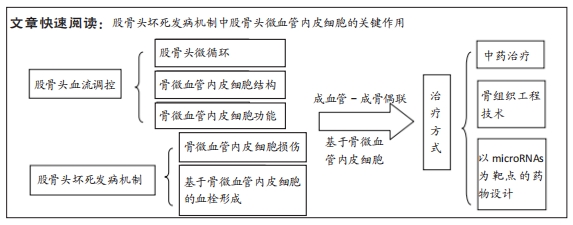
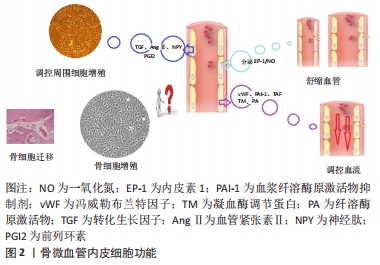
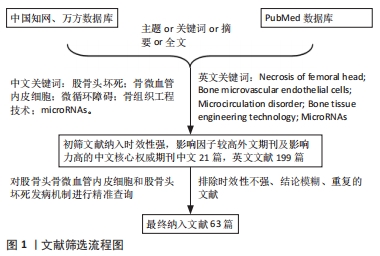
[1] AMANATULLAH DF, STRAUSS EJ, DI CESARE PE, et al. Current management options for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: part II, operative management. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2011;40(10): E216-225.
[2] KUBO T, UESHOMA K, SAITO M, et al. Clinical and basic research on steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Japan. J Orthop Sci. 2016;21(4):407-413.
[3] LARSON E, JONES LC, GOODMAN SB, et al. Early-stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head:where are we and where are we going in year 2018. Int Orthop. 2018;42(7):1723-1728.
[4] IKEUCHI K, HASEGAWA Y, SEKI T, et al. Epidemiology of nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Japan. Mod Rheumatol. 2015; 25(2):278-281.
[5] TAN B, LI W, ZENG P, et al. Epidemiological study based on Chinaosteonecrosis of the femoral head database. Orthop Surg. 2021; 13(1):153-160.
[6] ZHAO D, ZHANG F, WANG B. Guidelines for Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in Adults (2019 Version). J Orthop Translat. 2020;21:100-110.
[7] JOHNSON AJ,MONT ML A, TSAO AK, et al. Treatment of femoral head osteonecrosis in the United States: 16-year analysis of the Nationwide Inpatient Sample. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472:617-623.
[8] XU H, WANG C, LIU C, et al. Cotransplantation of mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells for treating steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021;10: 781-796.
[9] YU H, VANDEVORD PJ, MAO L, et al. Improved tissue-engineered bone regeneration by endothelial cell mediated vascularization. Biomaterials. 2009;30(4):508-517.
[10] RABQUER BJ, TAN GJ, SHAHEEN PJ, et al. Synovial inflammation in patients with osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Transl Sci. 2009; 2(4):273-280.
[11] COHEN-ROSENBLUM A, CUI Q. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Orthop Clin North Am. 2019;50(3):139-149.
[12] KALHOR M, HOROWITZ K, GHAREHDAO HI, et al. Anatomic variations in femor al head circulation. Hip int. 2012;22(3):307-312.
[13] 赵德伟,邱兴.股骨头血液供应及其临床意义[J].临床外科杂志, 2017,25(8):568-570.
[14] 张向南,耿凯龙,巨积辉,等.股骨头血供评估在股骨颈骨折诊断与治疗中的应用[J].国际骨科学杂志,2021,42(6):333-337.
[15] PRIES AR, SECOMB TW, GAEHTGENA P, et al. Blood Flow in microvascular Networks-Experiments and Simulation. Circulation Res. 1990;67(4):826-834.
[16] 张建色,张崇智,姜文学,等.大剂量激素对兔股骨头内血管影响的研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2009,15(5):351-353.
[17] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis by a Specific Vessel Subtype in Bone. Nature. 2007; 507(7492):323-328.
