中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (3): 486-492.doi: 10.12307/2023.836
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇
近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程领域的应用
徐 静1,吕慧欣1,鲍 鑫2,张 逸1,王一涵1,周延民1
- 吉林大学口腔医院,1种植科,吉林省牙发育及颌骨重塑与再生重点实验室,2修复科,吉林省长春市 130021
-
收稿日期:2022-11-07接受日期:2022-12-13出版日期:2024-01-28发布日期:2023-07-10 -
通讯作者:周延民,教授,主任医师,博士生导师,吉林大学口腔医院种植科,吉林省牙发育及颌骨重塑与再生重点实验室,吉林省长春市 130021 -
作者简介:徐静,女,1995年生,山东省临沂市人,汉族,吉林大学口腔医学院在读硕士,主要从事口腔临床医学和骨组织工程相关研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(82071152),项目负责人:周延民
Application of near infrared responsive hydrogels in tissue engineering
Xu Jing1, Lyu Huixin1, Bao Xin2, Zhang Yi1, Wang Yihan1, Zhou Yanmin1
- 1Department of Implantology, Hospital of Stomatology, Jilin University, Jilin Provincial Key Laboratory of Tooth Development and Bone Remodeling, 2Department of Prosthodontics, Hospital of Stomatology, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-07Accepted:2022-12-13Online:2024-01-28Published:2023-07-10 -
Contact:Zhou Yanmin, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Implantology, Hospital of Stomatology, Jilin University, Jilin Provincial Key Laboratory of Tooth Development and Bone Remodeling, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Xu Jing, Master candidate, Department of Implantology, Hospital of Stomatology, Jilin University, Jilin Provincial Key Laboratory of Tooth Development and Bone Remodeling, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82071152 (to ZYM)
摘要:
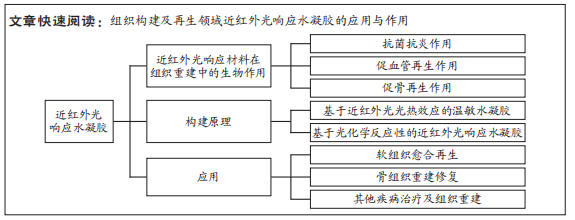
文题释义:
近红外光响应水凝胶:由聚合物网络和近红外光响应官能团组成,通过光敏基团将近红外光信号转化为物理或化学信号,继而调控水凝胶的理化性质。由于其能够实现远程时空控制和动态调节材料行为,成为一类新兴的生物医用材料。近红外光响应水凝胶的组织工程应用特性:近红外光响应水凝胶不仅可作为骨引导生物支架,而且具有光热效应并可实现生长因子药物递送等过程,从而实现诊断治疗一体化,拥有可视化成像、精准监测细胞分子水平变化、动态可调的组织再生修复等功能。
背景:近红外光响应水凝胶具有高度时空精准性、远程可调性及安全无创性等多种优异特性,为组织工程的发展提供了新的探索方向。
目的:总结近年来近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程领域的应用进展。方法:利用计算机检索中国知网及PubMed数据库相关文献,中文检索词为“近红外光响应水凝胶、组织工程、骨缺损、骨修复、骨再生、伤口愈合、伤口敷料、血管生成”,英文检索词为“near infrared responsive hydrogels,tissue engineering,bone defect,bone repair,bone regeneration,wound healing,wound dressing,angiogenesis”,检索时限为2006年5月至2022年10月,部分经典文献延长检索时间限制,分析所得文献的摘要及内容,通过纳入和排除标准得到相关文献,最终纳入97篇符合标准的文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①近红外光响应材料通过控制感染减轻炎症、促进血管生成、促进成骨细胞分化和新骨形成等过程参与组织修复。②近红外光响应材料可以通过构建具有光热效应的热敏水凝胶或者利用光化学反应制备近红外光响应水凝胶。③近红外光响应水凝胶作为伤口敷料在软组织愈合再生过程中,通过聚合物单体的聚合作用实现快速止血及组织黏附等作用,利用光热纳米材料局部光热效应促进抗菌抗炎、促进血管形成和上皮再生等功能。④近红外光响应水凝胶在骨重建修复过程中,通过促进间充质干细胞成骨分化、刺激热休克蛋白的表达、增加血管新生等发挥促进修复作用。⑤目前近红外光响应水凝胶与多种治疗策略的组合已呈现出显著协同治疗功能,也被逐步开发应用于其他组织重建和疾病治疗场景。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0831-0196(徐静);https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4173-6765(周延民)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
徐 静, 吕慧欣, 鲍 鑫, 张 逸, 王一涵, 周延民. 近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程领域的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 486-492.
Xu Jing, Lyu Huixin, Bao Xin, Zhang Yi, Wang Yihan, Zhou Yanmin. Application of near infrared responsive hydrogels in tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 486-492.
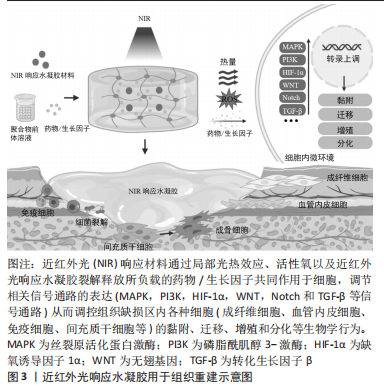
2.1.1 抗菌抗炎作用 近红外光响应水凝胶因其优异的光热转换性能,可以通过抗菌来控制炎症,加速组织愈合,抗菌机制包括:①破坏细菌细胞膜、细胞壁结构[14];②诱导细菌氧化应激产生活性氧[15];③导致蛋白质、DNA变性失活[16]。另一方面近红外光响应水凝胶可以调控免疫微环境,调节炎症细胞的表达和趋化因子的释放,如增强巨噬细胞和嗜中性粒细胞对细菌的吞噬作用,诱导巨噬细胞向M2表型的极化,M2表型巨噬细胞通过产生生长因子如血管内皮生长因子和分泌抗炎因子(如白细胞介素4和白细胞介素10等)可促进血管生成,减少炎症反应[14,17-18]。
2.1.2 促血管再生作用 血管生成是组织愈合过程中至关重要的一环,近红外光响应水凝胶可提供伤口区域成血管微环境,促进原位血管生成。其作用机制包括:①通过活性氧激活内皮型一氧化氮合酶或者递送一氧化氮释放分子,促进一氧化氮产生,进而促进血管生成[19-20];②输送CO2通过玻尔效应影响血管生成[21-22];③通过激活缺氧诱导因子1α信号或者递送生长因子上调血管内皮生长因子和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子等表达,促进细胞增殖和血管生成[18,23-25]。此外,温和的热量(40-41 ℃)可以通过诱导血管内皮细胞的增殖,有效地增加新生肉芽组织中的血管密度[26]。
2.1.3 促骨再生作用 间充质干细胞被募集活化、分化成为成骨细胞[27],成骨细胞促进胶原沉积进而矿化是新骨形成最为关键的环节。多种生化和生物物理因素可以在不同的修复和再生阶段来调节细胞行为和骨再生。近红外光响应水凝胶参与调节骨再生机制:①周期性光热治疗可刺激骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖及成骨分化[28-29];②通过胞外信号分子如生长因子递送系统,上调相关成骨信号通路[30]。此外,温和的光热水凝胶增加了热休克蛋白的表达,而且热休克蛋白70可以增强细胞的耐热性,热休克蛋白47促进Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的成熟,两者都可以促进成骨细胞活性[28,31-32]。
2.2 近红外光响应水凝胶的构建原理 近红外光响应水凝胶是通过近红外光基团将近红外光转换成物理化学信号,继而控制水凝胶理化性质,起到递送相关细胞因子或调控细胞生物学行为等作用。光热纳米材料作为光敏剂被引入近红外光响应水凝胶将吸收的波长长、能量低的近红外光转换为热量或波长短、能量高的光。常用的无机纳米光热材料主要包括:金属纳米材料[17,33-35]、碳基纳米材料[36-38]、过渡金属氧化物及硫化物[39-40]、上转换纳米材料等[41-44];有机纳米光热材料主要包括:共轭聚合物大分子(如聚多巴胺)[19,45-47]、小分子染料(如吲哚菁绿、IR-780)等[7,48]。无机材料具有高光稳定性的优势,也可以提高水凝胶机械性能,但需要改性以提高其生物降解能力[18,49-50]。有机材料通常具有更好的生物相容性,一般不影响水凝胶力学性能,但光稳定性差[7,45,51],详情见表1。
