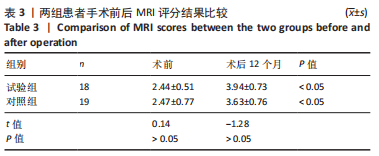
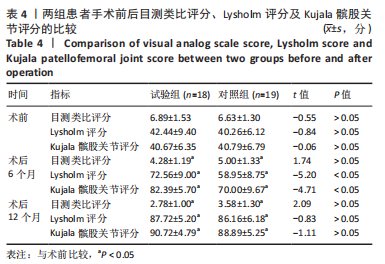
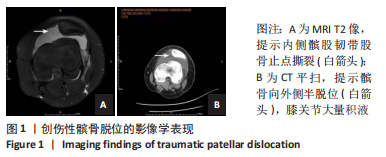
[1] LEE BJ, CHRISTINO MA, DANIELS AH, et al. Adolescent patellar osteochondral fracture following patellar dislocation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(8):1856-1861.
[2] GURUSAMY P, PEDOWITZ JM, CARROLL AN, et al. Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction for Adolescents With Acute First-Time Patellar Dislocation With an Associated Loose Body. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(8):2159-2164.
[3] JAQUITH BP, PARIKH SN. Predictors of Recurrent Patellar Instability in Children and Adolescents After First-time Dislocation. J Pediatr Orthop. 2017;37(7):484-490.
[4] IBRAHIM SA, SHOHDY EM, RAMADAN SA, et al. Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction in Traumatic Patellar Dislocation without Patellar Fixation. J Knee Surg. 2020;33(10):998-1003.
[5] NWACHUKWU BU, SO C, SCHAIRER WW, et al. Surgical versus conservative management of acute patellar dislocation in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(3):760-767.
[6] LIND M, ENDERLEIN D, NIELSEN T, et al. Clinical outcome after reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament in paediatric patients with recurrent patella instability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(3):666-671.
[7] PARK MJ, LEE MC, SEONG SC. A comparative study of the healing of tendon autograft and tendon-bone autograft using patellar tendon in rabbits. Int Orthop. 2001;25(1):35-39.
[8] SOON MY, HASSAN A, HUI JH, et al. An analysis of soft tissue allograft anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in a rabbit model: a short-term study of the use of mesenchymal stem cells to enhance tendon osteointegration. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(6):962-971.
[9] ROTHRAUFF BB, TUAN RS. Cellular therapy in bone-tendon interface regeneration. Organogenesis. 2014;10(1):13-28.
[10] MIRON RJ, FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, BISHARA M, et al. Platelet-Rich Fibrin and Soft Tissue Wound Healing: A Systematic Review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2017;23(1):83-99.
[11] MASUKI H, OKUDERA T, WATANEBE T, et al. Growth factor and pro-inflammatory cytokine contents in platelet-rich plasma (PRP), plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF), advanced platelet-rich fibrin (A-PRF), and concentrated growth factors (CGF). Int J Implant Dent. 2016;2(1):19.
[12] MIJIRITSKY E, ASSAF HD, PELEG O, et al. Use of PRP, PRF and CGF in Periodontal Regeneration and Facial Rejuvenation-A Narrative Review. Biology (Basel). 2021; 10(4).317-340.
[13] LANDESBERG R, ROY M, GLICKMAN RS. Quantification of growth factor evels using a simplified method of platelet-rich plasma gel preparation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;58(3):297-300,300-301.
[14] WEBER-SPICKSCHEN TS, SPANG J, KOHN L, et al. The relationship between trochlear dysplasia and medial patellofemoral ligament rupture location after patellar dislocation: an MRI evaluation. Knee. 2011;18(3).185-188.
[15] FIGUEROA D, MELEAN P, CALVO R, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of the integration and maturation of semitendinosus-gracilis graft in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using autologous platelet concentrate. Arthroscopy. 2010;26(10):1318-1325.
[16] DEL TM, ENEA D, PANFOLI N, et al. Hamstrings anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with and without platelet rich fibrin matrix. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(12):3614-3622.
[17] ZHANG Z, ZHANG H, SONG G, et al. A High-Grade J Sign Is More Likely to Yield Higher Postoperative Patellar Laxity and Residual Maltracking in Patients With Recurrent Patellar Dislocation Treated With Derotational Distal Femoral Osteotomy. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(1):117-127.
[18] MULLIEZ A, LAMBRECHT D, VERBRUGGEN D, et al. Clinical outcome in MPFL reconstruction with and without tuberositas transposition. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(9):2708-2714.
[19] DONG S, XIE G, ZHANG Y, et al. Ligamentization of Autogenous Hamstring Grafts After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Midterm Versus Long-term Results. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(8):1908-1917.
[20] BENJAMIN M, KUMAI T, MILZ S, et al. The skeletal attachment of tendons--tendon “entheses”. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2002;133(4):931-945.
[21] BI F, SHI Z, JIANG S, et al. Intermittently administered parathyroid hormone [1-34] promotes tendon-bone healing in a rat model. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(10):17366-17379.
