中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (3): 472-478.doi: 10.12307/2023.973
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
骨组织工程中研究水凝胶微球的特征
龙智睿1,黄 雷1,肖 放1,王 琳1,2,王晓蓓2
- 华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院,1组织工程与再生医学研究中心,2检验科, 湖北省武汉市 430022
-
收稿日期:2022-12-09接受日期:2023-01-13出版日期:2024-01-28发布日期:2023-07-10 -
通讯作者:王晓蓓,副主任医师,华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院检验科,湖北省武汉市 430022 王琳,教授,华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院,组织工程与再生医学研究中心,检验科,湖北省武汉市 430022 -
作者简介:龙智睿,1997年生,广西壮族自治区河池市人,壮族,华中科技大学在读硕士,主要从事骨组织工程、肿瘤治疗相关研究。
Characteristics of hydrogel microspheres in bone tissue engineering
Long Zhirui1, Huang Lei1, Xiao Fang1, Wang Lin1, 2, Wang Xiaobei2
- 1Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine Research Center, 2Department of Clinical Laboratory, Union Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2022-12-09Accepted:2023-01-13Online:2024-01-28Published:2023-07-10 -
Contact:Wang Xiaobei, Associate chief physician, Department of Clinical Laboratory, Union Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, Hubei Province, China Wang Lin, Professor, Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine Research Center, and Department of Clinical Laboratory, Union Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Long Zhirui, Master candidate, Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine Research Center, Union Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
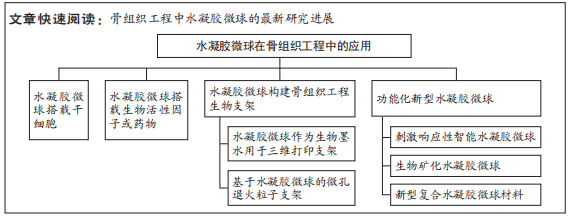
文题释义:
水凝胶微球:由交联的亲水或两亲性聚合物组成的尺寸在1-1 000 µm的球形水凝胶。骨组织工程:用各种材料制备的搭载种子细胞或生物活性因子的具有良好生物相容性、机械性能、在体内可逐步被降解吸收的仿生支架,用于受损骨组织的修复和再生。
背景:水凝胶微球由于其多孔性和可注射性等在递送细胞和生物活性因子/药物、构建组织修复支架等生物医学领域展现独特优势,具有广阔的应用前景。
目的:综述基于水凝胶微球的骨组织工程最新研究进展,讨论基于水凝胶微球的骨组织工程研究面临的关键问题和挑战。方法:应用计算机检索PubMed和中国知网数据库收录的相关文献。英文检索词为“hydrogels,microparticles,microspheres,microcarriers,bone,bone defect,bone repair,bone healing,bone tissue engineering”,中文检索词为“水凝胶,微球,微粒,骨组织工程,骨缺损,骨修复,骨再生”。检索文献时限为2002-2022年,最终纳入127篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①目前,不同的水凝胶微球材料已被开发用于骨组织工程策略并取得了较好的效果,如搭载细胞或生物活性因子/药物的水凝胶微球、作为生物支架的水凝胶微球、刺激响应性水凝胶微球、生物矿化水凝胶微球、与其他生物材料结合的水凝胶微球等。②基于水凝胶微球的骨组织工程修复策略主要通过促进干细胞的招募与成骨分化、调节损伤局部炎症微环境以及促进损伤部位血管生成等机制来调控骨修复。但目前的研究没有深入探索基于水凝胶微球的骨组织工程诱导内源性干细胞招募与分化,以及水凝胶微球的理化性质对炎症微环境的调控,且水凝胶微球的体内长期不良反应尚未探明,批量生产存在困难,因此,未来的研究需要在机制探索和技术路线上加强深入,从而为开发能够用于临床转化的水凝胶微球材料提供合理参考。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9502-2568(龙智睿)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
龙智睿, 黄 雷, 肖 放, 王 琳, 王晓蓓. 骨组织工程中研究水凝胶微球的特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 472-478.
Long Zhirui, Huang Lei, Xiao Fang, Wang Lin, Wang Xiaobei. Characteristics of hydrogel microspheres in bone tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 472-478.
2.1.1 水凝胶微球概述 传统块状水凝胶存在尺寸过大(毫米级及以上)、细胞培养周期长、需要手术植入病变或坏死区域、术后创伤大等问题,于是研究人员开发出微米级水凝胶微球(1-1 000 μm)作为优化方案。水凝胶微球不仅被广泛用于生物制剂的微创递送,而且可以作为一种颗粒状水凝胶的聚合体来形成微孔支架,以促进细胞的浸润,或者被嵌入大块水凝胶中构建多级结构材料,用于组织工程再生[12-17]。近来,水凝胶微球在递送细胞、生物活性因子/药物和构建组织修复支架等生物医学领域展现独特优势,具有广阔的应用前景。
2.1.2 水凝胶微球的优越性质
高比表面积与高孔隙率:与大块生物支架、水凝胶或生物膜相比,水凝胶微球最优越的一个特点是能为细胞黏附、增殖和维持细胞分化表型提供更大的比表面积[15]。同时,水凝胶微球可以制备为多孔结构,以及根据搭载细胞的尺寸或药物分子大小可自主设计水凝胶微球材料的孔隙,方便细胞渗透并穿过水凝胶到达目标部位或达到药物缓释的目的[18-19]。水凝胶微球高的比表面积与高孔隙率,不仅有利于细胞间的相互作用、交换营养物质和代谢废物,而且有利于水凝胶微球的功能化修饰,以及药物与生物活性因子的高效负载与递送[20-21]。
可注射性:传统的块状水凝胶不能很好应对需要注射或需要较小尺寸的情况,通常只能通过前体溶液注射,在注射部位通过原位杂交或化学交联成胶。而水凝胶微球由于其颗粒特性和小尺寸,可进行细胞和生物制剂的微创递送。水凝胶微球的可注射性已被广泛开发用于伤口愈合和生物打印,例如将修饰的透明质酸水凝胶微球注射到大鼠、小鼠心脏和大脑缺血部位,能以微创形式促进伤口愈合[22-23]。
高适配性:水凝胶微球能被设计成任何所需形状,如球形、椭圆形、菱形、圆盘形等,以适配各种不规则的损伤创面[11,24]。
此外,由随机填充的水凝胶微球经原位交联,制备由微凝胶结构单元组成的微孔退火粒子支架,不仅达到适配特定损伤创面的目的,同时这种微孔支架具有相互贯通的微孔,更利于细胞的迁移与生长。
2.1.3 水凝胶微球的制备技术 迄今为止,研究人员开发了各种水凝胶微球的制备技术,主流方法包括以下几种:
乳化法:是制备水凝胶微球最常用的方法,使用不同的乳化技术将聚合材料制备成水包油、油包水、水包油包水或油包水包油的乳浊液,随后溶剂根据其用于固化聚合材料的性质通过洗涤、离心、过滤等一系列步骤被去除,从而获得微球[25-26]。搅拌和乳化的速度和时间等,显著影响微球的粒径和分散性。
微流控法:利用互不混溶的两种液体分别以一定的流速从微流体通道的不同端口进入并相遇,通过调整两相的流速比激发两种液体层流的界面不稳定性,在表面张力和黏性力的共同作用下形成均一分散的液滴,进而通过乳滴固化或聚合得到微球[27-29]。
电喷法:是将水凝胶前体溶液通过喷嘴喷射到固体接收装置(通常是金属收集板)或导电液体接收器中制备微球的技术。水凝胶前体溶液通入喷嘴后,喷嘴连接正极,收集装置连接负极,前体溶液在喷嘴出口处受到表面张力和电场力的作用形成泰勒锥,强电场使锥面爆裂,进而使喷出的液滴形成更小的粒子[30-32]。电喷法的设备组件包括高压电源、注射泵、导电材料制成的喷嘴、溶液接收器或接地金属板收集装置。
光刻法:主要通过光掩模对水凝胶前体进行交联后固化或直接进行选择性固化来制备水凝胶微球[33]。光刻法的特点是可以通过控制模具的几何形状来控制水凝胶微球的分散性和几何形状,但这也限制了可制备的水凝胶微球结构的多元性。
不同制备方法的优缺点如表1所示。根据不同的需求,在实际制备过程中需要选择合适的制备方法、制备条件和设备,以平衡成本和效率。

2.2 水凝胶微球在骨组织工程中的应用
2.2.1 水凝胶微球用于搭载和递送干细胞 干细胞可以从不同的组织中分离,具有自我更新、调节炎症和多向分化的潜能[34-35]。用于搭载到水凝胶微球中的干细胞主要有3种来源:①骨髓间充质干细胞:通常可以从髂骨翼、胫骨近端内侧和肱骨近端的骨髓中获取,具有成纤维细胞样形态能够轻易黏附到塑料表面,在移植到稳定的骨损伤部位后显示出直接的成骨作用[36-37]。体外扩增的骨髓间充质干细胞能够向成骨、软骨或脂肪细胞系分化,但其向成骨细胞系分化的潜能与后两者相比要大得多[38]。②脂肪来源的间充质干细胞:可以从内脏脂肪、皮下脂肪等组织中获取,能够通过抑制激活的同种异体淋巴细胞的增殖来发挥免疫抑制作用,因此可能在急性移植物抗宿主病中具有保护作用[39]。由于能分泌抑制软骨细胞增殖并诱导其凋亡的因子,在应用于软骨内骨修复时,要谨慎选择脂肪来源的间充质干细胞[40]。③骨膜来源的干细胞:骨膜来源的干细胞只能从骨膜中获取,经过特定刺激的诱导能够在体外和体内显示出多向分化的潜力[41]。在骨愈合早期形成的骨痂中,骨膜来源的干细胞不仅参与形成了70%左右的软骨和编织骨,还可以分化为血管内皮细胞分泌血管内皮生长因子直接促进血管形成[42-43]。
