[1] WITTE F. Reprint of: The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: A review. Acta Biomater. 2015;23:S28-S40.
[2] BIBER R, PAUSER J, BREM M, et al. Bioabsorbable metal screws in traumatology: A promising innovation. Trauma Case Rep. 2017;8:11-15.
[3] KÖNNEKER S, SCHÄCHINGER U, VOGT PM. Magnesium-Based Compression Screws in Acute Scaphoid Fractures and Nonunions. World J Surg. 2023;47(5):1129-1135.
[4] WENG WJ,ARNE BIESIEKIERSKI A, LI YC, et al. A review of the physiological impact of rare earth elements and their uses in biomedical Mg alloys. Acta Biomater. 2021;130:80-97.
[5] ZARTNER PA, SCHRANZ D, MINI N, et al. Acute treatment of critical vascular stenoses with a bioabsorbable magnesium scaffold in infants with CHDs. Cardiol Young. 2020; 30(4):493-499.
[6] HAUDE M, TOELG R, LEMOS PA, et al. Sustained Safety and Performance of a Second-Generation Sirolimus-Eluting Absorbable Metal Scaffold: Long-Term Data of the BIOSOLVE-II First-in-Man Trial at 5 Years. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2022;38:106-110.
[7] WEN Y, LIU Q, ZHAO W, et al. In Vitro Studies on Mg-Zn-Sn-Based Alloys Developed as a New Kind of Biodegradable Metal. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(7):1606.
[8] REDDY ST, SOMAN SS, YEE J. Magnesium Balance and Measurement. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018;25(3):224-229.
[9] 王舒,赵贵然,王茹,等.骨内型镁合金牵引器在犬牙槽骨垂直骨增量中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(25):4045-4050.
[10] LI W, QIAO W, LIU X, et al. Biomimicking Bone–Implant Interface Facilitates the Bioadaption of a New Degradable Magnesium Alloy to the Bone Tissue Microenvironment. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(23):2102035.
[11] WEN Y, LIU Q, WANG J, et al. Improving in vitro and in vivo corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of Mg-1Zn-1Sn alloys by microalloying with Sr. Bioact Mater. 2021; 6(12):4654-4669.
[12] WINDHAGEN H, RADTKE K, WEIZBAUER A, et al. Biodegradable magnesium-based screw clinically equivalent to titanium screw in hallux valgus surgery: short term results of the first prospective, randomized, controlled clinical pilot study. Biomed Eng OnLine. 2013;12:62.
[13] ROLA P, WŁODARCZAK A, ŁANOCHA M, et al. Outcomes of the two generations of bioresorbable scaffolds (Magmaris vs. Absorb) in acute coronary syndrome in routine clinical practice. Cardiol J. 2022. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2022.0047.
[14] ESPIRITU J, BERANGI M, YIANNAKOU C, et al. Evaluating metallic artefact of biodegradable magnesium-based implants in magnetic resonance imaging. Bioact Mater. 2022;15:382-391.
[15] MERINO E, DURÁN A, CERÉ S, et al. Hybrid Epoxy-Alkyl Sol-Gel Coatings Reinforced with SiO2 Nanoparticles for Corrosion Protection of Anodized AZ31B Mg Alloy. Gels. 2022;8(4):242.
[16] LIANG M J, CUN WU, MA Y, et al. Influences of aggressive ions in human plasma on the corrosion behavior of AZ80 magnesium alloy. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;119(53):111521.
[17] HZ A, RH A, JY A, et al. Influence of Zirconium (Zr) on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of biodegradable zinc-magnesium alloys. J Alloy Compd. 2020;840:155792.
[18] DUAN Y, GAO Q, ZHANG Z, et al. Chemical Ordering induced Strengthening in Lightweight Mg Alloys. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022;12(19):3488.
[19] SUN J, XU B, YANG Z, et al. Mediating the strength, ductility and corrosion resistance of high aluminum containing magnesium alloy by engineering hierarchical precipitates. J Alloy Compd. 2021;857:158277.
[20] XIE B, ZHAO M, XU R, et al. Biodegradation, Antibacterial Performance, and Cytocompatibility of a Novel ZK30-Cu-Mn Biomedical Alloy Produced by Selective Laser Melting. Int J Bioprint. 2020;7(1):300.
