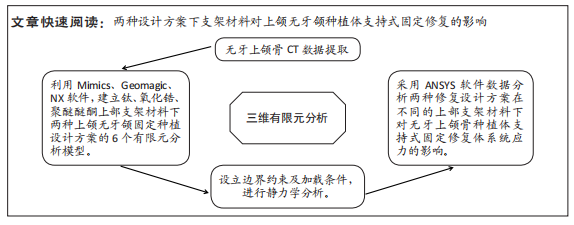
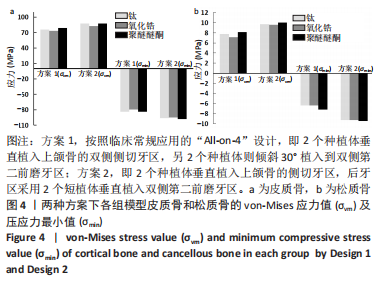
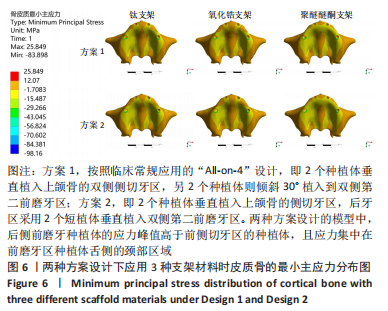
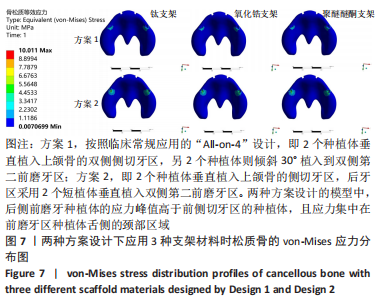
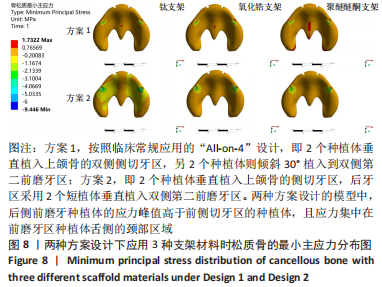
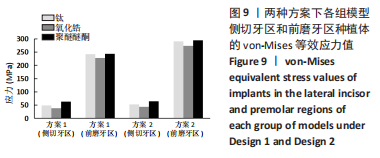
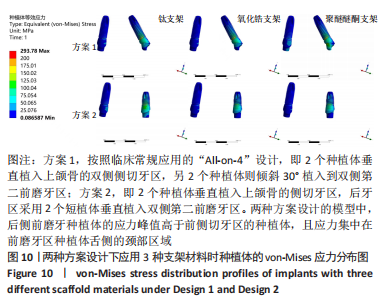
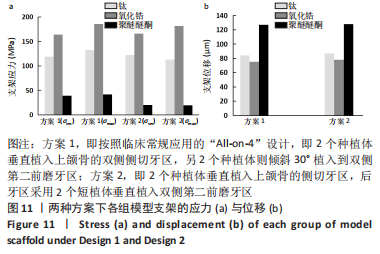
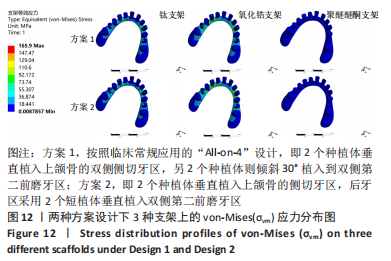
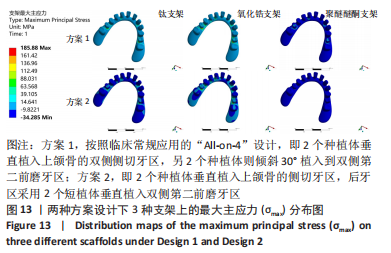
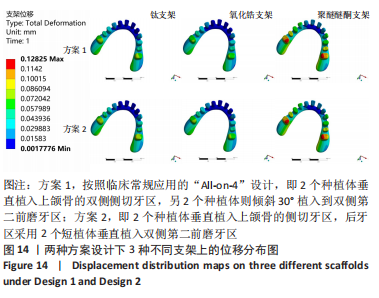
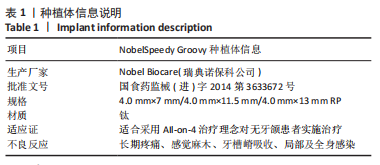
[1] RAGHOEBAR GERRY M, PIETER O, CARINA BG, et al. Long-term effectiveness of maxillary sinus floor augmentation:A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46 Suppl 21(s21):307-318.