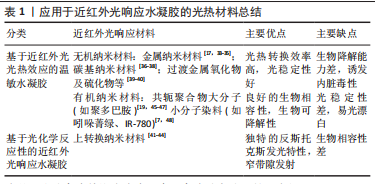
在近红外光照射下,依据水凝胶结构和性能的改变介绍目前常见的两种制备策略:①基于近红外光光热效应的温敏水凝胶;②基于光化学反应性的近红外光响应水凝胶。
2.2.1 基于近红外光光热效应的温敏水凝胶 一般而言,温敏性水凝胶依赖于外界温度变化而产生相应相态转变,而光激发的温敏性水凝胶则可以利用光热效应实现相态转换。光热效应是指光热材料被光激发时由于表面等离子体激元共振效应或能级跃迁原理表现出强烈的光吸收,并将所吸收的光能转换为热能。基于光热效应的温敏性水凝胶,不仅可以实现光热治疗,同时水凝胶网络在热刺激下改变物理结构,发生相转变现象,实现分子递送和靶向治疗等。将近红外光响应的光敏剂与温敏性水凝胶通过聚合物链的物理缠结或分子间相互作用力(如氢键、疏水作用、静电相互作用、配位键和希夫碱反应等)而形成非共价键作用的交联网络,水凝胶交联点没有形成新的化学键[34,52-54]。
基于光热效应的温敏性水凝胶由于其内部可逆键的存在,具有较好的热可逆性,这对于模仿机体组织微环境和动态调控释放具有重要意义。通常,温敏水凝胶按照其临界溶解温度可分为正温敏水凝胶(如明胶、琼脂糖等)和负温敏水凝胶(壳聚糖,聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺[poly (N-isopropylacrylamide),PNIPAAM])等[55]。正温敏水凝胶在达到相变温度时凝胶-溶胶相变,软化或融化水凝胶的纳米结构从而实现分子递送[56]。但是,正温敏凝胶药物递送的过程需要在较高温度下进行,这可能会导致某些不稳定的药物或者生物分子失活,从而影响药物的生物医用要求[57]。与此相反,负温敏水凝胶聚合物网络在超过最低临界溶解温度(lower critical solution temperature,LCST)时从溶胀态转变为收缩态。LCST与人体体温相近的负温敏水凝胶具有广泛的生物应用[47,58-60]。常用的负温敏聚合物有PNIPAAM及其衍生物、壳聚糖及其衍生物等[47,57],因其与水分子形成氢键而具有亲水性,在最低临界溶解温度LCST以下呈现溶胀状态,可使药物分散于聚合物网络结构中[61]。
近红外光照射凝胶激发光热转换,当温度超过LCST氢键断裂导致凝胶亲水疏水转变,聚合物网络收缩从而实现药物释放和改善局部药物渗透性[46]。温敏水凝胶可逆的凝胶-溶胶相变是实现药物按需释放的关键。调整光敏剂含量、浓度、光照强度大小和暴露时间长短等可实现控制水凝胶网络来调整分子释放速率[46-47,62]。另一方面,在光热效应作用下的凝胶超过LCST实现相态转化,凝胶化的聚合物网络可以作为组织工程支架调控细胞的行为如黏附、迁移和分化,也为制造可注射原位水凝胶应用于机体提供了可能[34,63]。
2.2.2 基于光化学反应性的近红外光响应水凝胶 化学交联水凝胶是基于共价键作用的化学偶联形成水凝胶结构,具有更好的结构稳定性及机械性能[19,43]。光化学反应性近红外光响应水凝胶,通过改变光响应官能团的结构,进而调控水凝胶网络结构,达到调控水凝胶的物理或化学性质的目的。上转换效应指的是通过能量传输将吸收低能量的光,发射出高能量的光,即经波长长、频率低的光激发,材料发射出波长短及频率高的光[64]。上转换纳米粒子(up-conversion nanoparticles,UCNPs)由于其离子独特的阶梯状能级结构,较双/多光子系统吸收效率高[65],因而光化学反应性近红外光响应水凝胶通常利用UCNPs实现近红外光向紫外光/可见光转换,激活相应光响应官能基团,引起水凝胶光化学反应改变聚合物基质交联密度或相转变、降解等现象,并可作为药物递送系统,释放抗菌药物或者生长因子等促进组织修复。
目前合成应用于组织工程近红外光响应水凝胶的光化学反应主要包括光聚合和光裂解反应等[41,43,66-68]。光聚合反应通常分为自由基链式聚合与生物正交点击反应两类[69-70]。大多数光聚合水凝胶通过自由基链式聚合,其机制为光敏剂例如UCNPs吸收近红外光发出紫外光或可见光,引起相应的光响应基团活化形成自由基而引发不饱和化学键的聚合,从而导致聚合物的化学交联。调整照射光强度、照射时间、调节聚合物基质浓度等可影响水凝胶聚合物交联密度[43],进而影响其理化性质,例如改变水凝胶硬度可调控干细胞黏附、迁移和分化等[14]。生物正交反应由于其具有高度专一性、良好生物相容性以及快速反应能力,被引入构建光化学反应性近红外光响应水凝胶以实现对生物体系的标记和功能调控[71]。目前最常见反应类型主要是叠氮-烷烃的环化加成反应[72-73],可通过互补官能团的特定配对实现化学交联,选择性修饰报告基团,从而实现可视化成像。此外,UCNPs将近红外光转化为紫外光信号引起水凝胶上的光裂解基团发生化学键断裂使得聚合物网络发生不可逆的部分或者完全降解的光裂解反应,为近红外光响应水凝胶递送系统在组织工程领域的应用提供了新的可能性,以实现远程时空控制、动态可调节的精准治疗[43]。
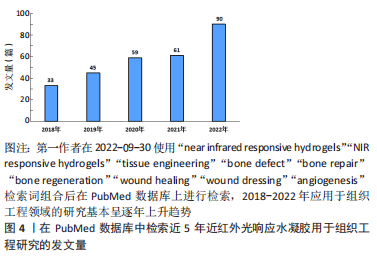
2.3 近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程领域的应用 在功能性人体组织再生医学和生物组织工程致力于重塑组织结构层次,实现组织及器官修复、再生或替换需求。近红外光响应水凝胶在缺损处构建可降解的生物桥梁,通过聚合物支架的高度排列结构以及多种近红外光响应基团及生物活性因子的刺激,引导细胞定向生长形成新组织完成缺损的修复。此外,近红外光荧光基团的应用还为诊断治疗一体化的精准医疗蓝图描绘了可能性,包括实现可视化成像、精准监测分子水平变化、动态可调节的组织再生修复等功能。近红外光响应水凝胶因其优良的结构动态可调性、操作安全无创性、功能可设计性,在软组织愈合再生、骨组织重建修复以及其他组织再生领域具有广阔的应用前景[74-75]。近5年来近红外光响应水凝胶用于组织工程研究的发文量不断攀升,见图4。近5年来近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程领域相关研究进展成果见表2。
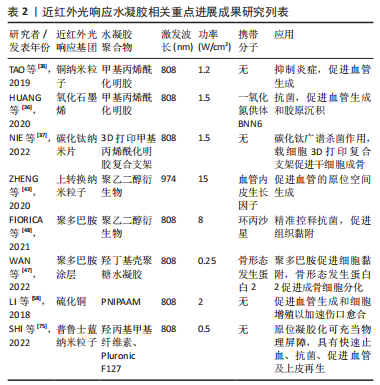
2.3.1 软组织愈合再生 伤口愈合是由多种细胞、细胞因子参与的复杂的调节过程,由止血和凝血、炎症期、增殖期和重塑期4个连续而重叠的阶段构成[76]。近红外光响应水凝胶作为伤口敷料,因其含有不同组分可在伤口愈合的不同阶段发挥作用,因而在预防创伤感染和促进软组织再生方面具有广阔的应用前景。
及时的止血对于伤口愈合的第一阶段十分关键。在伤口愈合的早期阶段,血细胞、血小板的聚集和纤维蛋白凝块的形成会加速止血过程,以实现伤口封闭[77]。近红外光响应水凝胶作为伤口敷料具有水凝胶的固有优势,通过优异的溶胀能力吸收大量渗出物,并黏附在伤口组织充当物理屏障,维持伤口的湿润环境,同时,还可以促血小板的聚集和纤维蛋白凝块的形成产生止血作用[78-80]。具有优异的组织黏附性的光热材料聚多巴胺的加入有助于加速伤口敷料水凝胶的止血过程[45],聚多巴胺涂层可以将疏水表面转化为亲水表面,为伤口愈合提供潮湿密闭的环境,以增强水凝胶对细胞/组织的亲和力、促进其与细胞/组织的黏附。聚多巴胺复合物的黏附性和优异的延展性、机械性能和自愈合性能,使聚多巴胺复合物在伤口表面形成长期稳定的愈合环境,这避免了由于需要重复更换传统敷料而导致的伤口二次撕裂[45]。基于季铵化壳聚糖/单宁酸/三价铁复合近红外光响应的可注射水凝胶有效加速止血过程。热敏水凝胶基质壳聚糖使水凝胶在LCST以下具有可注射性以适应不同伤口形状,此外壳聚糖的氨基在血液中由于静电吸附作用产生NH3+,增加血小板黏附,并促进受损部位红细胞的快速黏附和聚集,有助于血栓的形成,实现快速止血[34]。
伤口止血后迅速转入炎症期,有效控制感染、减轻炎症是伤口愈合的另一个关键。近红外光响应水凝胶的抗菌作用通过光热效应产生局部热能、大量自由基和活性氧来治疗细菌感染[15-17,19]。具有抗菌抗炎成血管等多种功能的光热控释氧气的载有碳化钛/聚多巴胺/透明质酸复合水凝胶在近红外光照射后最高温度迅速达到47.5 ℃,可有效杀菌,并能刺激巨噬细胞向M2表型分化分泌白细胞介素10对抗炎症,近红外光辐照碳化钛纳米片产生的热量刺激氧合血红蛋白释放氧气,促进血管内皮细胞的增殖和迁移[81]。近红外光辐射诱导的高温具有短期抗菌作用,当近红外光照射停止时,随光热效应减弱,残留的细菌不能被有效抑制。
为了增强水凝胶的抗菌性能,已有多种载有抗菌药物的水凝胶被应用于协同治疗[82-84]。水凝胶可以与药物结合,通过π-π堆积、可逆共价交联来改善抗菌性能[85],或者直接封装[86],通过光热触发来控制药物释放[87],改变光热引发剂含量、浓度,调整近红外光辐照强度和暴露时间等可实现部分破坏水凝胶网络[46-47,62],从而实现抗菌药物的可控释放。HAN等[59]制备的近红外光响应的载多西环素和聚多巴胺的PNIPAAM水凝胶具有精确控制药物释放、促进组织修复再生的双重效应。聚多巴胺吸收近红外光能量转化为热能,使负温敏水凝胶PNIPAAM被加热到LCST以上,聚合物网络原位凝胶化,作为细胞生长的支架。溶胀状态的水凝胶网络结构收缩而释放药物,停止近红外光照射,可快速关闭药物释放通道,从而准确控制多西环素释放速率。总体而言,近红外光响应水凝胶将具有杀菌特性的光热材料、抗菌药物等与水凝胶结合,以高精度地在时间和空间上靶向微生物,同时避免了日益严重的抗生素耐药性问题。此外,近红外光响应水凝胶可以调控伤口区域募集的免疫细胞分泌多种趋化因子和生长因子[15,18,25],继而吸引包括成纤维细胞和血管内皮细胞在内的各种细胞迁移至伤口区域[27,88],引导组织愈合进入增殖阶段。
近红外光响应水凝胶在增殖阶段通过促进上皮再生、血管生成和胶原沉积等发挥作用。许多金属元素具有抗菌及成血管作用如Cu2+,Mg2+,Zn2+也被负载于水凝胶,在近红外光照射下不仅发挥光热治疗抗菌作用,还能有效刺激血管生成,加速伤口愈合[17,49,50]。功能化聚乙烯吡咯烷酮通过非共价电化学相互作用与银纳米粒子交联,为了避免纳米材料的聚集,普鲁士蓝可以通过聚多巴胺进行表面修饰以锚定银离子,实现银离子的控制释放[35]。此外,由于普鲁士蓝的高光热转换特性和优异的稳定性,普鲁士蓝已应用于抗菌治疗和伤口愈合。普鲁士蓝纳米粒子作为近红外光响应开关的纳米纤维素复合水凝胶在治疗10 d后即可实现伤口愈合,促进更多新生血管形成、胶原沉积和上皮再形成[75]。
