中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (5): 804-812.doi: 10.12307/2024.243
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
金属离子促血管生成机制及在骨组织工程中的应用
王嘉旎,陈俊宇
- 口腔疾病研究国家重点实验室,国家口腔疾病临床医学中心,四川大学华西口腔医院修复科,四川省成都市 610041
-
收稿日期:2022-12-19接受日期:2023-03-15出版日期:2024-02-18发布日期:2023-08-17 -
通讯作者:陈俊宇,副教授,硕士生导师,口腔疾病研究国家重点实验室,国家口腔疾病临床医学中心,四川大学华西口腔医院修复科,四川省成都市 610041 -
作者简介:王嘉旎,女,2004年生,汉族,主要从事血管化组织工程学方向的研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(81901060,82270961),项目负责人:陈俊宇;中国博士后科学基金特别资助项目(2021T140483),项目负责人:陈俊宇
Angiogenesis mechanism of metal ions and their application in bone tissue engineering
Wang Jiani, Chen Junyu
- State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2022-12-19Accepted:2023-03-15Online:2024-02-18Published:2023-08-17 -
Contact:Chen Junyu, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Wang Jiani, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 81901060, 82270961 (to CJY); Special Funded Project of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, No. 2021T140483 (to CJY)
摘要:
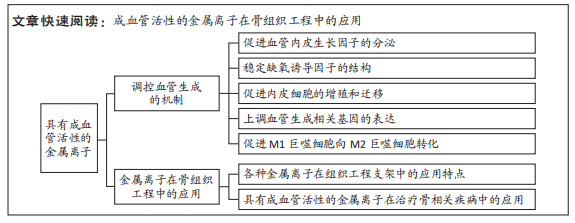
文题释义:
金属离子的成血管活性:部分金属离子,如铜、镁离子等,可通过上调血管内皮生长因子的表达等途径调控血管生成,从而促进血管化的过程。金属离子的成血管活性受到其浓度的影响,不同浓度的金属离子对于血管生成的作用存在较大差异,高浓度的金属离子一般具有细胞毒性,而低浓度的金属离子具有成血管效应。骨组织工程:自体的骨髓基质干细胞等细胞经过体外扩增后,种植在具有良好生物相容性的细胞支架或细胞外基质上,从而制得一个有助于细胞黏附的支架。这种含有细胞的支架可为植入部位提供营养物质,促进组织细胞间的气体交换和废物的排出,目前广泛地用于骨组织缺损的修复。
背景:多种金属离子因具有良好的血管生成活性,并参与成骨中血管新生等生理过程,在骨组织工程领域的研究和应用正日益深入。
目的:系统性阐释铜(Cu2+)、镁(Mg2+)、锶(Sr2+)、锌(Zn2+)、钴(Co2+)离子的促血管生成机制及其在骨组织工程的应用现状和主要治疗的疾病类型。方法:2位作者利用PubMed和中国知网数据库检索2017-2022年间发表的文献,中文检索词为“铜离子,镁离子,锶离子,锌离子,钴离子,骨,血管生成”;英文检索词为“copper,cuprum,Cu,magnesium,Mg,strontium,Sr,zinc,Zn,cobalt,Co,metal ion,angiogenesis,bone”。通过阅读标题、摘要对所得文献进行初筛,排除不相关文献后,最终纳入114篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①金属离子可以通过作用于血管内皮生长因子、缺氧诱导因子、血管生成相关基因、内皮细胞以及对巨噬细胞进行免疫调节等途径调控血管生成。②铜、镁、锶、锌、钴等金属离子因具有显著的血管生成效应,常用于组织工程支架的性能改善,其中水凝胶、生物陶瓷和合成聚合物材料目前应用较为广泛,镁及其合金也因其优良的承重能力颇具优势,但这些材料均存在一些缺陷,目前暂时没有一种理想的骨替代材料。③不同的离子作用特点如下:铜具有抗菌、成血管和成骨等性能,主要用于感染及肿瘤等引起的骨缺损;镁、锌具有较强的生物降解性,需要对降解速率进行控制;镁具有腐蚀性,主要以合金形式应用;锌的成血管机制涉及较少;镁、锶用于治疗骨质疏松性骨缺损效果显著。④以上5种金属离子(铜、镁、锶、锌、钴)具有显著的促血管生成作用,也通过成血管来促进成骨,个别离子如铜离子具有杀菌作用,这些金属离子可以作为治疗肿瘤、骨质疏松症、感染和创伤等引起的骨缺损的新策略,但是目前的临床试验和产品的应用性研究相对不足。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6467-1941(王嘉旎);https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1717-5782(陈俊宇)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
王嘉旎, 陈俊宇. 金属离子促血管生成机制及在骨组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 804-812.
Wang Jiani, Chen Junyu. Angiogenesis mechanism of metal ions and their application in bone tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 804-812.
2.1.1 骨再生中的血管生成过程及重要性 在骨缺损后,由于骨骼自身的愈合能力,受损部位会分泌细胞因子,通过协同作用刺激骨再生[9]。损伤后的血管扩张使受损部位形成血肿,进一步刺激炎症相关细胞因子的分泌[10]。因为骨缺损造成的局部机械损伤和营养支持的丧失,受损部位可能出现坏死和缺氧[10]。为保证愈合过程的正常进行,坏死组织需要被及时吸收,并进行血管的重建。当组织出现缺氧时,以血管内皮生长因子为主的细胞因子开始介导血管生成,加速内皮细胞产生蛋白酶,从而降解基底膜,导致内皮细胞迁移到血管生成刺激区域[11-12]。随后,迁移到特定部位的内皮细胞形成新生血管芽,并进行增殖,拉长血管芽而成管[12]。随后,内皮细胞逐步成熟,相邻的细胞之间形成细胞连接[13-14]。随着血管成熟过程的结束,内皮细胞停止增殖,血管生成过程终止[13-14]。
充足的血管新生是骨移植成功的关键[15]。在骨骼重建的过程中,新生血管为缺损部位的骨再生带来氧气、营养、矿物质和生长因子,并为代谢废物提供出口,于移植区域形成健康的骨组织。此外,血管也为软骨细胞和骨前体细胞抵达受损部位提供途径。因此,骨组织工程的支架应当保证血管网络的正常发育,为新生组织提供有利的微环境。
2.1.2 金属离子的成血管机制 多种金属离子已通过体外实验证明了其成血管活性,文章总结了铜、镁、锶、锌和钴离子调控血管生成的作用机制,见图3。

多数金属离子调控血管生成的分子机制与血管内皮生长因子的分泌调节密切相关[16]。血管内皮生长因子由血管诱导产生,具有促进内皮细胞增殖和迁移的作用,是在血管生成过程中最重要的一种细胞因子[17]。人体内含量最多的血管内皮生长因子形式为血管内皮生长因子A[9]。铜、钴、镁、锌和锶离子均可使血管内皮生长因子分泌增加,从而加速血管化[18-20]。
通过模拟缺氧等方式避免缺氧诱导因子的降解也是多种金属离子上调血管生成过程的途径之一。缺氧诱导因子是组织在低氧分压条件下的主要调控因子[21]。常氧条件下,缺氧诱导因子可顺利被脯氨酸羟化酶羟基化,随后进入泛素化降解途径;而在缺氧条件下,由于脯氨酸羟化酶正常作用需要氧气参与,缺氧诱导因子未能被降解,并稳定存在[22]。完整的缺氧诱导因子可进入细胞核上调缺氧相关基因的表达,如血管内皮生长因子A[18]。铜、钴离子均可降低氧张力模拟缺氧,稳定缺氧诱导因子1α的结构,进而诱导血管内皮生长因子A的转录[23-25]。铜离子也通过下调脯氨酰羟化酶的活性,促进缺氧诱导因子1α的积累和活化,最终改善了血管的生成[26]。此外,钴离子也可取代缺氧诱导因子催化位点上的亚铁离子,下调脯氨酰羟化酶的活性,从而上调缺氧诱导因子的含量,引发局部因缺氧引起的血管生成[27]。
多数离子在调控血管生成时显著促进了内皮细胞的增殖、迁移、小管形成等行为,并最终表现出对血管生成的促进作用。成熟的内皮细胞大多处于静止状态,新血管的发生需要激活内皮细胞,使其增殖、迁移到受损部位[28]。目前评估生物材料的体外成骨和成血管性能最常用的两大细胞是骨髓间充质干细胞和人脐静脉内皮细胞[18]。大量的体外实验证明,从骨组织工程支架中释放的铜离子促进了人脐静脉内皮细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和迁移[15,18,29]。此外,铜离子可与血管生成素紧密结合,增加血管生成素对内皮细胞的亲和力,而血管生成素是一种具有促进内皮细胞黏附和迁移作用的黏附分子,因此铜离子也促进了血管的新生[30]。铜、镁离子均可以上调内皮型一氧化氮合酶基因的表达,从而升高一氧化氮的浓度,而一氧化氮浓度升高可以刺激内皮细胞的细胞周期转向分裂期,从而促进内皮细胞的增殖[31-32]。锌离子可激活p38信号通路,诱导单核细胞向破骨细胞的分化,并分泌较高水平的基质细胞趋化因子1、转化生长因子β1、血管内皮生长因子和血小板生长因子[33],这些细胞因子均对血管生成、伤口愈合和组织修复具有正向调控作用,同时也促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和对内皮细胞的募集[33]。此外,锶离子和钴离子的掺入也显著促进了内皮细胞的增殖和迁移[20]。
除此之外,一些金属离子可改变巨噬细胞的表型从而影响其旁分泌,诱导血管新生。根据不同巨噬细胞分泌细胞因子等方面的差异,可以将巨噬细胞大致地分为M1型和M2型两个亚群[34]。M1巨噬细胞主要分泌促炎细胞因子参与抗病毒、抗菌反应,而M2巨噬细胞与组织重塑和伤口愈合相关,可促进血管内皮生长因子等血管生成相关因子的分泌,从而表现出血管生成特性[34]。锌、镁和锶离子均可促进M1巨噬细胞向M2表型转化[35-37],诱导血管内皮生长因子、血小板衍生生长因子的分泌,促进血管生成。锌离子也刺激M2巨噬细胞产生外泌体,这些外泌体高表达miR-155-5p和miR-221-5p,可通过结合转录因子基因的3'UTR抑制其表达,促进内皮细胞的迁移[35]。
多种成血管活性离子也通过上调内皮细胞血管生成相关基因的表达,对血管生成过程进行调控。铜离子可提高一氧化氮合酶3、成纤维细胞生长因子2、血管内皮生长因子受体及血管内皮生长因子A等关键血管生成基因的转录水平[29,38]。在一项增殖实验中,钴离子上调了血管生成相关基因血管内皮生长因子A和一氧化氮合酶3的表达水平,其中一氧化氮合酶3对于调节内皮细胞增殖、迁移和血管稳定性相当重要[20]。镁离子可以诱导缺氧诱导因子1α和血管内皮生长因子A的表达[19],而锶离子的作用也上调了血管内皮生长因子A的表达[20]。一项体内血管生成实验的结果显示,锌离子可显著促进血管生成相关基因血管内皮生长因子A和血小板与内皮细胞黏附分子1的表达[6]。
2.1.3 金属离子在成血管-成骨偶联中的作用 血管内皮细胞和骨细胞之间存在密切的关联和复杂的信号转导途径,成血管与成骨是不可分割的生物过程[15]。研究发现,H型血管是成血管-成骨偶联作用的重要载体,其产生缺氧诱导因子等促进骨祖细胞增殖、分化的细胞因子调控骨生成。H型血管周围骨祖细胞排列密集[39],可以分化为破骨细胞、软骨细胞,这些细胞也可分泌狭缝导向配体3和血小板衍生因子等对血管生成进行调控[40]。金属离子如铜、钴和镁离子等,可通过模拟缺氧或直接调控血管内皮生长因子A基因表达的方式显著促进血管内皮生长因子的分
泌[24,38,41]。由于这些细胞因子也在H型血管中分泌,此类成血管活性的金属离子可与H型血管协同作用,增进成血管-成骨偶联作用,使血管内皮和骨细胞的联系更加紧密,从而加速血管生成和成骨。此外,HAN等[41]的研究也证明了镁离子可以促进H型血管的生成,并且促进骨祖细胞在H型血管周围聚集。

