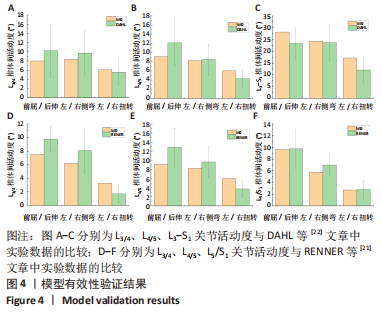
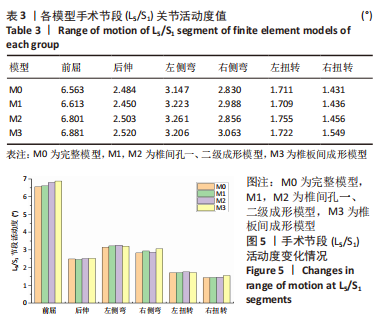
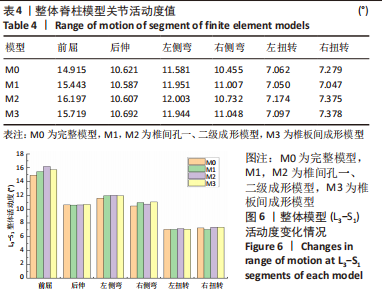
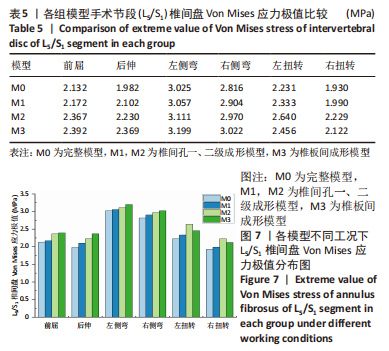
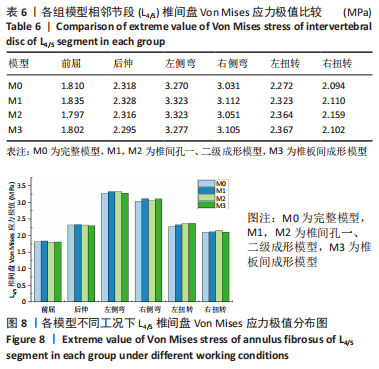
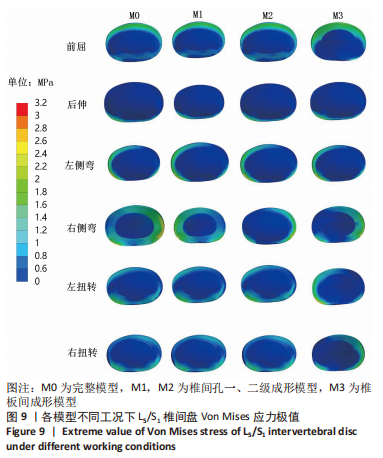
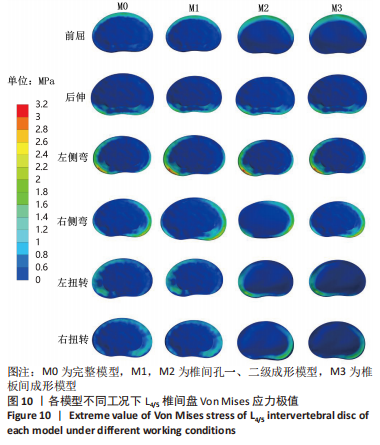
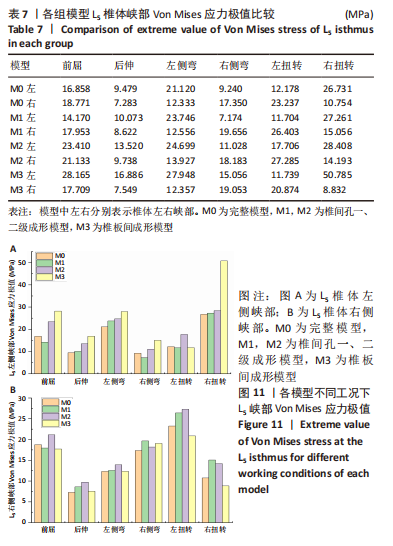
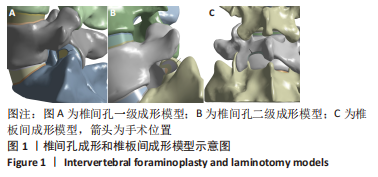
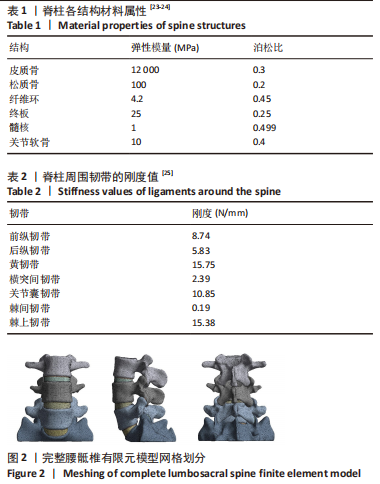
[1] GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016; 388(10053):1545-1602.
[2] HARTVIGSEN J, HANCOCK MJ, KONGSTED A, et al. What low back pain is and why we need to pay attention. Lancet. 2018;391(10137):2356-2367.
[3] WEBER H. Lumbar disc herniation. A controlled, prospective study with ten years of observation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1983;8(2):131-140.
[4] BENOIST M. The natural history of lumbar disc herniation and radiculopathy. Joint Bone Spine. 2002;69(2):155-160.
[5] DEYO RA, MIRZA SK. CLINICAL PRACTICE. Herniated Lumbar Intervertebral Disk. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(18):1763-1772.
[6] CHEN BL, GUO JB, ZHANG HW, et al. Surgical versus non-operative treatment for lumbar disc herniation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2018;32(2):146-160.
[7] KAMBIN P, SAMPSON S. Posterolateral percutaneous suction-excision of herniated lumbar intervertebral discs. Report of interim results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(207):37-43.