近红外光响应水凝胶作为伤口敷料在软组织愈合再生过程中发挥快速止血、组织黏附、抗菌抗炎、促进血管形成和上皮再生等多种功能。近红外光水凝胶可以维持伤口愈合的湿性环境;具有可注射性的近红外光响应水凝胶的自适应使其适用于各种不同的伤口形状,可实现良好的封闭性[34],良好的组织黏附性避免了由于需要重复更换传统敷料而导致的伤口二次撕裂[75]。
2.3.2 骨组织重建修复 骨缺损修复通常需要骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和分化、血管生成和钙化沉积[1]。然而,常见的临床骨缺损治疗,如开放性骨折的治疗,常伴随着严重的感染和组织缺血性坏死。作为一种可重复使用、无毒性、非侵入性的新治疗策略,光热疗法诱导的局部光热效应在体内外均表现出优异的成骨能力。水凝胶优异的生物相容性、可调节的降解性和多孔结构可以减少植入材料产生的炎症反应,并为新骨生长提供支架[89]。
近红外光响应水凝胶可以实现原位组织再生重建。ZHENG等[43]制备的近红外光光响应4D细胞培养模型,在近红外光照射下,UCNPs将近红外光转换为紫外光,从而激活细胞黏附肽,使得封装在水凝胶内的血管内皮细胞的附着和迁移增强,释放血管内皮生长因子,促进血管的空间生成,血管生成可以为新生组织提供氧气和营养,从而有助于加速骨修复进程。LEE等[69]通过近红外光照射复合水凝胶前体溶液,利用近红外光响应二维二硫化钼片与PNIPAAM共轭的原理实现聚合物的原位凝胶化,为原位骨再生提供了支架材料。光热剂的引入可以增强水凝胶的成骨性能,温和的热刺激(40-42 ℃)可以增加热休克蛋白的表达[30,32]。
周期性光热治疗可刺激骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和分化,这归因于热效应的延长。轻度热刺激(41 ℃,1次/周,1 h/次)可增强碱性磷酸酶的表达,促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化[29]。载聚多巴胺的复合光热水凝胶由于聚多巴胺表面丰富官能团赋予的优异生物黏附性而显示出高的成骨能力[90],在长期的骨再生过程中,成骨细胞逐渐增殖、分化并迁移至缺损区。
对于感染性骨缺损而言,近红外光响应水凝胶可发挥抗菌成骨的双重效应。3D打印碳化钛纳米片复合水凝胶支架可对革兰阳性菌和革兰阴性菌产生明显的抑菌效果,载细胞3D生物打印支架可实现间充质干细胞的增殖和分化,在感染条件下同时实现抗菌和成骨效果[37]。顺序递送抗炎药物阿司匹林和骨形态发生蛋白2的近红外光响应聚多巴胺/镁-碳酸钙微球/羟丁基壳聚糖复合水凝胶,通过阿司匹林的快速释放减轻了骨愈合早期的急性炎症反应,近红外光可控释放骨形态发生蛋白2,上调成骨通路表达,使其在骨再生中的治疗效果最大化[47]。此外,近红外光荧光染料具有自荧光弱,对组织细胞的低毒性,高敏感性、易与蛋白结合形成非共价荧光复合物等特性[7,48],为构建具有原位监测骨组织再生能力的骨组织工程支架提供了可行的策略。Kim等[7]利用近红外荧光团CTNF127,ZW800-1C双荧光基团结合在聚乳酸-聚己内酯-聚乙醇酸共聚物,高分辨率生物成像实时示踪干细胞分化、监测体内支架降解情况。Yang等[91]利用一种新的半菁染料LET-3,通过光声双模式成像实现对碱性磷酸酶表达的非侵入性、高分辨率、实时可视化和半定量分析。
近红外光响应水凝胶在骨重建修复过程中,通过促进间充质干细胞成骨分化、刺激热休克蛋白的表达、促进血管新生、递送生长因子上调相关成骨通路表达等过程发挥作用。原位凝胶具有更好的形状适应性,可与伤口紧密接触,同时发挥光热协同成骨作用[30,69]。值得注意的是,目前近红外光响应水凝胶应用于骨组织工程的研究较少,可能是由于近红外光的深组织穿透性差,光照射需要特定部位和角度,且不适用于位置较深的腔隙内骨缺损的重塑。
2.3.3 其他疾病治疗及原位组织重建 随着组织工程的不断发展,具有疾病治疗和组织再生能力的多功能水凝胶有望成为人体组织、器官衰竭及受损的有效治疗手段,改善目前疾病治疗所面临的困境[92]。手术治疗肿瘤后并不能完全根除癌细胞和恢复正常组织功能,因此,开发有效的根除癌细胞和同时治愈由手术扩大切除肿瘤组织所产生伤口的创新方法是非常必要的[93]。光触发消融肿瘤可以通过光热治疗的局部热效应杀死癌细胞,或者光动力治疗的局部化学损伤杀死癌细胞。
近红外光响应水凝胶将多种治疗策略的组合呈现出显著的协同治疗功能,已被开发用于皮肤肿瘤引起的伤口的愈合。光动力治疗药物可以与抗肿瘤药物、光敏剂共同负载于水凝胶基质中,通过近红外光照射,预加载的药物以可控的方式释放或产生,从而实现协同治疗效果[94-95]。将Mg2+离子和二氧化钛纳米颗粒嵌入壳聚糖水凝胶,在808 nm激光下精准地照射肿瘤部位,黑色二氧化钛纳米颗粒产生热量,直接通过热消融肿瘤,水凝胶基质存在可避免热扩散对周围正常组织造成损伤。另一方面,从水凝胶中释放的Mg2+离子可以促进皮肤细胞的增殖、黏附和迁移,从而导致加速伤口闭合[50]。近红外光响应水凝胶对于原位癌的治疗具有独特优势,将多种治疗策略的组合呈现出显著的协同治疗功能,可以通过光热消融肿瘤细胞,抗癌药物产生局部化学损伤,减少全身血液系统等疾病,在实现微创治疗同时完成损伤部位的组织重建。对于已经出现远端转移的癌症,近红外光响应水凝胶的治疗效果较局限。
最近,也有学者将近红外光响应水凝胶应用其他的组织再生领域,实现动态监测的支架降解,量化组织再生过程,无创体内3D生物打印等目标。例如用800 nm荧光团ZW800-3a、700 nm脑特异性对比剂OX1标记支架,通过多光谱功能的高分辨率成像定位和量化脑组织生长,同时监测支架降解情况[96]。LU等[63]制备的基于胶原蛋白的可注射复合水凝胶可通过转化生长因子β/SMAD信号通路调控软骨修复。基于数字近红外光光聚合的3D打印技术,将数字光图案和UCNPs水凝胶结合使用,在没有手术植入的情况下,在体内获得了具有球粒化的个性化耳样组织结构和肌肉组织可修复的细胞性适形支架[97]。这也为近红外光响应水凝胶结合生物打印应用于原位组织重建创造了新思路。
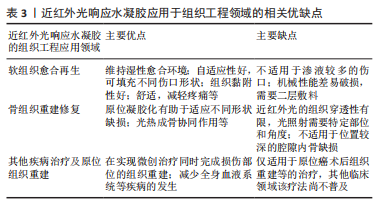
近红外光响应水凝胶将多种治疗策略的组合呈现出显著协同治疗功能,也被逐步开发应用于其他组织重建场景中,例如促进皮肤肿瘤引起的伤口愈合,动态监测体内生物支架降解、量化组织再生情况,构建无创体内3D生物打印等。近红外光响应水凝胶应用于组织工程各领域的相关优缺点见表3。
| [1] LOPES D, MARTINS-CRUZ C, OLIVEIRA MB, et al. Bone physiology as inspiration for tissue regenerative therapies. Biomaterials. 2018;185:240-275. [2] HO-SHUI-LING A, BOLANDER J, RUSTOM LE, et al. Bone regeneration strategies: engineered scaffolds, bioactive molecules and stem cells current stage and future perspectives. Biomaterials. 2018;180:143-162. [3] GALLIOT B, CRESCENZI M, JACINTO A, et al. Trends in tissue repair and regeneration. Development. 2017;144(3):357-364. [4] SONG R, MURPHY M, LI C, et al. Current development of biodegradable polymeric materials for biomedical applications. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018;12:3117-3145. [5] MOREIRA TEIXEIRA LS, PATTERSON J, LUYTEN FP. Skeletal tissue regeneration: where can hydrogels play a role? Int Orthop. 2014;38(9):1861-1876. [6] STEPHANOPOULOS N, ORTONY JH, STUPP SI. Self-assembly for the synthesis of functional biomaterials. Acta Mater. 2013;61(3):912-930. [7] KIM SH, PARK JH, KWON JS, et al. NIR fluorescence for monitoring in vivo scaffold degradation along with stem cell tracking in bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2020;258:120267. [8] LI L, SCHEIGER JM, LEVKIN PA. Design and applications of photoresponsive hydrogels. Adv Mater. 2019;31(26):e1807333. [9] WAN Z, ZHANG P, LV L, et al. NIR light-assisted phototherapies for bone-related diseases and bone tissue regeneration: a systematic review. Theranostics. 