2.2 成血管活性金属离子在骨组织工程中的应用 为了增强生物材料的成骨和成血管活性,许多研究者们尝试将药物和生长因子等添加到生物材料中,例如血管内皮细胞生长因子等,但是这些制剂常具有成本高及半衰期短等缺点,这限制了其应用[30]。最近,生物活性的金属离子因在各种体内外实验中均表现出优良的血管生成活性,已经被广泛地添加到生物材料中,以增强生物材料的成骨和成血管性能。目前的研究已经发现了铜、钴、镁、锌和锶离子等金属离子具有成骨活性、血管生成活性和抗菌活性等特性,但是由于血管生成先于成骨过程,以及骨整合对营养物质和氧气的需要,为骨组织工程材料配备血管生成潜能可能更需要研究者们的高度重视[24,33,38,41-42]。
2.2.1 铜离子 铜离子是维持人体骨骼健康的必需微量元素[52]。据报道,铜离子是一种优良的血管生成剂和抗菌剂[25]。适宜浓度的铜离子具有刺激内皮细胞增殖分化的作用,并且通过模拟缺氧,稳定缺氧诱导因子的结构,上调血管内皮生长因子等血管生成相关因子的表达,促进血管的新生,进而促进成骨[25]。目前,铜离子是骨组织工程治疗方案中一个颇具吸引力的选择。
分析所纳入文献后,发现铜离子在生物活性玻璃中应用最为广泛,各种形式的含铜生物活性玻璃均表现出良好的生物相容性和骨再生潜能。例如,RYAN等[15]制备的含铜生物活性玻璃显著地促进了细胞增殖、增强了细胞活力,与此同时也促进了钙沉积。此外,也有部分研究将含铜涂层包被在各种可降解支架上,如聚醚醚酮和聚己内酯等[25,38],或者将铜和其他金属(如钛)制成合金[53]。在不同的材料中,铜离子均表现出促血管生成性能、成骨活性和抗菌效应,从而改善了材料的性能,有利于骨缺损等疾病的治疗。然而,骨缺损可能由简单的创伤,或是肿瘤、感染等不同情况引起,因而采用的材料可能存在差异[1]。
铜离子作为一种优良的抗菌剂可赋予骨植入物显著的杀菌性能,用于需要抗感染的骨缺损治疗效果令人瞩目[25]。以往的部分研究采用抗生素来保证植入物具有杀菌作用,但考虑到抗生素的耐药性及研发速度缓慢等因素,更多的抗生素替代物有待研究[15,54]。近年来,针对铜离子抗菌性的研究对于骨移植的抗感染具有重要的作用。研究表明,铜离子可以杀死金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、结核分枝杆菌和空肠弯曲菌等,具有良好的抗菌效果[25,55-56]。掺铜的骨植入物不仅具有抗菌性,还表现出生物相容性,具有显著的血管生成和成骨反应,因而可以在减少感染的同时促进骨愈合[15]。
作为一种优良的血管生成剂,铜离子可显著改善骨组织工程材料的血管化。从生物活性材料中释放出来的铜离子可显著刺激血管内皮生长因子A和一氧化氮合酶3等血管生成相关基因的表达,随后可促进人脐静脉内皮细胞形成血管[29]。铜离子也可以有助于刺激血管生成相关基因的调控因子分泌,如一氧化氮合酶、碱性成纤维生长因子受体及血管内皮生长因子受体等,并改善内皮细胞的行为(迁移和血管形成),从而显著促进内皮细胞的血管生成[18]。此外,铜离子也通过模拟缺氧稳定缺氧诱导因子的结构,促进血管周围细胞分泌血管内皮生长因子,诱导血管的生成[25]。在与其他活性离子如镁离子协同作用时,铜离子的作用也主要表现在促进血管生成上[57]。同时,由于肿瘤性骨缺损治疗对于血管生成的需求,最近的一些研究将铜离子纳入了修复癌性骨缺损的材料中,以改善血管化[29,38]。以上研究表明,铜离子是一种优良的促进血管生成和抗感染的生物活性离子,在需要避免感染的骨缺损以及肿瘤引起的骨缺损等骨相关疾病的治疗具有良好的应用前景。
此外,铜离子的作用效果与其浓度密切相关。据报道,约0.05 mg/L剂量的铜离子能显著刺激再生组织的血管生成,而高于0.5 mmol/L(约32 mg/L)浓度的铜离子可能产生细胞毒性[58]。低浓度的铜离子不具有细胞毒性,但是当游离铜离子的浓度达到25 μmol/L时,其在培养5 d后显著抑制细胞增殖。铜离子在高浓度时表现出的细胞毒性可能源自其诱导活性氧积累的作用。铜离子表现出成骨、血管化还是抗菌的效果也与其浓度高度相关,一般认为是低浓度促进成骨和促血管化,高浓度抑制细菌生长[25]。
2.2.2 镁离子 镁离子是人体第四丰富的元素,也是体内数百种酶促反应的关键辅助因子[59-60]。适当浓度(如10 mmol/L)的镁离子具有促进骨骼生成、血管新生的作用,可应用于各种类型的骨缺损修复的治疗[61]。由于镁离子具有优良的促血管生成和成骨效应,许多研究将其纳入各种支架和生物材料,以改善材料的力学性能、成骨和血管生成反应。此外,金属镁及其合金因具有优良的机械性能、生物降解性和生物相容性,目前是一种颇具潜力的骨科植入物。
不同于铜和锶,镁主要以合金的形式应用于骨缺损的治疗中。高纯度的镁合金同时具备机械强度和可降解性,因而具备制成多种骨组织工程植入物的潜能[62]。然而,镁离子易发电偶腐蚀,高纯镁植入物的腐蚀率较高,导致镁植入物丧失了机械完整性[63]。植入物的降解速率应与骨愈合速率相匹配[64]。由于骨愈合的早期感染、愈合修复和重塑需要至少12周,植入物需要在此期间保持稳定[64]。近年来,不少研究者们采取了加入合适的合金元素、进行表面改性等策略以延缓骨植入物降解速率,改善了镁植入物的应用。HAN等[41]发现临床上批准的新型镁合金Mg5Ca1Zn可使镁、钙、锌离子以有利于成血管-成骨耦合的速率释放,表现出优秀的力学性能和合适的降解速率,有助于骨愈合的顺利进行。在另一项研究中,研究者们在镁合金上设计了一种上层富含铁、下层富含锰的双氢氧化物涂层,经过体内、外分析后发现,上层富铁层生物相容性、抗菌性良好,下层富锰层具有防腐作用[65]。此外,释放的镁、铁、锰离子均有助于血管生成和骨再生[65]。
镁离子在骨组织工程中应用时也可加入生物陶瓷及其他复合材料。磷酸钙生物陶瓷主要包括羟基磷灰石和β-磷酸三钙,具备良好的生物相容性,且与天然骨骼存在相似的化学成分[66]。而相较于羟基磷灰石,β-磷酸三钙表现出更佳的生物活性和可吸收性。与此同时,纯β-磷酸三钙支架降解速度快,难以在骨愈合完成前保持力学完整性。QI等[67]发现,与纯磷酸三钙支架相比,掺杂了镁离子的β-磷酸三钙支架表现出更高的抗压强度,并且显著降低了β-磷酸三钙支架的降解率;在进一步的伤口愈合、细胞侵袭、血管形成实验和RT-PCR检测中,他们发现掺镁的磷酸三钙支架相比于纯磷酸三钙支架表现出更高的细胞迁移率、血管分支数量和血管长度以及血管生成相关基因的表达水平,如血管内皮生长因子、血管内皮生长因子受体、血小板内皮细胞黏附分子1。在近几年的研究中,掺杂镁离子的3D打印多孔钽支架和含有生物功能镁涂层的多孔钛支架等骨植入物材料也表现出广阔的应用前景。钽具备良好的耐腐蚀性和生物相容性,但钽过高的弹性模量产生了应力屏蔽,可能引起再生骨的萎缩和种植体松动,不利于骨整合[19,68-69]。MA等[69]利用聚多巴胺的黏附作用将镁离子掺杂在3D打印的钽支架中,合成的钽-聚多巴胺-镁支架弹性模量接近天然骨,并在体内外均明显改善了血管生成和成骨反应,从而显著改善了多孔钽支架的性能。钛作为骨科植入物的一种优良材料,依然存在成骨反应和骨整合不足的问题[19]。GAO等[19]将具有生物活性的镁涂层沉积在Ti6Al4V支架表面,有效地促进了体内外成血管活性。此外,该系统也利用了3D打印技术降低了钛支架的应力屏蔽,从而改善骨整合[19]。
尽管各种含有镁涂层的骨组织工程生物材料表现出显著的促血管生成能力,这些材料多数被动地与镁进行混合,难以主动捕获镁离子并持续释放镁离子。作为一种微创治疗手段的极佳选择,由天然微糖制成的可注射水凝胶近期引起了研究者们的注意。ZHAO等[43]构建了一种双磷酸盐官能化微球体系,该体系利用金属离子配体配位反应产生强大的镁离子捕获和缓释能力,有利于抑制破骨细胞并促进骨再生和血管生成,从而治疗骨质疏松性骨缺损。CHEN等[68]将氧化镁、羟基磷灰石纳米晶体混合纳入水凝胶支架中,利用镁离子和半胱氨酸修饰的γ-聚谷氨酸之间的螯合作用实现了镁离子的长久释放(长达8周)。这种羟基磷灰石/氧化镁水凝胶支架表现出更有效的骨修复作用,有效诱导成骨分化,对于糖尿病患者的骨缺损治疗效果显著。目前,掺杂镁离子的可注射水凝胶具有创口小、降低感染风险、骨整合效应显著、适用于不规则缺损部位等优势,在临界大小骨缺损的修复治疗中显示出巨大的前景。
以上研究表明,镁具有优良的生物降解性和促血管生成作用,主要以合金的形式应用于骨组织工程中,也有部分研究将镁离子纳入生物陶瓷及其他复合材料中。镁的主要特性是易腐蚀性,在应用时需要对其镁合金的降解以及离子的释放速率进行严格的控制。
2.2.3 锶离子 锶离子是人体的必需微量元素之一,人体内的锶离子有90%存在于骨骼中,参与骨的形成[70]。在临床上,锶离子可以雷奈酸锶的形式用于骨质疏松症的治疗[71]。这是由于锶离子能刺激成骨细胞合成新的骨组织,阻止单核细胞分化为破骨细胞,可以显著减少骨吸收的发生[72]。同时因为锶离子诱导成骨分化、促进骨形成和血管新生的作用,在骨替代材料中掺入锶离子可改善材料的既有缺陷,从而更好地修复骨缺损。
掺入锶离子对骨替代材料的性能具有显著的改善作用,同时也影响植入部位的细胞行为,最终实现骨再生和血管生成。当质量分数15% 的含锶矿物(SrHPO4,SrP)掺入丝素-明胶支架时,其抗压强度、静态压缩模量明显高于丝基纤维弹性蛋白支架[37]。与磷酸钙骨水泥相比,掺入锶离子的磷酸钙骨水泥的抗压强度显著提高(从11.21 MPa提高到了45.52 Mpa)[45]。WU等[45]在磷酸钙混合水泥中掺入锶离子,发现相比于单纯的磷酸钙水泥,骨髓间充质干细胞在掺锶磷酸钙混合水泥组表面的黏附和增殖得到了显著的改善,这表明掺锶磷酸钙混合水泥具有良好的生物相容性。此外,在成骨诱导的第4,7天,掺锶磷酸钙混合水泥的碱性磷酸酶蛋白浓度都显著高于对照组;而碱性磷酸酶是成骨细胞增殖成熟的早期标志物,说明锶诱导了早期的成骨分化,在成骨诱导第7天后,掺锶磷酸钙混合水泥组的成骨相关基因,如Runt相关转录因子2和Ⅰ型胶原蛋白均显著上调,证明了锶的成骨作用[45]。此外,锶离子掺入介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒后,也通过增强骨髓间充质干细胞对血管内皮细胞生长因子的分泌从而加速血管生成[46]。
临床上治疗骨质疏松症的一种手段是口服雷奈酸锶,通过其主要成分锶离子促进成骨细胞形成新骨,并减少破骨细胞造成的骨吸收[73]。但由于口服给药存在血栓、过敏等不良反应,目前已经转向使用负载锶的生物材料治疗骨质疏松性骨再生[74-75]。LEE等[76]将锶离子掺入纳米骨水泥中,分别对前成骨细胞和破骨细胞进行处理,发现锶离子显著刺激了前成骨细胞的骨再生活动,并抑制破骨细胞的骨吸收。为了进一步验证掺锶纳米骨水泥在体内治疗骨质疏松症的效果,他们构建了切除卵巢的骨质疏松大鼠模型,3个月后植入掺锶纳米骨水泥,结果表明掺锶纳米骨水泥组相对于对照组显著增加了骨体积和骨密度,并保留了无锶纳米骨水泥的促血管生成作用。WU等[37]将磷酸氢锶和人参皂苷掺入丝素-明胶支架中,并构建了骨质疏松且具有临界性骨缺损的大鼠模型,在体内实验中表现出显著的修复效果。
以上研究表明,锶离子具有减少骨吸收和诱导成骨分化的作用,有助于治疗骨质疏松症。锶离子对于骨替代材料性能的改善效果显著,可以提升材料的机械性能、改善材料的血管化效应。
2.2.4 锌离子 锌离子也是人体中一种含量较为丰富的微量元素,参与各种生物反应,尤其是骨骼代谢[77]。在人体内有一些金属酶受到锌离子的调节、催化等作用,例如与新骨成熟密切相关的碱性磷酸酶。碱性磷酸酶是一种含有锌的糖蛋白,可以为骨再生过程提供碱性环境,促进矿化过程[38]。作为一种可降解的金属,锌的腐蚀速率仅次于镁。然而,锌离子释放速率过高可能抑制内皮细胞的活性,从而影响血管生成和成骨过程。在骨组织工程中,锌离子可以掺入生物活性玻璃、生物陶瓷、磷酸钙骨水泥以及各种其他具有生物活性的聚合物中,以改善这些材料的性能。此外,锌离子常作为硅、银、镁等离子的共掺杂剂,这些生物活性离子可协同作用赋予植入物成骨、成血管和抗菌的特性[78-79]。值得注意的是,锌离子对于血管生成和成骨过程的调控与其浓度密切相关。适当浓度的锌离子在体内外均能促进血管生成和成骨,并能激活丝裂原活化蛋白激酶/细胞外调节蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase/mitogen-activated kinase,MAPK/ERK)信号通路,影响成骨细胞分化,而高浓度的锌离子不利于血管生成和成骨分化[47]。