[8] KAMBIN P. Arthroscopic microdiskectomy. Mt Sinai J Med. 1991;58(2): 159-164.
[9] YEUNG AT. Minimally Invasive Disc Surgery with the Yeung Endoscopic Spine System (YESS). Surg Technol Int. 1999;8:267-277.
[10] HOOGLAND T, SCHUBERT M, MIKLITZ B, et al. Transforaminal posterolateral endoscopic discectomy with or without the combination of a low-dose chymopapain: a prospective randomized study in 280 consecutive cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(24):E890-E897.
[11] 李长青,周跃,王建,等.经皮椎间孔内窥镜下靶向穿刺椎间盘切除术治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(3):193-197.
[12] 张西峰,张琳.脊柱内镜技术的历史、现状与发展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2015,21(2):81-85.
[13] 李振宙,吴闻文,侯树勋,等.经皮腰椎间孔成形内窥镜下椎间盘切除术治疗腰椎间盘突出症的疗效观察[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2008,18(10): 752-756+801.
[14] LI ZZ, HOU SX, SHANG WL, et al. Percutaneous lumbar foraminoplasty and percutaneous endoscopic lumbar decompression for lateral recess stenosis through transforaminal approach: Technique notes and 2 years follow-up. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016;143:90-94.
[15] 蓝彬,柳达,周广平,等.腰椎间孔成形技术在脊柱内镜手术应用中的研究进展[J].实用骨科杂志,2018,24(5):434-437.
[16] NIE H, ZENG J, SONG Y, et al. Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy for L5-S1 Disc Herniation Via an Interlaminar Approach Versus a Transforaminal Approach: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Study With 2-Year Follow Up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016; 41 Suppl 19:B30-B37.