如何将细胞按适宜的数量移植到骨损伤部位并保持细胞活力,是骨组织工程领域的热点和难题。水凝胶生物材料为细胞在受损部位的黏附、增殖提供物理平台和生化环境,以促进细胞分化并发挥功能。但传统块状水凝胶由于有限的孔隙率和可注射性差,不利于细胞迁移和细胞间的物质交换。尽管块状水凝胶可以通过剪切稀化改变其可注射性,但会严重影响其搭载的细胞活力[44-45]。水凝胶微球得益于其小尺寸颗粒的特性,不仅搭载细胞效率高,同时注射行为产生的颗粒间相对运动引起的力传递被大幅削减,从而能够保持较好的细胞活力。ZHAO
等[46]使用微流控法制备了一种甲基丙烯酸酐化明胶水凝胶微球,搭载了骨髓间充质干细胞和骨形态发生蛋白2,组织学分析表明,与空白对照和单独对照相比,实验组在移植到兔的股骨缺损部位4周后显示出最多的新骨形成,表明了该微球载体的有效性以及骨髓间充质干细胞与骨形态发生蛋白2的协同作用。YANG等[47]制备了搭载骨髓间充质干细胞的甲基丙烯酸酐化明胶-富勒醇水凝胶微球,能够保护骨髓间充质干细胞免受活性氧的伤害,利于骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和向成骨细胞系分化,从而有效促进大鼠颅骨修复。
干细胞在骨组织工程中能够与各种生物材料结合以促进修复功能,如表2所示。

2.2.2 水凝胶微球搭载生物活性因子或药物 在骨修复过程中,多种生物活性因子如骨形态发生蛋白、成纤维细胞生长因子、转化生长因子β、血小板衍生因子等能够刺激成骨细胞增殖分化,诱导新骨形成和矿化[54]。药物如非类固醇抗炎药等凭借减轻疼痛和炎症的功能成为治疗骨损伤的常用药物[55-56]。传统的给药系统(如口服、局部注射、静脉注射等)由于需要高剂量多次给药和脱靶效应等存在很大的局限性。水凝胶微球由于小尺寸、高比表面积、高孔隙率、可注射等优势,能够以较好的效率封装因子/药物并进行微创注射,促进其向靶细胞或靶组织高效递送并可控释放,因此逐渐成为新型给药系统中必不可少的一部分。
PATEL等[57]制备了搭载血管内皮生长因子和骨形态发生蛋白2的明胶微球双因子系统并植入大鼠颅骨缺损处,12周时通过显微计算机断层扫描和组织学分析表明,与空白对照和单独对照相比,双因子实验组有62.5%的大鼠实现了完全愈合,血管和新骨形成最为显著。CAI等[58]制备了能够分别缓释骨形态发生蛋白2和抗菌剂盐酸小檗碱的壳聚糖微球,能够在兔股骨髁缺损早期预防感染并控制炎症,在12周内持续促进骨修复。双氯芬酸钠是一种常用的非类固醇抗炎药,HAN等[59]将甲基丙烯酸酐化明胶微球表面包裹一层多巴胺甲基丙烯酰胺-2-甲基丙烯酰氧乙基磷酸胆碱和双氯芬酸钠,制备了表面润滑的GelMA@DMA-MPC@DS,用于大鼠骨关节炎治疗,组织学结果显示在8周的疗程中,GelMA@DMA-MPC@DS由于双氯芬酸钠的持续释放和多巴胺甲基丙烯酰胺-2-甲基丙烯酰氧乙基磷酸胆碱的润滑作用,有效促进了糖胺聚糖沉积,显著减少了关节间隙狭窄和炎症水平,治疗效果最好。
此外,可以通过将搭载不同因子的水凝胶微球混用来开发具有多重功能性的混合材料,从而响应给药部位局部变化的不同微环境来实现选择性给药[60]。水凝胶微球也可以与块状水凝胶基质结合来开发复合材料以实现更强大的缓释效果,这种复合材料能够同时结合单独水凝胶微球和传统块状水凝胶的优点。在复合材料中,不同的因子也可以同时装载到水凝胶微球和水凝胶基质中做到相互独立的释放。搭载于微球中的因子通常由于扩散距离和比表面积有限的原因过早释放,而复合材料中的基质部分能在微球周围形成一道物理屏障从而达到缓释效果[61]。复合材料的另一个优势在于:可以将因子搭载在微球中,将细胞搭载在基质中,以实现材料更高级的功能化。一个成功的例子是利用水凝胶微球复合材料同时搭载生长因子和干细胞,其中微球里搭载的生长因子成功诱导了基质中大量干细胞的分化[62]。
多种因素都能够影响水凝胶微球搭载和缓释因子的效率,在设计目标微球时需要进行权衡。水凝胶微球的尺寸直接影响其能搭载的因子总量,大尺寸的微球得益于其内部更大的分散距离和更小的比表面积,能做到更为持久的缓释[63]。在更微观的尺度上,水凝胶微球的网格尺寸也影响分子的扩散,网格尺寸越小的微球其缓释效果越好[64]。通过在水凝胶微球的制备过程中增加前体物质的浓度或交联密度可以得到网格尺寸更小的微球。此外,因子与水凝胶微球之间的作用力也会影响释放,这种作用力主要包括共价作用力、静电力和疏水结合力[65]。
2.2.3 水凝胶微球用于骨组织工程生物支架的构建
(1)水凝胶微球作为生物墨水用于三维打印骨组织工程生物支架:基于生物墨水的三维打印技术已经被用于构建骨组织工程生物支架。其中,挤压法由于其简便、灵活、精准和有利于细胞存活的优点成为了众多三维打印技术中最受青睐的方法[66-67]。水凝胶微球在堵塞状态紧密堆积时会表现出固体的性质,而施加外力后会表现出流体性质,这种特性使得水凝胶微球能够用于挤压法生物打印[67]。此外,基于水凝胶微球的生物墨水优势在于,它允许在不进行额外修饰或添加交联剂的条件下打印,这有利于最大程度地维持细胞活力和分化潜能,并且能根据目标部位的空间格局进行个性化打印,且在打印后迅速呈现良好的机械性能[68-69]。
研究人员可以针对不同的细胞和生物活性因子来对生物墨水的局部微环境进行个性化的设计。HIGHLEY等[70]分别利用降冰片烯修饰的透明质酸、聚乙二醇(乙二醇)二丙烯酸酯和琼脂糖制备了微球,通过流变学和光学表征测试了它们通过挤压打印后能够迅速稳定成胶,且在以各种形式搭载成纤维细胞后,降冰片烯修饰的透明质酸微球能够很好地维持细胞活力。KAMPERMAN等[71]利用聚乙二醇微球与可挤压的块状水凝胶前体结合,设计出一种在宏观和微观上具备不同结构特点的复合生物墨水平台,该平台具有优越的多模块化属性,间充质干细胞被搭载到聚乙二醇微球中,其周围充斥着搭载内皮细胞的块状纤维蛋白水凝胶,具有强大的促血管生成功能。此外,LEVATO等[72]的研究表明,以甲基丙烯酸酐化明胶-结冷胶生物墨水为载体,通过打印载有间充质干细胞的聚乳酸微球来制造三维骨组织模型是可行的,因为它能够促进间充质干细胞分泌骨钙素,从而支持骨基质的钙化沉积。
(2)基于水凝胶微球的微孔退火粒子的骨组织工程生物支架:微孔退火粒子支架是近年来较为热门的一种典型水凝胶微球支架,它由随机填充的水凝胶微球和相互交联的空间网络组成,不仅能适配特定损伤创面,并在高度含水的环境中或是机械力的作用下保持稳定性,同时这种具有相互贯通的微孔结构,有利于细胞在支架内的迁移与生长[73]。针对共价键进行退火的支架具有较稳定的机械性能。实现共价交联的各种不同方法已经有大量研究使用,常用的包括:酶法、羧酸与胺的反应、光介导的自由基反应、光介导的硫醇烯反应、叠氮化合物与炔烃的点击反应、四嗪-降冰片烯反应[74-81]。在HU等[82]的研究中,通过非共价的可逆退火技术合成肝素修饰的明胶水凝胶微球支架,将其应用于大鼠2型糖尿病模型中的下颌骨缺损,该支架搭载的白细胞介素4促使巨噬细胞向抗炎的M2表型极化,从而减轻炎症,促进成骨分化和骨再生。
微孔退火粒子的机械性能受到以下4种因素的影响:微球硬度、退火技术、微球间作用力的大小以及堆积密度。退火技术可以改变微孔退火粒子的整体机械性能而不影响局部,因此微孔退火粒子支架可以分别在整体和局部层面上呈现不同的机械特性。微球硬度可以通过增加制备过程中前体物质的浓度或交联程度来改变[75,77]。由不同硬度微球组成的微孔退火粒子支架对细胞有不同的影响,较硬的微球会促进细胞扩散和增殖[75,81]。DE RUTTE等[81]制备的具有软硬梯度的聚乙二醇微球能够诱导成纤维细胞向较硬的一端迁移,从而有助于骨损伤处的血管生成。微球的堆积密度可以通过调节退火前的沉降时间以及利用抽真空或离心的方法去除液相来改变,但如果堆积密度达到一个超饱和的状态,将会使水凝胶微球变形并失去间隙,微孔退火粒子也就不再具备生物支架的结构和功能,而是表现出与块状水凝胶相似的特性[83]。此外,微球表面和微球之间的空隙为细胞提供了适宜的微观结构,因此微球的大小和形貌从根本上影响搭载细胞的活动[84-85]。TRUONG等[75]将成纤维细胞分别接种在由不同尺寸水凝胶微球组成的微孔退火粒子支架上,结果发现细胞在大尺寸支架中增殖最为活跃。
2.2.4 用于骨组织工程的功能化的新型水凝胶微球
(1)刺激响应性智能水凝胶微球:以动态地感知如温度、酸碱度、光、离子、分子、磁场等环境刺激的变化,并相应地通过改变其物理化学特性而做出反应,类似于自然界生物系统的自我调节和适应能力[86]。机械力已经被证明能够触发参与骨修复和再生过程的细胞内级联信号的活化[87-88],因此,近年来具有磁响应性的磁致伸缩微球在骨组织工程中呈现巨大的潜力,它们在磁场中发生形变,从而能够动态触发细胞内的机械力传导。此前,FERNANDES PATRíCIO等[89]利用亚铁离子/铁离子掺杂羟基磷灰石矿化的Ⅰ型胶原样肽基质制备了一种超顺磁性RCPFeHA微球,能够很好地维持成骨前体细胞的活力和分化潜力。HERMENEGILDO等[90]的研究将四氧二铁酸钴-聚偏二氟乙烯与甲基丙烯酸结冷胶水凝胶结合,获得了磁响应型支架。在此基础上,CARVALHO等[91]报道了一种基于聚左旋乳酸微球和磁性微球复合物的支架,其具备的磁致伸缩性能显著促进成骨前体细胞的增殖。虽然上述研究尚未在动物实验中成功得到效果验证,但已经为这一类磁性响应微球的进一步发展提供了借鉴和参考。
(2)生物矿化的水凝胶微球:生物矿化是一种骨组织工程微球常用的后处理技术,通过在水凝胶微球中引入各种无机矿物质实现[92-93]。这项技术的优势是能够改善水凝胶微球的机械强度,更好地模拟天然的骨质成分,从而为骨再生提供有利的自然环境。
根据天然骨组织中无机成分的种类,在骨组织工程中最常使用磷酸钙类化合物作为矿化物质引入水凝胶微球。目前,已经确定钙磷比为1.67的羟基磷灰石,即Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2,是磷酸钙矿物质中最稳定的一种,且具有骨整合和骨传导性[94-95]。特定的蛋白质和多糖与矿物质结合经常被用于模拟骨的自然生理环境。HSU等[24]制备了羟基磷灰石-重组胶原微球并将其压缩成圆盘形,在植入大鼠颅骨圆形缺损处4周后开始观察到骨组织再生,16周后微球被完全吸收,显示出良好的骨再生效果。此外,SHEN等[96]利用乳液交联法和凝聚沉淀法制备了壳聚糖微球,并在表面包裹羟基磷灰石矿化涂层,在搭载成骨前体细胞后,凝聚沉淀法微球可能由于较粗糙的表面形貌促进了细胞增殖,并且在矿化涂层存在的情况下促细胞增殖效果得到进一步加强。
磷酸三钙是一种与羟基磷灰石结构相似的矿物质,生物可吸收性更好,但其钙磷比相对较低,经过烧结或化学处理可以转化为羟基磷灰石[97]。MANKANI等[98]制备了直径在100-250 μm的羟基磷灰石-磷酸三钙复合微球,其中搭载骨髓间充质干细胞,在植入小鼠颅骨和下颌骨缺损部位6周内产生了显著的新骨形成。在这种微球中,羟基磷灰石成分促进了矿化,而磷酸三钙成分的降解为骨组织的再生提供了空间。HENRIQUES LOUREN?O等[99]利用锶能够有效抑制破骨细胞活性同时促进成骨细胞代谢的特点,将引入了锶的羟基磷灰石微球与可注射的原位交联精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸序列-海藻酸盐水凝胶基质相结合,用来治疗大鼠股骨髁缺损,结果显示与无锶组对照相比,锶的引入使材料具备更强的新骨形成能力,含锶的材料降解更快,在植入部位的残留更少、胶原沉积更多。