以往的多数研究认为锌离子的作用主要体现在成骨方面,锌离子在促进骨植入物的成骨作用表现出卓越的效能。VU等[79]将3种生物活性元素掺入羟基磷灰石中,其中含有0.25% 氧化锌用于诱导成骨,其余的两种元素(硅、银)分别用于诱导血管生成和抗菌。在植入5周后,掺杂了氧化锌、氧化硅、氧化银涂层的羟基磷灰石组的骨矿化率和骨生成率均显著高于无涂层的羟基磷灰石组,表明锌具有显著的诱导成骨的作用。由于锌离子促进成骨分化和抑制破骨细胞分化的作用,也有研究将其联合对骨再生有益的硅离子用于改善骨质疏松症患者的骨再生[80]。XIONG等[80]制备了含有氧化石墨烯、硅酸锌和硅酸钙的复合材料,证明了其在体外的促进成骨和血管生成的性能,有望用于骨质疏松引起的骨折治疗。
近几年的研究证实了锌离子促进血管生成的作用,并且发现其血管生成与成骨关系紧密。SONG等[6]发现,他们制备的含锌支架释放出的锌离子可以通过激活p38信号通路促进单核细胞分化为破骨细胞,同时大量分泌趋化因子、血管内皮细胞生长因子等促进内皮细胞的增殖、迁移和血管生成。在大鼠颅骨缺损模型中评估含锌金属-有机框架材料改性膜时,术后8周,金属-有机框架材料的晶体显示出成骨诱导和血管形成的迹象,证明了锌离子在生物材料中的成血管效应[33]。锌离子也可上调巨噬细胞分泌型转化生长因子β1、人骨形态发生蛋白2和血管内皮生长因子A的表达,从而通过激活相关信号通路促进血管生成和成骨[35]。WANG 等[81]评估了Mg-Zn合金增强成骨和血管的效果,表明Zn-Mg合金中的镁离子和锌离子显示出协同效应,即可促进内皮细胞的增殖和血管的新生。
以上研究表明,锌离子的作用主要表现在成骨方面,也有部分研究证明了锌离子的掺入在植入后改善了血管生成,但锌离子调控血管生成的具体机制相对较少。由于锌离子促进成骨分化和抑制破骨细胞分化的作用,锌离子也可以作为治疗骨质疏松症的新策略。
2.2.5 钴离子 近年来,钴离子逐渐成为一种非常有前景的仿生剂。作为一种低氧模拟剂,钴离子通过稳定缺氧诱导因子1α来激活缺氧诱导因子途径,增强低氧反应基因的转录,包括血管内皮生长因子A和一氧化氮合酶3[82],这些低氧反应基因与血管生成相关,因此钴离子模拟缺氧的作用也促进了血管的生成。在骨组织工程中,掺入钴离子用于改善性能的生物材料包括聚己内酯等可降解材料、甲基丙烯酸化水凝胶、生物活性玻璃及磷酸钙生物陶瓷等[23-24]。
钴离子调控血管生成的作用在多项研究中得以证明。当成纤维细胞在含有氯化钴的条件培养基中培养时,可观察到缺氧诱导因子1α稳定性增加,且血管内皮生长因子A表达显著高于对照组[24]。SUN等[23]将人脐静脉内皮细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞与复合水凝胶共培养以评估血管生成能力时,发现人脐静脉内皮细胞中血管内皮生长因子A的表达水平以剂量依赖的方式显著增加,缺氧诱导因子1α也被激活。这些实验均有力地证明了钴离子在上调细胞血管新生方面的潜力。此外,也有人提出了钴离子对于血管生成的双重作用,即促进血管内皮生长因子分泌和抑制内皮网络形成。他们在实验中发现,钴离子显著上调了体外血管内皮生长因子A的表达,但也同时抑制共培养物中人脐静脉内皮细胞网络的形成,这些抑制作用在较低的钴离子浓度(5,10或25 μmol/L)下减轻,而血管内皮生长因子A表达仍然显著上调[83]。钴离子的浓度可能需要有效控制,以避免其对内皮细胞网络形成的产生抑制。除了钴离子浓度的影响可能导致其对血管生成的双重作用,AMBIKA等[84]的一项研究也发现了钴离子的价态可能对其调控血管生成的作用产生影响,研究中,他们合成的钴(Ⅲ)席夫碱配合物对血管生成具有明显的抑制作用,这可能说明Co3+会对血管生成具有抑制作用,而目前广泛认为具有促血管生成能力的钴离子是二价态的钴离子(Co2+)。鉴于钴离子调控血管生成作用的多重影响因素,将钴离子掺入骨组织工程材料中,其浓度和价态的控制均应引起高度重视,以避免其抑制骨再生。
对于钴离子作用的浓度范围,目前广泛认为0.1-5.0 ppm的钴浓度不会引起细胞毒性[85]。而SUN等[23]针对钴离子释放的时间点提出了新的见解,他们认为,骨再生过程主要发生在早期,而骨吸收主要活跃于中晚期,所以钴离子的输送不应该贯穿整个骨再生过程,而应该控制在早期。以往的研究主要关注于以一种适宜的浓度将钴离子释放出来,确保没有细胞毒性,但是却忽略了钴离子作用的适宜时间[23-24]。既存的缓释系统虽然能将钴离子缓慢地释放,但是由于钴离子释放的时间过长,在骨再生过程的早期血管生成过程完成后依然存在,可能会造成一定程度的骨吸收,不利于骨再生[23]。因此,目前需要一种新型的缓释系统,以实现钴离子在适宜的时间段(即骨再生的早期血管生成阶段)的释放。
以上研究表明,钴离子改善骨替代材料血管生成的作用主要通过模拟缺氧和调控血管生成相关基因实现。钴离子的价态对于其调控血管生成的作用也可产生影响,三价的钴离子对血管生成具有抑制作用。既存的钴离子缓释系统较少涉及到将钴离子在适宜的时间段释放,有待进一步研究和开发。
2.2.6 其他离子 硅离子是骨骼正常发育所必需的离子[86]。骨基质主要由胶原蛋白组成[87],而体外和动物模型研究表明,硅与糖胺聚糖相连,在胶原蛋白和蛋白聚糖之间交联的形成中具有关键作用[88]。目前已有多种硅酸盐基或含有硅酸盐的生物材料广泛应用于骨移植和骨再生的领域,这些生物材料在溶解过程中释放硅酸盐离子,其中的硅对血管生成过程产生影响。LI等[49]研究发现,含有铜和海藻酸钠生物活性玻璃纳米颗粒促进内皮祖细胞在体外的活力、增殖和血管生成。在掺入钛植入物时,硅离子上调了人脐静脉内皮细胞中的一氧化氮含量和血管生成相关基因血管内皮生长因子A、成纤维细胞生长因子2及一氧化氮合酶3的表达,再次印证了其血管生成能力[50]。
钛被认为是具有最佳生物安全性的金属材料,也常用于与骨骼接触的永久性植入物。然而,钛及其合金的种植体存在骨整合、骨吸收和种植体周围炎等问题,限制了它们的应用[89]。目前关于钛离子的血管生成能力的研究较少,但是在一项研究中,发现制备的3D打印多孔Ti6Al4V支架上调了成骨相关基因碱性磷酸酶和骨钙素以及血管生成相关基因缺氧诱导因子1α和血管内皮生长因子A的表达水平,这证明钛离子可能是一种血管生成的启动因子[51]。
以上研究证明,硅离子和钛离子也是具有血管生成促进作用的生物活性离子。有关硅离子的血管生成作用研究较多,而钛离子涉及甚少。钛主要作为一种机械性能优良的金属材料作为骨组织工程中的骨替代物,可与其他金属离子混合,并改善性能。
2.2.7 骨相关疾病 肿瘤(如骨软骨瘤、软骨肉瘤)、骨质疏松及骨骺发育异常并发的骨关节炎等疾病均可能引起骨缺损,继而需要进行骨移植手术。多种金属离子如铜离子、镁离子和锶离子具有优良的血管生成活性和成骨活性,用于骨替代物中可刺激植入部位的成骨和血管新生。在治疗骨质疏松症、多种病理情况下的骨缺损等骨相关疾病方面表现出显著的效果。而这些金属离子在骨组织工程中治疗的骨相关疾病存在一个共同点——多由外泌体糖基转移酶 1(exostosin glycosyltransferase 1,EXT1)基因的突变引起[94-97]。
EXT1基因负责编码硫酸乙酰肝素的必需糖基转移酶,其突变会造成硫酸乙酰肝素的合成缺陷[98]。硫酸乙酰肝素可以结合并调节几乎所有参与软骨内成骨的关键因子,如骨形态发生蛋白、成纤维细胞生长因子、Wnt配体和印度刺猬因子,因此,硫酸乙酰肝素与骨骼的正常发育密切相关[99]。例如,骨质疏松症是由于骨吸收大于骨形成所引起的疾病,而调节成、破骨的关键机制在于由核因子κ B受体活化因子配体 (receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B ligand,RANKL)介导的成骨细胞和破骨细胞之间的跨膜信号转导。RANKL受到成骨细胞表达的骨保护素的负调控[100]。研究发现,骨保护素需要胫骨与硫酸乙酰肝素的相互作用后方可与成骨细胞进行结合,随后抑制RANKL/RANK信号通路,从而减少骨吸收。而EXT1基因的突变导致硫酸乙酰肝素无法正常合成,进而造成了骨吸收的异常增加,导致了骨质疏松症的发生[101]。遗传性多发性外生骨病是一种由硫酸乙酰肝素的缺乏所引起的疾病,其特征是生长在长骨、肋骨等处的骨软骨瘤[102]。骨软骨瘤的形成是由异位骨形态发生蛋白信号介导的,而硫酸乙酰肝素对骨形态发生蛋白的活性和信号传导具有较强的抑制作用。在硫酸乙酰肝素缺乏的情况下,骨形态发生蛋白信号转导增加,从而引起了骨软骨瘤的形成[103]。
研究骨相关疾病的发病机制对于其临床治疗具有重要的意义。骨肿瘤,如骨软骨瘤和软骨肉瘤,目前主要通过手术切除病变部位并植入骨替代物进行治疗。然而,对于移植性和不可切除的骨肿瘤,手术方法收效甚微[104]。基于骨软骨瘤的发病机制,研究者们可以采取干预的手段阻止骨软骨瘤的形成,比如干扰骨形态发生蛋白信号通路从而阻止软骨形成[102]。对于其他骨相关疾病,确定其发病机制与EXT1基因突变的相关性也为进一步改善治疗策略提供了潜在的治疗靶点。
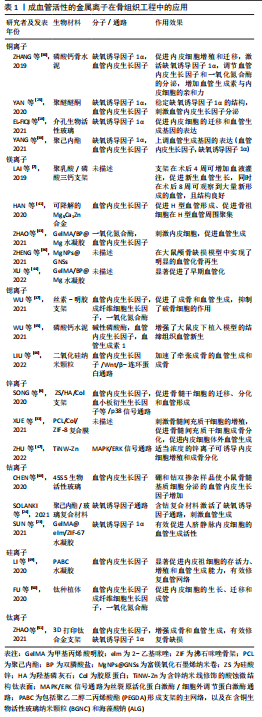
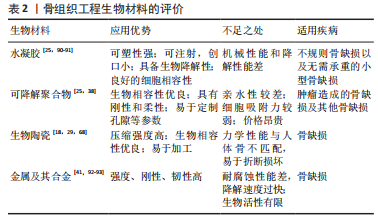
表1总结了具有成血管活性的金属离子在骨组织工程支架的应用,这些金属离子所应用的生物材料的性能评估见表2。表3总结了成血管活性的金属离子在治疗骨相关疾病的研究中所建立的动物模型和主要作用。

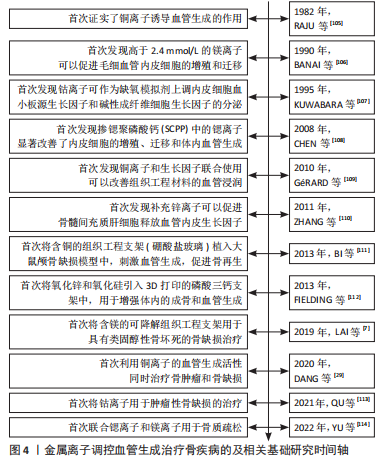
文章总结了载有金属离子的组织工程支架调控血管生成和治疗骨疾病的相关研究时间线[105-114],见图4。

| [1] XUE N, DING X, HUANG R, et al. Bone tissue engineering in the treatment of bone defects. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022;15(7):879. [2] SALAMANCA E, HSU CC, HUANG HM, et al. Bone regeneration using a porcine bone substitute collagen composite in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):984. [3] SHEIKH Z, NAJEEB S, KHURSHID Z, et al. Biodegradable materials for bone repair and tissue engineering applications. Materials (Basel). 2015;8(9):5744-5794. [4] BARRALET J, GBURECK U, HABIBOVIC P, et al. Angiogenesis in calcium phosphate scaffolds by inorganic copper ion release. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(7):1601-1609. [5] WANG L, ZOU D, ZHANG S, et al. Repair of bone defects around dental implants with bone morphogenetic protein/fibroblast growth factor-loaded porous calcium phosphate cement: a pilot study in a canine model. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22(2):173-181. [6] SONG Y, WU H, GAO Y, et al. Zinc silicate/nano-hydroxyapatite/collagen scaffolds promote angiogenesis and bone regeneration via the p38 MAPK pathway in activated monocytes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(14):16058-16075. [7] LAI Y, LI Y, CAO H, et al. Osteogenic magnesium incorporated into PLGA/TCP porous scaffold by 3D printing for repairing challenging bone defect. Biomaterials. 