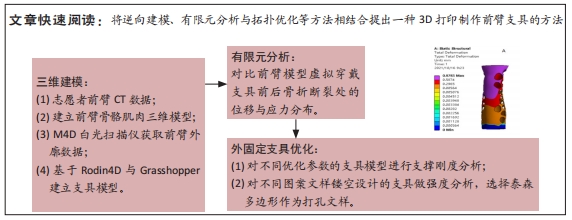
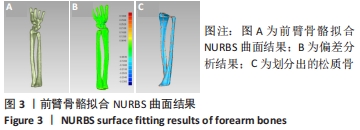
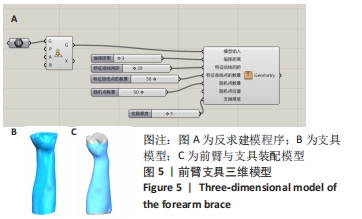
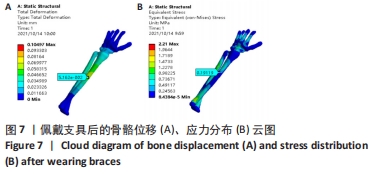
[1] 高军茂,王鹏程,孙鹏,等. 前臂骨折的治疗进展[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2011,20(3):383-385.
[2] HAMN MP, RICHTER D, MUHR G, et al. Forearm fractures in children Diagnosis, treatment, and possible complications. Der Unfallchirurg. 1997;100(10):760-769.
[3] LOOSE O, FERNANDEZ F, MORRISON S, et al. Treatment of nonunion after forearm fractures in children: a conservative approach. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2021;47(2):293-301.
[4] ELIA G, BLOOD T, GOT C. The Management of Pediatric Open Forearm Fractures. J Hand Surg. 2020;45(6):523-527.
[5] BARTOLOTTA R, DANIELS S, VERRET C, et al. Current Fixation Options for Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, and Hand Fractures. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2019;23(2):109-125.
[6] WU JC, LILLY R, VARA AD, et al. Posttraumatic Bifid Ulna in a Pediatric Galeazzi-Equivalent Forearm Fracture. J Hand Surg. 2018;44(9):802-801.
[7] 张妙林,高志朝,郑国富,等. 桡骨远端骨折闭合复位后再移位相关危险因素分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(3):44-47.
[8] CHA SM, SHIN HD. Risk factors for atypical forearm fractures associated with bisphosphonate usage. Injury. 2021;52(6):1423-1428.
[9] TRIVELLAS M, HENNRIKUS W, GUPTA R, et al. Waterproof Cast Liners for Pediatric Forearm Fractures — a Comparison of Two Products. Trauma. 2020;23(1):51-53.
[10] MUNTEANU A, CHITARIU D, CIOATA F. The FDM 3D Printing Application for Orthopedic Splints. Appl Mech Mater. 2015;809-810:375-380.
[11] JANZING HMJ, BESSEMS SAM, LIGHTHART MAP, et al. Treatment of dorsally dislocated distal radius fractures with individualized 3D printed bracing: an exploratory study. 3D Print Med. 2020;6(1):22.
[12] WEI Y, MAO D, XIAO BX, et al. Lightweight splint design for individualized treatment of distal radius fracture. J Med Syst. 2019;43(8):1-10.
[13] 曾焘,高大伟,吴宇峰,等. 小夹板结合3D打印支具外固定治疗Colles骨折[J].中国骨伤,2019,32(6):513-518.
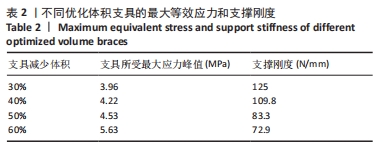
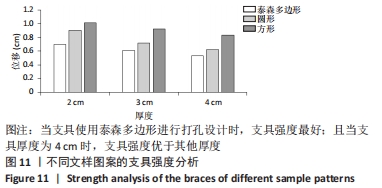
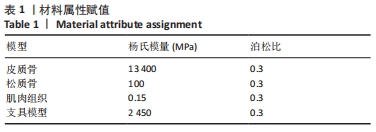
[14] 张朝驹, 何川, 陈洪卫,等. 基于有限元模型分析伸直型桡骨远端骨折的生物力学特点[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(12):1898-1902.
[15] BLAYA F, PEDRO PS, SILVA JL, et al. Design of an Orthopedic Product by Using Additive Manufacturing Technology: The Arm Splint. J Med Syst. 2018;42(3):54.
