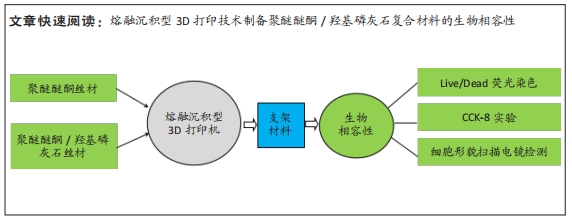
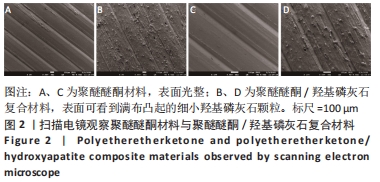
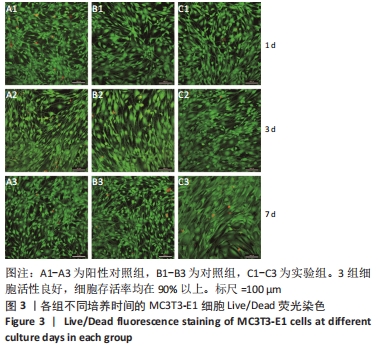
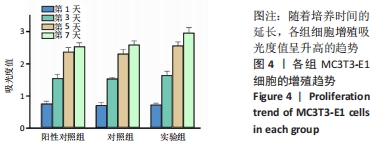
[1] MA R, TANG T. Current strategies to improve the bioactivity of PEEK. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(4):5426-5445.
[2] MOO IH, KAM CJW, LAI MWS, et al. A comparison of contiguous two-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion using a structural allograft versus a Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cage: the results of a three-year follow-up. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):331.
[3] HU B, YANG X, HU Y, et al. The n-HA/PA66 Cage Versus the PEEK Cage in Anterior Cervical Fusion with Single-Level Discectomy During 7 Years of Follow-Up. World Neurosurg. 2019;123:e678-e684.
[4] WANG H, XU M, ZHANG W, et al. Mechanical and biological characteristics of diamond-like carbon coated poly aryl-ether-ether-ketone. Biomaterials. 2010;31(32):8181-8187.
[5] LIAO C, LI Y, TJONG SC. Polyetheretherketone and Its Composites for Bone Replacement and Regeneration. Polymers (Basel). 2020;12(12): 2858.
[6] CHU L, LI R, LIAO Z, et al. Highly Effective Bone Fusion Induced by the Interbody Cage Made of Calcium Silicate/Polyetheretherketone in a Goat Model. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(5):2409-2416.
[7] RAMESH N, MORATTI SC, DIAS GJ. Hydroxyapatite-polymer biocomposites for bone regeneration: A review of current trends. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(5):2046-2057.
[8] GUILLEN-ROMERO LD, OROPEZA-GUZMAN MT, LOPEZ-MALDONADO EA, et al. Synthetic hydroxyapatite and its use in bioactive coatings. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2019;17(1):585949623.
[9] 胡超然,邱冰,周祝兴,等.3D打印聚己内酯/纳米羟基磷灰石复合支架与骨髓间充质干细胞的体外生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(4):589-595.
[10] 王鹏,孙桂森,李红旗,等.高分子材料椎间融合器的应用现况[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(2):310-315.
[11] AWASTHI S, PANDEY SK, ARUNAN E, et al. A review on hydroxyapatite coatings for the biomedical applications: experimental and theoretical perspectives. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(2):228-249.
[12] ARRES M, SALAMA M, RECHENA D, et al. Surface and mechanical properties of a nanostructured citrate hydroxyapatite coating on pure titanium. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;108:103794.
[13] 余文,孟昊业,孙逊,等.3D打印生物陶瓷在骨组织工程中的研究现状[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(14):1306-1310.
[14] MANZOOR F, GOLBANG A, JINDAL S, et al. 3D printed PEEK/HA composites for bone tissue engineering applications: Effect of material formulation on mechanical performance and bioactive potential. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;121:104601.
[15] DURHAM JR, MONTELONGO SA, ONG JL, et al. Hydroxyapatite coating on PEEK implants: Biomechanical and histological study in a rabbit model. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;68:723-731.
[16] HU X, MEI S, WANG F, et al. Implantable PEKK/tantalum microparticles composite with improved surface performances for regulating cell behaviors, promoting bone formation and osseointegration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(4):928-940.
[17] HU X, MEI S, WANG F, et al. A microporous surface containing Si3N4/Ta microparticles of PEKK exhibits both antibacterial and osteogenic activity for inducing cellular response and improving osseointegration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(10):3136-3149.
