[1] EL-RASHIDY AA, ROETHER JA, HARHAUS L, et al. Regenerating bone with bioactive glass scaffolds: A review of in vivo studies in bone defect models. Acta Biomater. 2017;62:1-28.
[2] KARALASHVILI L, KAKABADZE A, UHRYN M, et al. Bone grafts for reconstruction of bone defects (REVIEW). Georgian Med News. 2018;282: 44-49.
[3] BALDWIN P, LI DJ, AUSTON DA, et al. Autograft, Allograft, and Bone Graft Substitutes: Clinical Evidence and Indications for Use in the Setting of Orthopaedic Trauma Surgery. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33(4):203-213.
[4] HOLZAPFEL BM, RUDERT M, HUTMACHER DW.[Scaffold-based Bone Tissue Engineering]. Der Orthopade. 2017;46(8):701-710.
[5] CUNNIFFE GM, DÍAZ-PAYNO PJ, RAMEY JS, et al. Growth plate extracellular matrix-derived scaffolds for large bone defect healing. Eur Cell Mater. 2017;33:130-142.
[6] WUBNEH A, TSEKOURA EK, AYRANCI C, et al. Current state of fabrication technologies and materials for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2018;80:1-30.
[7] FENG Y, ZHU S, MEI D, et al. Application of 3D Printing Technology in Bone Tissue Engineering: A Review. Curr Drug Deliv. 2021;18(7):102-111.
[8] SHAKIBANIA S, GHAZANFARI L, RAEEZADEH-SARMAZDEH M, et al. Medical application of biomimetic 4D printing. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2021;47(4): 521-534.
[9] CLEGG JR, WAGNER AM, SHIN SR, et al. Modular Fabrication of Intelligent Material-Tissue Interfaces for Bioinspired and Biomimetic Devices. Prog Mater Sci. 2019;106:100589.
[10] GHILAN A, CHIRIAC AP, NITA LE, et al.Trends in 3D Printing Processes for Biomedical Field:Opportunities and Challenges. J Polym Environ. 2020; 28(5):1345-1367.
[11] LI BL, LIU L, ZHAO WB, et al. Bottleneck and development trend of bone xenograft for the treatment of bone defect. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2015; 28(12):1166-1170.
[12] KIM JK, YOON JO, BAEK H. Corticocancellous bone graft vs cancellous bone graft for the management of unstable scaphoid nonunion. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2018;104(1):115-120.
[13] 殷渠东,顾三军,芮永军,等.松质骨包裹植骨技术治疗长骨节段性骨缺损[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(9):775-781.
[14] SHARIFI M, KHERADMANDI R, SALEHI M, et al. Criteria, Challenges, and Opportunities for Acellularized Allogeneic/Xenogeneic Bone Grafts in Bone Repairing. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022;8(8):3199-3219.
[15] 胡小晓,叶剑平,蒋志勇,等.微创方法结合自体外周血干细胞及同种异体冻干骨载体治疗四肢骨干术后骨不愈合[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(5):536-537.
[16] 李忠杰,李绍波.磷酸钙人工骨修复骨缺损的研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2021,18(4): 87-91.
[17] 贾乐,葛建华.Masquelet技术修复骨缺损应用及研究进展[J].西南医科大学学报,2020,43(4):421-424.
[18] KLEIN C, MONET M, BARBIER V, et al. The Masquelet technique: Current concepts, animal models, and perspectives. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020; 14(9):1349-1359.
[19] ALFORD AI, NICOLAOU D, HAKE M, et al. Masquelet’s induced membrane technique: Review of current concepts and future directions. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(4):707-718.
[20] 王有为.Masquelet技术与骨移植治疗感染性骨缺损的临床效果分析[J].中外医学研究,2022,20(11):151-154.
[21] 黄旋平,谢庆条,江献芳,等.慢病毒载体介导的基因治疗在骨缺损修复中的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(14):1284-1287.
[22] 刘亚军,张先启,官建中.骨折愈合的基因治疗进展[J].医学综述,2015, 21(10):1796-1799.
[23] GUAN J, ZHANG J, ZHU Z, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 2gene transduction enhances the osteogenic potential of human urine-derived stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6(1):5.
[24] BAKHSHANDEH B, ZARRINTAJ P, OFTADEH MO, et al. Tissue engineering; strategies, tissues, and biomaterials. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2017;33(2): 144-172.