[18] ZHANG JK, PAN J, JING W. Motivating role of type H vessels in bone regeneration. Cell Prolif. 2020;53:e12874.
[19] ZHOU CH, MENG JH, ZHAO CC, et al. PTH[1-34] improves the effects of core decompression in early-stage steroid-associated osteonecrosis model by enhancing bone repair and revascularization. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0178781.
[20] LANE NE, MOHAN G, YAO W, et al. Prevalence of glucocorticoid induced osteonecrosis in the mouse is not affected by treatments that maintain bone vascularity. Bone Rep. 2018;9:181-187.
[21] GAO F, MAO T, ZHANG Q, et al. H subtype vascular endothelial cells in human femoral head: an experimental verification. Ann Palliat Med. 2020;9(4):1497-1505.
[22] lE NOBLE F, LE NOBLE J. Bone biology: Vessels of rejuvenation. Nature. 2014;507:313-314.
[23] 黄钰婷,张恺,苏菁,等.射血分数保留型心力衰竭与微血管内皮炎症[J].临床心血管病杂,2021,37(6):512-515.
[24] LI H, HORKE S, FRSTERMANN U. Vascular oxidative stress,nitric oxide and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2014;237:208-219.
[25] 潘丽娜,汪泽扬,陈丽媛,等.血小板微囊泡对人微血管内皮细胞功能的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2020,42(8):758-764.
[26] 周占国,郭浩山,关涛,等.股骨头坏死病因的相关因素分析[J].中医正骨,2020,32(1):7-10.
[27] 沈俊杰,李华灿,乐宇民.股骨头缺血性坏死数字减影血管造影及介入治疗效果观察[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2009,34(1):53-55.
[28] YANG Y, LOU J, LI Z, et al. Effect of glucocorticoid on production of reactive oxygen species in bone microvascular endothelial cells. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011;25:533-537.
[29] XUE Y, XING Z, HELLEM S, et al. Endothelial cells influence the osteogenic potential of bone marrow stromal cells. Biomed Eng Online. 2009;8(17):34.
[30] 王佰亮,李子荣,娄晋宁,等.淫羊藿苷对糖皮质激素诱导的骨微血管内皮细胞损伤的保护作用[J].中国微循环,2009,13(6):461-464.
[31] VOGT CJ, SCHMID-SCHNBEIN GW. Microvascular endothelial cell death and rarefaction in the glucocorticoid - induced hypertensive rat. Microcirculation. 2001;8:129-139.
[32] XU JZ. Animal models of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head-a comprehensive research review up to 2018. Int Orthop. 2018; 42(7):1729-1737.
[33] YOON BH. Alcohol intake and the risk of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Japanese populations: a dose-response meta-analysis of case-control studies. Clin Rheumatology. 2017;36(11): 2517-2524.
[34] NASEER ZA, BACHABI M, JONES LC, et al. Osteonecrosis in Sickle Cell Disease. South Med J. 2016;109(9):525-530.
[35] 彭雯雯,刘国英,潘燕霞,等.ACE2基因过表达减轻血管紧张素Ⅱ诱导的神经细胞氧化应激[J].中国病理生理杂志,2019,35(6):1081-1088.
[36] YAMAMOTO Y, ISHIZU A, IKEDA H, et al. Dexamethasone increased plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression on human umbilical vein endothelial cells: an additive effect to tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Pathobiology. 2004;71(6):295-301.
[37] 孙伟,李子荣,史振才,等.严重急性呼吸综合征后激素性骨坏死患者的凝血和纤溶指标观察[J].中华全科医师杂志,2006,5(2):89-94.
[38] KROL J, LOEDIGE I, FILIPOWICZ W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11: 597-610.
[39] AMBROS V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350-355.
[40] YUE J, WAN F, ZHANG QD, et al. Effect of glucocorticoids on miRNA expression spectrum of rat femoral head microcirculation endothelial cells. Gene. 2018;651:126-133.
[41] NGUYEN NH, TRAN GB, NGUYEN CT. Anti-oxidative effects of superoxide dismutase 3 on inflammatory diseases. J Mol Med (Berl). 2020;98:59-69.
