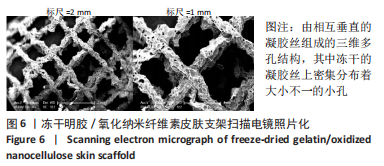
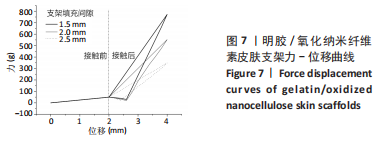
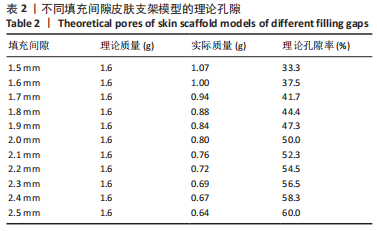
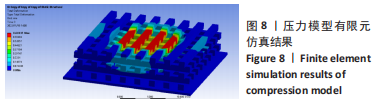
[1] GAO D, WANG Z, WU Z, et al. 3D-printing of solvent exchange deposition modeling (SEDM) for a bilayered flexible skin substitute of poly (lactide-co-glycolide) with bioorthogonally engineered EGF. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;112:110942.
[2] 余海洋,游德淑,顾晓诚,等.基于生物3D打印技术的芍药苷-海藻酸钠-明胶皮肤支架体外生物相容性研究[J].介入放射学杂志, 2022,31(6):582-586.
[3] TORRES M, SINHA R, MOTA C, et al.Improving cell distribution on 3D additive manufactured scaffolds through engineered seeding media density and viscosity. Acta Biomater. 2020;101:183-195.
[4] EDMONDS M. Apligraf in the treatment of neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2009;8(1):11-18.
[5] TASHAKORI M,RAKHSHAN K,RAMEZ M, et al. Conductive carbon nanofibers incorporated into collagen bio-scaffold assists myocardial injury repair. Int J Biol Macromol.2020;163:1136-1146.
[6] INTINI C, EIVIN, CABRAL J, et al. 3D-printed chitosan-based scaffolds: An in vitro study of human skin cell growth and an in-vivo wound healing evaluation in experimental diabetes in rats. Carbohyd Polym. 2018;199:593-602.
[7] ORYAN A, SAHVIEH S. Effectiveness of chitosan scaffold in skin, bone and cartilage healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;104:1003-1011.
[8] KOCH L, KUHN S, SORG H, et al. Laser printing of skin cells and human stem cells. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(5):847-854.
[9] YOON H, LEE J, YIM H, et al. Development of cell-laden 3D scaffolds for efficient engineered skin substitutes by collagen gelation. Rsc Adv. 2016;6(26):21439-21447.
[10] 刘煜凡,黄沙,姚斌,等.3D生物打印的微结构促进小鼠表皮干细胞的增殖和活性[J].南方医科大学学报,2017,37(6):761-766.
[11] 曹思玮,安佰超,乡世健,等.3D打印隐丹参酮水凝胶面膜的抗痤疮作用及皮肤安全性评价[J].中国皮肤性病学杂志,2019,33(3): 371-378.
[12] BILLIET T, GEVAERT E, SCHRYVER T, et al. The 3D printing of gelatin methacrylamide cell-laden tissue-engineered constructs with high cell viability. Biomaterials. 2014;35(1):49-62.
[13] CRABTREE RH. Hypervalency, secondary bonding and hydrogen bonding: siblings under the skin. Chem Soc Rev. 2017;46(6):1720-1729.
[14] YANG W, XU H, LAN Y, et al. Preparation and characterisation of a novel silk fibroin/hyaluronic acid/sodium alginate scaffold for skin repair. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;130:58-67.
[15] PAL P, SRIVAS P, DADHICH P, et al. Nano-/microfibrous cotton-wool-like 3D scaffold with core–shell architecture by emulsion electrospinning for skin tissue regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2017;3(12):3563-3575.
[16] WANG J, SUN X, CHENG N, et al. In vitro and in vivo studies of a collagen-based scaffold carrying PLGA microspheres for sustained release of epidermal growth factor in skin regeneration. J Biomater Tiss Eng. 2017;7(12):1336-1343.
[17] MIAO Z,S EO J, HICKNER MA. Solvent-cast 3D printing of polysulfone and polyaniline composites. Polymer. 2018;152:18-24.
[18] ATOUFI Z, ZARRINTAJ P, MOTLAGH GH, et al. A novel bio electro active alginate-aniline tetramer/agarose scaffold for tissue engineering: synthesis, characterization, drug release and cell culture study. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2017;28(15):1617-1638.
[19] HAN S, LEE JY, HEO EY, et al. Implantation of a Matrigel-loaded agarose scaffold promotes functional regeneration of axons after spinal cord injury in rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;496(3):785-791.
[20] HUANG Y, WANG J, YANG F, et al. Modification and evaluation of micro-nano structured porous bacterial cellulose scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;75:1034-1041.
[21] DANIELE M, ADAMS A, NACIRI J, et al. Interpenetrating networks based on gelatin methacrylamide and PEG formed using concurrent thiol click chemistries for hydrogel tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2014;35(6):1845-1856.
[22] 冯辰,周骥平,许晓东,等.3D打印生物材料微小力学性能自动测量系统的设计[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(21):3306-3311.
[23] JIANG Y, ZHOU J, ZHANG Q, et al. Preparation of cellulose nanocrystals from Humulus japonicus stem and the influence of high temperature pretreatment. Carbohyd Polym. 2017;164:284-293.
[24] 鲍晶晶,谢璠,党婉斌,等.TEMPO氧化纳米纤维素增强芳纶云母纸基复合材料及其性能研究[J].陕西科技大学学报,2019,37(5):1-7.
[25] 薛刚,何易,李小白,等.超声辅助硫酸水解法制备银杏果壳纳米纤维素及其特性表征[J].食品工业科技,2021,42(14):204-211.
[26] 姜亚妮.草源性纳米纤维素复合明胶的制备及生物3D打印皮肤支架成型工艺的研究[D].扬州:扬州大学,2018.
[27] XU X, ZHOU J, JIANG Y, et al. 3D printing process of oxidized nanocellulose and gelatin scaffold. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018; 29(12):1498-1513.
[28] 刘东方,周骥平,许晓东,等.基于FLUENT3D 生物打印喷头内部流场的数值模拟分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(2):274-280. |