[22] SAPPEY-MARINIER E, SONNERY-COTTET B, O’LOUGHLIN P, et al. Clinical Outcomes and Predictive Factors for Failure With Isolated MPFL Reconstruction for Recurrent Patellar Instability: A Series of 211 Reconstructions With a Minimum Follow-up of 3 Years. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(6):1323-1330.
[23] GUO R, GAO L, XU B. Current Evidence of Adult Stem Cells to Enhance Anterior Cruciate Ligament Treatment: A Systematic Review of Animal Trials. Arthroscopy. 2018;34(1):331-340.
[24] HEXTER AT, KARALI A, KAO A, et al. Effect of Demineralized Bone Matrix, Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells, and Platelet-Rich Plasma on Bone Tunnel Healing After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Comparative Micro-Computed Tomography Study in a Tendon Allograft Sheep Model. Orthop J Sports Med. 2021;9(9):941639222.
[25] MAYR R, SMEKAL V, KOIDL C, et al. Tunnel widening after ACL reconstruction with aperture screw fixation or all-inside reconstruction with suspensory cortical button fixation: Volumetric measurements on CT and MRI scans. Knee. 2017;24(5):1047-1054.
[26] ALVES R, GRIMALT R. A Review of Platelet-Rich Plasma: History, Biology, Mechanism of Action, and Classification. Skin Appendage Disord. 2018;4(1):18-24.
[27] YOU JS, KIM SG, OH JS, et al. Effects of Platelet-Derived Material (Platelet-Rich Fibrin) on Bone Regeneration. Implant Dent. 2019;28(3):244-255.
[28] 张松,张涛,付桂红,等.自体富血小板血浆联合骨髓间充质干细胞治疗长骨干骨折术后骨不连[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017,21(29):4716-4721.
[29] KANAZAWA T, SOEJIMA T, NOGUCHI K, et al. Tendon-to-bone healing using autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in ACL reconstruction without a tibial bone tunnel-A histological study-. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014;4(2):201-206.
[30] QIAO J, AN N, OUYANG X. Quantification of growth factors in different platelet concentrates. Platelets. 2017;28(8):774-778.
[31] KANNO T, TAKAHASHI T, TSUJISAWA T, et al. Platelet-rich plasma enhances human osteoblast-like cell proliferation and differentiation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005; 63(3):362-369.
[32] MASUKI H, OKUDERA T, WATANEBE T, et al. Growth factor and pro-inflammatory cytokine contents in platelet-rich plasma (PRP), plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF), advanced platelet-rich fibrin (A-PRF), and concentrated growth factors (CGF). Int J Implant Dent. 2016;2(1):19.
[33] TAKAHASHI A, TSUJINO T, YAMAGUCHI S, et al. Distribution of platelets, transforming growth factor-β1, platelet-derived growth factor-BB, vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloprotease-9 in advanced platelet-rich fibrin and concentrated growth factor matrices. J Investig Clin Dent. 2019;10(4):e12458.
[34] BIERCEVICZ AM, AKELMAN MR, FADALE PD, et al. MRI volume and signal intensity of ACL graft predict clinical, functional, and patient-oriented outcome measures after ACL reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(3):693-699.
[35] STARANTZIS KA, MASTROKALOS D, KOULALIS D, et al. The Potentially Positive Role of PRPs in Preventing Femoral Tunnel Widening in ACL Reconstruction Surgery Using Hamstrings: A Clinical Study in 51 Patients. J Sports Med (Hindawi Publ Corp). 2014;2014:789317.
[36] SILVA A, SAMPAIO R. Anatomic ACL reconstruction: does the platelet-rich plasma accelerate tendon healing? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009;17(6):676-682.
[37] HONG S, CHEN W, JIANG B. A Comparative Evaluation of Concentrated Growth Factor and Platelet-rich Fibrin on the Proliferation, Migration, and Differentiation of Human Stem Cells of the Apical Papilla. J Endod. 2018;44(6):977-983.
[38] DRAGOO JL, BRAUN HJ, DURHAM JL, et al. Comparison of the acute inflammatory response of two commercial platelet-rich plasma systems in healthy rabbit tendons. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(6):1274-1281.
[39] HU Y, JIANG Y, WANG M, et al. Concentrated Growth Factor Enhanced Fat Graft Survival: A Comparative Study. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44(7):976-984.
[40] VENTURA A, TERZAGHI C, BORGO E, et al. Use of growth factors in ACL surgery: preliminary study. J Orthop Traumatol. 2005;6(2):76-79.
[41] KIM TH, KIM SH, SÁNDOR GK, et al. Comparison of platelet-rich plasma (PRP), platelet-rich fibrin (PRF), and concentrated growth factor (CGF) in rabbit-skull defect healing. Arch Oral Biol. 2014;59(5):550-558.
[42] LIOU JJ, ROTHRAUFF BB, ALEXANDER PG, et al. Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Chondrogenic Differentiation of Adipose- and Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24(19-20):1432-1443.
|