[1] PARKER M, JOHANSEN A. Hip fracture. BMJ. 2006;333(7557):27-30.
[2] LAW GW, WONG YR, GARDNER A, et al. Intramedullary nailing confers an increased risk of medial migration compared to dynamic hip screw fixation in unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures. Injury. 2021;52(11):3440-3445.
[3] ZHANG Z, QIU YD, ZHANG YW, et al. Global Trends in Intertrochanteric Hip Fracture Research From 2001 to 2020: A Bibliometric and Visualized Study. Front Surg. 2021;8:756614.
[4] CHANG SM, HOU ZY, HU SJ, et al. Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture Treatment in Asia: What We Know and What the World Can Learn. Orthop Clin North Am. 2020;51(2):189-205.
[5] TU DP, LIU Z, YU YK, et al. Internal Fixation versus Hemiarthroplasty in the Treatment of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures in the Elderly: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(4):1053-1064.
[6] NIU E, YANG A, HARRIS AH, et al. Which Fixation Device is Preferred for Surgical Treatment of Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures in the United States? A Survey of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(11):3647-3655.
[7] PALM H. Hip Fracture: The Choice of Surgery//FALASCHI P, MARSH D. Orthogeriatrics: The Management of Older Patients with Fragility Fractures. Cham (CH). 2021:125-141.
[8] FTOUH S, MORGA A, SWIFT C. Management of hip fracture in adults: summary of NICE guidance. BMJ. 2011;342:d3304.
[9] ROBERTS KC, BROX WT, JEVSEVAR DS, et al. Management of hip fractures in the elderly. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(2):131-137.
[10] SMITH L, ALBERSHEIM M, BLASCHKE B L, et al. Trend and Economic Implications of Implant Selection in the Treatment of Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures: A Review of the American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery Database From 2007 to 2017. Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021;29(18):789-795.
[11] WANG Y, CHEN W, ZHANG L, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Proximal Femur Bionic Nail (PFBN) Compared with Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation and InterTan in Treatment of Intertrochanteric Fractures. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(9):2245-2255.
[12] KULACHOTE N, SA-NGASOONGSONG P, SIRISREETREERUX N, et al. Predicting Factors for Return to Prefracture Ambulatory Level in High Surgical Risk Elderly Patients Sustained Intertrochanteric Fracture and Treated With Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) With and Without Cement Augmentation. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2020;11:2151459320912121.
[13] SERMON A, BONER V, BOGER A, et al. Potential of polymethylmethacrylate cement-augmented helical proximal femoral nail antirotation blades to improve implant stability--a biomechanical investigation in human cadaveric femoral heads. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;72(2):E54-E59.
[14] SERMON A, BONER V, SCHWIEGER K, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of bone-cement augmented Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation blades in a polyurethane foam model with low density. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2012;27(1):71-76.
[15] STRAMAZZO L, RATANO S, MONACHINO F, et al. Cement augmentation for trochanteric fracture in elderly: A systematic review. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021; 15:65-70.
[16] NI XH, ZHU XY, ZHANG ZY, et al. Clinical effect of cement-enhanced APFN in the treatment of elderly osteoporotic intertrochanteric fractures. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022;26(11):3872-3877.
[17] 庄华烽,李毅中,林金矿,等.脆性股骨颈骨折患者股骨颈骨密度及结构的变化[J].中华老年医学杂志,2014,33(3):282-285.
[18] 陈心敏,李文标,熊凯凯,等.钉道强化股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年A3.3型股骨转子间骨折:最佳骨水泥量有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(9):1404-1409.
[19] GELLER JA, SAIFI C, MORRISON TA, et al. Tip-apex distance of intramedullary devices as a predictor of cut-out failure in the treatment of peritrochanteric elderly hip fractures. Int Orthop. 2010;34(5):719-722.
[20] ZHENG L, CHEN X, ZHENG Y, et al. Cement augmentation of the proximal femoral nail antirotation for the treatment of two intertrochanteric fractures-a comparative finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):1-13.
[21] WANG J, MA JX, LU B, et al. Comparative finite element analysis of three implants fixing stable and unstable subtrochanteric femoral fractures: Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA), Proximal Femoral Locking Plate (PFLP), and Reverse Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS). Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020;106(1):95-101.
[22] DHANOPIA A, BHARGAVA M. Finite Element Analysis of Human Fractured Femur Bone Implantation with PMMA Thermoplastic Prosthetic Plate. Procedia Eng. 2017;173(22):1658-1665.
[23] SERMON A, ZDERIC I, KHATCHADOURIAN R, et al. Bone cement augmentation of femoral nail head elements increases their cut-out resistance in poor bone quality- A biomechanical study. J Biomech. 2021;118:110301.
[24] CHRISTIAN K, DANIEL P, ADOLF L L, et al. Inability of Older Adult Patients with Hip Fracture to Maintain Postoperative Weight-Bearing Restrictions. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(11):936-941.
