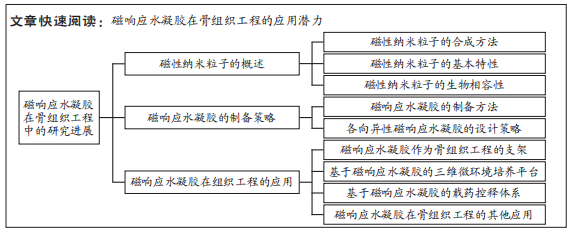
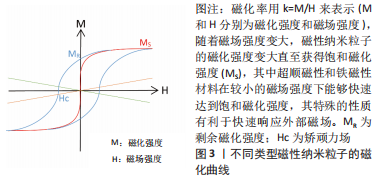
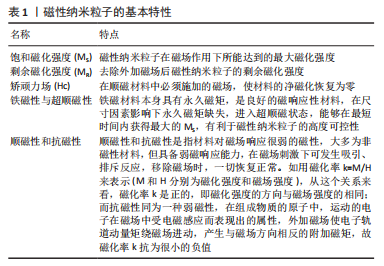
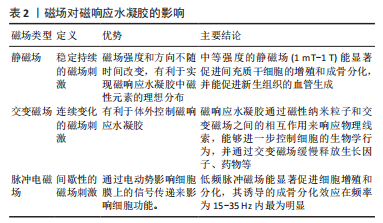
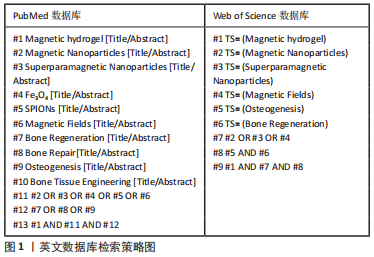
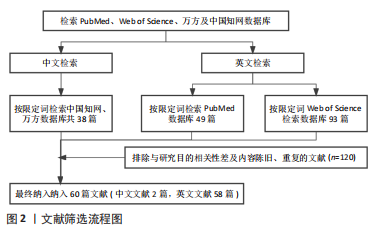
[1] 付正,李润泽,罗皓天,等.自修复水凝胶在骨组织工程中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(16):2590-2595.
[2] CUI Z, KIM S, BALJON JJ, et al. Microporous methacrylated glycol chitosan-montmorillonite nanocomposite hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):3523.
[3] ALFORD AI, KOZLOFF KM, HANKENSON KD. Extracellular matrix networks in bone remodeling. Int J Biochem Cell B. 2015;65:20-31.
[4] FILIPPI M, DASEN B, GUERRERO J, et al. Magnetic nanocomposite hydrogels and static magnetic field stimulate the osteoblastic and vasculogenic profile of adipose-derived cells. Biomaterials. 2019;223:119468.
[5] 沈梦杰,杨琨,刘琪.氧化铁纳米粒子在骨组织修复再生中的研究与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(14):2248-2253.
[6] LEE J, PARK B, KIM J, et al. Nanovesicles derived from iron oxide nanoparticles-incorporated mesenchymal stem cells for cardiac repair. Sci Adv. 2020;6(18):eaaz0952.
[7] FERNANDES MM, CORREIA DM, RIBEIRO C, et al. Bioinspired three-dimensional magnetoactive scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019; 11(48):45265-45275.
[8] QIAN W, QIAN M, WANG Y, et al. Combination glioma therapy mediated by a dual-targeted delivery system constructed using OMCN-PEG-Pep22/DOX. Small. 2018; 14(42):e1801905.
[9] YANG F, LU J, KE Q, et al. Magnetic mesoporous calcium sillicate/chitosan porous scaffolds for enhanced bone regeneration and photothermal-chemotherapy of osteosarcoma. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):7345.
[10] ANSARI F, SOBHANI A, SALAVATI-NIASARI M. Simple sol-gel synthesis and characterization of new CoTiO3/CoFe2O4 nanocomposite by using liquid glucose, maltose and starch as fuel, capping and reducing agents. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018; 514:723-732.
[11] DAOU TJ, POURROY G, BÉGIN-COLIN S, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of monodisperse magnetite nanoparticles. Chem Mater. 2006;18(18):4399-4404.
[12] LIN S, LIN K, LU D, et al. Preparation of uniform magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by co-precipitation in a helical module microchannel reactor. J Environ Chem Eng. 2017;5(1):303-309.
[13] KIM H, KIM D, JEONG C, et al. Assembly of plasmonic and magnetic nanoparticles with fluorescent silica shell layer for tri-functional SERS-magnetic-fluorescence probes and its bioapplications. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):13938.
