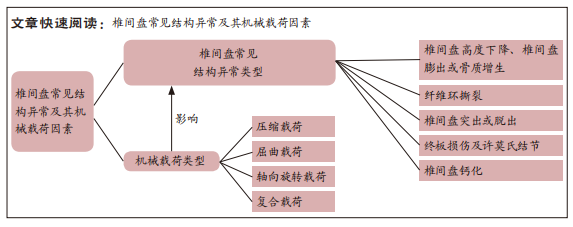
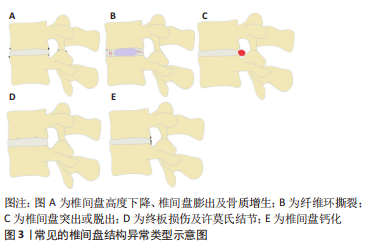
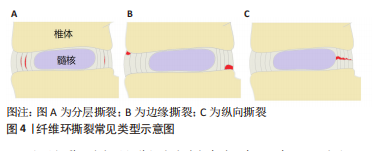
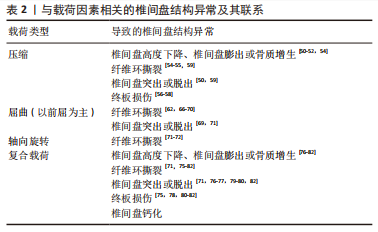
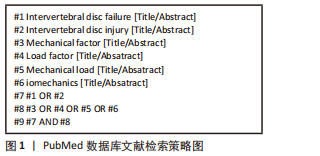
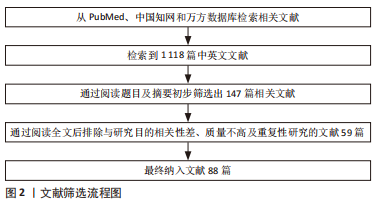
[1] NEIDLINGER-WILKE C, GALBUSERA F, PRATSINIS H, et al. Mechanical loading of the intervertebral disc: from the macroscopic to the cellular level. Eur Spine J. 2014;23 Suppl 3:S333-S343.
[2] AMIN DB, TAVAKOLI J, FREEMAN BJC, et al. Mechanisms of failure following simulated repetitive lifting: a clinically relevant biomechanical cadaveric study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(6):357-367.
[3] JO M, CHAE SW. Stress analysis of intervertebral disc during occupational activities. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021;208:106298.
[4] ROHLMANN A, PETERSEN R, SCHWACHMEYER V, et al. Spinal loads during position changes. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2012;27(8):754-758.
[5] LI JQ, KWONG WH, CHAN YL, et al. Comparison of in vivo intradiscal pressure between sitting and standing in human lumbar spine: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Life (Basel). 2022;12(3):457.
[6] STOKES IA, IATRIDIS JC. Mechanical conditions that accelerate intervertebral disc degeneration: overload versus immobilization. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(23):2724-2732.
[7] VERGROESEN PP, KINGMA I, EMANUEL KS, et al. Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: a vicious circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(7):1057-1070.
[8] HSIEH AH, TWOMEY JD. Cellular mechanobiology of the intervertebral disc: new directions and approaches. J Biomech. 2010;43(1):137-145.
[9] FRANCISCO V, PINO J, GONZÁLEZ-GAY MÁ, et al. A new immunometabolic perspective of intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022; 18(1):47-60.
[10] LAMA P, TEWARI J, ADAMS MA, et al. Degenerative physiochemical events in the pathological intervertebral disc. Histol Histopathol. 2022;37(1):11-20.
[11] GHEZELBASH F, SHIRAZI-ADL A, BAGHANI M, et al. On the modeling of human intervertebral disc annulus fibrosus: elastic, permanent deformation and failure responses. J Biomech. 2020;102:109463.
[12] GRUNHAGEN T, SHIRAZI-ADL A, FAIRBANK JC, et al. Intervertebral disk nutrition: a review of factors influencing concentrations of nutrients and metabolites. Orthop Clin North Am. 2011;42(4):465-477.
[13] FUJIWARA T, AKEDA K, YAMADA J, et al. Endplate and intervertebral disc injuries in acute and single level osteoporotic vertebral fractures: is there any association with the process of bone healing? BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):336.
[14] VERGROESEN PP, VAN DER VEEN AJ, VAN ROYEN BJ, et al. Intradiscal pressure depends on recent loading and correlates with disc height and compressive stiffness. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(11):2359-2368.
[15] STEFANAKIS M, LUO J, POLLINTINE P, et al. ISSLS Prize winner: Mechanical influences in progressive intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(17):1365-1372.
[16] MCMORRAN JG, GREGORY DE. The influence of axial compression on the cellular and mechanical function of spinal tissues; emphasis on the nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus: a review. J Biomech Eng. 2021;143(5):050802.