2020; 10(25):11837-11861. [10] VANGIPURAM R, FELDMAN SR. Ultraviolet phototherapy for cutaneous diseases: a concise review. Oral Dis. 2016;22(4):253-259. [11] SAKUDO A. Near-infrared spectroscopy for medical applications: current status and future perspectives. Clin Chim Acta. 2016;455:181-188. [12] LEE HP, GAHARWAR AK. Light-responsive inorganic biomaterials for biomedical applications. Adv Sci. 2020;7(17):2000863. [13] RAZA A, HAYAT U, RASHEED T, et al. “Smart” materials-based near-infrared light-responsive drug delivery systems for cancer treatment: a review. J Mater Res Technol. 2019;8(1):1497-1509. [14] TSOU YH, KHONEISSER J, HUANG PC, et al. Hydrogel as a bioactive material to regulate stem cell fate. Bioact Mater. 2016;1(1):39-55. [15] HAIDARI H, BRIGHT R, STRUDWICK XL, et al. Multifunctional ultrasmall AgNP hydrogel accelerates healing of S. aureus infected wounds. Acta Biomater. 2021; 128:420-434. [16] TONG C, ZHONG X, YANG Y, et al. PB@PDA@Ag nanosystem for synergistically eradicating MRSA and accelerating diabetic wound healing assisted with laser irradiation. Biomaterials. 2020;243:119936. [17] FENG L, CHEN Q, CHENG H, et al. Dually-thermoresponsive hydrogel with shape adaptability and synergetic bacterial elimination in the full course of wound healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(18):e2201049. [18] ZHOU L, ZHOU L, WEI C, et al. A bioactive dextran-based hydrogel promote the healing of infected wounds via antibacterial and immunomodulatory. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;291:119558. [19] LI Y, FU R, DUAN Z, et al. Artificial nonenzymatic antioxidant mxene nanosheet-anchored injectable hydrogel as a mild photothermal-controlled oxygen release platform for diabetic wound healing. ACS Nano. 2022;16(5):7486-7502. [20] LV X, XU Y, RUAN X, et al. An injectable and biodegradable hydrogel incorporated with photoregulated NO generators to heal MRSA-infected wounds. Acta Biomater. 2022;146:107-118. [21] WANG W, SHENG H, CAO D, et al. S-nitrosoglutathione functionalized polydopamine nanoparticles incorporated into chitosan/gelatin hydrogel films with NIR-controlled photothermal/NO-releasing therapy for enhanced wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;200:77-86. [22] LI WP, SU CH, WANG SJ, et al. CO2 delivery to accelerate incisional wound healing following single irradiation of near-infrared lamp on the coordinated colloids. ACS Nano. 2017;11(6):5826-5835. [23] XIE G, ZHOU N, GAO Y, et al. On-demand release of CO2 from photothermal hydrogels for accelerating skin wound healing. Chem Eng J. 2021;403:126353. [24] SHENG L, ZHANG Z, ZHANG Y, et al. A novel “hot spring”-mimetic hydrogel with excellent angiogenic properties for chronic wound healing. Biomaterials. 2021;264:120414. [25] JIN L, GUO X, GAO D, et al. An NIR photothermal-responsive hybrid hydrogel for enhanced wound healing. Bioact Mater. 2022;16:162-172. [26] HUANG S, XU S, HU Y, et al. Preparation of NIR-responsive, ROS-generating and antibacterial black phosphorus quantum dots for promoting the MRSA-infected wound healing in diabetic rats. Acta Biomater. 2022;137: 199-217. [27] MA H, ZHOU Q, CHANG J, et al. Grape seed-inspired smart hydrogel scaffolds for melanoma therapy and wound healing. ACS Nano. 2019;13(4):4302-4311. [28] LIANG B, BURLEY G, LIN S, et al. Osteoporosis pathogenesis and treatment: existing and emerging avenues. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022;27(1):72. [29] CHEN J, SHI ZD, JI X, et al. Enhanced osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells by periodic heat shock in self-assembling peptide hydrogel. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(5-6):716-728. [30] TONG L, LIAO Q, ZHAO Y, et al. Near-infrared light control of bone regeneration with biodegradable photothermal osteoimplant. Biomaterials. 2019;193:1-11. [31] SANCHEZ-CASANOVA S, MARTIN-SAAVEDRA FM, ESCUDERO-DUCH C, et al. Local delivery of bone morphogenetic protein-2 from near infrared-responsive hydrogels for bone tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2020;241:119909. [32] MA L, FENG X, LIANG H, et al. A novel photothermally controlled multifunctional scaffold for clinical treatment of osteosarcoma and tissue regeneration. Mater Today. 2020;36:48-62. [33] TAO B, LIN C, DENG Y, et al. Copper-nanoparticle-embedded hydrogel for killing bacteria and promoting wound healing with photothermal therapy. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(15):2534-2548. [34] GUO S, YAO M, ZHANG D, et al. One-step synthesis of multifunctional chitosan hydrogel for full-thickness wound closure and healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(4):e2101808. [35] MATAI I, KAUR G, SONI S, et al. Near-infrared stimulated hydrogel patch for photothermal therapeutics and thermoresponsive drug delivery. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2020;210:111960. [36] HUANG S, LIU H, LIAO K, et al. Functionalized GO nanovehicles with nitric oxide release and photothermal activity-based hydrogels for bacteria-infected wound healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(26):28952-28964. [37] NIE R, SUN Y, LV H, et al. 3D printing of MXene composite hydrogel scaffolds for photothermal antibacterial activity and bone regeneration in infected bone defect models. Nanoscale. 2022;14(22):8112-8129. [38] YIN J, HAN Q, ZHANG J, et al. MXene-based hydrogels endow polyetheretherketone with effective osteogenicity and combined treatment of osteosarcoma and bacterial infection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(41): 45891-45903. [39] LEE HP, LOKHANDE G, SINGH KA, et al. Light-Triggered in situ gelation of hydrogels using 2D molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanoassemblies as crosslink epicenter. Adv Mater. 2021;33(23):e2101238. [40] XU Y, ZHAO S, WENG Z, et al. Jelly-inspired injectable guided tissue regeneration strategy with shape auto-matched and dual-light-defined antibacterial/osteogenic pattern switch properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(49):54497-54506. [41] LI M, ZHANG Z, LIANG Y, et al. Multifunctional tissue-adhesive cryogel wound dressing for rapid nonpressing surface hemorrhage and wound repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(32):35856-35872. [42] YUAN P, LUO Y, LUO Y, et al. A “sandwich” cell culture platform with NIR-responsive dynamic stiffness to modulate macrophage phenotypes. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(7):2553-2561. [43] ZHENG Y, CHEN Z, JIANG Q, et al. Near-infrared-light regulated angiogenesis in a 4D hydrogel. Nanoscale. 2020;12(25):13654-13661. [44] ZHANG X, ZHANG Y, ZHANG C, et al. An injectable hydrogel co-loading with cyanobacteria and upconversion nanoparticles for enhanced photodynamic tumor therapy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;201:111640. [45] DONG Y, JIN G, JI C, et al. Non-invasive tracking of hydrogel degradation using upconversion nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2017;55:410-419. [46] GWON K, JO EJ, SAHU A, et al. Improved near infrared-mediated hydrogel formation using diacrylated Pluronic F127-coated upconversion nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;90:77-84. [47] WAN Z, DONG Q, GUO X, et al. A dual-responsive polydopamine-modified hydroxybutyl chitosan hydrogel for sequential regulation of bone regeneration. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;297:120027. [48] FIORICA C, PALUMBO FS, PITARRESI G, et al. Ciprofloxacin releasing gellan gum/polydopamine based hydrogels with near infrared activated photothermal properties. Int J Pharm. 2021;610:121231. [49] WANG X, QIU L, WANG C, et al. Nanodot-doped peptide hydrogels for antibacterial phototherapy and wound healing. Biomater Sci. 2022;10(3):654-664. [50] WANG X, MA B, XUE J, et al. Defective black nano-titania thermogels for cutaneous tumor-induced therapy and healing. Nano Lett. 2019;19(3):2138-2147. [51] LV S, MIAO Y, LIU D, et al. Recent development of photothermal agents (ptas) based on small organic molecular dyes. Chembiochem. 2020;21(15):2098-2110. [52] PICCHIONI F, MULJANA H. Hydrogels based on dynamic covalent and non covalent bonds: a chemistry perspective. Gels. 2018;4(1):21. [53] CHAKRABORTY A, ROY A, RAVI SP, et al. Exploiting the role of nanoparticles for use in hydrogel-based bioprinting applications: concept, design, and recent advances. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(19):6337-6354. [54] LIANG Y, LI Z, HUANG Y, et al. Dual-dynamic-bond cross-linked antibacterial adhesive hydrogel sealants with on-demand removability for post-wound-closure and infected wound healing. ACS Nano. 2021;15(4):7078-7093. [55] ALIPOUR S, NOUR S, ATTARI SM, et al. A review on in vitro/in vivo response of additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J Mater Chem B. 2022;10(46):9479-9534. [56] 冯茜,张琨雨,李睿,等.可注射水凝胶及其在再生医学领域的应用[J].高分子学报,2021,52(1):1-15. [57] YU Y, CHENG Y, TONG J, et al. Recent advances in thermo-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(13):2979-2992. [58] LI M, LIU X, TAN L, et al. Noninvasive rapid bacteria-killing and acceleration of wound healing through photothermal/photodynamic/copper ion synergistic action of a hybrid hydrogel. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(8):2110-2121. [59] HAN L, ZHANG Y, LU X, et al. Polydopamine nanoparticles modulating stimuli-responsive pnipam hydrogels with cell/tissue adhesiveness. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(42):29088-29100. [60] LIU S, LIU Z, WU M, et al. NIR as a “trigger switch” for rapid phase change, on-demand release, and photothermal synergistic antibacterial treatment with chitosan-based temperature-sensitive hydrogel. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021; 191:344-358. [61] GENG S, ZHAO H, ZHAN G, et al. Injectable in situ forming hydrogels of thermosensitive polypyrrole nanoplatforms for precisely synergistic photothermo-chemotherapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(7):7995-8005. [62] LIU B, SUN J, ZHU J, et al. Injectable and NIR-responsive DNA-inorganic hybrid hydrogels with outstanding photothermal therapy. Adv Mater. 2020;32(39): e2004460. [63] LU Z, LIU S, LE Y, et al. An injectable collagen-genipin-carbon dot hydrogel combined with photodynamic therapy to enhance chondrogenesis. Biomaterials. 2019;218:119190. [64] ZHANG L, JIN D, STENZEL MH. Polymer-functionalized upconversion nanoparticles for light/imaging-guided drug delivery. Biomacromolecules. 2021;22(8):3168-3201. [65] MAHATA MK, DE R, LEE KT. Near-infrared-triggered upconverting nanoparticles for biomedicine applications. Biomedicines. 2021;9(7):756. [66] CHUNG S, LEE H, KIM HS, et al. Transdermal thiol-acrylate polyethylene glycol hydrogel synthesis using near infrared light. Nanoscale. 2016;8(29):14213-14221. [67] HAO Y, DONG Z, CHEN M, et al. Near-infrared light and glucose dual-responsive cascading hydroxyl radical generation for in situ gelation and effective breast cancer treatment. Biomaterials. 2020;228:119568. [68] JALANI G, NACCACHE R, ROSENZWEIG DH, et al. Photocleavable hydrogel-coated upconverting nanoparticles: a multifunctional theranostic platform for NIR imaging and on-demand macromolecular delivery. J Am Chem Soc. 2016; 138(3):1078-1083. [69] LEE HP, LOKHANDE G, SINGH KA, et al. Light-triggered in situ gelation of hydrogels using 2D molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanoassemblies as crosslink epicenter. Adv Mater. 2021;33(23):e2101238. [70] ANNABI N, TAMAYOL A, UQUILLAS JA, et al. 25th anniversary article: Rational design and applications of hydrogels in regenerative medicine. Adv Mater. 2014;26(1):85-123. [71] BIRD RE, LEMMEL SA, YU X, et al. Bioorthogonal Chemistry and Its Applications. Bioconjug Chem. 2021;32(12):2457-2479. [72] DEFOREST CA, ANSETH KS. Cytocompatible click-based hydrogels with dynamically tunable properties through orthogonal photoconjugation and photocleavage reactions. Nat Chem. 2011;3(12):925-931. [73] MCNITT CD, CHENG H, ULLRICH S, et al. Multiphoton activation of photo-strain-promoted azide alkyne cycloaddition “click” reagents enables in situ labeling with submicrometer resolution. J Am Chem Soc. 2017;139(40):14029-14032. [74] WANG Q, QIU W, LI M, et al. Mussel-inspired multifunctional hydrogel dressing with hemostasis, hypoglycemic, photothermal antibacterial properties on diabetic wounds. Biomater Sci. 2022;10(17):4796-4814. [75] SHI X, CHEN Z, HE Y, et al. Dual light-responsive cellulose nanofibril-based in situ hydrogel for drug-resistant bacteria infected wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;297:120042. [76] FENG L, SHI W, CHEN Q, et al. Smart asymmetric hydrogel with integrated multi-functions of NIR-triggered tunable adhesion, self-deformation, and bacterial eradication. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(19):e2100784. [77] LU X, LI X, YU J, et al. Nanofibrous hemostatic materials: structural design, fabrication methods, and hemostatic mechanisms. Acta Biomater. 2022;154:49-62. [78] LIANG Y, ZHAO X, HU T, et al. Adhesive hemostatic conducting injectable composite hydrogels with sustained drug release and photothermal antibacterial activity to promote full-thickness skin regeneration during wound healing. Small. 2019;15(12):e1900046. [79] WANG X, WU B, ZHANG Y, et al. Polydopamine-doped supramolecular chiral hydrogels for postoperative tumor recurrence inhibition and simultaneously enhanced wound repair. Acta Biomater. 2022;153:204-215. [80] WU Z, ZHUANG H, MA B, et al. Manganese-doped calcium silicate nanowire composite hydrogels for melanoma treatment and wound healing. Research (Wash D C). 