[21] LIU Y, CHENG WL, GU XJ, et al. Tailoring the microstructural characteristic and improving the corrosion resistance of extruded dilute Mg-05Bi-0.5Sn alloy by microalloying with Mn. J Magnes Alloy. 2021;9(5):1656-1668.
[22] WANG Q, ZHAI H, WANG L, et al. Effect of Bi Addition on the Heat Resistance of As-Extruded AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. Materials (Basel). 2023;16(3):996.
[23] SOMEKAWA H, SINGH A, SAHARA R, et al. Excellent room temperature deformability in high strain rate regimes of magnesium alloy. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):656.
[24] MOHAMED A, EL-AZIZ A, BREITINGER HG. Study of the degradation behavior and the biocompatibility of Mg–0.8Ca alloy for orthopedic implant applications. J Magnes Alloy. 2019;7(2):249-257.
[25] ZHANG Y, LI JX, LI JY. Effects of calcium addition on phase characteristics and corrosion behaviors of Mg-2Zn-0.2Mn-xCa in simulated body fluid. J Alloy Compd. 2017; 728:37-46.
[26] QIN Y, WEN P, GUO H, et al. Additive manufacturing of biodegradable metals: Current research status and future perspectives. Acta Biomater. 2019;98:3-22.
[27] TIE D, HORT N, CHEN M, et al. In vivo urinary compatibility of Mg-Sr-Ag alloy in swine model. Bioact Mater. 2021;7:254-262.
[28] CHEN K, GE W, ZHAO L, et al. Endowing biodegradable Zinc implants with dual-function of antibacterial ability and osteogenic activity by micro-addition of Mg and Ag (≤0.1wt.%). Acta Biomater. 2023;157:683-700.
[29] LI YQ, XU DY, ZHA M, et al. Study on Bulk Texture and Mechanical Properties of As-Extruded Wide Mg-Al-Zn Alloy Sheets with Different Al Addition. Materials (Basel). 2022;L15(12):4147.
[30] RAPIEJKO C, MIKUSEK D, JANUSZEWICZ B, et al. Refinement of the Magnesium-Aluminium Alloy Microstructure with Zirconium. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(24):8982.
[31] KHAN MS, TABREZ S, REHMAN TM, et al. Al (III) metal augment thermal aggregation and fibrillation in protein: Role of metal toxicity in neurological diseases. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020;27(9):2221-2226.
[32] HU Y, GUO X, QIAO Y, et al. Preparation of medical Mg-Zn alloys and the effect of different zinc contents on the alloy. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2022;33(1):9.
[33] PRABHU DB, GOPALAKRISHNAN P, RAVI KR. Morphological studies on the development of chemical conversion coating on surface of Mg–4Zn alloy and its corrosion and bio mineralisation behaviour in simulated body fluid. J Alloy Compd. 2020;812:152146.
[34] LESZ S, HRAPKOWICZ B, KAROLUS M, et al. Characteristics of the Mg-Zn-Ca-Gd Alloy after Mechanical Alloying. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(1):226.
[35] DROBYSHEV A, KOMISSAROV A, REDKO N, et al. Bone Remodeling Interaction with Magnesium Alloy Implants Studied by SEM and EDX. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(21): 7529.
[36] CHO DH, LEE BW, PARK JY, et al. Effect of Mn addition on corrosion properties of biodegradable Mg-4Zn-0.5Ca-xMn alloys. J Alloy Compd. 2017;695:1166-1174.
[37] BAHMANI A, SRINIVASAN ARTHANARI S, SHIN KS. Corrosion behavior of Mg-Mn-Ca alloy:Influences of Al,Sn and Zn. J Magnes Alloy. 2019;7(1):38-46.
[38] MARTINS AC JR, MORCILLO P, IJOMONE OM, et al. New Insights on the Role of Manganese in Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(19):3546.
[39] PONZER K, MILLISCHER V, SCHALLING M, et al. Lithium and risk of cardiovascular disease, dementia and venous thromboembolism. Bipolar Disord. 2023.doi: 10.1111/bdi.13300.
[40] ABOUTALEBIANARAKI N, ZEBLISKY P, SARKER MD, et al. An osteogenic magnesium alloy with improved corrosion resistance,antibacterial,and mechanical properties for orthopedic applications. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2023;111(4):556-574.