[17] RAVIKANTH R. Magnetic resonance evaluation of lumbar disc degenerative disease as an implication of low back pain: a prospective analysis. Neurol India. 2020;68(6):1378-1384.
[18] VIDEMAN T, BATTIÉ MC, GILL K, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging findings and their relationships in the thoracic and lumbar spine. Insights into the etiopathogenesis of spinal degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(8):928-935.
[19] POLLINTINE P, PRZYBYLA AS, DOLAN P, et al. Neural arch load-bearing in old and degenerated spines. J Biomech. 2004;37(2):197-204.
[20] DESMOULIN GT, PRADHAN V, MILNER TE. Mechanical aspects of intervertebral disc injury and implications on biomechanics. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(8):E457-E464.
[21] GOEL VK, MONROE BT, GILBERTSON LG, et al. Interlaminar shear stresses and laminae separation in a disc. Finite element analysis of the L3-L4 motion segment subjected to axial compressive loads. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20(6):689-698.
[22] SCHMIDT H, HEUER F, WILKE HJ. Dependency of disc degeneration on shear and tensile strains between annular fiber layers for complex loads. Med Eng Phys. 2009;31(6):642-649.
[23] OSTI OL, VERNON-ROBERTS B, MOORE R, et al. Annular tears and disc degeneration in the lumbar spine. A post-mortem study of 135 discs. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992;74(5):678-682.
[24] VERNON-ROBERTS B, MOORE RJ, FRASER RD. The natural history of age-related disc degeneration: the pathology and sequelae of tears. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(25):2797-2804.
[25] SENCK S, TRIEB K, KASTNER J, et al. Visualization of intervertebral disc degeneration in a cadaveric human lumbar spine using microcomputed tomography. J Anat. 2020;236(2):243-251.
[26] WANG W, PEI B, PEI Y, et al. Biomechanical effects of over lordotic curvature after spinal fusion on adjacent intervertebral discs under continuous compressive load. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2020;73:149-156.
[27] KRYSTKIEWICZ K, MAŚLANKA M, SKADORWA T, et al. Meningovertebral ligaments could be a barrier for migration of a herniated intervertebral disc: an anatomical study. Front Surg. 2022;9:969244.
[28] HEESWIJK VM, THAMBYAH A, ROBERTSON PA, et al. Posterolateral disc prolapse in flexion initiated by lateral inner annular failure: an investigation of the herniation pathway. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(21):1604-1613.
[29] ADAMS MA, ROUGHLEY PJ. What is intervertebral disc degeneration, and what causes it? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(18):2151-2161.
[30] LOTZ JC, FIELDS AJ, LIEBENBERG EC. The role of the vertebral end plate in low back pain. Global Spine J. 2013;3(3):153-164.
[31] MOK FP, SAMARTZIS D, KARPPINEN J, et al. ISSLS prize winner: prevalence, determinants, and association of Schmorl nodes of the lumbar spine with disc degeneration: a population-based study of 2449 individuals. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(21):1944-1952.
[32] VON FORELL GA, NELSON TG, SAMARTZIS D, et al. Changes in vertebral strain energy correlate with increased presence of Schmorl’s nodes in multi-level lumbar disk degeneration. J Biomech Eng. 2014;136(6): 061002.
[33] GIERS MB, MUNTER BT, EYSTER KJ, et al. Biomechanical and endplate effects on nutrient transport in the intervertebral disc. World Neurosurg. 2017;99:395-402.
[34] TOMASZEWSKI KA, ADAMEK D, KONOPKA T, et al. Endplate calcification and cervical intervertebral disc degeneration: the role of endplate marrow contact channel occlusion. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2015;74(1):84-92.
[35] ZEHRA U, BOW C, CHEUNG JPY, et al. The association of lumbar intervertebral disc calcification on plain radiographs with the UTE Disc Sign on MRI. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(5):1049-1057.
[36] SHAO J, YU M, JIANG L, et al. Differences in calcification and osteogenic potential of herniated discs according to the severity of degeneration based on Pfirrmann grade: a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:191.
[37] ZEHRA U, TRYFONIDOU M, IATRIDIS JC, et al. Mechanisms and clinical implications of intervertebral disc calcification. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022; 18(6):352-362.
[38] KRZYZANOWSKA AK, FRAWLEY RJ, DAMLE S, et al. Activation of nuclear factor-kappa B by TNF promotes nucleus pulposus mineralization through inhibition of ANKH and ENPP1. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):8271.
[39] ILLIEN-JÜNGER S, TORRE OM, KINDSCHUH WF, et al. AGEs induce ectopic endochondral ossification in intervertebral discs. Eur Cell Mater. 2016;32: 257-270.
