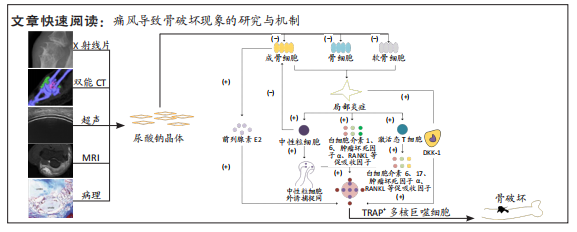
[1] SINGH JA, REDDY SG, KUNDUKULAM J. Risk factors for gout and prevention: a systematic review of the literature. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23(2):192-202.
[2] 高尿酸血症相关疾病诊疗多学科共识专家组. 中国高尿酸血症相关疾病诊疗多学科专家共识[J]. 中华内科杂志,2017,56(3):235-248.
[3] DANVE A, SEHRA ST, NEOGI T. Role of diet in hyperuricemia and gout. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2021;35(4):101723.
[4] FU T, CAO H, YIN R, et al. Associated factors with functional disability and health-related quality of life in Chinese patients with gout: a case-control study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):429.
[5] 朱坤智,卢涛,罗张风,等.四肢痛风石外科治疗时机和适应证[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(30):4883-4890.
[6] LI Q, LI X, WANG J, et al. Diagnosis and treatment for hyperuricemia and gout: a systematic review of clinical practice guidelines and consensus statements. BMJ Open. 2019;9(8):e026677.
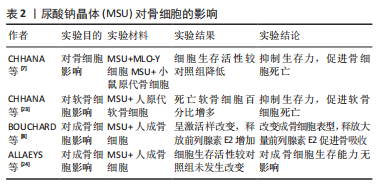
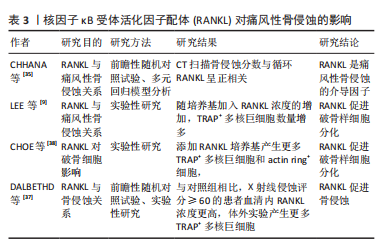
[7] CHHANA A, POOL B, CALLON KE, et al. Monosodium urate crystals reduce osteocyte viability and indirectly promote a shift in osteocyte function towards a proinflammatory and proresorptive state. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):208.
[8] BOUCHARD L, DE MÉDICIS R, LUSSIER A, et al. Inflammatory microcrystals alter the functional phenotype of human osteoblast-like cells in vitro: synergism with IL-1 to overexpress cyclooxygenase-2. J Immunol. 2002;168(10):5310-5317.
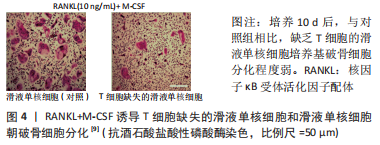
[9] LEE SJ, NAM KI, JIN HM, et al. Bone destruction by receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand-expressing T cells in chronic gouty arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(5):R164.
[10] RESNICK D, BRODERICK TW. Intraosseous calcifications in tophaceous gout. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981;137(6):1157-1161.
[11] BARTHELEMY CR, NAKAYAMA DA, CARRERA GF, et al. Gouty arthritis: a prospective radiographic evaluation of sixty patients. Skeletal Radiol. 1984;11(1):1-8.
[12] CARTER JD, KEDAR RP, ANDERSON SR, et al. An analysis of MRI and ultrasound imaging in patients with gout who have normal plain radiographs. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48(11):1442-1446.
[13] YANG Y, GUO Y, YU S, et al. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging findings in gouty arthritis involving large joints of the upper extremities. BMC Med Imaging. 2022;22(1):167.
[14] TOWIWAT P, DOYLE AJ, GAMBLE GD, et al. Urate crystal deposition and bone erosion in gout: ‘inside-out’ or ‘outside-in’? A dual-energy computed tomography study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18(1):208.
[15] MCQUEEN FM, DOYLE A, DALBETH N. Imaging in gout--what can we learn from MRI, CT, DECT and US?. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(6):246.
[16] SLOT O, TERSLEV L. Ultrasonographic signs of gout in symmetric polyarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(11):3487.
[17] NAREDO E, USON J, JIMÉNEZ-PALOP M, et al. Ultrasound-detected musculoskeletal urate crystal deposition: which joints and what findings should be assessed for diagnosing gout? Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(8):1522-1528.
[18] NEOGI T, JANSEN TL, DALBETH N, et al. 2015 Gout classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(10):1789-1798.