[18] SHIMIZU T, FUJIBAYASHI S, YAMAGUCHI S, et al. Bioactivity of sol-gel-derived TiO2 coating on polyetheretherketone: In vitro and in vivo studies. Acta Biomater. 2016;35:305-317.
[19] THANIGACHALAM M, MUTHUSAMY SUBRAMANIAN AV. Evaluation of PEEK-TiO2- SiO2 nanocomposite as biomedical implants with regard to in-vitro biocompatibility and material characterization. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2021;1-20. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2021.2014028.
[20] HASEGAWA T, USHIROZAKO H, SHIGETO E, et al. The Titanium-coated PEEK Cage Maintains Better Bone Fusion With the Endplate Than the PEEK Cage 6 Months After PLIF Surgery: A Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(15):E892-E902.
[21] WANG H, WAN Y, LIU X, et al. The biomechanical effects of Ti versus PEEK used in the PLIF surgery on lumbar spine: a finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2021;24(10):1115-1124.
[22] SCHULZ C, MAUER UM, MATHIEU R. PEEK cage fusion after anterior cervical corpectomy : Clinical and radiological results in patients with spondylotic myelopathy. Orthopade. 2017;46(3): 242-248.
[23] SORPRESO RS, MARTINS DE, KANAS M, et al. Transforaminal intersomatic lumbar arthrodesis: comparison between autograft and cage in PEEK. Acta Ortop Bras. 2020;28(6):296-302.
[24] 金贺荣,崔敬斌,邵苍.椎间融合器材料:临床应用的优势与关注热点[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(22):3592-3597.
[25] KUSHIOKA J, KAITO T, MAKINO T, et al. Difference in the fusion rate and bone formationbetween artificial bone and iliac autograftinside an inter-body fusion cage - A comparison between porous hydroxyapatite/type 1 collagen composite and autologousiliac bone. J Orthop Sci. 2018;23(4):622-626.
[26] JACKLE K, BRIX T, OBERTHUR S, et al. Cage or Pelvic Graft-Study on Bony Fusion of the Ventral Thoracic and Lumbar Spine in Traumatic Vertebral Fractures. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(8):786.
[27] BUSER Z, BRODKED S, YOUSSEFJ A, et al. Synthetic bone graft versus autograft or allograftforspinalfusion: a systematic review. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;25(4):509-516.
[28] PANAYOTOV IV, ORTI V, CUISINIER F, et al. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) for medical applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016;27(7):118.
[29] ABDULLAH MR, GOHARIAN A, ABDUL KM, et al. Biomechanical and bioactivity concepts of polyetheretherketone composites for use in orthopedic implants-a review. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(11): 3689-3702.
[30] TURNBULL G, CLARKE J, PICARD F, et al. 3D bioactive composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2018;3(3):278-314.
[31] FATHI AM, AHMED MK, AFIFI M, et al. Taking Hydroxyapatite- Coated Titanium Implants Two Steps Forward: Surface Modification Using Graphene Mesolayers and a Hydroxyapatite-Reinforced Polymeric Scaffold. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(1):360-372.
[32] LEE JH, JANG HL, LEE KM, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the bioactivity of hydroxyapatite-coated polyetheretherketone biocomposites created by cold spray technology. Acta Biomater. 2013; 9(4):6177-6187.
[33] LEE JH, JANG HL, LEE KM, et al. Cold-spray coating of hydroxyapatite on a three-dimensional polyetheretherketone implant and its biocompatibility evaluated by in vitro and in vivo minipig model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(3):647-657.
[34] CASAGRANDE RB, BALDIN EK, STEFFENS D, et al. HA-hybrid matrix composite coating on Ti-Cp for biomedical application. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020;31(10):82.
[35] ADAMSKI R, SIUTA D. Mechanical, Structural, and Biological Properties of Chitosan/Hydroxyapatite/Silica Composites for Bone Tissue Engineering. Molecules. 2021;26(7):1976.
[36] STEVANOVIC M, DJOSIC M, JANKOVIC A, et al. Antibacterial graphene-based hydroxyapatite/chitosan coating with gentamicin for potential applications in bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020; 108(11):2175-2189.
[37] NAKAMURA M, NAGAI A, TANAKA Y, et al. Polarized hydroxyapatite promotes spread and motility of osteoblastic cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;92(2): 783-790.
[38] QIAO SC, DU J, ZHAO JM, et al. Effects of a hydroxyapatite-coated nanotube surface of titanium on MC3T3-E1 cells: an in vitro study. Implant Dent. 2015;24(2): 204-210.
|