[41] ABOUTALEBIANARAKI N, NEAL CJ, SEAL S, et al. Biodegradable Mg-Sc-Sr Alloy Improves Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis to Accelerate Bone Defect Restoration. J Funct Biomater. 2022;13(4):261.
[42] TOSCHKA A, PÖHLE G, QUADBECK P, et al. Molybdenum as a Potential Biocompatible and Resorbable Material for Osteosynthesis in Craniomaxillofacial Surgery-An In Vitro Study. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(24):15710.
[43] SIKORA-JASINSKA M, MORATH LM, KWESIGA MP, et al. In-vivo evaluation of molybdenum as bioabsorbable stent candidate. Bioact Mater. 2022;14:262-271.
[44] BAZHENOV V, LI A, ILIASOV A, et al. Corrosion Behavior and Biocompatibility of Hot-Extruded Mg-Zn-Ga-(Y) Biodegradable Alloys. J Funct Biomater. 2022;13(4):294.
[45] LIU J, BIAN D, ZHENG Y, et al. Comparative in vitro study on binary Mg-RE (Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu) alloy systems. Acta Biomater. 2020; 102:508-528.
[46] JIANG W, WANG J, ZHAO W, et al. Effect of Sn addition on the mechanical properties and bio-corrosion behavior of cytocompatible Mg-4Zn based alloys. J Magnes Alloy. 2019;7(1):15-26.
[47] ABDELGHANY AK, GAMAL A, ABDEL-WAHAB A, et al. Evaluating the neuroprotective effect of Spirulina platensis-loaded niosomes against Alzheimer’ s disease induced in rats. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023:1-13. doi: 10.1007/s13346-023-01301-2.
[48] FERRERO ME. Neuron Protection by EDTA May Explain the Successful Outcomes of Toxic Metal Chelation Therapy in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2476.
[49] BALGOON MJ. Assessment of the Protective Effect of Lepidium sativum against Aluminum-Induced Liver and Kidney Effects in Albino Rat. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:4516730.
[50] LI H, FAN M, WANG K, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine extracts as novel corrosion inhibitors for AZ91 magnesium alloy in saline environment. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):7367.
[51] ERIŞEN DE, ZHANG Y, ZHANG B, et al. Biosafety and biodegradation studies of AZ31B magnesium alloy carotid artery stent in vitro and in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2022;110(1):239-248.
[52] YANG X, CHEN S, ZHANG S, et al. Intracellular zinc protects Kv7 K+ channels from Ca2+calmodulin-mediated inhibition. J Biol Chem. 2023;299(2):102819.
[53] LIU H, GALE J, REYNOLDS I, et al. The Multifaceted Roles of Zinc in Neuronal Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Biomedicines. 2021;9(5):489.
[54] ALATEYAH AI, ALAWAD MO, ALJOHANI TA, et al. Influence of Ultrafine-Grained Microstructure and Texture Evolution of ECAPed ZK30 Magnesium Alloy on the Corrosion Behavior in Different Corrosive Agents. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(16):5515.
[55] ZHANG Y, WU H, YUAN B, et al. Enhanced osteogenic activity and antibacterial performance in vitro of polyetheretherketone by plasma-induced graft polymerization of acrylic acid and incorporation of zinc ions. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(36):7506-7515.
[56] MIAH MR, IJOMONE OM, OKOH COA, et al. The effects of manganese overexposure on brain health. Neurochem Int. 2020;135:104688.
[57] DOU ZL, CHEN SL, WANG JC, et al. A “built-up” composite film with synergistic functionalities on Mg–2Zn–1Mn bioresorbable stents improves corrosion control effects and biocompatibility. Bioact Mater. 2023;25:223-238.
[58] KEIKHOSRAVANI P, MALEKI-GHALEH H, KAHAIE KHOSROWSHAHI A, et al. Bioactivity and Antibacterial Behaviors of Nanostructured Lithium-Doped Hydroxyapatite for Bone Scaffold Application. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9214.
[59] TAN Z, ZHOU B, ZHENG J, et al. Lithium and Copper Induce the Osteogenesis-Angiogenesis Coupling of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Crosstalk between Canonical Wnt and HIF-1α Signaling Pathways. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:6662164.
[60] LI J, ZHOU P, WANG L, et al. Investigation of Mg-xLi-Zn alloys for potential application of biodegradable bone implant materials. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021;32(4):43.