2021;2021:9780943. [81] HARDY JG, LEE JY, SCHMIDT CE. Biomimetic conducting polymer-based tissue scaffolds. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2013;24(5):847-854. [82] XI J, WU Q, XU Z, et al. Aloe-Emodin/carbon nanoparticle hybrid gels with light-induced and long-term antibacterial activity. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018; 4(12):4391-4400. [83] HUANG Y, MU L, ZHAO X, et al. Bacterial growth-induced tobramycin smart release self-healing hydrogel for pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected burn wound healing. ACS Nano. 2022;16(8):13022-13036. [84] YE JJ, LI LF, HAO RN, et al. Phase-change composite filled natural nanotubes in hydrogel promote wound healing under photothermally triggered drug release. Bioact Mater. 2022;21:284-298. [85] CHAMBRE L, ROSSELLE L, BARRAS A, et al. Photothermally active cryogel devices for effective release of antimicrobial peptides: on-demand treatment of infections. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(51):56805-56814. [86] Liang Y, Chen B, Li M, et al. Injectable antimicrobial conductive hydrogels for wound disinfection and infectious wound healing. Biomacromolecules. 2020;21(5):1841-1852. [87] QIAO B, PANG Q, YUAN P, et al. Smart wound dressing for infection monitoring and NIR-triggered antibacterial treatment. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(6):1649-1657. [88] WANG X, YU Y, YANG C, et al. Dynamically responsive scaffolds from microfluidic 3d printing for skin flap regeneration. Adv Sci. 2022;9(22):e2201155. [89] WANG X, FANG J, ZHU W, et al. Bioinspired highly anisotropic, ultrastrong and stiff, and osteoconductive mineralized wood hydrogel composites for bone repair. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31(20):2010068. [90] LUO S, WU J, JIA Z, et al. An Injectable, bifunctional hydrogel with photothermal effects for tumor therapy and bone regeneration. Macromol Biosci. 2019;19(9): e1900047. [91] YANG C, GAO X, YOUNIS MR, et al. Non-invasive monitoring of in vivo bone regeneration based on alkaline phosphatase-responsive scaffolds. Chem Eng J. 2021;408:127959. [92] CHEN B, XIANG H, PAN S, et al. Advanced theragenerative biomaterials with therapeutic and regeneration multifunctionality. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(34): 2002621. [93] GARBE C, PERIS K, HAUSCHILD A, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of melanoma. European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline -Update 2016. Eur J Cancer. 2016;63:201-217. [94] YANG Z, LI Z, ZHAO Y, et al. Lotus seedpod-inspired crosslinking-assembled hydrogels based on gold nanoclusters for synergistic osteosarcoma multimode imaging and therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(30):34377-34387. [95] SUN Y, FANG K, HU X, et al. NIR-light-controlled G-quadruplex hydrogel for synergistically enhancing photodynamic therapy via sustained delivery of metformin and catalase-like activity in breast cancer. Mater Today Bio. 2022; 16:100375. [96] PARK GK, KIM SH, KIM K, et al. Dual-channel fluorescence imaging of hydrogel degradation and tissue regeneration in the brain. Theranostics. 2019;9(15): 4255-4264. [97] CHEN Y, ZHANG J, LIU X, et al. Noninvasive in vivo 3D bioprinting. Sci Adv. 2020; 6(23):eaba7406. |
| [1] | 戴 京, 刘沙沙, 沈明敬. 负载外泌体的可注射水凝胶修复种植体周围骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 347-354. |
| [2] | 谷明西, 王常成, 田丰德, 安 宁, 郝瑞胡, 郭 林. 丝素蛋白/明胶/壳聚糖三维多孔软骨组织支架的制备及体外评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 366-372. |
| [3] | 曹 胜, 孔令伟, 徐 昆, 孙志杰. 负载丹酚酸B甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶对椎间盘退变的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 380-386. |
| [4] | 王新民, 闫文凯, 宋亚辉, 刘 飞. 自体富白细胞-血小板纤维蛋白凝胶与腘绳肌腱修复创伤性髌骨脱位[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 404-410. |
| [5] | 毕玉杰, 马笃军, 彭力平, 周紫琼, 赵 静, 朱厚均, 钟秋辉, 杨玉鑫. 中医药联合医用水凝胶治疗疾病的策略及意义[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 419-425. |
| [6] | 王欣怡, 谢宪瑞, 陈玉杰, 王晓宇, 徐小青, 沈怿弘, 莫秀梅. 软组织和硬组织再生过程中的电纺纳米纤维支架[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 426-432. |
| [7] | 高雪钰, 张文涛, 孙天泽, 张 警, 李忠海. 金属离子在骨组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 439-444. |
| [8] | 杨 杰, 胡浩磊, 李 硕, 岳 玮, 徐 弢, 李 谊. 3D打印生物墨水在组织修复与再生医学中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 445-451. |
| [9] | 陈品叡, 裴锡波, 薛轶元. 磁响应水凝胶在骨组织工程中的作用与优势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 452-457. |