此外,通过调节含有羟基磷灰石和磷酸三钙的复合矿物质中二者的比例,可以制备基于双相磷酸钙的微球,具有良好的矿化性能和降解性能[100-101]。CHEN等[102]利用锶取代部分钙制备了锶-双相磷酸钙微球,在植入大鼠颅骨缺损后12周后,显微计算机断层扫描结果表示锶-双相磷酸钙组的缺损区骨体积分数最高,组织学分析也显示该实验组存在最多的骨钙素和胶原纤维,且材料几乎完全降解,充分说明了锶-双相磷酸钙微球用于骨再生的良好潜力。
(3)新型复合水凝胶微球材料:目前,已经有部分研究提出将水凝胶微球与其他新型生物材料结合的方法,如金属-有机框架、纳米粒子和纳米酶等,在各个领域提供了功能多样的有效策略,同样有希望应用于骨组织工程。
在金属-有机框架生长的各种基底中,具有丰富基团的多孔水凝胶微球可以为组装无缺陷金属-有机框架层并衍生制备中空结构复合材料提供良好的条件[103]。QIN等[104]采用原位生长金属-有机框架-海藻酸钠微球为模板,通过二茂铁化学气相沉积-热解一步法合成了一种独特的磁性核壳四氧化三铁-氧化铜-中空碳复合微球,利用正己烷冷冻置换技术进一步开发了具备高稳定性的椰壳形结构,实现了金属活性位点在无缺陷界面上的均匀分布,从而显著提高了材料的机械强度、磁性和光催化活性。这项成果为进一步开发用于骨组织工程的刺激响应性水凝胶微球复合材料提供了新思路。
最近,LI等[105]使用精氨酸、组氨酸和苯丙氨酸修饰的第5代聚酰胺胺与软骨中特异性表达的microRNA-140构成复合物来制备纳米粒子,然后将该纳米粒子包裹在单分散明胶甲基丙烯酰基水凝胶微球中,合成出“纳米-微米”复合基因水凝胶材料。第5代聚酰胺胺与miR-140具有协同作用,可促进细胞内吞miR-140,提高转染效率,同时保护其免受核酸酶切割,增强了在靶细胞中的稳定性,而水凝胶微球的包裹保证了其可注射性。在小鼠骨关节炎模型中,研究人员证明了该复合材料显著抑制病情进展的功能。作为一种新型局部基因治疗策略,这项研究成果呈现出有效治疗骨折等局限性骨损伤的潜力。
SHEN等[106]以微流控技术制造的透明质酸甲基丙烯酸酯微球为基础,通过酰胺反应接枝二氧化锰-乳酸氧化酶复合纳米酶,构建了一种能局部持续耗竭乳酸的可注射微球。体外和体内结果显示,该微球能够通过下调局部微环境的乳酸水平,抑制促炎因子表达,有效消除氧化应激和炎症反应,并促进细胞外基质合成代谢和细胞生存。这种可注射的纳米酶功能化微球为开发通过针对局部靶标以实现骨组织修复的微球复合材料提供了新的策略。
2.3 水凝胶微球用于骨组织工程的再生修复机制探讨 基于水凝胶微球的骨组织工程修复策略主要通过3种机制调控骨组织修复:①促进干细胞的招募与成骨分化;②调节损伤局部炎症微环境;③促进损伤部位血管生成。
诱导干细胞成骨分化的水凝胶微球的骨组织工程修复策略主要有两种:①递送外源性因子(如生物活性因子、药物、金属离子等)。生物活性因子(如骨形态发生蛋白、转化生长因子β等)和药物(如他汀类、双膦酸盐类等)通过影响信号通路(如转化生长因子β1/SMAD通路、Wnt/β连环蛋白通路、MAPK通路等),上调干细胞的成骨相关蛋白(如SMAD、骨桥蛋白、骨钙素等)和基因表达(如Runx、Osx、Dlx、Sox9等),以诱导其成骨分化,促进新骨形成并抑制过度骨吸收[46,107-113]。金属离子(如钙离子、镁离子、锶离子等)本身就是骨骼的主要成分,同时也可以激活相关信号通路,促进骨基质矿化,诱导成骨分化[102,114]。
②通过表面修饰将水凝胶微球本身功能化以促进内源性干细胞黏附、增殖和分化[115-117]。SUN等[115]在壳聚糖微球表面修饰了CD271抗体,CD271是骨髓间充质干细胞的特异性标志物,该微球能靶向募集CD271阳性骨髓间充质干细胞,并促进这些干细胞的黏附和增殖,显著诱导其成骨分化。
基于水凝胶微球的骨组织工程策略调节损伤局部炎症微环境主要包括两方面内容:①维持氧化还原稳态:由糖尿病、关节炎等引起的骨损伤处存在增强的炎症和氧化应激[118-119]。现有策略通过抗氧化剂(如富勒醇、白藜芦醇等)、金属离子或其他生物材料(如纳米酶等)对水凝胶微球进行功能化,以消除活性氧,上调抗炎基因表达,恢复氧化还原稳态,从而为干细胞创造利于增殖和成骨分化的微环境[47,106,120-121]。②调控免疫细胞行为与功能:巨噬细胞和中性粒细胞是参与骨愈合早期炎症反应的主要免疫细胞[122]。中性粒细胞能清除死细胞,并分泌趋化因子和细胞因子以招募巨噬细胞;巨噬细胞在骨损伤部位吞噬坏死细胞和细胞碎片,并分化为破骨细胞发挥骨吸收功能;同时,巨噬细胞可以极化成促炎的M1型和抗炎的M2型,M1型巨噬细胞通过环氧化酶2-前列腺素E2途径调控间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,M2型巨噬细胞促进胶原沉积,并通过产生抗炎因子来恢复组织稳态[122-123]。因此,目前水凝胶微球在这方面最广泛的应用是调控巨噬细胞的极化和分化[82,108,122-124]。如ZHANG等[108]利用搭载白细胞介素4的富钙结冷胶微球刺激巨噬细胞向M2型极化,通过转化生长因子β1/SMAD通路上调Sox9、Runx2等基因表达,并激活SMAD蛋白磷酸化,从而促进了骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。虽然现有研究通过调控巨噬细胞取得了较好的骨修复效果,但该过程中是否会诱导巨噬细胞向其他亚表型极化,且这些亚表型对骨修复又有何影响均尚未明确。
血管化在骨修复过程中也起到关键作用,不仅为细胞提供氧气和营养物质、代谢废物,还有利于发挥促修复作用的细胞募集到受损部位[125]。促进血管化的基于水凝胶微球的骨组织工程策略主要有2种:一是直接递送可溶性因子[57,61,126],二是基于细胞的策略[48-49,71,81]。可溶性因子主要是通过与血管相关细胞上的受体结合激活细胞内的相关信号通路,从而诱导其增殖和分化[122]。基于细胞的策略,主要是利用水凝胶微球递送干细胞和/或内皮细胞来实现的,递送内皮细胞可以直接促进血管化。递送干细胞是基于有研究报道间充质干细胞与内皮祖细胞共培养能够相互促进各自的成骨和血管化活性,因为间充质干细胞也能表达一些血管生成因子,从而刺激血管细胞迁移、增殖和分化[127]。

| [1] WEI H, CUI J, LIN K, et al. Recent advances in smart stimuli-responsive biomaterials for bone therapeutics and regeneration. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):1-19. [2] PENG Z, ZHAO T, ZHOU Y, et al. Bone tissue engineering via carbon‐based nanomaterials. Advanced Healthcare Materials. 2020;9(5):1901495. [3] WILDEMANN B, IGNATIUS A, LEUNG F, et al. Non-union bone fractures. Nature Reviews Disease Primers. 2021;7(1):1-21. [4] XUE N, DING X, HUANG R, et al. Bone Tissue Engineering in the Treatment of Bone Defects. Pharmaceuticals. 2022;15(7):879. [5] GIANNOUDIS PV, DINOPOULOS H, TSIRIDIS E. Bone substitutes: an update. Injury. 2005; 36(3):S20-S27. [6] FINKEMEIER CG. Bone-grafting and bone-graft substitutes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84(3):454-464. [7] SORDI MB, CRUZ A, FREDEL MC, et al. Three-dimensional bioactive hydrogel-based scaffolds for bone regeneration in implant dentistry. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;124:112055. [8] YIN S, CAO Y. Hydrogels for large-scale expansion of stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2021;128: 1-20. [9] ZHENG Y, WU G, CHEN L, et al. Neuro-regenerative imidazole-functionalized GelMA hydrogel loaded with hAMSC and SDF-1α promote stem cell differentiation and repair focal brain injury. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(3):627-637. [10] LUO C, HUANG M, SUN X, et al. Super-Strong, Nonswellable, and Biocompatible Hydrogels Inspired by Human Tendons. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(2):2638-2649. [11] ZHANG H, WU S, CHEN W, et al. Bone/cartilage targeted hydrogel: Strategies and applications. Bioact Mater. 2023;23:156-169. [12] ZHOU Z, WU W, FANG J, et al. Polymer-based porous microcarriers as cell delivery systems for applications in bone and cartilage tissue engineering. International Materials Reviews. 2021;66(2):77-113. [13] DASHTIMOGHADAM E, FAHIMIPOUR F, TONGAS N, et al. Microfluidic fabrication of microcarriers with sequential delivery of VEGF and BMP-2 for bone regeneration. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):1-14. [14] FISCHER A, LILIENTHAL S, VÁZQUEZ-GONZÁLEZ M, et al. Triggered release of loads from microcapsule-in-microcapsule hydrogel microcarriers: en-route to an “artificial pancreas”. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;142(9):4223-4234. [15] HUANG L, ABDALLA AM, XIAO L, et al. Biopolymer-based microcarriers for three-dimensional cell culture and engineered tissue formation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(5): 1895. [16] LAMPARELLI EP, LOVECCHIO J, CIARDULLI MC, et al. Chondrogenic commitment of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a perfused collagen hydrogel functionalized with hTGF-β1-releasing PLGA microcarrier. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(3):399. [17] ZHANG H, LIU Y, CHEN C, et al. Responsive drug-delivery microcarriers based on the silk fibroin inverse opal scaffolds for controllable drug release. Appl Mater Today. 2020; 19:100540. [18] RILEY L, SCHIRMER L, SEGURA T. Granular hydrogels: emergent properties of jammed hydrogel microparticles and their applications in tissue repair and regeneration. Curr Opin Biotechno. 2019;60:1-8. [19] CALDWELL AS, CAMPBELL GT, SHEKIRO KMT, et al. Clickable Microgel Scaffolds as Platforms for 3D Cell Encapsulation. Adv Healthc Materi. 2017;6(15):1700254. [20] KUANG R, ZHANG Z, JIN X, et al. Nanofibrous Spongy Microspheres Enhance Odontogenic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells. Adv Healthc Mate. 2015;4(13):1993-2000. [21] KANKALA RK, ZHAO J, LIU CG, et al. Highly Porous Microcarriers for Minimally Invasive In Situ Skeletal Muscle Cell Delivery. Small. 2019;15(25):1901397. [22] MEALY JE, CHUNG JJ, JEONG HH, et al. Injectable Granular Hydrogels with Multifunctional Properties for Biomedical Applications. Adv Mater. 2018;30(20):1705912. [23] NIH LR, SIDERIS E, CARMICHAEL ST, et al. Injection of Microporous Annealing Particle (MAP) Hydrogels in the Stroke Cavity Reduces Gliosis and Inflammation and Promotes NPC Migration to the Lesion. Adv Mater. 2017;29(32):1606471. [24] HSU FY, TSAI SW, LAN CW, et al. An in vivo study of a bone grafting material consisting of hydroxyapatite and reconstituted collagen. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2005;16(4):341-345. [25] YUAN Z, YUAN X, ZHAO Y, et al. Injectable GelMA Cryogel Microspheres for Modularized Cell Delivery and Potential Vascularized Bone Regeneration. Small. 2021; 17(11):2006596. [26] VILABRIL S, NADINE S, NEVES CMSS, et al. One-Step All-Aqueous Interfacial Assembly of Robust Membranes for Long-Term Encapsulation and Culture of Adherent Stem/Stromal Cells. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(10):2100266. [27] CHUNG CH, LAU CML, SIN DT, et al. Droplet-Based Microfluidic Synthesis of Hydrogel Microparticles via Click Chemistry-Based Cross-Linking for the Controlled Release of Proteins. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021;4(8):6186-6194. [28] MOREIRA A, CARNEIRO J, CAMPOS J, et al. Production of hydrogel microparticles in microfluidic devices: a review. Microfluid Nanofluidics. 2021;25(2):1-24. [29] ZHAO Z, WANG Z, LI G, et al. Injectable microfluidic hydrogel microspheres for cell and drug delivery. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31(31):2103339. [30] CHEN C, WANG Y, ZHANG D, et al. Natural polysaccharide based complex drug delivery system from microfluidic electrospray for wound healing. Appl Mater Today. 2021;23:101000. [31] LUO Z, CHE J, SUN L, et al. Microfluidic electrospray photo-crosslinkable κ-Carrageenan microparticles for wound healing. Eng Regen. 2021;2:257-262. [32] 李远晴,赵锋,马银玲,等.电喷雾技术在微粒制备中的进展[J].中国新药杂志, 2022,31(10):965-971. [33] SAHIN MA, WERNER H, UDANI S, et al. Flow lithography for structured microparticles: fundamentals, methods and applications. Lab Chip. 2022;22(21):4007-4042. [34] MAZINI L, ROCHETTE L, ADMOU B, et al. Hopes and Limits of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) and Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4):1306. [35] ARTHUR A, GRONTHOS S. Clinical Application of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells to Repair Skeletal Tissue. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9759. [36] AL-QADHI G, SOLIMAN M, ABOU-SHADY I, et al. Gingival mesenchymal stem cells as an alternative source to bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in regeneration of bone defects: in vivo study. Tissue Cell. 2020;63:101325. [37] WEICKERT MT, HECKER JS, BUCK MC, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells from MDS and AML patients show increased adipogenic potential with reduced Delta-like-1 expression. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1-12. [38] MINIERI V, SAVIOZZI S, GAMBAROTTA G, et al. Persistent DNA damage-induced premature senescence alters the functional features of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(4):734-743. [39] AL-GHADBAN S, BUNNELL BA. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells: immunomodulatory effects and therapeutic potential. Physiology. 2020;35(2):125-133. [40] LEE CSD, BURNSED OA, RAGHURAM V, et al. Adipose stem cells can secrete angiogenic factors that inhibit hyaline cartilage regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012;3(4):35. [41] JEYARAMAN M, MUTHU S, GANGADARAN P, et al. Osteogenic and Chondrogenic Potential of Periosteum-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Do They Hold the Key to the Future? Pharmaceuticals. 2021;14(11):1133. [42] HOFFMAN MD, BENOIT DS. Emulating native periosteum cell population and subsequent paracrine factor production to promote tissue engineered periosteum-mediated allograft healing. Biomaterials. 2015;52:426-440. [43] ZHANG X, XIE C, LIN AS, et al. Periosteal progenitor cell fate in segmental cortical bone graft transplantations: implications for functional tissue engineering. J Bone Miner Res. 2005;20(12):2124-2137. [44] CHEN MH, WANG LL, CHUNG JJ, et al. Methods To Assess Shear-Thinning Hydrogels for Application As Injectable Biomaterials. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2017;3(12):3146-3160. [45] BLAESER A, DUARTE CAMPOS DF, PUSTER U, et al. Controlling Shear Stress in 3D Bioprinting is a Key Factor to Balance Printing Resolution and Stem Cell Integrity. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(3):326-333. [46] ZHAO X, LIU S, YILDIRIMER L, et al. Injectable stem cell‐laden photocrosslinkable microspheres fabricated using microfluidics for rapid generation of osteogenic tissue constructs. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;26(17):2809-2819. [47] YANG J, LIANG J, ZHU Y, et al. Fullerol-hydrogel microfluidic spheres for in situ redox regulation of stem cell fate and refractory bone healing. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(12):4801-4815. [48] LIU X, LI L, GAIHRE B, et al. Scaffold-Free Spheroids with Two-Dimensional Heteronano-Layers (2DHNL) Enabling Stem Cell and Osteogenic Factor Codelivery for Bone Repair. ACS Nano. 2022;16(2):2741-2755. [49] XIE C, LIANG R, YE J, et al. High-efficient engineering of osteo-callus organoids for rapid bone regeneration within one month. Biomaterials. 2022;288:121741. [50] PROBST FA, FLIEFEL R, BURIAN E, et al. Bone regeneration of minipig mandibular defect by adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells seeded tri-calcium phosphate- poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) scaffolds. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):2062. [51] BARRIENTOS-LEZCANO FJ, REDONDO-GONZÁLEZ LM, ALBERCA-ZEBALLOS M, et al. Mandibular bone regeneration with autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and coralline hydroxyapatite: experimental study in rats. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021;59(10):1192-1199. [52] YIN J, QIU S, SHI B, et al. Controlled release of FGF-2 and BMP-2 in tissue engineered periosteum promotes bone repair in rats. Biomed Mater. 2018;13(2):025001. [53] GONZÁLEZ-GIL AB, LAMO-ESPINOSA JM, MUIÑOS-LÓPEZ E, et al. Periosteum-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells in engineered implants promote fracture healing in a critical-size defect rat model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(5):742-752. [54] TOOSI S, BEHRAVAN J. Osteogenesis and bone remodeling: A focus on growth factors and bioactive peptides. Biofactors. 2020;46(3):326-340. [55] WHITE AE, HENRY JK, DZIADOSZ D. The Effect of Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs and Selective COX-2 Inhibitors on Bone Healing. Hss J. 2021;17(2):231-234. [56] MÁRQUEZ-GRANT N, BALDINI E, JEYNES V, et al. How Do Drugs Affect the Skeleton? Implications for Forensic Anthropology. Biology (Basel). 2022;11(4):524. [57] PATEL ZS, YOUNG S, TABATA Y, et al. Dual delivery of an angiogenic and an osteogenic growth factor for bone regeneration in a critical size defect model. Bone. 2008;43(5):931-940. [58] CAI B, ZOU Q, ZUO Y, et al. Injectable Gel Constructs with Regenerative and Anti-Infective Dual Effects Based on Assembled Chitosan Microspheres. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(30):25099-25112. [59] HAN Y, YANG J, ZHAO W, et al. Biomimetic injectable hydrogel microspheres with enhanced lubrication and controllable drug release for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(10):3596-3607. [60] WANG Y, COOKE MJ, SACHEWSKY N, et al. Bioengineered sequential growth factor delivery stimulates brain tissue regeneration after stroke. J Control Release. 2013;172(1):1-11. [61] SIVAKUMARAN D, MAITLAND D, HOARE T. Injectable microgel-hydrogel composites for prolonged small-molecule drug delivery. Biomacromolecules. 