[1] NORRIS B L, VANDERKARR M, SPARKS C, et al. Treatments, cost and healthcare utilization of patients with segmental bone defects. Injury. 2021;52(10):2935-2940.
[2] DAHL MT, MORRISON S. Segmental bone defects and the history of bone transport. J Orthop Trauma. 2021;35(Suppl 4):S1-S7.
[3] SCHMIDT AH. Autologous bone graft: Is it still the gold standard? Injury. 2021;52 Suppl 2:S18-S22.
[4] MASQUELET A. The induced membrane technique. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020;106(5):785-787..
[5] VALTANEN RS, YANG YP, GURTNER GC, et al. Synthetic and bone tissue engineering graft substitutes: what is the future? Injury. 2021;52 Suppl 2:S72-S77.
[6] 王海波,杨新明,张瑛,等.大段骨缺损修复的组织工程学研究进展[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2013,19(1):73-76.
[7] 周思睿,邓江.修复临界及超临界骨缺损的组织工程材料研究进展[J].山东医药,2016,56(48):103-105.
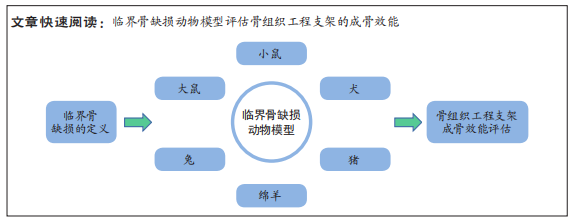
[8] SCHMITZ J, HOLLINGER J. The Critical size defect as an experimental model for craniomandibulofacial nonunions. Clin Orthop Related Res. 1986;205:299-308.
[9] MAUFFREY C, BARLOW BT, SMITH W. Management of segmental bone defects. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(3):143-153.
[10] HOLLINGER JO, KLEINSCHMIDT JC. The critical size defect as an experimental model to test bone repair materials. J Craniofac Surg. 1990;1(1):60-68.
[11] BHARADWAZ A, JAYASURIYA AC. Recent trends in the application of widely used natural and synthetic polymer nanocomposites in bone tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;110:110698.
[12] GUGALA Z, GOGOLEWSKI S. Regeneration of segmental diaphyseal defects in sheep tibiae using resorbable polymeric membranes: a preliminary study. J Orthop Trauma. 1999;13(3):187-195.
[13] KOLK A, HANDSCHEL J, DRESCHER W, et al. Current trends and future perspectives of bone substitute materials-from space holders to innovative biomaterials. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012;40(8):706-718.
[14] HOBURG A, KESHLAF S, SCHMIDT T, et al. Fractionation of high-dose electron beam irradiation of BPTB grafts provides significantly improved viscoelastic and structural properties compared to standard gamma irradiation. Knee surgery, sports traumatology, arthroscopy: official journal of the ESSKA. 2011;19:1955-1961.
[15] 陈胡贵,覃建国,李理,等.大动物节段性骨缺损模型的研究进展[J].北京生物医学工程,2021,40(2):203-208.
[16] RHINELANDER FW, PHILLIPS RS, STEEL WM, et al. Microangiography in bone healing. II. Displaced closed fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1968;50(4):643-662.
[17] 李福兵,徐永清,潘兴华,等.小鼠胫骨中段1/3不同缺损直径单层骨皮质缺损模型比较研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(10):1218-1222.
[18] HUANG S, XU L, SUN Y, et al. An improved protocol for isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse bone marrow. J Orthop Translat. 2015;3(1):26-33.
[19] AWADEEN MA, AL-BELASY FA, AMEEN LE, et al. Early therapeutic effect of platelet-rich fibrin combined with allogeneic bone marrow-derived stem cells on rats’ critical-sized mandibular defects. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(1):55-69.
[20] GUO T, YUAN X, LI X, et al. Bone regeneration of mouse critical-sized calvarial defects with human mesenchymal stem cell sheets co-expressing BMP2 and VEGF. Lab Anim Res. 2013;29(4):196-203.
[21] TAZAWA R, UCHIDA K, MINEHARA H, et al. Poly(POG)n loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 accelerates new bone formation in a critical-sized bone defect mouse model. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15:471.
[22] MEEK S, MASHIMO T, BURDON T. From engineering to editing the rat genome. Mamm Genome. 2017;28(7-8):302-314.
[23] 王昕.基因编辑技术创新构建大鼠药物代谢模型及其应用[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2019,33(10):814.