[61] WU J, ZHAO D, LEE B, et al. Effect of Lithium and Aluminum on the Mechanical Properties, In Vivo and In Vitro Degradation, and Toxicity of Multiphase Ultrahigh Ductility Mg-Li-Al-Zn Quaternary Alloys for Vascular Stent Application. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(4):1950-1964.
[62] MA D, WANG J, ZHENG MR, et al. Degradation behavior of ZE21C magnesium alloy suture anchors and their effect on ligament-bone junction repair. Bioact Mater. 2023; 26:128-141.
[63] KLINGELHÖFER D, BRAUN M, DRÖGE J, et al. Environmental and health-related research on application and production of rare earth elements under scrutiny. Global Health. 2022;18(1):86.
[64] CHEN Y, ZHU Z, ZHOU J, et al. Study on the Strengthening Mechanism of Rare Earth Ce in Magnesium Alloys,Based on First-Principle Calculations and Electronegativity Theory. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(21):6681.
[65] LI X, LIU C, WANG J, et al. Tailoring the strength and formability of Mg alloys through rare earth element additions (Gd and Dy) and dynamic recrystallizations. Mater Today Commun. 2021;28:102627.
[66] BASSOUS NJ, GARCIA CB, WEBSTER TJ. A Study of the Chemistries,Growth Mechanisms,and Antibacterial Properties of Cerium- and Yttrium-Containing Nanoparticles. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(5):1787-1807.
[67] ANISIMOVA N, KISELEVSKIY M, MARTYNENKO N, et al. Anti-tumour activity of Mg-6%Ag and Mg-10%Gd alloys in mice with inoculated melanoma. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;130:112464.
[68] NILSSON AHMAN H, D’ ELIA F, MELLIN P, et al. Microstructural Origins of the Corrosion Resistance of a Mg-Y-Nd-Zr Alloy Processed by Powder Bed Fusion-Laser Beam. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:917812.
[69] ZEMKOVÁ M, MINÁRIK P, JABLONSKÁ E, et al. Concurrence of High Corrosion Resistance and Strength with Excellent Ductility in Ultrafine-Grained Mg-3Y Alloy. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(21):7571.
[70] WANG H, YUAN H, WANG J, et al. Influence of the second phase on protein adsorption on biodegradable Mg alloys’ surfaces: Comparative experimental and molecular dynamics simulation studies. Acta Biomater. 2021;129:323-332. |
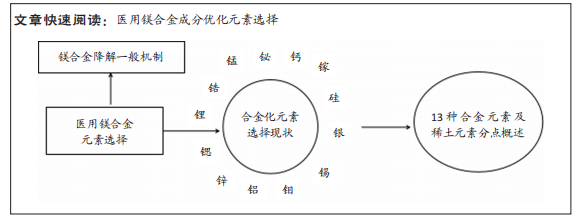
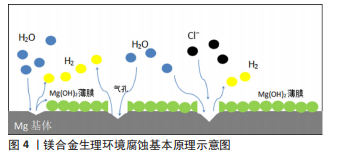
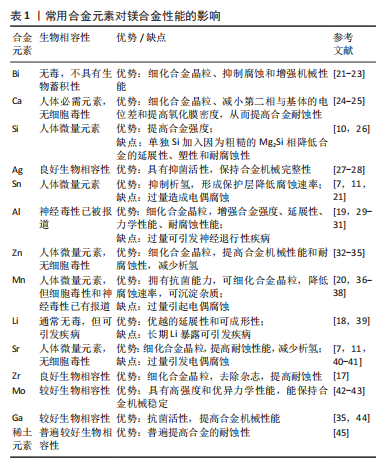

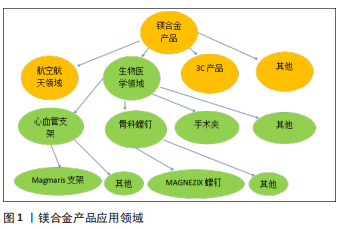 该文综述了镁及其合金处于生理环境下降解的一般基本原理,重点从安全性及对镁及其合金性能的影响两方面介绍了目前镁合金化元素选择的研究现状,并对医用镁合金未来的发展方向进行了展望。
该文综述了镁及其合金处于生理环境下降解的一般基本原理,重点从安全性及对镁及其合金性能的影响两方面介绍了目前镁合金化元素选择的研究现状,并对医用镁合金未来的发展方向进行了展望。