[42] LEI Z, VAN MIL A, BRANDT MM, et al. MicroRNA-132/212 family enhances arteriogenesis after hindlimb ischaemia through modulation of the Ras-MAPK pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(8):1994-2005.
[43] ZHOU H, MEHTA S, SRIVASTAVA SP, et al. Endothelial cell-glucocorticoid receptor interactions and regulation of Wnt signaling. JCI Insight. 2020; 5:314-319.
[44] 陈培生,林小凤,林凤飞,等.H型血管耦联成血管-成骨机制在骨微环境重构机制的研究进展[J].中华创伤杂志,2021,37(11):1048-1054.
[45] 章友财,刘金浪,蔡声麟,等.三七总皂苷对兔酒精性股骨头坏死微血管血供及超微结构的影响[J].江西医药,2016,51(1):23-25.
[46] 赵丁岩,俞庆声,郭万首,等.淫羊藿甘对激素诱导损伤人股骨头微血管内皮细胞蛋白质表达谱的影响[J]. 中华医学杂志,2016, 96(13):1026-1030.
[47] 李新建,齐振熙,余航,等.髓芯减压术联合羟基红花黄色素A对激素性股骨头坏死模免股骨头微循环的影响[J].中华中医药杂志, 2015,30(5):1538-1541.
[48] 张蕾蕾,梁大伟,刘又文,等.微创粗通道减压病灶清除植骨术 联合中药治疗非创伤性股骨头坏死32例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2019,27(6):63-65.
[49] 任博文.温肾活血汤合钽棒植入治疗早期非创伤性股骨头 缺血性坏死的临床观察[D].郑州:河南中医药大学,2016.
[50] 秦宇星,任前贵,沈佩锋,等.组织工程技术治疗骨缺损:应用于临床还有多远?[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(29):4703-4708.
[51] 冯勇.内皮祖细胞在股骨头坏死发病机制及治疗中的作用研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2010.
[52] 王新刚,封占增,郭明峰,等.组织工程促血管化策略的研究进展[J].中华烧伤杂志,2012,28(5):374-377.
[53] ZIGDON-GILADI H, BICK T, LEWINSON D, et al. Co-transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem cells promote neovascularization and bone regeneration. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015;17(2):353-359.
[54] KRUGER-GENGE A, BLOCKI A, FRANKE RP. et al. Vascular Endothelial Cell Biology:An Update. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(18):4411
[55] 明华伟,何芸,夏德林,等.VEGF 165基因转染HUVEC促进大鼠血管生成的实验研究[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2017,27(3):161-165.
[56] JIN HT, XU TT, CHEN QQ, et al. The Fate and Distribution of Autologous Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Intra-Arterial Infusion in Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in Dogs. Stem Cells Int. 2016;86: 116-143.
[57] STONE OA, CARTER JG, LIN PC, et al. Differential regulation of blood flow-induced neovascularization and mural cell recruitment by vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin signalling. J Physiol. 2017; 595:1575-1591.
[58] 毕翔宇,孙安,何惠宇.联合VEGF-165和PDGF-BB促进骨髓间充质干细胞血管化的体内研究[J].口腔医学,2020,40(1):7-12.
[59] 任前贵,王瞾,张坤.仿生控释BMP-2和VEGF的PELA微球支架对骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的Wnt/β-catenin通路的影响[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2018,31(10):1118-1121+1125.
[60] SIVARAJ KK, ADAMS RH. Blood vessel formation and function in bone. Development. 2016;143(15):2706-2715.
[61] 徐海侠.联合移植骨髓间充质干细胞和内皮祖细胞治疗兔激素性股骨头坏死的实验研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2021.
[62] ZHOU P, LI Y, DI R, et al. H19 and Foxc2 synergistically promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs via Wnt-beta-catenin pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(8):13799-13806.
[63] LIAO H, ZHONG Z, LIU Z, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cells coexpressing VEGF and BMP-6 genes to combat avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(1):954-962.
|