[19] CAO L, ZHAO T, XIE C, et al. Performance of Ultrasound in the Clinical Evaluation of Gout and Hyperuricemia. J Immunol Res. 2021;2021:5550626.
[20] ALLAEYS I, RUSU D, PICARD S, et al. Osteoblast retraction induced by adherent neutrophils promotes osteoclast bone resorption: implication for altered bone remodeling in chronic gout. Lab Invest. 2011;91(6):905-920.
[21] KOTAKE S, UDAGAWA N, HAKODA M, et al. Activated human T cells directly induce osteoclastogenesis from human monocytes: possible role of T cells in bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(5):1003-1012.
[22] CHHANA A, AATI O, GAMBLE GD, et al. Path Analysis Identifies Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand, Osteoprotegerin, and Sclerostin as Potential Mediators of the Tophus-bone Erosion Relationship in Gout. J Rheumatol. 2016;43(2):445-449.
[23] CHHANA A, CALLON KE, POOL B, et al. The effects of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals on chondrocyte viability and function: implications for development of cartilage damage in gout. J Rheumatol. 2013;40(12):2067-2074.
[24] ALLAEYS I, RUSU D, PICARD S, et al. Osteoblast retraction induced by adherent neutrophils promotes osteoclast bone resorption: implication for altered bone remodeling in chronic gout. Lab Invest. 2011;91(6):905-920.
[25] ZHANG Y, DAAKA Y. PGE2 promotes angiogenesis through EP4 and PKA Cγ pathway. Blood. 2011;118(19):5355-5364.
[26] LU W, YU W, HE J, et al. Reprogramming immunosuppressive myeloid cells facilitates immunotherapy for colorectal cancer. EMBO Mol Med. 2021;13(1):e12798.
[27] NI S, LING Z, WANG X, et al. Sensory innervation in porous endplates by Netrin-1 from osteoclasts mediates PGE2-induced spinal hypersensitivity in mice. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):5643.
[28] NAKANISHI M, ROSENBERG DW. Multifaceted roles of PGE2 in inflammation and cancer. Semin Immunopathol. 2013;35(2):123-137.
[29] JIN J, TANG Q, LI Z, et al. Prostaglandin E2 regulates renal function in C57/BL6 mouse with 5/6 nephrectomy. Life Sci. 2017;174:68-76.
[30] TU M, YANG M, YU N, et al. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 activity in subchondral bone modifies a subtype of osteoarthritis. Bone Res. 2019;7:29.
[31] JIANG W, JIN Y, ZHANG S, et al. PGE2 activates EP4 in subchondral bone osteoclasts to regulate osteoarthritis. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):27.
[32] CHOE JY, PARK KY, KIM SK. Monosodium Urate in the Presence of RANKL Promotes Osteoclast Formation through Activation of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase. Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:597512.
[33] 田晓玲,陈莉,刘满华,等.痛风性关节炎患者NETs表达水平与骨破坏、炎症因子的相关性分析[J]. 广州医科大学学报,2021,49(4):67-70.
[34] ZOU Y, FEI Y, GAO H, et al. Association between musculoskeletal ultrasonography and bone remodelling markers and its role in disease monitoring of gout and hyperuricaemia. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020;38(5):896-902.
[35] CHHANA A, AATI O, GAMBLE GD, et al. Path Analysis Identifies Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand, Osteoprotegerin, and Sclerostin as Potential Mediators of the Tophus-bone Erosion Relationship in Gout. J Rheumatol. 2016; 43(2):445-449.
[36] HARRE U, DERER A, SCHORN C, et al. T cells as key players for bone destruction in gouty arthritis?. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(6):135.
[37] DALBETH N, SMITH T, NICOLSON B, et al. Enhanced osteoclastogenesis in patients with tophaceous gout: urate crystals promote osteoclast development through interactions with stromal cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(6):1854-1865.
[38] CHOE JY, PARK KY, KIM SK. Monosodium Urate in the Presence of RANKL Promotes Osteoclast Formation through Activation of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase. Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:597512.
[39] MURAKAMI T, NAKAMINAMI Y, TAKAHATA Y, et al. Activation and Function of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Bone and Joint-Related Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(10):5365.
[40] GIAMARELLOS-BOURBOULIS EJ, MOUKTAROUDI M, BODAR E, et al. Crystalsof monosodium urate monohydrate enhance lipopolysaccharide-induced release of interleukin 1 beta by mononuclear cellsthrough a caspase 1-mediated process. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(2):273-278.