[40] ZEHRA U, CHEUNG JPY, BOW C, et al. Spinopelvic alignment predicts disc calcification, displacement, and modic changes: evidence of an evolutionary etiology for clinically-relevant spinal phenotypes. JOR Spine. 2020;3(1):e1083.
[41] FONTES RBV, BAPTISTA JS, RABBANI SR, et al. Normal aging in human lumbar discs: An ultrastructural comparison. PLoS One. 2019;14(6):e0218121.
[42] JIN L, LIU Q, SCOTT P, et al. Annulus fibrosus cell characteristics are a potential source of intervertebral disc pathogenesis. PLoS One. 2014;9(5): e96519.
[43] FENG G, YANG X, SHANG H, et al. Multipotential differentiation of human anulus fibrosus cells: an in vitro study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(3):675-685.
[44] RUIZ WILLS C, FOATA B, GONZÁLEZ BALLESTER MÁ, et al. Theoretical explorations generate new hypotheses about the role of the cartilage endplate in early intervertebral disk degeneration. Front Physiol. 2018;9: 1210.
[45] HOFMANN UK, STEIDLE J, DANALACHE M, et al. Chondrocyte death after mechanically overloading degenerated human intervertebral disk explants is associated with a structurally impaired pericellular matrix. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(9):2000-2010.
[46] PAUL CP, SCHOORL T, ZUIDERBAAN HA, et al. Dynamic and static overloading induce early degenerative processes in caprine lumbar intervertebral discs. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e62411.
[47] GULLBRAND SE, PETERSON J, AHLBORN J, et al. ISSLS prize winner: dynamic loading-induced convective transport enhances intervertebral disc nutrition. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(15):1158-1164.
[48] QASIM M, NATARAJAN RN, AN HS, et al. Damage accumulation location under cyclic loading in the lumbar disc shifts from inner annulus lamellae to peripheral annulus with increasing disc degeneration. J Biomech. 2014; 47(1):24-31.
[49] 解志锋,刘清,刘冰,等.腰椎间盘疲劳损伤的生物力学特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(3):339-343.
[50] PAUL CP, DE GRAAF M, BISSCHOP A, et al. Static axial overloading primes lumbar caprine intervertebral discs for posterior herniation. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0174278.
[51] EMANUEL KS, VERGROESEN PP, PEETERS M, et al. Poroelastic behaviour of the degenerating human intervertebral disc: a ten-day study in a loaded disc culture system. Eur Cell Mater. 2015;29:330-341.
[52] ZHU LG, FENG MS, ZHAN JW, et al. Effect of static load on the nucleus pulposus of rabbit intervertebral disc motion segment in ex vivo organ culture. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016;129(19):2338-2346.
[53] POLLINTINE P, PRZYBYLA AS, DOLAN P, et al. Neural arch load-bearing in old and degenerated spines. J Biomech. 2004;37(2):197-204.
[54] WADE KR, SCHOLLUM ML, ROBERTSON PA, et al. ISSLS prize winner: vibration really does disrupt the disc: a microanatomical investigation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(15):1185-1198.
[55] WADE KR, ROBERTSON PA, THAMBYAH A, et al. “Surprise” loading in flexion increases the risk of disc herniation due to annulus-endplate junction failure: a mechanical and microstructural investigation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(12):891-901.
[56] ADAMS MA, DOLAN P. Intervertebral disc degeneration: evidence for two distinct phenotypes. J Anat. 2012;221(6):497-506.
[57] DUDLI S, ENNS-BRAY W, PAUCHARD Y, et al. Larger vertebral endplate concavities cause higher failure load and work at failure under high-rate impact loading of rabbit spinal explants. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;80:104-110.
[58] DOLAN P, LUO J, POLLINTINE P, et al. Intervertebral disc decompression following endplate damage: implications for disc degeneration depend on spinal level and age. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(17):1473-1481.
[59] VERES SP, ROBERTSON PA, BROOM ND. ISSLS prize winner: microstructure and mechanical disruption of the lumbar disc annulus: part II: how the annulus fails under hydrostatic pressure. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33(25):2711-2720.
[60] SETTON LA, CHEN J. Mechanobiology of the intervertebral disc and relevance to disc degeneration. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 2:52-57.
[61] PETERSSON M, ABBOTT A. Lumbar interspinous pressure pain threshold values for healthy young men and women and the effect of prolonged fully flexed lumbar sitting posture: an observational study. World J Orthop. 2020;11(3):158-166.
[62] WADE KR, ROBERTSON PA, THAMBYAH A, et al. How healthy discs herniate: a biomechanical and microstructural study investigating the combined effects of compression rate and flexion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(13):1018-1028.