[17] CHOI KC, KIM JS, RYU KS, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for L5-S1 disc herniation: transforaminal versus interlaminar approach. Pain Physician. 2013;16(6):547-556.
[18] CHOI G, LEE SH, RAITURKER PP, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy for intracanalicular disc herniations at L5-S1 using a rigid working channel endoscope. Neurosurgery. 2006;58(1 Suppl):ONS59-68; discussion ONS59-68.
[19] CHEN KT, JABRI H, LOKANATH YK, et al. The evolution of interlaminar endoscopic spine surgery. J Spine Surg. 2020;6(2):502-512.
[20] CAO L, LIU Y, MEI W, et al. Biomechanical changes of degenerated adjacent segment and intact lumbar spine after lumbosacral topping-off surgery: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):104.
[21] RENNER SM, NATARAJAN RN, PATWARDHAN AG, et al. Novel model to analyze the effect of a large compressive follower pre-load on range of motions in a lumbar spine. J Biomech. 2007;40(6):1326-1332.
[22] DAHL MC, ELLINGSON AM, MEHTA HP, et al. The biomechanics of a multilevel lumbar spine hybrid using nucleus replacement in conjunction with fusion. Spine J. 2013;13(2):175-183.
[23] SHI Y, XIE YZ, ZHOU Q, et al. The biomechanical effect of the relevant segments after facet-disectomy in different diameters under posterior lumbar percutaneous endoscopes: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):593.
[24] VADAPALLI S, SAIRYO K, GOEL VK, et al. Biomechanical rationale for using polyetheretherketone (PEEK) spacers for lumbar interbody fusion-A finite element study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(26): E992-E998.
[25] 闫家智,吴志宏,汪学松,等.腰椎三维有限元模型建立和应力分析[J].中华医学杂志,2009,89(17):1162-1165.
[26] TEZUKA F, SAKAI T, ABE M, et al. Anatomical considerations of the iliac crest on percutaneous endoscopic discectomy using a transforaminal approach. Spine J. 2017;17(12):1875-1880.
[27] CHOI KC, PARK CK. Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy for L5-S1 Disc Herniation: Consideration of the Relation between the Iliac Crest and L5-S1 Disc. Pain Physician. 2016;19(2):E301-E308.
[28] WANG Z, CHEN Z, WU H, et al. Treatment of high-iliac-crest L5-S1 lumbar disc herniation via a transverse process endoscopic transforaminal approach. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020;197:106087.
[29] CHEN KT, TSENG C, SUN LW, et al. Technical Considerations of Interlaminar Approach for Lumbar Disc Herniation. World Neurosurg. 2021;145:612-620.
[30] DENIS F. The three column spine and its significance in the classification of acute thoracolumbar spinal injuries. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1983; 8(8):817-831.
[31] SPINA NT, MORENO GS, BRODKE DS, et al. Biomechanical effects of laminectomies in the human lumbar spine: a finite element study. Spine J. 2021;21(1):150-159.
[32] SHIRAZI-ADL A. Finite-element evaluation of contact loads on facets of an L2-L3 lumbar segment in complex loads. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991;16(5):533-541.
[33] PAHOLPAK P, DEDEOGULLARI E, LEE C, et al. Do modic changes, disc degeneration, translation and angular motion affect facet osteoarthritis of the lumbar spine. Eur J Radiol. 2018;98:193-199.
[34] 余洋,谢一舟,石银,等. 三维有限元法分析腰椎不同尺寸关节突成形后相关节段的生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(33):5288-5293.
[35] 张晗硕,丁宇,蒋强,等.脊柱内镜下椎板开窗减压与单侧入路双侧减压治疗腰椎管狭窄症的生物力学稳定性及有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(13):1981-1986.
[36] AOKI Y, TAKAHASHI H, NAKAJIMA A, et al. Prevalence of lumbar spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in patients with degenerative spinal disease. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):6739.
|