2011;12(11):4112-4120. [62] ALMEIDA HV, LIU Y, CUNNIFFE GM, et al. Controlled release of transforming growth factor-β3 from cartilage-extra-cellular-matrix-derived scaffolds to promote chondrogenesis of human-joint-tissue-derived stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(10): 4400-4409. [63] YOO J, WON YY. Phenomenology of the initial burst release of drugs from PLGA microparticles. ACS Biomater SciEng 2020;6(11):6053-6062. [64] NGUYEN AH, MCKINNEY J, MILLER T, et al. Gelatin methacrylate microspheres for controlled growth factor release. Acta Biomater. 2015;13:101-110. [65] ZHAO B, LI L, LV X, et al. Progress and prospects of modified starch-based carriers in anticancer drug delivery. Journal of Control Release. 2022;349:662-678. [66] ZHANG Y, ZHANG L, YANG G, et al. Recent advances in recyclable thermosets and thermoset composites based on covalent adaptable networks. Jf Mater Sci Techno. 2021;92:75-87. [67] CHENG W, ZHANG J, LIU J, et al. Granular hydrogels for 3D bioprinting applications. View. 2020;1(3):20200060. [68] LI H, CHENG F, ORGILL DP, et al. Handheld bioprinting strategies for in situ wound dressing. Essays Biochem. 2021;65(3):533-543. [69] YING G, MANRÍQUEZ J, WU D, et al. An open-source handheld extruder loaded with pore-forming bioink for in situ wound dressing. Mater Today Bio. 2020;8:100074. [70] HIGHLEY CB, SONG KH, DALY AC, et al. Jammed Microgel Inks for 3D Printing Applications. Adv Sci. 2019;6(1):1801076. [71] KAMPERMAN T, HENKE S, VAN DEN BERG A, et al. Single Cell Microgel Based Modular Bioinks for Uncoupled Cellular Micro- and Macroenvironments. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(3):1600913. [72] LEVATO R, VISSER J, PLANELL JA, et al. Biofabrication of tissue constructs by 3D bioprinting of cell-laden microcarriers. Biofabrication. 2014;6(3):035020. [73] SUTURIN AC, KRÜGER AJ, NEIDIG K, et al. Annealing High Aspect Ratio Microgels into Macroporous 3D Scaffolds Allows for Higher Porosities and Effective Cell Migration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(24):2200989. [74] GRIFFIN DR, WEAVER WM, SCUMPIA PO, et al. Accelerated wound healing by injectable microporous gel scaffolds assembled from annealed building blocks. Nat Mater. 2015; 14(7):737-744. [75] TRUONG NF, KURT E, TAHMIZYAN N, et al. Microporous annealed particle hydrogel stiffness, void space size, and adhesion properties impact cell proliferation, cell spreading, and gene transfer. Acta Biomater. 2019;94:160-172. [76] TRUONG NF, LESHER-PÉREZ SC, KURT E, et al. Pathways Governing Polyethylenimine Polyplex Transfection in Microporous Annealed Particle Scaffolds. Bioconjug Chem. 2019;30(2):476-486. [77] XIN S, WYMAN OM, ALGE DL. Assembly of PEG Microgels into Porous Cell-Instructive 3D Scaffolds via Thiol-Ene Click Chemistry. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018; 7(11):e1800160. [78] LI F, TRUONG VX, FISCH P, et al. Cartilage tissue formation through assembly of microgels containing mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2018;77:48-62. [79] SHEIKHI A, DE RUTTE J, HAGHNIAZ R, et al. Microfluidic-enabled bottom-up hydrogels from annealable naturally-derived protein microbeads. Biomaterials. 2019;192:560-568. [80] SIDERIS E, GRIFFIN DR, DING Y, et al. Particle Hydrogels Based on Hyaluronic Acid Building Blocks. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2016;2(11):2034-2041. [81] DE RUTTE JM, KOH J, DI CARLO D. Scalable high‐throughput production of modular microgels for in situ assembly of microporous tissue scaffolds. Adv Funct Mater. 2019; 29(25):1900071. [82] HU Z, MA C, RONG X, et al. Immunomodulatory ECM-like Microspheres for Accelerated Bone Regeneration in Diabetes Mellitus. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(3):2377-2390. [83] MENUT P, SEIFFERT S, SPRAKEL J, et al. Does size matter? Elasticity of compressed suspensions of colloidal-and granular-scale microgels. Soft Matter. 2012;8(1):156-164. [84] MITRA A, VENKATACHALAPATHY S, RATNA P, et al. Cell geometry dictates TNFα-induced genome response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(20):E3882-E3891. [85] WERNER M, BLANQUER SB, HAIMI SP, et al. Surface Curvature Differentially Regulates Stem Cell Migration and Differentiation via Altered Attachment Morphology and Nuclear Deformation. Adv Sci. 2017;4(2):1600347. [86] WANG W, LI PF, XIE R, et al. Designable Micro-/Nano-Structured Smart Polymeric Materials. Adv Mater. 2022;34(46):e2107877. [87] ANGULO-URARTE A, VAN DER WAL T, HUVENEERS S. Cell-cell junctions as sensors and transducers of mechanical forces. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020;1862(9): 183316. [88] QIN L, LIU W, CAO H, et al. Molecular mechanosensors in osteocytes. Bone Res. 2020;8(1):1-24. [89] FERNANDES PATRÍCIO TM, PANSERI S, MONTESI M, et al. Superparamagnetic hybrid microspheres affecting osteoblasts behaviour. