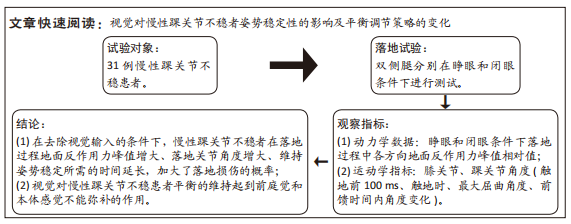
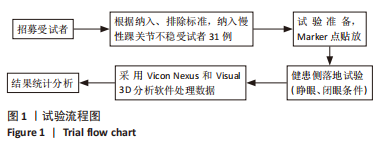
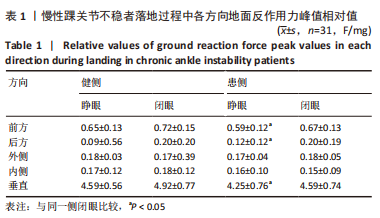
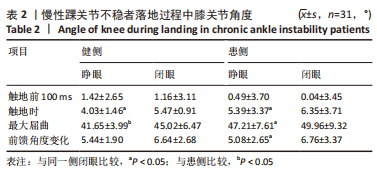
[1] ROOS KG, KERR ZY, MAUNTEL TC, et al. The Epidemiology of Lateral Ligament Complex Ankle Sprains in National Collegiate Athletic Association Sports.Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(1):201-209.
[2] FONG DT, CHAN YY, MOK KM, et al. Understanding acute ankle ligamentous sprain injury in sports.Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol. 2009;1:14.
[3] HAN S, LEE H, SON SJ, et al. The effects of visual feedback disruption on postural control with chronic ankle instability.J Sci Med Sport. 2022; 25(1):53-57.
[4] 覃华生, 潘玮敏, 李然, 等. 慢性踝关节不稳的运动康复:研究现状与特点[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(36):5865-5871.
[5] 张阳, 袁金风, 张秋霞, 等. 单侧功能性踝关节不稳者单腿下落过程的生物力学研究[J].北京体育大学学报,2014,37(8):87-91.
[6] 郝建源. 踝关节损伤的运动生物力学分析研究进展[J].当代体育科技,2022,12(16):155-158.
[7] LIEBERMANN DG, GOODMAN D. Pre-landing muscle timing and post-landing effects of falling with continuous vision and in blindfold conditions.J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2007;17(2):212-227.
[8] KE XH, HUANG DB, LI YY, et al. Effects of 12 weeks of Tai Chi Chuan intervention on the postural stability and self-reported instability in subjects with functional ankle instability: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Front Neurol. 2022;13:923669.
[9] GRIBBLE PA, DELAHUNT E, BLEAKLEY CM, et al. Selection criteria for patients with chronic ankle instability in controlled research: a position statement of the International Ankle Consortium.J Athl Train. 2014; 49(1):121-127.
[10] WIKSTROM EA, TILLMAN MD, BORSA PA. Detection of Dynamic Stability Deficits in Subjects with Functional Ankle Instability. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005;37(2):169-175.
[11] 张杰, 夏汶, 丁建伟, 等. 功能性踝关节不稳生物力学分析及康复训练研究进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(12):1337-1339.
[12] 王国栋, 毛晓锟, 张秋霞, 等. 功能性踝关节不稳者静态姿势控制中压力中心时域频域特征分析[J].中国运动医学杂志,2021,40(9): 691-697.
[13] SANTELLO M, MCDONAGH MJ, CHALLIS JH. Visual and non-visual control of landing movements in humans. J Physiol. 2001;537(Pt 1): 313-327.
[14] DE RIDDER R, WILLEMS T, VANRENTERGHEM J, et al. Multi-segment foot landing kinematics in subjects with chronic ankle instability. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2015;30(6):585-592.
[15] DOHERTY C, BLEAKLEY C, HERTEL J, et al. Single-leg drop landing movement strategies in participants with chronic ankle instability compared with lateral ankle sprain ‘copers’. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;24(4):1049-1059.
[16] GARRETT M, KERR T, CAULFIELD B. Phase-dependent inhibition of H-reflexes during walking in humans is independent of reduction in knee angular velocity. J Neurophysiol. 1999;82(2):747-753.
[17] BURCAL CJ, WIKSTROM EA. Plantar Cutaneous Sensitivity With and Without Cognitive Loading in People With Chronic Ankle Instability, Copers, and Uninjured Controls. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2016;46(4): 270-276.
[18] 吴一晗, 魏乔叶, 庞宇, 等. 功能性踝关节不稳本体感觉特征的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(18):2943-2952.
[19] MCKEON PO, BOOI MJ, BRANAM B, et al. Lateral ankle ligament anesthesia significantly alters single limb postural control.Gait Posture. 2010;32(3):374-377.
[20] MCKEON PO, STEIN AJ, INGERSOLL CD, et al. Altered plantar-receptor stimulation impairs postural control in those with chronic ankle instability. J Sport Rehabil. 2012;21(1):1-6.
[21] 王建国, 唐佳, 董继革, 等. 功能性踝关节不稳足底压力分析[J].中国康复理论与实践,2022,28(10):1217-1223.
[22] SONG K, BURCAL CJ, HERTEL J, et al. Increased Visual Use in Chronic Ankle Instability: A Meta-analysis.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2016;48(10): 2046-2056.
[23] HERTEL J. Sensorimotor deficits with ankle sprains and chronic ankle instability. Clin Sports Med. 2008;27(3):353-370.
[24] 宋法明, 王纯. 功能性踝关节不稳者斜面着地动作的生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(27):4380-4386.
[25] 章晨, 姜财, 郭进华, 等. 功能性踝关节不稳在不同运动下表面肌电的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2022,11(10):772-776.
[26] MINOONEJAD H, KARIMIZADEH ARDAKANI M, RAJABI R, et al. Hop Stabilization Training Improves Neuromuscular Control in College Basketball Players With Chronic Ankle Instability: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Sport Rehabil. 2019;28(6):576-583.
[27] SONG K, RHODES E, WIKSTROM EA. Balance Training Does Not Alter Reliance on Visual Information during Static Stance in Those with Chronic Ankle Instability: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2017;48(4):893-905.
[28] KOSIK KB, HOCH MC, HEEBNER NR, et al. A laboratory captured ‘giving way’ episode during a single-leg landing task in an individual with unilateral chronic ankle instability. J Biomech. 2019;90:153-158.
[29] CHIN M, LEPPANEN M, KULMALA JP, et al. A 3D motion capture analysis of a giving-way ankle episode during a 180-degree pivot turn: A case report. J Biomech. 2021;118:110318.
[30] CHU Y, SELL TC, ABT JP, et al. Air assault soldiers demonstrate more dangerous landing biomechanics when visual input is removed. Mil Med. 2012;177(1):41-47. |