2019;197:207-219. [8] LI S, CUI Y, LIU H, et al. Application of bioactive metal ions in the treatment of bone defects. J Mater Chem B. 2022;10(45):9369-9388. [9] DIOMEDE F, MARCONI GD, FONTICOLI L, et al. Functional relationship between osteogenesis and angiogenesis in tissue regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(9):3242. [10] WALMSLEY GG, RANSOM RC, ZIELINS ER, et al. Stem cells in bone regeneration. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2016;12(5):524-529. [11] GOUDAR RK, VLAHOVIC G. Hypoxia, angiogenesis, and lung cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2008;10(4):277-282. [12] KALEBIC T, GARBISA S, GLASER B, et al. Basement membrane collagen: degradation by migrating endothelial cells. Science. 1983;221(4607):281-283. [13] GARLANDA C, DEJANA E. Heterogeneity of endothelial cells. Specific markers. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997;17(7):1193-1202. [14] PEPPER MS. Manipulating angiogenesis. From basic science to the bedside. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997;17(4):605-619. [15] RYAN EJ, RYAN AJ, GONZALEZ-VAZQUEZ A, et al. Collagen scaffolds functionalised with copper-eluting bioactive glass reduce infection and enhance osteogenesis and angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials. 2019;197:405-416. [16] LI Y, SUN R, ZOU J, et al. Dual roles of the AMP-activated protein kinase pathway in angiogenesis. Cells. 2019;8(7):752. [17] PIZZICANNELLA J, GUGLIANDOLO A, ORSINI T, et al. Engineered extracellular vesicles from human periodontal-ligament stem cells increase VEGF/VEGFR2 expression during bone regeneration. Front Physiol. 2019;10:512. [18] EL-FIQI A, MANDAKHBAYAR N, JO SB, et al. Nanotherapeutics for regeneration of degenerated tissue infected by bacteria through the multiple delivery of bioactive ions and growth factor with antibacterial/angiogenic and osteogenic/odontogenic capacity. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(1):123-136. [19] GAO P, FAN B, YU X, et al. Biofunctional magnesium coated Ti6Al4V scaffold enhances osteogenesis and angiogenesis and for orthopedic application. Bioact Mater. 2020; 5(3):680-693. [20] KERMANI F, MOLLAZADEH BEIDOKHTI S, BAINO F, et al. Strontium- and cobalt-doped multicomponent mesoporous bioactive glasses (MBGs) for potential use in bone tissue engineering applications. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(6):1348. [21] KLING L, SCHREIBER A, ECKARDT KU, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factors not only regulate but also are myeloid-cell treatment targets. J Leukoc Biol. 2021;110(1):61-75. [22] CHOUDHRY H, HARRIS AL. Advances in hypoxia-inducible factor biology. Cell Metab. 2018;27(2):281-298. [23] SUN Y, LIU X, ZHU Y, et al. Tunable and controlled release of cobalt ions from metal-organic framework hydrogel nanocomposites enhances bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(49):59051-59066. [24] SOLANKI AK, LALI FV, AUTEFAGE H, et al. Bioactive glasses and electrospun composites that release cobalt to stimulate the HIF pathway for wound healing applications. Biomater Res. 2021;25(1):1. [25] YAN J, XIA D, ZHOU W, et al. pH-responsive silk fibroin-based CuO/Ag micro/nano coating endows polyetheretherketone with synergistic antibacterial ability, osteogenesis, and angiogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2020;115:220-234. [26] ZHANG R, JIANG G, GAO Q, et al. Sprayed copper peroxide nanodots for accelerating wound healing in a multidrug-resistant bacteria infected diabetic ulcer. Nanoscale. 2021;13(37):15937-15951. [27] CIOFFI CL, LIU XQ, KOSINSKI PA, et al. Differential regulation of HIF-1 alpha prolyl-4-hydroxylase genes by hypoxia in human cardiovascular cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;303(3):947-953. [28] XIAO X, XU S, LI L, et al. The Effect of velvet antler proteins on cardiac microvascular endothelial cells challenged with ischemia-hypoxia. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:601. [29] DANG W, MA B, LI B, et al. 3D printing of metal-organic framework nanosheets-structured scaffolds with tumor therapy and bone construction. Biofabrication. 2020; 12(2):025005. [30] ZHANG J, WU H, HE F, et al. Concentration-dependent osteogenic and angiogenic biological performances of calcium phosphate cement modified with copper ions. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;99:1199-1212. [31] MAIER JAM, BERNARDINI D, RAYSSIGUIER Y, et al. High concentrations of magnesium modulate vascular endothelial cell behaviour in vitro. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta. 2004;1689(1):6-12. [32] ZICHE M, MORBIDELLI L. Nitric oxide and angiogenesis. J Neurooncol. 2000;50(1-2): 139-148. [33] XUE Y, ZHU Z, ZHANG X, et al. Accelerated bone regeneration by mof modified multifunctional membranes through enhancement of osteogenic and angiogenic performance. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(6):e2001369. [34] YUNNA C, MENGRU H, LEI W, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;877:173090. [35] LIU J, ZHAO Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Exosomes derived from macrophages upon Zn ion stimulation promote osteoblast and endothelial cell functions. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(18):3800-3807. [36] ZHENG Z, CHEN Y, HONG H, et al. The “Yin and Yang” of immunomodulatory magnesium-enriched graphene oxide nanoscrolls decorated biomimetic scaffolds in promoting bone regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(2):e2000631. [37] WU T, LIU W, HUANG S, et al. Bioactive strontium ions/ginsenoside Rg1-incorporated biodegradable silk fibroin-gelatin scaffold promoted challenging osteoporotic bone regeneration. Materials today Bio. 2021;12:100141. [38] YANG C, MA H, WANG Z, et al. 3D printed wesselsite nanosheets functionalized scaffold facilitates NIR-II photothermal therapy and vascularized bone regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(20):e2100894. [39] NAKASHIMA K, ZHOU X, KUNKEL G, et al. The novel zinc finger-containing transcription factor osterix is required for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell. 2002; 108(1):17-29. [40] XU R, YALLOWITZ A, QIN A, et al. Targeting skeletal endothelium to ameliorate bone loss. Nat Med. 2018;24(6):823-833. [41] HAN HS, JUN I, SEOK HK, et al. Biodegradable magnesium alloys promote angio-osteogenesis to enhance bone repair. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(15):2000800. [42] JAIDEV LR, KUMAR S, CHATTERJEE K. Multi-biofunctional polymer graphene composite for bone tissue regeneration that elutes copper ions to impart angiogenic, osteogenic and bactericidal properties. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;159:293-302. [43] ZHAO Z, LI G, RUAN H, et al. Capturing magnesium ions via microfluidic hydrogel microspheres for promoting cancellous bone regeneration. ACS Nano. 2021;15(8): 13041-13054. [44] XU Y, XU C, HE L, et al. Stratified-structural hydrogel incorporated with magnesium-ion-modified black phosphorus nanosheets for promoting neuro-vascularized bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;16:271-284. [45] WU X, TANG Z, WU K, et al. Strontium-calcium phosphate hybrid cement with enhanced osteogenic and angiogenic properties for vascularised bone regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(30):5982-5997. [46] LIU X, SUN Y, SHEN J, et al. Strontium doped mesoporous silica nanoparticles accelerate osteogenesis and angiogenesis in distraction osteogenesis by activation of Wnt pathway. Nanomedicine. 2022;41:102496. [47] ZHU WQ, LI K, SU S, et al. Effects of Zinc ions released from Ti-NW-Zn surface on osteogenesis and angiogenesis and in an zebrafish model. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:848769. [48] CHEN S, MICHáLEK M, GALUSKOVá D, et al. Multi-targeted B and Co co-doped 45S5 bioactive glasses with angiogenic potential for bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;112:110909. [49] LI Y, XU T, TU Z, et al. Bioactive antibacterial silica-based nanocomposites hydrogel scaffolds with high angiogenesis for promoting diabetic wound healing and skin repair. Theranostics. 2020;10(11):4929-4943. [50] FU X, LIU P, ZHAO D, et al. Effects of nanotopography regulation and silicon doping on angiogenic and osteogenic activities of hydroxyapatite coating on titanium implant. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:4171-4189. [51] ZHAO H, SHEN S, ZHAO L, et al. 3D printing of dual-cell delivery titanium alloy scaffolds for improving osseointegration through enhancing angiogenesis and osteogenesis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):734. [52] DOLLWET HH, SORENSON JR. Roles of copper in bone maintenance and healing. Biol Trace Elem Res. 1988;18:39-48. [53] LI Y, LU Y, QIU B, et al. Copper-containing titanium alloys promote angiogenesis in irradiated bone through releasing copper ions and regulating immune microenvironment. Biomater Adv. 2022;139:213010. [54] STEWART PS, COSTERTON JW. Antibiotic resistance of bacteria in biofilms. Lancet. 2001; 358(9276):135-138. [55] DALECKI AG, HAEILI M, SHAH S, et al. Disulfiram and copper ions kill mycobacterium tuberculosis in a synergistic manner. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(8): 4835-4844. [56] FAúNDEZ G, TRONCOSO M, NAVARRETE P, et al. Antimicrobial activity of copper surfaces against suspensions of Salmonella enterica and Campylobacter jejuni. BMC Microbiol. 2004;4:19. [57] FAN L, KöRTE F, RUDT A, et al. Encapsulated vaterite-calcite CaCO(3) particles loaded with Mg(2+) and Cu(2+) ions with sustained release promoting osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:983988. [58] ZHENG K, DAI X, LU M, et al. Synthesis of copper-containing bioactive glass nanoparticles using a modified Stöber method for biomedical applications. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;150:159-167. [59] GU Y, ZHANG J, ZHANG X, et al. Three-dimensional printed Mg-doped β-TCP bone tissue engineering scaffolds: effects of magnesium ion concentration on osteogenesis and angiogenesis in vitro. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;16(4):415-429. [60] VERSCHUREN EHJ, HOENDEROP JGJ, PETERS DJM, et al. Tubular flow activates magnesium transport in the distal convoluted tubule. FASEB J. 2019;33(4):5034-5044. [61] ZHANG Y, XU J, RUAN YC, et al. Implant-derived magnesium induces local neuronal production of CGRP to improve bone-fracture healing in rats. Nat Med. 2016;22(10): 1160-1169. [62] CHAYA A, YOSHIZAWA S, VERDELIS K, et al. Fracture healing using degradable magnesium fixation plates and screws. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;73(2):295-305. [63] QIU L, ZHANG C, YANG X, et al. A SiO(2) layer on PEO-treated Mg for enhanced corrosion resistance and bone regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:1053944. [64] LIU C, REN Z, XU Y, et al. Biodegradable magnesium alloys developed as bone repair materials: a review. Scanning. 