[14] LIU R, ZHAO J, HAN Q, et al. One‐step assembly of a biomimetic biopolymer coating for particle surface engineering. Adv Mater. 2018;30(38):e1802851.
[15] UNNI M, UHL AM, SAVLIWALA S, et al. Thermal decomposition synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles with diminished magnetic dead layer by controlled addition of oxygen. ACS Nano. 2017;11(2):2284-2303.
[16] IWASA K, REDDI AH. Pulsed electromagnetic fields and tissue engineering of the joints. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2018;24(2):144-154.
[17] LUO C, YANG X, LI M, et al. A novel strategy forin vivo angiogenesis and osteogenesis: magnetic micro-movement in a bone scaffold. Artif Cell Nanomed B. 2018;46(sup2):636-645.
[18] SHOKROLLAHI H. Structure, synthetic methods, magnetic properties and biomedical applications of ferrofluids. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater. 2013;33(5):2476-2487.
[19] KHAN I, SAEED K, KHAN I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab J Chem. 2019;12(7):908-931.
[20] JIANG Z, SHAN K, SONG J, et al. Toxic effects of magnetic nanoparticles on normal cells and organs. Life Sci. 2019;220:156-161.
[21] PETROV DA, ZAKHLEVNYKH AN. Statistical theory of magnetic field induced phase transitions in negative diamagnetic anisotropy liquid crystals doped with carbon nanotubes. J Mol Liq. 2019;287:110901.
[22] THERUVATH AJ, NEJADNIK H, MUEHE AM, et al. Tracking cell transplants in femoral osteonecrosis with magnetic resonance imaging: a proof-of-concept study in patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(24):6223-6229.
[23] AUERBACH M, CHERTOW GM, ROSNER M. Ferumoxytol for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia. Expert Rev Hematol. 2018;11(10):829-834.
[24] VENTOLA CL. Progress in nanomedicine: approved and investigational nanodrugs. Pharmacol Therapeut. 2017;42(12):742-755.
[25] SUN C, LEE JSH, ZHANG M. Magnetic nanoparticles in MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2008;60(11):1252-1265.
[26] ARAMI H, KHANDHAR A, LIGGITT D, et al. In vivo delivery, pharmacokinetics, biodistribution and toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44(23):8576-8607.
[27] SHI L, ZENG Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Biocompatible injectable magnetic hydrogel formed by dynamic coordination network. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(49):46233-46240.
[28] LIU K, HAN L, TANG P, et al. An Anisotropic hydrogel based on mussel-inspired conductive ferrofluid composed of electromagnetic nanohybrids. Nano Lett. 2019; 19(12):8343-8356.
[29] ARIAS SL, SHETTY A, DEVORKIN J, et al. Magnetic targeting of smooth muscle cells in vitro using a magnetic bacterial cellulose to improve cell retention in tissue-engineering vascular grafts. Acta Biomater. 2018;77:172-181.
[30] HU X, NIAN G, LIANG X, et al. Adhesive tough magnetic hydrogels with high Fe3O4 content. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(10):10292-10300.
[31] CHAU M, DE FRANCE KJ, KOPERA B, et al. Composite hydrogels with tunable anisotropic morphologies and mechanical properties. Chem Mater. 2016;28(10):3406-3415.
[32] LU Q, BAI S, DING Z, et al. Hydrogel assembly with hierarchical alignment by balancing electrostatic forces. Adv Mater Interfaces. 2016;3(8):1500687.
[33] WANG N, MA M, LUO Y, et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles-reinforced hydrogel scaffold together with pinacidil loading to improve stem cell adhesion. Chem Nano Mat. 2018;4(7):631-641.
[34] LIN XY, WANG ZJ, PAN PJ, et al. Monodomain hydrogels prepared by shear-induced orientation and subsequent gelation. Rsc Adv. 2016;6(97):95239-95245.
[35] OMIDINIA ANARKOLI A, BOESVELD S, TUVSHINDORJ U, et al. An injectable hybrid hydrogel with oriented short fibers induces unidirectional growth of functional nerve cells. Small. 2017;13(36):1702207.
[36] ECHAVE MC, DOMINGUES RMA, GÓMEZ-FLORIT M, et al. Biphasic hydrogels integrating mineralized and anisotropic features for interfacial tissue engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(51):47771-47784.
[37] ARAÚJO-CUSTÓDIO S, GOMEZ-FLORIT M, TOMÁS AR, et al. Injectable and magnetic responsive hydrogels with bioinspired ordered structures. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019; 5(3):1392-1404.
