玉,辛茂源,等.经皮微创桥接组合式内固定系统治疗骨盆后环损伤[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(19):1794-1798.
[26] MITSUZAWA S, KUSAKABE K, NAKAO S, et al. Minimally invasive transiliac anatomical locking plate for posterior pelvic ring injury: a retrospective analysis of clinical outcomes and radiographic parameters for the gull wing plate. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):880.
[27] ZIRAN N, COLLINGE CA, SMITH W, et al. Trans-sacral screw fixation of posterior pelvic ring injuries: review and expert opinion. Patient Saf Surg. 2022;16(1):1-12.
[28] 杨锡明,于蕾,刘志.经皮空心钉固定骶髂关节脱位合并耻骨支骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(18):1642-1645.
[29] LU S, YANG K, LU C, et al. O-arm navigation for sacroiliac screw placement in the treatment for posterior pelvic ring injury. Int Orthops. 2021;45:1803-1810.
[30] 宗吉魁. 一种新型骶髂关节解剖接骨板治疗骶髂关节脱位的有限元分析[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2022.
[31] ZHANG W, YU C, DIARRA M, et al. Finite element analysis of sacral‐alar‐iliac screw fixation for sacroiliac joint dislocation. J Orthop Res. 2023. doi: 10.1002/jor.25525.
[32] LU Y, HE Y, LI W, et al. Comparison of biomechanical performance of five different treatment approaches for fixing posterior pelvic ring injury. J Healthc Eng. J Healthc Eng. 2020;2020:5379593.
|