2018;2018:9216314. [65] ZHANG D, LI M, XU R, et al. Complementary and synergistic design of bi-layered double hydroxides modified magnesium alloy toward multifunctional orthopedic implants. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;12(2):e2201367. [66] ZHAO Z, ZHANG J, YANG Z, et al. Biodegradation of HA and β-TCP ceramics regulated by T-cells. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(9):1962. [67] QI D, SU J, LI S, et al. 3D printed magnesium-doped beta-TCP gyroid scaffold with osteogenesis, angiogenesis, immunomodulation properties and bone regeneration capability in vivo. Biomater Adv. 2022;136:212759. [68] CHEN R, CHEN HB, XUE PP, et al. HA/MgO nanocrystal-based hybrid hydrogel with high mechanical strength and osteoinductive potential for bone reconstruction in diabetic rats. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(4):1107-1122. [69] MA L, CHENG S, JI X, et al. Immobilizing magnesium ions on 3D printed porous tantalum scaffolds with polydopamine for improved vascularization and osteogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;117:111303. [70] CANALIS E, HOTT M, DELOFFRE P, et al. The divalent strontium salt S12911 enhances bone cell replication and bone formation in vitro. Bone. 1996;18(6):517-523. [71] BONNELYE E, CHABADEL A, SALTEL F, et al. Dual effect of strontium ranelate: stimulation of osteoblast differentiation and inhibition of osteoclast formation and resorption in vitro. Bone. 2008;42(1):129-138. [72] BARON R, TSOUDEROS Y. In vitro effects of S12911-2 on osteoclast function and bone marrow macrophage differentiation. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002;450(1):11-17. [73] LAVET C, MABILLEAU G, CHAPPARD D, et al. Strontium ranelate stimulates trabecular bone formation in a rat tibial bone defect healing process. Osteoporos Int. 2017; 28(12):3475-3487. [74] REGINSTER JY. Cardiac concerns associated with strontium ranelate. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2014;13(9):1209-1213. [75] GE C, CHEN F, MAO L, et al. Strontium ranelate-loaded POFC/β-TCP porous scaffolds for osteoporotic bone repair. RSC Adv. 2020;10(15):9016-9025. [76] LEE NH, KANG MS, KIM TH, et al. Dual actions of osteoclastic-inhibition and osteogenic-stimulation through strontium-releasing bioactive nanoscale cement imply biomaterial-enabled osteoporosis therapy. Biomaterials. 2021;276:121025. [77] STEFANIDOU M, MARAVELIAS C, DONA A, et al. Zinc: a multipurpose trace element. Arch Toxicol. 2006;80(1):1-9. [78] LU T, ZHANG J, YUAN X, et al. Enhanced osteogenesis and angiogenesis of calcium phosphate cement incorporated with zinc silicate by synergy effect of zinc and silicon ions. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;131:112490. [79] VU AA, ROBERTSON SF, KE D, et al. Mechanical and biological properties of ZnO, SiO(2), and Ag(2)O doped plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coating for orthopaedic and dental applications. Acta Biomater. 2019;92:325-335. [80] XIONG K, WU T, FAN Q, et al. Novel reduced graphene oxide/zinc silicate/calcium silicate electroconductive biocomposite for stimulating osteoporotic bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(51):44356-44368. [81] WANG Z, WANG W, ZHANG X, et al. Modulation of osteogenesis and angiogenesis activities based on ionic release from Zn-Mg alloys. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(20):7117. [82] RANA NK, SINGH P, KOCH B. CoCl simulated hypoxia induce cell proliferation and alter the expression pattern of hypoxia associated genes involved in angiogenesis and apoptosis. Biol Res. 2019;52(1):12. [83] CHAI YC, MENDES LF, VAN GASTEL N, et al. Fine-tuning pro-angiogenic effects of cobalt for simultaneous enhancement of vascular endothelial growth factor secretion and implant neovascularization. Acta Biomater. 2018;72:447-460. [84] AMBIKA S, MANOJKUMAR Y, ARUNACHALAM S, et al. Biomolecular interaction, anti-cancer and anti-angiogenic properties of cobalt (III) schiff base complexes. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):2721. [85] LIU G, WANG X, ZHOU X, et al. Modulating the cobalt dose range to manipulate multisystem cooperation in bone environment: a strategy to resolve the controversies about cobalt use for orthopedic applications. Theranostics. 2020;10(3):1074-1089. [86] PRESCHA A, ZABŁOCKA-SŁOWIŃSKA K, GRAJETA H. Dietary silicon and its impact on plasma silicon levels in the polish population. Nutrients. 2019;11(5):980. [87] QIN D, WANG N, YOU X-G, et al. Collagen-based biocomposites inspired by bone hierarchical structures for advanced bone regeneration: ongoing research and perspectives. Biomater Sci. 2022;10(2):318-353. [88] RONDANELLI M, FALIVA MA, PERONI G, et al. Silicon: A neglected micronutrient essential for bone health. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021;246(13):1500-1511. [89] ZHOU Z, SHI Q, WANG J, et al. The unfavorable role of titanium particles released from dental implants. Nanotheranostics. 2021;5(3):321-332. [90] HU Q, LU R, LIU S, et al. 3D Printing GelMA/PVA interpenetrating polymer networks scaffolds mediated with CuO nanoparticles for angiogenesis. Macromol Biosci. 2022; 22(10):e2200208. [91] GRITSCH L, LIVERANI L, LOVELL C, et al. Polycaprolactone electrospun fiber mats prepared using benign solvents: blending with copper(II)-chitosan increases the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor in a bone marrow stromal cell line. Macromol Biosci. 