[24] 孙筱品,董玉梅,汪海燕,等.Neuritin条件性基因打靶载体的构建和同源重组胚胎干细胞克隆鉴定[J].动物医学进展,2019,40(4):16-21.
[25] LIU F, FERREIRA E, PORTER RM, et al. Rapid and reliable healing of critical size bone defects with genetically modified sheep muscle. Eur Cell Mater. 2015;30:118-130: 130-131.
[26] 曾志奎,黄枫,黄培镇,等.大鼠股骨Masquelet诱导膜实验模型的建立[J].山东医药,2017,57(48):1-4.
[27] 马云飞.医用硫酸钙介导的Masquelet技术修复SD大鼠大段骨缺损的实验研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2017.
[28] DRENO M, BLERY P, GUICHEUX J, et al. Development of a rat model of mandibular irradiation sequelae for preclinical studies of bone repair. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2020;26(8):447-455.
[29] MIGUEZ PA, TUIN SA, ROBINSON AG, et al. Hesperidin promotes osteogenesis and modulates collagen matrix organization and mineralization in vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(6):3223.
[30] ZHANG W, SHI W, WU S, et al. 3D printed composite scaffolds with dual small molecule delivery for mandibular bone regeneration. Biofabrication. 2020,12(3):35020.
[31] MANJU V, ANITHA A, MENON D, et al. Nanofibrous yarn reinforced HA-gelatin composite scaffolds promote bone formation in critical sized alveolar defects in rabbit model. Biomed Mater. 2018;13(6):65011.
[32] 田彬,胡磊,江青松,等.兔颅顶骨临界骨缺损模型的构建[J].北京口腔医学, 2022,30(2):88-92.
[33] 徐石庄,王进,潘文振,等.兔股骨髁临界性骨缺损动物模型制备及临界骨缺损值[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(20):3191-3195.
[34] LIU F, CHEN K, HOU L, et al. Determining the critical size of a rabbit rib segmental bone defect model. Regen Biomater. 2016;3(5):323-328.
[35] LEE JS, PARK TH, RYU JY, et al. Osteogenesis of 3D-Printed PCL/TCP/bdECM scaffold using adipose-derived stem cells aggregates: an experimental study in the canine mandible. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):5409.
[36] KAWAI T, MATSUI K, IIBUCHI S, et al. Reconstruction of critical-sized bone defect in dog skull by octacalcium phosphate combined with collagen. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2011;13(2):112-123.
[37] ALVIRA-GONZALEZ J, SANCHEZ-GARCES MA, CAIRO JR, et al. Assessment of bone regeneration using adipose-derived stem cells in critical-size alveolar ridge defects: an experimental study in a dog model. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016;31(1):196-203.
[38] LUNNEY JK, Van GOOR A, WALKER KE, et al. Importance of the pig as a human biomedical model. Sci Transl Med. 2021;13(621):d5758.
[39] MOEST T, SCHLEGEL KA, KESTING M, et al. A new standardized critical size bone defect model in the pig forehead for comparative testing of bone regeneration materials. Clin Oral Investig. 2020;24(5):1651-1661.
[40] JOHNSON ZM, YUAN Y, LI X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and three-dimensional-osteoconductive scaffold regenerate calvarial bone in critical size defects in swine. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021;10(8):1170-1183.
[41] LI Y, CHEN SK, LI L, et al. Bone defect animal models for testing efficacy of bone substitute biomaterials. J Orthop Translat. 2015;3(3):95-104.
[42] REICHERT JC, SAIFZADEH S, WULLSCHLEGER ME, et al. The challenge of establishing preclinical models for segmental bone defect research. Biomaterials. 2009,30(12):2149-2163.
[43] GOODMAN R, INSKEEP K. Chapter 44. Neuroendocrine Control of the Ovarian Cycle of the Sheep. 2006:2389-2447.
[44] CROVACE AM, LACITIGNOLA L, FORLEO DM, et al. 3D biomimetic porous titanium (Ti(6)Al(4)V ELI) scaffolds for large bone critical defect reconstruction: an experimental study in sheep. Animals (Basel). 2020;10(8):1389.
[45] KABIR M A, MURATA M, SHAKYA M, et al. Bio-absorption of human dentin-derived biomaterial in sheep critical-size iliac defects. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(1):223.
[46] HETTWER W, HORSTMANN PF, BISCHOFF S, et al. Establishment and effects of allograft and synthetic bone graft substitute treatment of a critical size metaphyseal bone defect model in the sheep femur. APMIS. 2019;127(2):53-63.