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;96: 234-247. [90] HERMENEGILDO B, RIBEIRO C, PÉREZ-ÁLVAREZ L, et al. Hydrogel-based magnetoelectric microenvironments for tissue stimulation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;181: 1041-1047. [91] CARVALHO EO, RIBEIRO C, CORREIA DM, et al. Biodegradable Hydrogels Loaded with Magnetically Responsive Microspheres as 2D and 3D Scaffolds. Nanomaterials. 2020;10(12):2421. [92] HWANG ET, LEE S, KIM JS, et al. Highly Stable and Fine-Textured Hybrid Microspheres for Entrapment of Cosmetic Active Ingredients. ACS Omega. 2020; 5(45):29577-29584. [93] HU D, REN Q, LI Z, et al. Chitosan-Based Biomimetically Mineralized Composite Materials in Human Hard Tissue Repair. Molecules. 2020;25(20):4785. [94] CHAHARMAHALI R, FATTAH-ALHOSSEINI A, BABAEI K. Surface characterization and corrosion behavior of calcium phosphate (Ca-P) base composite layer on Mg and its alloys using plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO): A review. JMA. 2021;9(1):21-40. [95] LING L, CAI S, LI Q, et al. Recent advances in hydrothermal modification of calcium phosphorus coating on magnesium alloy. JMA. 2021;10(1):62-80. [96] SHEN S, FU D, XU F, et al. The design and features of apatite-coated chitosan microspheres as injectable scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 2013; 8(2):025007. [97] BOHNER M, SANTONI BLG, DÖBELIN N. β-tricalcium phosphate for bone substitution: Synthesis and properties. Acta Biomater. 2020;113:23-41. [98] MANKANI MH, KUZNETSOV SA, WOLFE RM, et al. In vivo bone formation by human bone marrow stromal cells: reconstruction of the mouse calvarium and mandible. Stem Cells. 2006;24(9):2140-2149. [99] HENRIQUES LOURENÇO A, NEVES N, RIBEIRO-MACHADO C, et al. Injectable hybrid system for strontium local delivery promotes bone regeneration in a rat critical-sized defect model. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1-15. [100] HERRADA-MANCHÓN H, RODRÍGUEZ-GONZÁLEZ D, FERNÁNDEZ MA, et al. Effect on Rheological Properties and 3D Printability of Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Microporous Particles in Hydrocolloid-Based Hydrogels. Gels. 2022;8(1):28. [101] CHOI JB, KIM YK, BYEON SM, et al. Fabrication and characterization of biodegradable gelatin methacrylate/biphasic calcium phosphate composite hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Nanomaterials. 2021;11(3):617. [102] CHEN Y, LIU Z, JIANG T, et al. Strontium-substituted biphasic calcium phosphate microspheres promoted degradation performance and enhanced bone regeneration.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(4):895-905. [103] YANG Y, LI Z, HUANG Y, et al. Preparation and application of MOF-based hydrogels. Prog Chem. 2021;33(5):726-739. [104] QIN L, RU R, MAO J, et al. Assembly of MOFs/polymer hydrogel derived Fe3O4-CuO@hollow carbon spheres for photochemical oxidation: Freezing replacement for structural adjustment. Appl Catal B. 2020;269:118754. [105] LI B, WANG F, HU F, et al. Injectable “nano-micron” combined gene-hydrogel microspheres for local treatment of osteoarthritis. NPG Asia Mater. 2022;14(1):1-15. [106] SHEN J, CHEN A, CAI Z, et al. Exhausted local lactate accumulation via injectable nanozyme-functionalized hydrogel microsphere for inflammation relief and tissue regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;12:153-168. [107] ORTEGA-OLLER I, PADIAL-MOLINA M, GALINDO-MORENO P, et al. Bone regeneration from PLGA micro-nanoparticles. BioMed Res Int. 2015;2015:415289. [108] ZHANG J, SHI H, ZHANG N, et al. Interleukin-4-loaded hydrogel scaffold regulates macrophages polarization to promote bone mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation via TGF-β1/Smad pathway for repair of bone defect. Cell Prolif. 2020; 53(10):e12907. [109] ASLANKOOHI N, LIN S, MEQUANINT K. Bioactive fluorescent hybrid microparticles as a stand-alone osteogenic differentiation inducer. Mater Today Bio. 2022;13:100187. [110] ZHANG L, ZHANG J, LING Y, et al. Sustained release of melatonin from poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) microspheres to induce osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. J Pineal Res. 2013;54(1):24-32. [111] SHOKROLAHI F, KHODABAKHSHI K, SHOKROLLAHI P, et al. Atorvastatin loaded PLGA microspheres: Preparation, HAp coating, drug release and effect on osteogenic differentiation of ADMSCs. Int J Pharm. 2019;565:95-107. [112] DOLCI LS, PANZAVOLTA S, TORRICELLI P, et al. Modulation of Alendronate release from a calcium phosphate bone cement: An in vitro osteoblast-osteoclast co-culture study. Int J Pharm. 2019;554:245-255. [113] DOLCI LS, PANZAVOLTA S, ALBERTINI B, et al. Spray-congealed solid lipid microparticles as a new tool for the controlled release of bisphosphonates from a calcium phosphate bone cement. