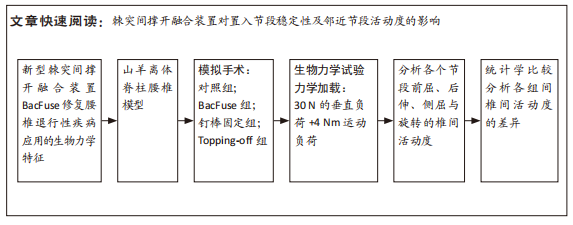
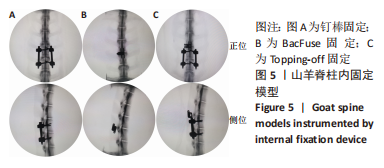
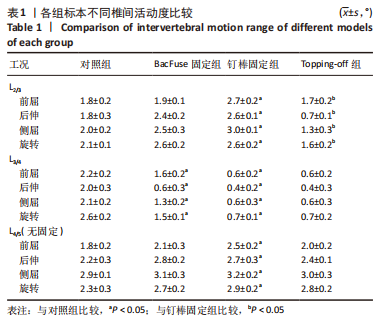
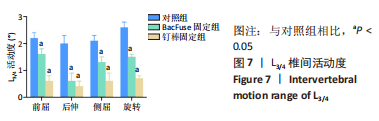
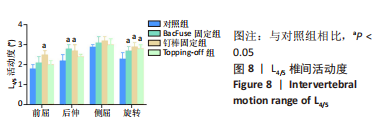
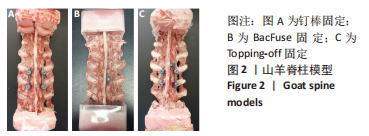
[1] 唐海,张体栋,陈浩,等. 棘突融合钢板治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2016,36(6):344-352.
[2] FALOWSKI SM, MANGAL V, POPE J, et al. Multicenter Retrospective Review of Safety and Efficacy of a Novel Minimally Invasive Lumbar Interspinous Fusion Device. J Pain Res. 2021;14:1525-1531.
[3] WANG R, JI X, LIU L, et al. Changes of MRI in inter-spinal distraction fusion for lumbar degenerative disease: A retrospective analysis covering 3 years. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;81:455-461.
[4] WEI H, TANG H, ZHANG T, et al. Preliminary efficacy of inter-spinal distraction fusion which is a new technique for lumbar disc herniation. Int Orthop. 2019;43(4):899-907.
[5] 陈萌萌,唐海.棘突间装置在腰椎退行性变疾病的相关生物力学研究进展[J]. 国际外科学杂志,2021,48(8):572-576.
[6] LIU Z, ZHANG S, LI J, et al. Biomechanical comparison of different interspinous process devices in the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis: a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):585.
[7] 王宝东,侯继春,何人可,等. 国产新型腰椎棘突间撑开器体外生物力学测试及有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(12):1897-1904.
[8] BONALDI G. Minimally invasive dynamic stabilization of the degenerated lumbar spine. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2010;20(2):229-241.
[9] MANFRE L, DE VIVO AE, AL QATAMI H, et al. Successful use of percutaneous interspinous spacers and adjunctive spinoplasty in a 9 year cohort of patients. J Neurointerv Surg. 2020;12(7):673-677.
[10] VERHOOF OJ, BRON JL, WAPSTRA FH, et al. High failure rate of the interspinous distraction device (X-Stop) for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis caused by degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2008; 17(2):188-192.
[11] WANG K, ZHU Z, WANG B, et al. Bone resorption during the first year after implantation of a single-segment dynamic interspinous stabilization device and its risk factors. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:117.
[12] RAIKAR SV, PATIL AA, PANDEY DK, et al. Inter Spinal Fixation and Stabilization Device for Lumbar Radiculopathy and Back Pain. Cureus. 2021;13(11): e19956.
[13] POSTACCHINI F, POSTACCHINI R, MENCHETTI PP, et al. Lumbar Interspinous Process Fixation and Fusion with Stand-Alone Interlaminar Lumbar Instrumented Fusion Implant in Patients with Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Undergoing Decompression for Spinal Stenosis. Asian Spine J. 2016;10(1): 27-37.