[47] 孙东东,孙明林,高丽兰.生长因子在软骨组织工程中的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(10):645-652.
[48] RAINA DB, MATUSZEWSKI LM, VATER C, et al. A facile one-stage treatment of critical bone defects using a calcium sulfate/hydroxyapatite biomaterial providing spatiotemporal delivery of bone morphogenic protein-2 and zoledronic acid. Sci Adv. 2020;6(48):eabc1779.
[49] WEI X, ZHOU W, TANG Z, et al. Magnesium surface-activated 3D printed porous PEEK scaffolds for in vivo osseointegration by promoting angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Bioact Mater. 2023;20:16-28.
[50] KIM DS, LEE JK, KIM JH, et al. Advanced PLGA hybrid scaffold with a bioactive PDRN/BMP2 nanocomplex for angiogenesis and bone regeneration using human fetal MSCs. Sci Adv. 2021;7(50):j1083.
[51] SHUAI C, YANG W, FENG P, et al. Accelerated degradation of HAP/PLLA bone scaffold by PGA blending facilitates bioactivity and osteoconductivity. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(2):490-502.
[52] 邢晓敏,邓蕊.第三类医疗器械临床试验伦理问题案例探讨[J].中国新药与临床杂志,2018,37(8):467-471.
[53] CAO H, LI L, LI L, et al. New use for old drug: local delivery of puerarin facilitates critical-size defect repair in rats by promoting angiogenesis and osteogenesis. J Orthop Translat. 2022;36:52-63.
[54] SUVARNAPATHAKI S, WU X, ZHANG T, et al. Oxygen generating scaffolds regenerate critical size bone defects. Bioact Mater. 2022;13:64-81.
[55] YAN ZY, ZHU JH, LIU GQ, et al. Feasibility and efficacy of a degradable magnesium-alloy GBR membrane for bone augmentation in a distal bone-defect model in beagle dogs. Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2022;2022:4941635.
[56] DEWEY MJ, MILNER DJ, WEISGERBER D, et al. Repair of critical-size porcine craniofacial bone defects using a collagen-polycaprolactone composite biomaterial. Biofabrication. 2021;14(1):10.
[57] DEBAUN MR, STAHL AM, DAOUD AI, et al. Preclinical induced membrane model to evaluate synthetic implants for healing critical bone defects without autograft. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(1):60-68.
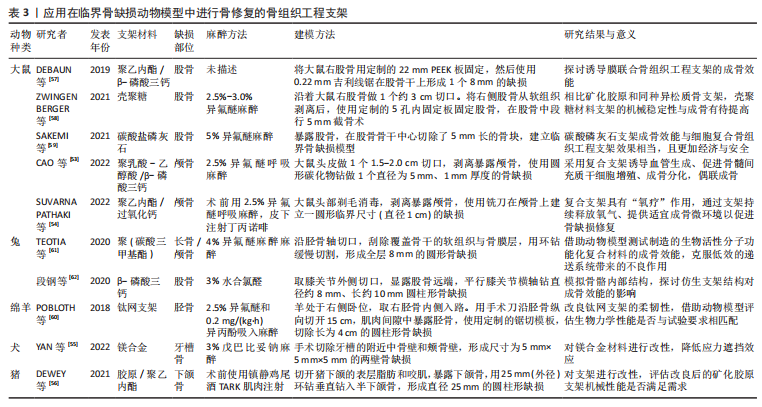
[58] ZWINGENBERGER B, VATER C, BELL RL, et al. Treatment of critical-size femoral bone defects with chitosan scaffolds produced by a novel process from textile engineering. Biomedicines. 2021;9(8):1015.
[59] SAKEMI Y, HAYASHI K, TSUCHIYA A, et al. Reconstruction of critical-size segmental defects in rat femurs using carbonate apatite honeycomb scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021;109(9):1613-1622.
[60] POBLOTH AM, CHECA S, RAZI H, et al. Mechanobiologically optimized 3D titanium-mesh scaffolds enhance bone regeneration in critical segmental defects in sheep. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(423):eaam8828.
[61] TEOTIA AK, DIENEL K, QAYOOM I, et al. Improved bone regeneration in rabbit bone defects using 3d printed composite scaffolds functionalized with osteoinductive factors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(43):48340-48356.
[62] 段钢,陈宏亮,郭开今,等.3D打印β-磷酸三钙仿生骨支架修复兔股骨髁骨缺损[J]. 骨科临床与研究杂志,2020,5(4):243-250.
|