[2] HENDRIK N, KLAAS L,AYDIN G, et al. Effect of enriched bone-marrow aspirates on the dimensional stability of cortico-cancellous iliac bone grafts in alveolar ridgeaugmentation. Int J Implant Dent. 2022;8(1):34-34.
[3] 吴炯睿,高益鸣.上颌窦解剖与上颌窦外提升手术并发症的研究进展[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2022,20(1):93-97.
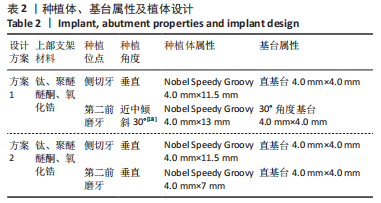
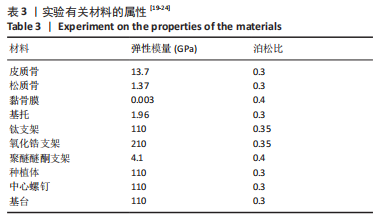
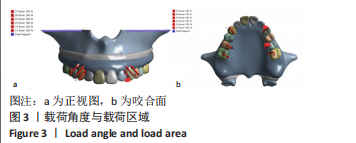
[4] 木志翔,刘婷,陈陶,等.两种上颌无牙颌种植固定修复方案的有限元分析[J].口腔医学研究,2019,35(10):931-935.
[5] MALÓ P, RANGERT O, NOBRE M, et al.“All‐on‐Four” Immediate‐Function Concept with Brånemark System Implants for Completely Edentulous Mandibles:A Retrospective Clinical Study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003;5 Suppl 1:2-9.
[6] 何添荣.两种解决上颌后牙区骨量不足的种植修复方式的临床对照试验[D].上海:上海交通大学,2012.
[7] SANTANA LCL, GUASTALDI FPS, IDOGAVA HT, et al. Mechanical Stress Analysis of Different Configurations of the All-on-4 Concept in Atrophic Mandible: A 3D Finite Element Study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2021; 36(1):75-85.
[8] VETROMILLA BM, MAZZETTI T, PEREIRA-CENCI T. Short versus standard implants associated with sinus floor elevation:an umbrella review of meta-analyses of multiple outcomes. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;126(4):503-511.
[9] CAROSI P, LORENZI C, LAURETI M, et al. Short dental implants(≤6 mm) to rehabilitate severe mandibular atrophy:a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofacial Implants. 2021;36(1):30-37.
[10] YAN Q, WU X, SU M, et al. Short implants(≤6 mm) versus longer implants with sinus floor elevation in atrophic posterior maxilla:a systematic review and meta analysis. BMJ Open. 2019;9(10):e029826.
[11] LOFAJ F, KUCERA J, NÉMETH D, et al. Optimization of Tilted implant geometry for stress reduction in All-on-4 treatment concept:finite element analysis study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(6):1287-1295.
[12] BARBIN T, SILVA LDR, VELOSO DV, et al. Biomechanical behavior of CAD/CAM cobalt-chromium and zirconia full-arch fixed prostheses. J Adv Prosthodont. 2020;12(6):329-337.
[13] BAGEGNI A, ABOU-AYASH S, RÜCKER G, et al. The influence of prosthetic materialon implant and prosthetic survival of implant-supported fixed complete dentures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Prosthodont Res. 2019;63(3):251-265.
[14] WONG C, NARVEKAR U, PETRIDIS H. Prosthodontic complications of metal‑ceramic and all‑ceramic,complete‑arch fixed implant prostheses with minimum 5years mean follow‑up period.A systematic review and meta‑analysis. J Prosthodont. 2019;28(2):e722-e735.
[15] BIDRA AS, TISCHLER M, PATCH C. Survival of 2039 complete arch fixed implant-supported zirconia prostheses:a retrospective study. J Prosthet Dent. 2018;119(2):220-224.
[16] WAGNER F, SEEMANN R, MARINCOLA M, et al. Fiber-reinforced resin fixed prostheses on 4 short implants in severely atrophic maxillas:1-year results of a prospective cohort study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;76(6):1194-1199.