[63] ALESSA F, NING X. Changes of lumbar posture and tissue loading during static trunk bending. Hum Mov Sci. 2018;57:59-68.
[64] MCGILL SM, BROWN S. Creep response of the lumbar spine to prolonged full flexion. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1992;7(1):43-46.
[65] PETERSSON M, ABBOTT A. Lumbar interspinous pressure pain threshold values for healthy young men and women and the effect of prolonged fully flexed lumbar sitting posture: an observational study. World J Orthop. 2020;11(3):158-166.
[66] SOLOMONOW M. Neuromuscular manifestations of viscoelastic tissue degradation following high and low risk repetitive lumbar flexion. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2012;22(2):155-175.
[67] GALE NC, ZEIGLER SL, TOWLER C, et al. Increased lumbar spinal column laxity due to low-angle, low-load cyclic flexion may predispose to acute injury. JOR Spine. 2018;1(4):e1038.
[68] GALLAGHER S, MARRAS WS, LITSKY AS, et al. Torso flexion loads and the fatigue failure of human lumbosacral motion segments. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(20):2265-2273.
[69] GALLAGHER S, MARRAS WS, LITSKY AS, et al. A comparison of fatigue failure responses of old versus middle-aged lumbar motion segments in simulated flexed lifting. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(17):1832-1839.
[70] SCHOLLUM ML, WADE KR, ROBERTSON PA, et al. A Microstructural Investigation of Disc Disruption Induced by Low Frequency Cyclic Loading. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(3):E132-E142.
[71] MARSHALL LW, MCGILL SM. The role of axial torque in disc herniation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2010;25(1):6-9.
[72] HARVEY-BURGESS M, GREGORY DE. The effect of axial torsion on the mechanical properties of the annulus fibrosus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019; 44(4):E195-E201.
[73] RONG X, LIU Z, WANG B, et al. The facet orientation of the subaxial cervical spine and the implications for cervical movements and clinical conditions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(6):E320-E325.
[74] 翁汭,叶林强,姚珍松,等.颈椎关节突关节矢状角不对称对颈椎间盘纤维环应力影响的三维有限元研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2022,32(2): 149-159.
[75] VERES SP, ROBERTSON PA, BROOM ND. The influence of torsion on disc herniation when combined with flexion. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(9): 1468-1478.
[76] AMIN DB, TAVAKOLI J, FREEMAN BJC, et al. Mechanisms of failure following simulated repetitive lifting: a clinically relevant biomechanical cadaveric study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(6):357-367.
[77] AMIN DB, MOAWAD CM, COSTI JJ. New findings confirm regional internal disc strain changes during simulation of repetitive lifting motions. Ann Biomed Eng. 2019;47(6):1378-1390.
[78] SHAN Z, WADE KR, SCHOLLUM ML, et al. A more realistic disc herniation model incorporating compression, flexion and facet-constrained shear: a mechanical and microstructural analysis. Part II: high rate or ‘surprise’ loading. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(10):2629-2641.
[79] CALLAGHAN JP, MCGILL SM. Intervertebral disc herniation: studies on a porcine model exposed to highly repetitive flexion/extension motion with compressive force. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2001;16(1):28-37.
[80] NOGUCHI M, GOOYERS CE, KARAKOLIS T, et al. Is intervertebral disc pressure linked to herniation? An in-vitro study using a porcine model. J Biomech. 2016;49(9):1824-1830.
[81] BERGER-ROSCHER N, CASAROLI G, RASCHE V, et al. Influence of complex loading conditions on intervertebral disc failure. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(2):E78-E85.
[82] WADE K, BERGER-ROSCHER N, RASCHE V, et al. Disc wall structural abnormalities can act as initiation sites for herniation. Eur Cell Mater. 2020; 40:227-238.
[83] SCHMIDT H, KETTLER A, HEUER F, et al. Intradiscal pressure, shear strain, and fiber strain in the intervertebral disc under combined loading. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(7):748-755.
[84] WANG Z, HUTTON WC, YOON ST. ISSLS Prize winner: effect of link protein peptide on human intervertebral disc cells. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38(17):1501-1507.
[85] HRISTOVA GI, JARZEM P, OUELLET JA, et al. Calcification in human intervertebral disc degeneration and scoliosis. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(12): 1888-1895.
[86] EYVAZOV K, SAMARTZIS D, CHEUNG JP. The association of lumbar curve magnitude and spinal range of motion in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):51.
[87] IATRIDIS JC, AP GWYNN I. Mechanisms for mechanical damage in the intervertebral disc annulus fibrosus. J Biomech. 2004;37(8):1165-1175.
[88] 祝永刚,孙旗,陈江,等. 退变椎间盘生物力学研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(15):1400-1404. |