[25] 周思佳,姜文学,尤佳.骨缺损修复材料:现状与需求和未来[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2018,22(14):2251-2258.
[26] ATLAS Y, GORIN C, NOVAIS A, et al. Microvascular maturation by mesenchymal stem cells in vitro improves blood perfusion in implanted tissue constructs. Biomaterials. 2021;268:120594.
[27] NULTY J, FREEMAN FE, BROWE DC, et al. 3D bioprinting of prevascularised implants for the repair of critically-sized bone defects. Acta Biomater. 2021; 126:154-169.
[28] FILIPOWSKA J, TOMASZEWSKI KA, NIEDŹWIEDZKI Ł, et al. The role of vasculature in bone development, regeneration and proper systemic functioning. Angiogenesis. 2017;20(3): 291-302.
[29] 黄孟全,樊简,马子扬,等.预血管化多孔β-磷酸三钙组织工程骨的构建及其生物学效应评价[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(5):625-632.
[30] GAO Q, ZHU X, XIANG J, et al. [Strategies to choose scaffold materials for tissue engineering]. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2016;32(2): 172-184.
[31] FU M, WANG F, LIN G. Design and research of bone repair scaffold based on two-way fluid-structure interaction. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021;204:106055.
[32] CHEN FM, LIU XH. Advancing biomaterials of human origin for tissue engineering. Prog Polym Sci. 2016;53:86-168.
[33] CHEN G, LV Y, DONG C, et al. Effect of internal structure of collagen/hydroxyapatite scaffold on the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;10(2):99-108.
[34] ZHOU YY, YAO HC, WANG JS, et al. Greener synthesis of electrospun collagen/hydroxyapatite composite fibers with an excellent microstructure for bone tissue engineering. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:3203-3215.
[35] 赵少华,菅炎鹏, 王一公,等.具有抗炎作用的载双氯芬酸钠明胶多孔支架促进体内软骨再生研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(1):91-100.
[36] 常思佳,杨柳,李冉.明胶-羟基磷灰石-磷酸三钙支架对hDPSCs的成骨刺激作用[J].上海口腔医学,2020,29(5):492-498.
[37] ZANG SQ, ZHU L, LUO KF, et al. Chitosan composite scaffold combined with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for bone regeneration: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Oncotarget. 2017;8(67):110890.
[38] 崔升,袁美玉,付俊杰,等.抗菌用壳聚糖及其金属粒子复合材料研究进展[J].精细化工,2021,38(9):1757-1764+1778.
[39] 李扬,刘怡卓,沈超,等.生物玻璃/壳聚糖三维多孔支架的抗感染性能和生物相容性研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2020,17(2):49-54.
[40] YANG Y, CHU LY, YANG SB, et al. Dual-functional 3D-printed composite scaffold for inhibiting bacterial infection and promoting bone regeneration in infected bone defect models. Acta Biomater. 2018;79:265-275.
[41] 陈亮.丝素蛋白支架在骨组织工程中的应用进展[J].中华骨科杂志, 2016,14(36): 932-937.
[42] 贾明鲲,闫景龙.生物可降解丝素蛋白在骨科中的应用与进展[J].北京生物医学工程,2021,40(6):629-634.
[43] ZHANG HT, CHENG JQ, AO Q. Preparation of Alginate-Based Biomaterials and Their Applications in Biomedicine. Mar Drugs. 2021;19(5):264-264.
[44] 张汉波,张睿凌,王汉虎,等.藻酸盐水凝胶的研究进展[J].药学与临床研究,2022,30(4):347-351+358.
[45] 练胜.藻酸盐凝胶细胞微球与双相磷酸钙陶瓷复合修复骨缺损的研究[D].南昌:南昌大学,2021.
[46] 耿丽鑫,甘洪全,王茜,等.国产多孔钽对成骨细胞生物相容性及其相关成骨基因表达的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2014,36(11):1163-1167.
[47] 吴海啸,张超,GORYAEVA GL,等.β-TCP/α-CSH复合材料骨支架在骨缺损治疗中的应用研究进展[J].山东医药,2016,56(32):104-106.
[48] HIEP TN, KHON H, HAI ND, et al. Biocompatibility of PCL/PLGA-BCP porous scaffold for bone tissue engineering applications. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2017;28(9):864-878.