[25] SCHUETZE K, EHINGER S, EICKHOFF A, et al. Cement augmentation of the proximal femur nail antirotation: is it safe? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021; 141(5):803-811.
[26] PASTOR T, ZDERIC I, GEHWEILER D, et al. Biomechanical analysis of recently released cephalomedullary nails for trochanteric femoral fracture fixation in a human cadaveric model. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;142(12):3787-3796.
[27] WANG Y, CHEN W, ZHANG L, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Proximal Femur Bionic Nail (PFBN) Compared with Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation and InterTan in Treatment of Intertrochanteric Fractures. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(9): 2245-2255.
|
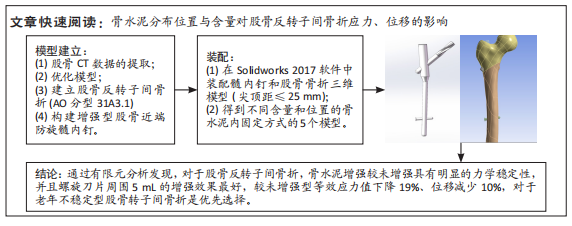
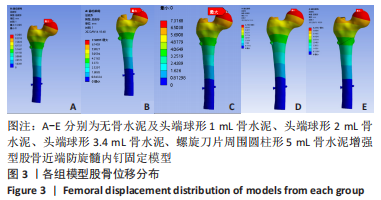
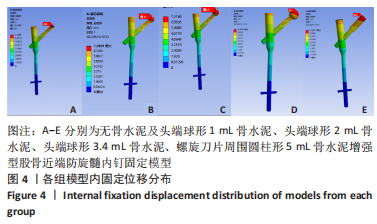
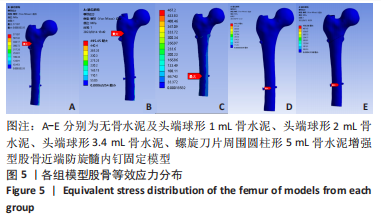
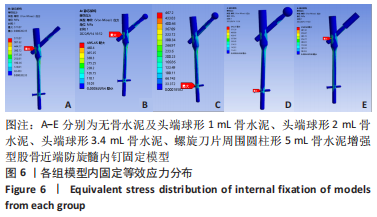
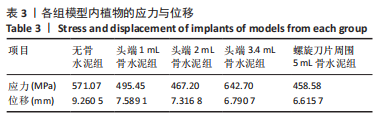

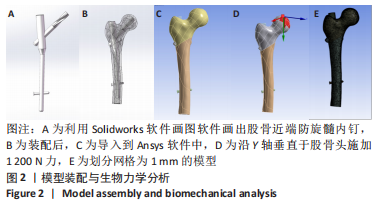
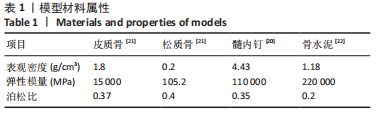
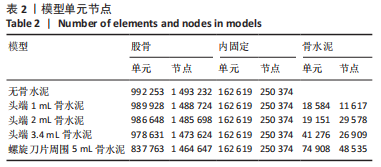
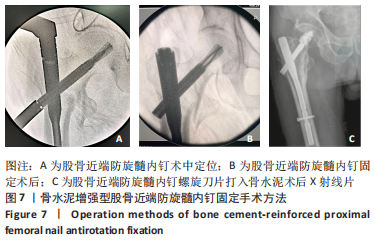 有限元分析是用于评估内固定治疗股骨骨折效果的有效工具,与传统的实验生物力学测试相比,它具有成本低、周期短、效率高等优点[27],不仅揭示了形状和功能之间的联系,还为外科医生提供了有价值的信息[21]。在生理条件下,骨折发生后股骨头皮质骨的应力不再均匀地传导到周围骨骼,而是传递到嵌入股骨头的螺钉,因此,股骨头处存在局部应力集中,最大位移大于正常股骨。因此,骨折内固定后,股骨头尖端会发生一定的变形,变形越大,意味着相应的局部应力越集中,叶片或螺钉断裂的风险越高[11]。
有限元分析是用于评估内固定治疗股骨骨折效果的有效工具,与传统的实验生物力学测试相比,它具有成本低、周期短、效率高等优点[27],不仅揭示了形状和功能之间的联系,还为外科医生提供了有价值的信息[21]。在生理条件下,骨折发生后股骨头皮质骨的应力不再均匀地传导到周围骨骼,而是传递到嵌入股骨头的螺钉,因此,股骨头处存在局部应力集中,最大位移大于正常股骨。因此,骨折内固定后,股骨头尖端会发生一定的变形,变形越大,意味着相应的局部应力越集中,叶片或螺钉断裂的风险越高[11]。