2020;20(3):e1900355. [92] QI H, WANG K, LI M, et al. Co-culture of BMSCs and HUVECs with simvastatin-loaded gelatin nanosphere/chitosan coating on Mg alloy for osteogenic differentiation and vasculogenesis. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;193(Pt B):2021-2028. [93] CHENG S, LAN L, LI M, et al. Pure Mg-Al layered double hydroxide film on magnesium alloys for orthopedic applications. ACS omega. 2021;6(38):24575-24584. [94] LEMOS MC, KOTANKO P, CHRISTIE PT, et al. A novel EXT1 splice site mutation in a kindred with hereditary multiple exostosis and osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(9):5386-5392. [95] MATSUMOTO K, OGAWA H, NOZAWA S, et al. An analysis of osteoporosis in patients with hereditary multiple exostoses. Osteoporos Int. 2020;31(12):2355-2361. [96] SENTCHORDI-MONTANé L, BENITO-SANZ S, AZA-CARMONA M, et al. High prevalence of variants in skeletal dysplasia associated genes in individuals with short stature and minor skeletal anomalies. Eur J Endocrinol. 2021;185(5):691-705. [97] JOCHMANN K, BACHVAROVA V, VORTKAMP A. Heparan sulfate as a regulator of endochondral ossification and osteochondroma development. Matrix Biol. 2014; 34:55-63. [98] MCCORMICK C, LEDUC Y, MARTINDALE D, et al. The putative tumour suppressor EXT1 alters the expression of cell-surface heparan sulfate. Nat Genet. 1998;19(2):158-161. [99] MATSUMOTO Y, MATSUMOTO K, IRIE F, et al. Conditional ablation of the heparan sulfate-synthesizing enzyme Ext1 leads to dysregulation of bone morphogenic protein signaling and severe skeletal defects. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(25):19227-19234. [100] ZAIDI M. Skeletal remodeling in health and disease. Nat Med. 2007;13(7):791-801. [101] NOZAWA S, INUBUSHI T, IRIE F, et al. Osteoblastic heparan sulfate regulates osteoprotegerin function and bone mass. JCI Insight. 2018;3(3):e89624. [102] PACIFICI M. Hereditary multiple exostoses: new insights into pathogenesis, clinical complications, and potential treatments. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2017;15(3):142-152. [103] MUNDY C, YANG E, TAKANO H, et al. Heparan sulfate antagonism alters bone morphogenetic protein signaling and receptor dynamics, suggesting a mechanism in hereditary multiple exostoses. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(20):7703-7716. [104] MERY B, ESPENEL S, GUY JB, et al. Biological aspects of chondrosarcoma: Leaps and hurdles. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2018;126:32-36. [105] RAJU KS, ALESSANDRI G, ZICHE M, et al. Ceruloplasmin, copper ions, and angiogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982;69(5):1183-1188. [106] BANAI S, HAGGROTH L, EPSTEIN SE, et al. Influence of extracellular magnesium on capillary endothelial cell proliferation and migration. Circ Res. 1990;67(3):645-650. [107] KUWABARA K, OGAWA S, MATSUMOTO M, et al. Hypoxia-mediated induction of acidic/basic fibroblast growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor in mononuclear phagocytes stimulates growth of hypoxic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Sci U S A. 1995; 92(10):4606-4610. [108] CHEN YW, SHI GQ, DING YL, et al. In vitro study on the influence of strontium-doped calcium polyphosphate on the angiogenesis-related behaviors of HUVECs. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19(7):2655-2662. [109] GéRARD C, BORDELEAU LJ, BARRALET J, et al. The stimulation of angiogenesis and collagen deposition by copper. Biomaterials. 2010;31(5):824-831. [110] ZHANG D, LI Y, ZHU T, et al. Zinc supplementation results in improved therapeutic potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in a mouse ischemic limb model. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(2):156-164. [111] BI L, RAHAMAN MN, DAY DE, et al. Effect of bioactive borate glass microstructure on bone regeneration, angiogenesis, and hydroxyapatite conversion in a rat calvarial defect model. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(8):8015-8026. [112] FIELDING G, BOSE S. SiO2 and ZnO dopants in three-dimensionally printed tricalcium phosphate bone tissue engineering scaffolds enhance osteogenesis and angiogenesis in vivo. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(11):9137-9148. [113] QU Y, ZHUANG H, ZHANG M, et al. Bone cements for therapy and regeneration for minimally invasive treatment of neoplastic bone defects. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(21): 4355-4364. [114] YU S, SUN T, LIU W, et al. PLGA cage-like structures loaded with Sr/Mg-doped hydroxyapatite for repairing osteoporotic bone defects. Macromol Biosci. 2022;22(8): e2200092. |
| [1] | 杨玉芳, 杨芷姗, 段棉棉, 刘毅恒, 唐正龙, 王 宇. 促红细胞生成素在骨组织工程中的应用及前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [2] | 王姗姗, 舒 晴, 田 峻. 物理因子促进干细胞的成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [3] | 张 娅, 牟秋菊, 王自林, 刘宏杰, 祝丽丽. 负载富血小板血浆的水凝胶促进糖尿病大鼠创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 690-696. |
| [4] | 朱礼威, 王江玥, 白 丁. 纳米复合甲基丙烯酰明胶水凝胶在不同骨缺损环境中应用的价值[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 753-758. |
| [5] | 尹 彤, 杨吉垒, 李友瑞, 刘卓冉, 姜 明. 核壳结构纳米纤维在口腔组织再生中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 766-770. |
| [6] | 王业元, 杜易朗, 于德浩, 宁凤婷, 白 冰. 微弧氧化处理对医用金属生物活性的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 771-776. |