[41] MARTINON F, PÉTRILLI V, MAYOR A, et al. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature. 2006;440(7081):237-241.
[42] CHEN CJ, SHI Y, HEARN A, et al. MyD88-dependent IL-1 receptorsignaling is essential for gouty inflammation stimulated by monosodium urate crystals. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(8):2262-2271.
[43] SO A, DE SMEDT T, REVAZ S, et al. A pilot study of IL-1 inhibition by anakinra in acute gout. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(2):R28.
[44] SCHLESINGER N, ALTEN RE, BARDIN T, et al. Canakinumab for acute gouty arthritis in patients with limited treatment options: Results from two randomised, multicentre,active-controlled, double-blind trials and their initial extensions. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(11):1839-1848.
[45] DALBETH N, GOSLING AL, GAFFO A, et al. Gout. Lancet. 2021;397(10287):1843-1855.
[46] NAREDO E, USON J, JIMÉNEZ-PALOP M, et al. Ultrasound-detected musculoskeletal urate crystal deposition: which joints and what findings should be assessed for diagnosing gout? Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(8):1522-1528.
[47] KOTAKE S, UDAGAWA N, HAKODA M, et al. Activated human T cells directly induce osteoclastogenesis from human monocytes: possible role of T cells in bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(5):1003-1012.
[48] TAO SS, CAO F, SAM NB, et al. Dickkopf-1 as a promising therapeutic target for autoimmune diseases. Clin Immunol. 2022;245:109156.
[49] HUANG Y, LIU L, LIU A. Dickkopf-1: Current knowledge and related diseases. Life Sci. 2018;209:249-254.
[50] 赵卫,高辉,朱佳鑫,等. 血清Dickkopf-1与原发性痛风性关节炎骨破坏的相关性[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2012,44(2):254-258.
[51] GAVRIATOPOULOU M, DIMOPOULOS MA, CHRISTOULAS D, et al. Dickkopf-1: a suitable target for the management of myeloma bone disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009;13(7):839-848.
[52] CHO YN, JEONG HS, PARK KJ, et al. Altered distribution and enhanced osteoclastogenesis of mucosal-associated invariant T cells in gouty arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59(8):2124-2134.
[53] CHUNG R, COOL JC, SCHERER MA, et al. Roles of neutrophil-mediated inflammatory response in the bony repair of injured growth plate cartilage in young rats. J Leukoc Biol. 2006;80(6):1272-1280.
[54] GUERRA M, HALLS VS, SCHATTERNY J, et al. Protease FRET Reporters Targeting Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;142(48):20299-20305.
[55] DANIEL C, LEPPKES M, MUÑOZ LE, et al. Extracellular DNA traps in inflammation, injury and healing. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2019;15(9):559-575.
[56] DAI XJ, TAO JH, FANG X, et al. Changes of Treg/Th17 Ratio in Spleen of Acute Gouty Arthri-tis Rat Induced by MSU Crystals. Inflammation. 2018;41(5):1955-1964.
[57] JIA E, LI Z, GENG H, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps induce the bone erosion of gout. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):1128.
[58] D HAYASHI R, YAMAOKA M, NISHIZAWA H, et al. Multiple Gouty Tophi with Bone Erosion and Destruction: A Report of an Early-onset Case in an Obese Patient. Intern Med. 2017;56(9):1071-1077.
[59] MATSUO H, TAKADA T, ICHIDA K, et al. Common defects of ABCG2, a high-capacity urate exporter, cause gout: a function-based genetic analysis in a Japanese population. Sci Transl Med. 2009;1(5):5ra11.
[60] NAKAYAMA A, MATSUO H, SHIMIZU T, et al. Common missense variant of monocarboxylate transporter 9 (MCT9/SLC16A9) gene is associated with renal overload gout, but not with all gout susceptibility. Hum Cell. 2013;26(4):133-136.
[61] HAINER BL, MATHESON E, WILKES RT. Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of gout. Am Fam Physician. 2014;90(12):831-836.
[62] 王旭,罗冬平,茹彦海,等.从慢性肾脏病角度看高尿酸血症与痛风的指南更新要点[J].中国全科医学,2021,24(33):4191-4195.
[63] FITZGERALD JD, DALBETH N, MIKULS T, et al. 2020 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Management of Gout. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(6):879-895.
[64] HU S, TERKELTAUB R, SUN M, et al. Palpable tophi and more comorbidities associated with adherence to urate-lowering medical therapy in a Chinese gout cohort. Joint Bone Spine. 2022;89(6):105435. |