[38] ROSE J C, CÁMARA-TORRES M, RAHIMI K, et al. Nerve cells decide to orient inside an injectable hydrogel with minimal structural guidance. Nano Lett. 2017;17(6):3782-3791.
[39] DE FRANCE KJ, YAGER KG, CHAN KJW, et al. Injectable anisotropic nanocomposite hydrogels direct in situ growth and alignment of myotubes. Nano Lett. 2017;17(10): 6487-6495.
[40] FARZANEH S, HOSSEINZADEH S, SAMANIPOUR R, et al. Fabrication and characterization of cobalt ferrite magnetic hydrogel combined with static magnetic field as a potential bio-composite for bone tissue engineering. J Drug Deliv Sci Tec. 2021;64:102525.
[41] WANG J, LI P, LI K, et al. The Effect of Magnetic Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) microsphere-gelatin hydrogel on the growth of pre-osteoblasts under static magnetic field. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2020;16(11):1658-1666.
[42] PETRETTA M, GAMBARDELLA A, DESANDO G, et al. Multifunctional 3D-printed magnetic polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Polymers. 2021;13(21):3825.
[43] HUANG WS, CHU IM. Injectable polypeptide hydrogel/inorganic nanoparticle composites for bone tissue engineering. PLoS One. 2019;14(1):e0210285.
[44] ABDEEN AA, LEE J, BHARADWAJ NA, et al. Temporal modulation of stem cell activity using magnetoactive hydrogels. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(19):2536-2544.
[45] HUANG D, XU K, HUANG X, et al. Remotely temporal scheduled macrophage phenotypic transition enables optimized immunomodulatory bone regeneration. Small. 2022; 18(39):2203680.
[46] CARVALHO EO, RIBEIRO C, CORREIA DM, et al. Biodegradable hydrogels loaded with magnetically responsive microspheres as 2D and 3D scaffolds. Nanomaterials. 2020;10(12):2421.
[47] PARFENOV VA, MIRONOV VA, KOUDAN EV, et al. Fabrication of calcium phosphate 3D scaffolds for bone repair using magnetic levitational assembly. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):4013.
[48] YUAN Z, MEMARZADEH K, STEPHEN AS, et al. Development of a 3D collagen model for the In vitro evaluation of magnetic-assisted osteogenesis. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):16270.
[49] HAN X, TANG S, WANG L, et al. Multicellular spheroids formation on hydrogel enhances osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells under magnetic nanoparticles induction. Int J Nanomed. 2021;16:5101-5115.
[50] PARDO A, GÓMEZ-FLORIT M, BARBOSA S, et al. Magnetic nanocomposite hydrogels for tissue engineering: design concepts and remote actuation strategies to control cell fate. ACS Nano. 2021;15(1):175-209.
[51] MOK H, ZHANG M. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle-based delivery systems for biotherapeutics. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2013;10(1):73-87.
[52] DENYER S, BHIMANI AD, PAPASTEFAN S, et al. Magnetic kyphoplasty: a novel drug delivery system for the spinal column. PLOS One. 2018;13(7):e201402.
[53] SILVA ED, BABO PS, COSTA-ALMEIDA R, et al. Multifunctional magnetic-responsive hydrogels to engineer tendon-to-bone interface. Nanomedicine. 2018;14(7):2375-2385.
[54] LI C, ARMSTRONG JP, PENCE IJ, et al. Glycosylated superparamagnetic nanoparticle gradients for osteochondral tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2018;176:24-33.
[55] MADANI SZM, REISCH A, ROXBURY D, et al. A magnetically responsive hydrogel system for controlling the timing of bone progenitor recruitment and differentiation factor deliveries. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(3):1522-1534.
[56] CAO Z, WANG D, LI Y, et al. Effect of nanoheat stimulation mediated by magnetic nanocomposite hydrogel on the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Sci China Life Sci. 2018;61(4):448-456.
[57] YUAN P, YANG T, LIU T, et al. Nanocomposite hydrogel with NIR/magnet/enzyme multiple responsiveness to accurately manipulate local drugs for on-demand tumor therapy. Biomaterials. 2020;262:120357.
[58] WANG L, HU P, JIANG H, et al. Mild hyperthermia-mediated osteogenesis and angiogenesis play a critical role in magnetothermal composite-induced bone regeneration. Nano Today. 2022;43:101401.
[59] CHEN J, HU H, FENG L, et al. Preparation and characterization of 3D porous conductive scaffolds with magnetic resonance enhancement in tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 2019;14(4):45013.
[60] LI H, YIN Y, XIANG Y, et al. A novel 3D printing PCL/GelMA scaffold containing USPIO for MRI-guided bile duct repair. Biomed Mater. 2020;15(4):45004. |