[14] CUELLAR JM, FIELD JS, BAE HW. Distraction Laminoplasty With Interlaminar Lumbar Instrumented Fusion (ILIF) for Lumbar Stenosis With or Without Grade 1 Spondylolisthesis: Technique and 2-Year Outcomes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41 Suppl 8:S97-S105.
[15] SCLAFANI JA, LIANG K, OHNMEISS DD, et al. Clinical outcomes of a polyaxial interspinous fusion system. Int J Spine Surg. 2014;8:35.
[16] CHEN M, JIA P, FENG F, et al. A novel minimally invasive technique of inter-spinal distraction fusion surgery for single-level lumbar spinal stenosis in octogenarians: a retrospective cohort study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022; 17(1):100.
[17] KAYE AD, EDINOFF AN, TEMPLE SN, et al. A Comprehensive Review of Novel Interventional Techniques for Chronic Pain: Spinal Stenosis and Degenerative Disc Disease-MILD Percutaneous Image Guided Lumbar Decompression, Vertiflex Interspinous Spacer, MinuteMan G3 Interspinous-Interlaminar Fusion. Adv Ther. 2021;38(9):4628-4645.
[18] CHEN M, TANG H, SHAN J, et al. A new interspinous process distraction device BacFuse in the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis with 5 years follow-up study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(26):e20925.
[19] WILKE HJ, DRUMM J, HAUSSLER K, et al. Biomechanical effect of different lumbar interspinous implants on flexibility and intradiscal pressure. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(8):1049-1056.
[20] LINDSEY DP, SWANSON KE, FUCHS P, et al. The effects of an interspinous implant on the kinematics of the instrumented and adjacent levels in the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(19):2192-2197.
[21] GUO Z, LIU G, WANG L, et al. Biomechanical effect of Coflex and X-STOP spacers on the lumbar spine: a finite element analysis. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(7):5155-5163.
[22] BRUSSEE P, HAUTH J, DONK RD, et al. Self-rated evaluation of outcome of the implantation of interspinous process distraction (X-Stop) for neurogenic claudication. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(2):200-203.
[23] KARAHALIOS DG, KAIBARA T, PORTER RW, et al. Biomechanics of a lumbar interspinous anchor with anterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010;12(4):372-380.
[24] TECHY F, MAGESWARAN P, COLBRUNN RW, et al. Properties of an interspinous fixation device (ISD) in lumbar fusion constructs: a biomechanical study. Spine J. 2013;13(5):572-579.
[25] GONZALEZ-BLOHM SA, DOULGERIS JJ, AGHAYEV K, et al. Biomechanical analysis of an interspinous fusion device as a stand-alone and as supplemental fixation to posterior expandable interbody cages in the lumbar spine. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;20(2):209-219.
[26] LEE CH, KIM YE, LEE HJ, et al. Biomechanical effects of hybrid stabilization on the risk of proximal adjacent-segment degeneration following lumbar spinal fusion using an interspinous device or a pedicle screw-based dynamic fixator. J Neurosurg Spine. 2017;27(6):643-649.
[27] SHEN H, FOGEL GR, ZHU J, et al. Biomechanical analysis of lumbar fusion with proximal interspinous process device implantation. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2021;37(8):e3498.
[28] KONG C, LU S, HAI Y, et al. Biomechanical effect of interspinous dynamic stabilization adjacent to single-level fusion on range of motion of the transition segment and the adjacent segment. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2015;30(4):355-359.
[29] 马亮,许永涛,佘远举.腰椎融合联合上一节段棘突间动态固定的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(23):3647-3653.
[30] DEER TR, SAYED D, MALINOWSKI MN, et al. A Review of Emerging Evidence for Utilization of a Percutaneous Interspinous Process Decompression Device to Treat Symptomatic Lumbar Adjacent-Segment Degeneration. Pain Med. 2019;20(Suppl 2):S9-S13.
[31] CHEN MM, JIA P, TANG H. Cortical bone trajectory fixation in cemented vertebrae in lumbar degenerative disease: A case report. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9(28):8609-8615. |