| [10] | 龙智睿, 黄 雷, 肖 放, 王 琳, 王晓蓓. 骨组织工程中研究水凝胶微球的特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 472-478. |
| [11] | 孔祥宇, 王 兴, 裴志伟, 常家乐, 李斯琴, 郝 廷, 何万雄, 张葆鑫, 贾燕飞. 生物支架材料及打印技术修复骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 479-485. |
| [12] | 范永晶, 王 姝, 金武龙. 颌骨来源骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的特点、优势与应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 100-106. |
| [13] | 孙可欣, 曾今实, 李佳, 蒋海越, 刘霞. 力学刺激提高生物3D打印软骨构建物基质的形成[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [14] | 柳晓琳, 穆新月, 马子雨, 刘树泰, 王文龙, 韩晓谦, 董志恒. 水凝胶复合载辛伐他汀蛋白微球对成骨细胞增殖分化的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [15] | 徐星星, 文超举, 孟茂花, 王勤英, 陈镜桥, 董 强. 口腔种植中的碳纳米材料[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
传统的静态水凝胶不具有各向异性因而不能满足生物医学中动态调控和模仿体内环境的要求,基于对环境变化敏感响应的智能水凝胶应运而生。与其他外部刺激相比,光响应水凝胶因其远程易操控性、高度时空精准性成为理想的智能水凝胶材料,可为患者提供个性化治疗,在组织工程领域具有广阔的应用前景[8]。
光的波长在确定光响应水凝胶的组织工程应用中具有至关重要的作用[9]。紫外光、可见光和红外光组织穿透力差,且可见光和红外光分别被血红蛋白和水吸收[10],紫外光辐射被DNA和蛋白质吸收[11],从而引起辐射相关损伤或改变治疗药物的生物活性。与其他波长的辐射相比,位于生物组织光学窗口的近红外光(Near Infrared)相对具有更好的组织透明度,对人体危害更小,从而更适用于体内治疗[12-13]。目前,近红外光作为一种光生物调节疗法通过低强度的激光照射相应组织产生非热效应,缓解疼痛,消除水肿,减轻炎症,促进伤口愈合,使深层组织修复再生,已经被广泛应用于神经外科、心外科、皮肤科、风湿科和口腔科等临床领域,以促进皮肤、牙龈和神经等组织再生,监测血氧饱和度,进行脑组织功能分析,治疗精神障碍和风湿关节病等疾病[11]。
近红外光响应水凝胶通过近红外光响应基团将近红外光转换成物理或化学信号,改变水凝胶物理结构或化学性质,继而调控细胞黏附、迁移和分化等生物学行为[14]。近红外光响应水凝胶不仅兼具常规水凝胶的优良性能,作为生物支架调控细胞及组织重建,不仅可以作为生物支架调控细胞及组织重建,而且通过光热效应或递送系统等促进组织再生过程。
近年来,多种近红外光响应水凝胶已被开发用于组织工程领域基础研究,目前对于此类研究整理归纳较少,文章总结了近红外光响应水凝胶在软组织愈合及骨组织再生过程中的潜在作用、溶胶-凝胶化机制和制备策略及其组织工程应用进展,并展望了近红外光响应水凝胶材料未来可能的发展前景和研究方向。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2022年10月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2006年5月至2022年10月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网和PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“near infrared responsive hydrogels,近红外光 responsive hydrogels,tissue engineering,bone defect,bone repair,bone regeneration,wound healing,wound dressing,angiogenesis”,中文检索词为“近红外光响应水凝胶、组织工程、骨缺损、骨修复、骨再生、伤口愈合、伤口敷料、血管生成”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 图书、期刊、研究原著和综述。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed数据库的检索策略为例,见图1。

1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①有关近红外光响应水凝胶的性质、合成等方面的相关文章;②与近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程领域应用相关的文章;③在发表于2006-2022年的文献中优先纳入近5年内发表的文献;④该领域中观点、论据可靠的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①重复性研究、内容质量较差的文献;②无法获取完整资料的部分文献。
1.3 文献质量评估与资料提取 初步共检索得到366篇文献,经初筛和阅读全文后最终纳入97篇文献进行综述,包括中国知网数据库中文文献1篇和PubMed数据库的英文文献96篇,见图2。

3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 目前对于近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程领域研究的整理归纳较少,该综述在总结前人实验和文章的基础上,总结了近红外光响应水凝胶通过控制感染减轻炎症、促进血管生成、促进成骨细胞分化和新骨形成等在伤口愈合及骨修复过程中发挥作用。文章还介绍了基于近红外光光热效应的热敏水凝胶和光化学反应性近红外光响应水凝胶的制备策略,阐述了近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程领域的最新研究进展,包括实现动态可调的软硬组织再生修复、成功地在细胞和分子水平表征靶组织中的改变并实现可视化成像等功能,并展望了近红外光响应水凝胶材料未来可能的发展前景和研究方向。
3.3 综述的局限性 目前对于近红外光响应水凝胶的研究主要集中在基于近红外光光热效应的温敏水凝胶,光化学反应性近红外光响应水凝胶的相关报道较少,并且近红外光响应水凝胶应用于骨组织工程的相关研究数据还较少,更多的作用机制仍待进一步的探究。虽然已有部分研究进行了一定量的动物模型实验,结果也表明近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程领域极具潜力,但这些近红外光响应水凝胶尚无可参考的临床试验数据,难以综述其在人体实际软组织及骨缺损修复环境中的作用。此外,近红外光响应水凝胶在癌症等疾病治疗中已经取得巨大进展,文章并未能详尽涵盖近红外光响应水凝胶在生物医学领域的广泛应用。
3.4 综述的重要意义 近红外光响应水凝胶作为近年来新兴起的智能水凝胶材料,不仅具有常规水凝胶的优越性能,而且在近红外光刺激下表现出独特的相态改变或可降解行为,并能可控的释放药物,近年来被逐步应用于组织工程领域。文章从潜在的生物学作用机制、近红外光响应水凝胶的分类、溶胶-凝胶化机制及其应用进展等多个角度总结了近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程的研究进展,并总结了近红外光响应水凝胶应用于各领域的优势与不足之处,为未来开展近红外光响应水凝胶材料研究提供了新思路和热点,例如可以依据不同的应用部位和治疗策略选择不同类型的近红外光响应水凝胶等。
3.5 课题组专家的建议 近红外光的能量较低,然而大多数光反应需要高能量的紫外光/可见光激发。因此利用UCNPs独特的反斯托克斯发光转化特性发射出高能量的紫外光/可见光,使得近红外光响应水凝胶兼具良好的生物安全性和更广泛的适用范围,提供了未来近红外光响应水凝胶新的研究方向和思路。此外,近红外光二区相较近红外光一区具有更良好的组织穿透性,其自身荧光背景极低,分辨率较高,故有更广阔的生物成像等应用前景,未来还应努力开发近红外光 二区触发的复合水凝胶材料以构建具有原位监测深组织再生能力的新一代组织工程支架。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
近红外光响应水凝胶:由聚合物网络和近红外光响应官能团组成,通过光敏基团将近红外光信号转化为物理或化学信号,继而调控水凝胶的理化性质。由于其能够实现远程时空控制和动态调节材料行为,成为一类新兴的生物医用材料。近红外光响应水凝胶的组织工程应用特性:近红外光响应水凝胶不仅可作为骨引导生物支架,而且具有光热效应并可实现生长因子药物递送等过程,从而实现诊断治疗一体化,拥有可视化成像、精准监测细胞分子水平变化、动态可调的组织再生修复等功能。
骨及软组织再生是一个涉及多种生物化学和生物物理信号调节复杂的生理过程,需要多种细胞、细胞外基质、生长分子的参与并相互作用。组织工程是再生医学的一个重要领域,它结合细胞、生长因子以及支持细胞附着、迁移和增殖的可降解支架来模拟骨及软组织再生过程。水凝胶是一种亲水性的三维聚合物网络,因其与天然细胞外基质相似,可以允许细胞和生物分子的附着,并具有出色的生物降解性、生物相容性,使其从体内排出而没有任何免疫或炎症反应,机械性能可调性强等特点,成为近年来发展极为迅速的高分子材料之一,已被广泛用于组织工程、药物递送及分子成像等生物医学领域。传统的静态水凝胶不具有各向异性因而不能满足生物医学中动态调控和模仿体内环境的要求。基于对环境变化敏感响应的智能水凝胶应运而生。与其他外部刺激相比,光响应水凝胶因其远程易操控性、高度时空精准性成为理想的智能水凝胶材料,可为患者提供个性化治疗,在组织工程领域具有巨大的应用前景。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||