[49] MOATAZ AE, KIM KH, PARK JW, et al. Hydrolytic degradation of polylactic acid (PLA) and its composites. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2017;79:1346-1352.
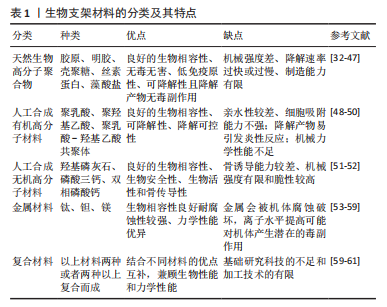
[50] 李雪雯,刘尧,李波.生物支架材料在骨组织工程中的应用[J].中国医科大学学报,2019,48(11):1024-1028.
[51] CASTRO AG, POLINI A, AZAMI Z, et al. Incorporation of PLLA micro-fillers for mechanical reinforcement of calcium-phosphate cement. J Mech Behav Biomed. 2017;71:286-294.
[52] 石永新,逄增金,羊明智,等.3D打印技术制备聚磷酸钙/淫羊藿苷骨支架诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化治疗骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(21):3309-3315.
[53] 张焕超,吕玉强,王茜,等.金属材料修复临界性骨缺损的实验研究进展[J].安徽医药,2019,23(7):1273-1276.
[54] 芮敏,郑欣,张云庆,等.3D打印多孔钛合金支架修复兔桡骨骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(18):2789-2793.
[55] 彭琳晶,干耀恺,姚怡飞.多孔钽植入物在骨缺损中的应用进展[J].材料工程,2022,50(11):1-13.
[56] 张倩,节云峰,朱璨,等.生物活性多孔钽骨修复材料促骨生长的实验研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2016,38(11):1245-1250.
[57] 党莹,李月,李瑞玉,等.骨组织工程支架材料在骨缺损修复及3D打印技术中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(14):2266-2273.
[58] 郑健茂,毛学理,凌均棨.镁基支架及其在动物骨缺损修复中的应用[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2015,42(6):720-723.
[59] 廖欣宇,王福科,王国梁.骨组织工程支架的进展与挑战[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(28):4553-4560.
[60] 刘星纲,邓旭亮,邹超,等.多孔β-磷酸三钙/胶原支架修复兔下颌牙槽骨缺损的实验研究[J].北京口腔医学,2014,22(1):1-4.
[61] 刘欢欢.基于胶原自组装/矿化协同策略制备掺杂生物活性元素的骨组织工程胶原支架[D].天津:天津医科大学,2020.
[62] LEE K, SILVA EA, MOONEY DJ. Growth factor delivery-based tissue engineering:general approaches and a review of recent developments. J R Soc Interface. 2011;8(55):153-170.
[63] 陈泽驹,冯少龙,刘桂宏,等.基于骨组织工程的骨再生策略[J].中国医药生物技术,2022,17(5):440-444.
[64] 燕朋程,王东.3D打印在组织工程骨预制及其骨缺损修复的作用探讨[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2019,6(12):188.
[65] BOSE S, VAHABZADEH S, BANDYOPADHYAY A. Bone tissue engineering using 3D printing. Mater Today. 2013;16(12):496-504.
[66] 赵静一, 禹娜娜, 邓平平.骨组织工程支架内微管孔结构的研究现状[J].机床与液压,2011,39(6):113-116.
[67] 张旭婧.3D同轴打印组织工程骨支架成型工艺与实验研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆大学,2017.
[68] REZANIA N, ASADI-EYDIVAND M, ABOLFATHI N, et al. Three-dimensional printing of polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite bone tissue engineering scaffolds mechanical properties and biological behavior. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2022;33(3):31.
[69] ENTEZARI A, ROOHANI I, LI G, et al. Architectural Design of 3D Printed Scaffolds Controls the Volume and Functionality of Newly Formed Bone. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(1):e1801353.
[70] TANG MS, ABDUL KADIR AZ, NGADIMAN NHA. Simulation analysis of different bone scaffold porous structures for fused deposition modelling fabrication process. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng. 2020;788(1):012023.
[71] MURPHY CM, HAUGH MG, O’BRIEN FJ. The effect of mean pore size on cell attachment, proliferation and migration in collagen–glycosaminoglycan scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2009;31(3):461-466.