[16] 阎金刚,张吉利,王建新,等. 基于逆向技术医疗外固定支具的设计[J].工业技术与职业教育,2021,19(1):21-23.
[17] SANTONI BG, AIRA JR, DIZA MA, et al. Radiographic evaluation of acute distal radius fracture stability: a comparative cadaveric study between a thermo-formable bracing system and traditional fiberglass casting. Clin Biomech. 2017;47:20-26.
[18] 刘非,邱冰,薛向东,等. 基于3D打印技术的个性化外固定支具设计[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(24):2260-2263.
[19] 唐鹏程,朱英,赵敏珠,等. 肘关节有限元模型模拟碰撞损伤的生物力学特性分析[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2018,40(7):596-602.
[20] HIRASHIMA T, MATSUURA Y, TAKANE SD, et al. Long-term Evaluation Using Finite Element Analysis of Bone Atrophy Changes after Locking Plate Fixation of Forearm Diaphyseal Fracture. J Hand Surg Glob Online. 2021;3(5):240-244.
[21] HAMMER VB, OLHOFF N. Topology optimization of continuum structures subjected to pressure loading. Struct Multidiscip O. 2000;19(2):85-92.
[22] 钟环,欧阳汉斌,魏波,等. 桡骨远端骨折锁定钢板的拓扑优化及有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(23):2189-2194.
[23] CHEN YJ, HUI L, HUANG WH, et al. Application of 3D-printed and patient-specific cast for the treatment of distal radius fractures: initial experience. 3D Print Med. 2017;3(1):11.
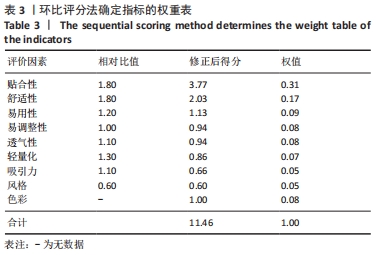
[24] 杜丹丹,胡惠惠,周芳, 等. 层次分析法在确定麻醉护理专业学位硕士核心能力评价指标权重中的应用[J].护士进修杂志,2021, 36(19):1755-1759+1766.
[25] 周晓宁. 腕关节三维有限元模型的建立及桡骨远端骨折发生机制的生物力学分析[D]. 北京:北京中医药大学,2014.
[26] LU PC, LIAO ZW, CHEN H, et al. Customized Three-Dimensional-Printed Orthopedic Close Contact Casts for the Treatment of Stable Ankle Fractures: Finite Element Analysis and a Pilot Study. ACS Omega. 2021; 6(4):3418-3426.
[27] DEATON JD, GRANDHI RV. A survey of structural and multidisciplinary continuum topology optimization: post 2000. Struct Multidiscip O. 2014;49(1):1-38.
[28] 阿依古丽•喀斯木, 乌日开西•艾依提, 滕勇,等. 基于3D打印的手指屈肌腱损伤定制化支具设计[J]. 机械设计与制造,2017,55(11): 215-219.
[29] 刘宁,刘宇,龚先政,等. 基于关联环比评分法的水足迹评价背景数据遴选模型研究[J].质量与认证,2021(6):65-68.
[30] CUI X, LIANG L, ZHANG HY, et al. The effectiveness and safety of plaster splint and splints for distal radius fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine. 2020;99(9):e19211.
[31] ZHANG YF, GUAN TM, GUO QG, et al. Digital design of personalized scoliosis orthopedic braces based on 3D printing technology. Chin J Tissue Eng Res. 2019;23(36):5824-5829.
[32] MASON-MACKAY AR, WHATMAN C, REID D, et al. The effect of ankle bracing on landing biomechanics in female netballers. Phys Ther Sport. 2016;20:13-18.
[33] HUA Z, WANG JW, LU ZF, et al. The biomechanical analysis of three-dimensional distal radius fracture model with different fixed splints. Technol Health Care. 2018;26(2):329-341.
[34] 魏成建,陶宝琛,张满臣,等. 动力气囊压垫纠正桡骨远端AO C3.1型骨折残余侧方移位的三维有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2018, 33(1):13-17.
[35] DESSERY Y, PALLARI J. Measurements agreement between low-cost and high-level handheld 3D scanners to scan the knee for designing a 3D printed knee brace. Plos One. 2018;13(4):e0196183.
|