[17] MOUNIR M, ATEF M, ABOU-ELFETOUH A, et al. Titanium and polyether ether ketone (PEEK) patient-specific sub-periosteal implants:two novel approaches for rehabilitation of the severely atrophic anterior maxillary ridge. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;47(5):658-664.
[18] MALÓ P, DE ARAÚJO NOBRE M, LOPES A, et al. All-on-4 treatment concept for the rehabilitation of the completely edentulous mandible: a 7-year clinical and 5-year radiographic retrospective case series with risk assessment for implant failure and marginal bone level. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015;17 Suppl 2:e531-e541.
[19] KIM WH, HONG K, LIM D, et al. Optimal position of attachment for removable thermoplastic aligner on the lower canine using finite element analysis. Materials. 2020;13:3369.
[20] SIRANDONI D, LEAL E, WEBER B, et al. Effect of different framework materials in implant-supported fixed mandibular prostheses:a finite element analysis. Int J Oral Max Implant. 2019;34(6):e107-e114.
[21] HA SR. Biomechanical three‑dimensional finite element analysis of monolithic zirconia crown with different cement type. J Adv Prosthodont. 2015;7:475-483.
[22] CHANG CH, CHEN CS, HSU ML, et al. Biomechanical effect of platform switching in implant dentistry:A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Max Implant. 2010;25:295-304.
[23] DÍEZ-PASCUAL AM, NAFFAKH M, GONZÁLEZ-DOMÍNGUEZ JM, et al. High performance PEEK/carbon nanotube composites compatibilized with polysulfones-Ⅱ.Mechanical and electrical properties. Carbon. 2010; 48(12):3500-3511.
[24] RADI IA, ELMAHROUKY N. Effect of two different soft liners and thicknesses mediating stress transfer for immediately loaded 2-implant supported mandibular overdentures: a finite element analysis study. J Prosthet Dent. 2016;116(3):356-361.
[25] FERREIRA MB, BARAO VA, DELBEN JA, et al. Non-linear 3D finite element analysis of full-arch implant-supported fixed dentures. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;38:306-314.
[26] SKIRBUTIS G, DZINGUTE A, MASILIUNAITE V, et al. A review of PEEK polymer’s properties and its use in prosthodontics. Stomatologija. 2017;19(1):19-23.
[27] DESTE G, DURKAN R. Effects of all-on-four implant designs in mandible on implants and the surrounding bone: A 3-D finite element analysis. Niger J Clin Pract. 2020;23(4):456-463.
[28] DAYAN SC, GECKILI O. The influence of framework material on stress distribution in maxillary complete-arch fixed prostheses supported by four dental implants: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2021;24(14):1606-1617.
[29] 董泽文,张小军,李彦生,等.不同牙合方式下人体下颌骨膜下种植体的生物力学特性[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(6):655-660.
[30] 于文倩,李晓茜,陈思艺,等.上部结构材料对无牙下颌种植固定修复影响的三维有限元分析[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2021,56(2):190-195.
[31] HAROUN F, OZAN O. Evaluation of Stresses on Implant, Bone, and Restorative Materials Caused by Different Opposing Arch Materials in Hybrid Prosthetic Restorations Using the All-on-4 Technique. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(15):4308.
[32] 温颖,郑东翔,张振庭,等.全口无牙领应用种植固定修复后的咬合力分布研究[J].北京口腔医学,2008,16(6):325-328.
[33] FERREIRA MB, BARÃO VA, FAVERANI LP, et al. The role of superstructure material on the stress distribution in mandibular full-arch implant-supported fixed dentures. A CT-based 3D-FEA.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;35:92-99.
[34] DAS NEVES FD, FONES D, BERNARDES SR, et al. Short implants--an analysis of longitudinal studies. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2006;21(1):86-93.
[35] OZAN O, KURTULMUS-YILMAZ S. Biomechanical Comparison of Different Implant Inclinations and Cantilever Lengths in All-on-4 Treatment Concept by Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(1):64-71.
[36] 唐庭,张磊,侯永福,等.All-on-4种植即刻修复对口腔健康相关生活质量的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2018,27(1):52-55.
[37] LIU T, MU Z, YU T, et al. Biomechanical comparison of implant inclinations and load times with the all-on-4 treatment concept: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2019;22(6):585-594.
[38] 范震,刘月,王佐林.牙列缺失倾斜种植设计[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2021,39(4):377-385.
[39] ASAWA N, BULBULE N, KAKADE D, et al. Angulated implants: an alternative to bone augmentation and sinus lift procedure: systematic review. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9(3):ZE10-ZE13.