| [7] | 刘安宏, 蔡萌萌, 韩 笑, 王战会. 医用镁合金元素选择的研究现状[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 777-782. |
| [8] | 杨雨晴, 陈志宇. 早期短暂M1巨噬细胞在骨组织工程中的作用及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 594-601. |
| [9] | 龙智睿, 黄 雷, 肖 放, 王 琳, 王晓蓓. 骨组织工程中研究水凝胶微球的特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 472-478. |
| [10] | 徐 静, 吕慧欣, 鲍 鑫, 张 逸, 王一涵, 周延民. 近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程领域的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 486-492. |
| [11] | 高雪钰, 张文涛, 孙天泽, 张 警, 李忠海. 金属离子在骨组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 439-444. |
| [12] | 陈品叡, 裴锡波, 薛轶元. 磁响应水凝胶在骨组织工程中的作用与优势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 452-457. |
| [13] | 潘成镇, 陈 锋, 林宗汉, 莫 坚, 张 驰, 韦沅汛, 韦宗波. 萜类中药单体调控核转录因子κB信号通路防治骨质疏松症的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(14): 2234-2241. |
| [14] | 翟浩嫣, 赵 圆, 范登莹, 刘春艳. 活性氧影响牙周炎发生发展及牙周组织再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(14): 2254-2260. |
| [15] | 范永晶, 王 姝, 金武龙. 颌骨来源骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的特点、优势与应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 100-106. |
骨组织工程可整合支架、细胞和具有生物活性的生长因子,利于骨组织的修复和再生。在骨修复过程中,充足的血管生成对于骨基质的重建与再生至关重要。血管新生为骨再生的活动提供必需的营养物质和细胞因子,以调控成血管和成骨过程[4]。当骨缺损较大时,生物材料促进血管生成的效果有限,这也限制了其在组织工程中的应用。因此,改善骨修复生物材料的血管生成对于提高骨再生的成功率具有重要的意义。负载血管内皮生长因子等生物活性物质可促进生物材料的血管化,但生长因子作用时间短,价格昂贵,不易保存[5]。近年来,在生物材料中掺杂成血管活性的金属离子成为了增强生物材料成血管和成骨活性的有效途径。铜、钴、镁、锌、锶等金属离子已被证明具有血管生成活性,并且广泛应用于水凝胶、复合支架、引导组织再生膜等生物材料中,进而治疗多种骨骼相关疾病[6-7]。然而,这几种金属离子的成血管机制缺乏系统性的归纳。
以往综述多关注于单个金属离子的成骨、成血管或抗菌活性,系统性总结多种金属离子调控血管生成机制的文献相对较少。而LI等[8]的综述虽然总结了多种离子的成血管和成骨机制,但依然存在机制总结不全的问题,并且纳入的离子有相当一部分在组织工程中应用较少。此外,多数综述总结金属离子在骨组织工程中的应用时未对每个离子的应用特点着重分析,主要关注纳入离子的材料类型。
文章主要总结了5种在骨组织工程应用最为广泛的治疗性金属离子的促血管生成机制,分析当前具有成血管活性的金属离子在骨组织工程中的应用和进展,并提出了目前研究的不足和对金属离子未来应用的展望。文章目的在于阐明铜、镁、锶、锌、钴5种金属离子调控血管生成的具体机制及其在组织工程的极大应用潜力。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 文章全部作者于2022年9月进行独立检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2017年1月至2022年9月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed和中国知网数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“铜离子,镁离子,锶离子,锌离子,钴离子,骨,血管生成”,英文检索词为“copper,cuprum,Cu,magnesium,Mg,strontium,Sr,zinc,Zn,cobalt,Co,metal ion,angiogenesis,bone”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著和综述。
1.1.6 检索策略 通过上述中、英文检索词在PubMed和中国知网数据库对主题进行检索,中文检索式为主题:(铜离子OR镁离子OR锶离子OR锌离子OR钴离子) and主题:(骨) and主题:(血管生成),PubMed数据库的英文检索式见图1。

1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 PICOS问题 该综述旨在系统地检索和分析研究具有成血管活性的金属离子的促血管生成机制及其在骨组织工程中的应用,运用了PICOS原则,该综述的PICOS问题是:具有成血管活性的金属离子在掺入生物活性材料后的血管化效果如何?其中,P(Participant):骨缺损相关的动物模型;I(Intervention):具有成血管活性的金属离子;C(Comparison):未掺入具有成血管活性的金属离子的生物材料;O(Outcome):骨缺损修复过程中的成血管及成骨效果;S(Study design):基础研究。
1.2.2 纳入标准 ①研究对象:具有成血管活性的金属离子;②研究类型:符合PICOS原则的基础性研究论著。
1.2.3 排除标准 排除内容与该综述主题无关或重复性研究。
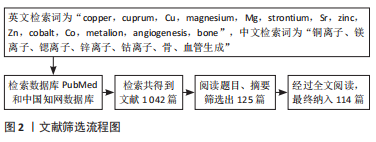
1.3 文献质量评估和数据提取 利用计算机初筛得到文献1 042篇。其中中文文献19篇,英文文献1 023篇。根据阅读标题和摘要排除不相关和重复性文献,得125篇。经过全文阅读后,最终纳入PubMed数据库文献114篇、中国知网数据库文献0篇,见图2。
然而,在以往的研究中也发现了一些问题:锌离子的成血管机制尚未阐述清楚;锶离子的作用浓度范围鲜有讨论;有关金属离子可控释放体系的相关研究依然不足;实现在特定时间段(骨再生的早期)释放金属离子的缓释体系较少;多种离子在体内的信号转导通路之间的联系和细胞之间的相互作用研究不足;相关的临床产品几乎空白、临床试验少;在不同实验中各种金属离子的浓度范围存在较大的差异。有些方面仍有待进一步研究。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 近年来,多种金属离子因具有优良的血管生成活性,已经引起国内外学者的广泛关注。但国内外综述大多未能系统性地总结多种金属离子调控血管生成的机制及其在骨组织工程中的基础和临床应用。文章在回顾了近5年的文献的基础上,对铜、镁、锶、锌和钴离子等多种金属离子的成血管机制进行了总结,并从作用于血管内皮生长因子、缺氧诱导因子、内皮细胞、血管生成相关基因和对巨噬细胞的免疫调节五个层面进行分别阐述。此外,文章检索并总结了金属离子近年来在骨组织工程中基础和临床的应用,根据不同离子的应用现状和特点进行了针对性的分析,并关注了这些金属离子在掺入各种组织工程材料后可有效治疗的疾病类型,对涉及到的骨相关疾病也进行了总结。
3.3 综述的局限性 文章简述了多种金属离子在骨组织工程中的应用,以及血管生成过程和金属离子与成血管-成骨偶联之间的关系,并着重总结了5种金属离子(铜、镁、锶、锌及钴离子)的血管生成机制。然而,现阶段研究中有关金属离子成血管机制的研究较少,特别是对于成血管-成骨的相关偶联机制研究不够深入,故于此方面的综述较为局限。此外,虽然金属离子在骨组织工程中的促血管生成方面的基础研究较为系统,目前在临床上将掺有金属离子的骨替代材料用于骨缺损治疗较少,缺乏相关的临床产品和临床试验,有待进一步的开发和研究。
3.4 综述的重要意义 具有血管生成活性的金属离子,如铜、钴、镁、锌和锶离子,目前在多种生物活性材料中应用广泛,提升生物材料的血管生成活性效果明显。文章对这5种具有血管生成活性的金属离子的成血管机制进行了综述,各离子涉及到的调控血管生成的通路见图 3。
铜、钴、镁、锌及锶离子可以促进血管内皮生长因子的分泌。铜离子、钴离子均可通过降低氧张力模拟缺氧,避免缺氧诱导因子的降解,继而刺激血管内皮生长因子的分泌。铜离子可抑制脯氨酰羟化酶的作用,引起缺氧诱导因子的积累。钴离子可以取代缺氧诱导因子中的亚铁离子,从而抑制其活性。铜、锶、镁、锌、钴均具有促进内皮细胞增殖、迁移的作用,其中铜离子和镁离子通过促进一氧化氮的释放,从而刺激内皮细胞的增殖。锌离子则调节单核细胞的分化和分泌活性,增加促血管生成的因子分泌和对内皮细胞的募集。锌、镁及锶离子均可通过免疫调节,即促进巨噬细胞由M1型转为M2型,从而促进血管内皮生长因子等有利于血管化的因子分泌。在基因层面,铜离子可提高 一氧化氮合酶3、转录因子2、血管内皮生长因子受体、血管内皮生长因子A的转录水平,钴离子可上调血管内皮生长因子A、一氧化氮合酶3的表达,镁离子可诱导缺氧诱导因子1α和血管内皮生长因子A的表达,锶离子可促进血管内皮生长因子A的表达,锌离子则作用于血管内皮生长因子A 和血小板与内皮细胞黏附分子 。
这些具备血管生成活性的金属离子在治疗骨相关疾病方面也效果显著,铜、镁、锶、锌及钴离子均具有治疗骨缺损修复和促进伤口愈合的作用。而铜离子在肿瘤及感染引起的骨缺损治疗中具有应用价值,镁离子和锶离子对于骨质疏松症的治疗有效。另外,也有研究将掺镁支架用于糖尿病骨缺损的治疗和类固醇性骨坏死的骨缺损治疗,而这两种基础疾病可能导致骨缺损治疗难度增加,说明镁离子具有良好的修复作用。
3.5 未来展望 铜、镁、锶、钴及锌离子等金属离子具有显著的血管生成活性,已有较多研究将这些成血管活性的金属离子纳入各种生物材料中,成功地改善了生物材料的骨再生和血管新生。目前关于金属离子成血管活性的研究仅停留在基础研究方面,临床上的相关试验和产品相对较少。各种金属离子(特别是锌离子)的血管生成机制还有待进一步的研究,在成血管-成骨的偶联机制方面研究不够深入。未来需要拓展纳入金属离子的骨替代材料在临床上的应用,同时继续深入探究各种离子的成骨、成血管等效应的机制及不同离子的作用强度和有效性。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
金属离子的成血管活性:部分金属离子,如铜、镁离子等,可通过上调血管内皮生长因子的表达等途径调控血管生成,从而促进血管化的过程。金属离子的成血管活性受到其浓度的影响,不同浓度的金属离子对于血管生成的作用存在较大差异,高浓度的金属离子一般具有细胞毒性,而低浓度的金属离子具有成血管效应。骨组织工程:自体的骨髓基质干细胞等细胞经过体外扩增后,种植在具有良好生物相容性的细胞支架或细胞外基质上,从而制得一个有助于细胞黏附的支架。这种含有细胞的支架可为植入部位提供营养物质,促进组织细胞间的气体交换和废物的排出,目前广泛地用于骨组织缺损的修复。
骨缺损通常可由创伤、肿瘤、感染及骨骼疾病等先天或后天因素引起。由于骨组织具有自我修复能力,较小的骨缺损可自行愈合。但在多数情况下,仅凭骨的自然愈合无法修复骨缺损,需要采取临床干预。临床上常用的自体骨具备成骨诱导能力和骨传导的特性,是治疗骨缺损的金标准[2]。然而,自体骨移植可能引起局部并发症,移植的新骨也可能自溶,修复效果较差。异体骨移植所需的材料更易获得,但由于存在免疫排斥风险,可能传染疾病,临床应用受限。因此,开发一种集微创、优良成血管和成骨效应、组织相容性、生物安全性、良好的物化性质于一体的诱导骨再生的新治疗策略势在必行。近年来,骨组织工程领域在骨替代生物材料上取得了重大的进展,极大地避免了其他骨替代物的潜在风险,具有广阔的应用前景。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||