[72] HUNG KS, CHEN MS, LAN WC, et al.Three-Dimensional Printing of a Hybrid Bioceramic and Biopolymer Porous Scaffold for Promoting Bone Regeneration Potential. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(5):1971-1971.
[73] 张伟蒙,汪杰,胡晶.3D打印骨组织支架孔隙结构对支架性能影响的研究进展[J].中国塑料,2022,36(12):155-166.
[74] MANGIRDAS M, SIMA R, LAURYNAS L, et al. 3D Microporous Scaffolds Manufactured via Combination of Fused Filament Fabrication and Direct Laser Writing Ablation. Micromachines. 2014;5(4):839-858.
[75] 吕超凡,朱莉娅,李客楼,等.3D打印在软骨组织损伤修复中的应用进展[J].南京师范大学学报(工程技术版),2017,17(1):12-17.
[76] WAN Z, ZHANG P, LIU Y, et al. Four-dimensional bioprinting:Current developments and applications in bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2020;101:26-42.
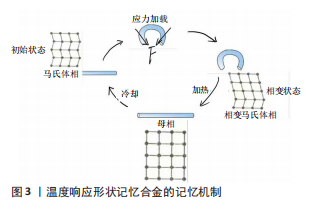
[77] ZHANG X, YANG Y, YANG Z, et al. Four-Dimensional Printing and Shape Memory Materials in Bone Tissue Engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(1):814.
[78] WAN Z, ZHANG P, LIU Y, et al. Four-dimensional bioprinting: Current developments and applications in bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2020;101:26-42.
[79] WANG C, YUE H, LIU J, et al. Advanced reconfigurable scaffolds fabricated by 4D printing for treating critical-size bone defects of irregular shapes. Biofabrication. 2020;12(4):045025.
[80] CHEN X, HAN S, WU W, et al. Harnessing 4D Printing Bioscaffolds for Advanced Orthopedics. Small. 2022;18(36):e2106824.
[81] QASIM M, CHAE DS, LEE NY. Advancements and frontiers in nano-based 3D and 4D scaffolds for bone and cartilage tissue engineering. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:4333-4351.
[82] SU M, SONG Y. Printable Smart Materials and Devices: Strategies and Applications. Chem Rev. 2022;122(5):5144-5164.
[83] HOLMAN H, KAVARANA MN, RAJAB TK. Smart materials in cardiovascular implants: Shape memory alloys and shape memory polymers. Artificial organs. 2021;45(5):454-463.
[84] WU SD, HSU SH. 4D bioprintable self-healing hydrogel with shape memory and cryopreserving properties. Biofabrication. 2021;13(4).doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/ac2789.
[85] ZHANG Y, DESAI MS, WANG T, et al. Elastin-Based Thermoresponsive Shape-Memory Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules. 2020;21(3):1149-1156.
[86] YING G, JIANG N, PARRA C, et al. Bioprinted Injectable Hierarchically Porous Gelatin Methacryloyl Hydrogel Constructs with Shape-Memory Properties. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(46):2003740.
[87] 刘若锦,王丽,刘华,等.4D打印用水凝胶在植入性医疗器械领域的研究进展[J].中国医疗器械杂志,2021,45(5):524-529.
[88] GRAHAM S, MARINA PF, BLENCOWE A. Thermoresponsive polysaccharides and their thermoreversible physical hydrogel networks. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;207:143-159.
[89] 关健,贾燕飞,张葆鑫,等.4D生物打印在组织工程的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(3):446-455.
[90] 党竞医,朱东泽,刘鑫成,等.4D打印技术的医学应用与展望[J].解放军医学杂志,2021,46(6):598-602.
[91] SENATOV FS, NIAZA KV, ZADOROZHNYY MY, et al. Mechanical properties and shape memory effect of 3D-printed PLA-based porous scaffolds. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016;57:139-148.
[92] 董学明.4D打印载药形状记忆多孔聚乳酸复合支架用于骨组织修复[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨商业大学,2020.
[93] ARONSSON C, JURY M, NAEIMIPOUR S, et al. Dynamic peptide-folding mediated biofunctionalization and modulation of hydrogels for 4D bioprinting. Biofabrication. 2020;12(3):035031. |