[40] ERCAL P, TAYSI AE, AYVALIOGLU DC, et al. Impact of peri-implant bone resorption,prosthetic material,and crown to implant ratio on the stress distribution of short implants:a finite element analysis. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2021;59(4):813-824.
[41] 施斌,廖一林,晏奇.短种植体在上颌后牙区的应用与风险[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2021,26(4):213-218.
[42] LOMBARDO G, SIGNORIELLO A, SIMAN CAS-PALLARES M, et al. Survival of short and ultra-short locking-taper implants supporting single crowns in the posterior mandible: a 3-year retrospective study. J Oral Implantol. 2020;46(4):396-406.
[43] LIN ZZ, JIAO YQ, YE ZY, et al. The survival rate of transcrestal sinus floor elevation combined with short implants:a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Int J lmplant Dent. 2021;7(1):41.
[44] KUL E, KORKMAZ IH. Effect of different design of abutment and implant on stress distribution in 2 implants and peripheral bone:a finite element analysis study. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;126(5):664.e1-664.e9.
[45] NIELSEN HB, SCHOU S, BRUUN NH, et al. Single-crown restorations supported by short implants(6 mm)compared with standard length implants(13mm)in conjunction with maxillary sinus floor augmentation:a randomized,controlled clinical trial. Int J Implant Dent. 2021;7(1):66.
[46] AYNA M, WESSING B, GUTWALD R, et al. A 5-year prospective clinical trial on short implants (6mm)for single tooth re-placement in the posterior maxilla:immediate versus delayed loading. Odontology. 2019;107(2):244-253.
[47] CAROSI P, LORENZI C, LIO F, et al. Short implants (≤6mm) as an alternative treatment option to maxillary sinus lift. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021; 50(11):1502-1510.
[48] LOPEZ C, VASCO M, RUALES E, et al. Three‑dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution in zirconia and titanium dental implants. J Oral Implantol. 2018;44(6):409-415.
[49] SEEMANN R, WAGNER F, MARINCOLA M, et al. Fixed,fiber-reinforced resin bridges on 5.0-mm implants in severely atrophic mandibles: up to 5 years′ follow-up of a prospective cohort study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;76(5): 956-962.
[50] 皮昕.口腔解剖生理学[M]. 6版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2007:294.
[51] VERRI FR, CRUZ RS, DE SOUZA BATISTA VE, et al. Can the modeling for simplification of a dental implant surface affect the accuracy of 3D finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2016;19(15):1665-1672.
[52] DOGANAY O, KILIC E. Comparative finite element analysis of short implants with different treatment approaches in the atrophic mandible. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2020;35(4):e69-76.
[53] BHERING CLB, MESQUITA MF, KEMMOKU DT, et al. Comparison between all-on-four and all-on-six treatment concepts and framework material on stressdistribution in atrophic maxilla: A prototyping guided 3D-FEA study. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater. 2016;69:715-725.
[54] AZCARATE-VELAZQUEZ F, CASTILLO-OYAGUE R, OLIVEROS-LOPEZ LG, et al. Influence of bone quality on the mechanical interaction between implant and bone: a finite element analysis. J Dent. 2019;88:103161.
[55] OLIVEIRA MR, GONÇALVES A, GABRIELLI MA, et al. Evaluation of alveolar bone quality: correlation between histomorphometric analysis and Lekholm and Zarb classification. J Craniofac Surg. 2021;32(6):2114-2118.
[56] SIRANDONI D, LEAL E, WEBER B, et al. Effect of different framework materials in implant-supported fixed mandibular prostheses: a finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;34:107-114.
[57] MUMCU E, DAYAN SC, GENCELI E, et al. Comparison of four-implant-retained overdentures and implant-supported fixed prostheses using the All-on-4 concept in the maxilla in terms of patient satisfaction,quality of life, and marginal bone loss: a 2-year retrospective study. Quintessence Int. 2020; 51:388-396.
[58] MALO P, DE ARA UJO NOBRE M, MOURA GUEDES C, et al. Short-term report of an ongoing prospective cohort study evaluating the outcome of full-arch implant-supported fixed hybrid polyetheretherketone-acrylic resin prostheses and the All-on-Four concept. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2018;20(5):692-702.
[59] FERREIRA MB, BARÃO VA, DELBEN JA, et al. Non-linear 3D finite element analysis of full-arch implant-supported fixed dentures. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;38:306-314. |