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018;122:6-16. [114] ZHAO Z, LI G, RUAN H, et al. Capturing Magnesium Ions via Microfluidic Hydrogel Microspheres for Promoting Cancellous Bone Regeneration. ACS Nano. 2021;15(8): 13041-13054. [115] SUN H, GUO Q, SHI C, et al. CD271 antibody-functionalized microspheres capable of selective recruitment of reparative endogenous stem cells for in situ bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2022;280:121243. [116] GAO T, ZHANG N, WANG Z, et al. Biodegradable Microcarriers of Poly(Lactide-co-Glycolide) and Nano-Hydroxyapatite Decorated with IGF-1 via Polydopamine Coating for Enhancing Cell Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation. Macromol Biosci. 2015;15(8):1070-1080. [117] ZHANG D, ZHENG H, GENG K, et al. Large fuzzy biodegradable polyester microspheres with dopamine deposition enhance cell adhesion and bone regeneration in vivo. Biomaterials. 2021;272:120783. [118] ANSARI MY, AHMAD N, HAQQI TM. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110452. [119] JIAO H, XIAO E, GRAVES DT. Diabetes and Its Effect on Bone and Fracture Healing. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2015;13(5):327-335. [120] LI L, YU M, LI Y, et al. Synergistic anti-inflammatory and osteogenic n-HA/resveratrol/chitosan composite microspheres for osteoporotic bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(5):1255-1266. [121] TAN S, WANG Y, DU Y, et al. Injectable bone cement with magnesium-containing microspheres enhances osteogenesis via anti-inflammatory immunoregulation. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(10):3411-3423. [122] ARMIENTO AR, HATT LP, SANCHEZ ROSENBERG G, et al. Functional Biomaterials for Bone Regeneration: A Lesson in Complex Biology. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(44): 1909874. [123] NIU Y, WANG Z, SHI Y, et al. Modulating macrophage activities to promote endogenous bone regeneration: Biological mechanisms and engineering approaches. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(1):244-261. [124] LI D, YANG Z, ZHAO X, et al. Osteoimmunomodulatory injectable Lithium-Heparin hydrogel with Microspheres/TGF-β1 delivery promotes M2 macrophage polarization and osteogenesis for guided bone regeneration. Chem Eng J. 2022;435:134991. [125] KANCZLER J, OREFFO R. Osteogenesis and angiogenesis: the potential for engineering bone. Eur Cell Mater. 2008;15(2):100-114. [126] ORTH M, SHENAR AK, SCHEUER C, et al. VEGF-loaded mineral-coated microparticles improve bone repair and are associated with increased expression of epo and RUNX-2 in murine non-unions. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(4):821-831. [127] LI Q, WANG Z. Influence of Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Co-culture on Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis: An In Vitro Study. Arch Med Res. 2013;44(7):504-513. |
| [1] | 戴 京, 刘沙沙, 沈明敬. 负载外泌体的可注射水凝胶修复种植体周围骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 347-354. |
| [2] | 谷明西, 王常成, 田丰德, 安 宁, 郝瑞胡, 郭 林. 丝素蛋白/明胶/壳聚糖三维多孔软骨组织支架的制备及体外评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 366-372. |
| [3] | 高雪钰, 张文涛, 孙天泽, 张 警, 李忠海. 金属离子在骨组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 439-444. |
| [4] | 陈品叡, 裴锡波, 薛轶元. 磁响应水凝胶在骨组织工程中的作用与优势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 452-457. |
| [5] | 孔祥宇, 王 兴, 裴志伟, 常家乐, 李斯琴, 郝 廷, 何万雄, 张葆鑫, 贾燕飞. 生物支架材料及打印技术修复骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 479-485. |
| [6] | 徐 静, 吕慧欣, 鲍 鑫, 张 逸, 王一涵, 周延民. 近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程领域的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 486-492. |
| [7] | 范永晶, 王 姝, 金武龙. 颌骨来源骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的特点、优势与应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 100-106. |
| [8] | 温星花, 丁焕文, 成 凯, 闫晓楠, 彭元昊, 王宇宁, 刘 康, 张挥武. 比格犬股骨大段骨缺损髓内钉固定方案设计的三维有限元建模分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1371-1376. |
| [9] | 唐昊天, 廖荣东, 田 京. 压电材料修复骨缺损的应用及设计思路[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [10] | 许 言, 李 平, 赖春花, 朱培君, 杨 烁, 徐淑兰. 血管化骨再生中压电生物材料的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1126-1132. |
| [11] | 秦宇星, 任前贵, 李子龙, 全嘉星, 沈佩锋, 孙 韬, 王浩宇. 骨微血管内皮细胞在股骨头坏死中的作用机制及前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 955-961. |
| [12] | 张 敏, 张晓明, 刘童斌. 柚皮苷在骨组织再生领域的应用潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(5): 787-792. |
| [13] | 熊 伟, 袁灵梅, 钱国文, 黄锦阳, 潘 斌, 郭 灵, 曾志奎. 临界骨缺损动物模型评估骨组织工程支架成骨效能的价值[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(35): 5714-5720. |
| [14] | 周 杰, 叶 鹏, 张天喜, 李兴屿, 李沙沙, 喻安永, 邓 江. 载神经生长因子软骨及软骨下骨双层仿生支架修复兔软骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(34): 5421-5429. |
| [15] | 刘子璇, 李 岩, 伋 琳, 夏德林. 纳米羟基磷灰石-氧化锌复合支架生物性能及对MC3T3-E1成骨细胞行为的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(34): 5441-5447. |
骨组织工程是利用生物相容性支架搭载种子细胞或生物活性因子,促进骨修复与再生,重建受损骨组织的新方法。骨组织工程支架将细胞和药物/因子高效地递送到受损部位,为骨组织的修复与再生提供机械支持和生化环境,是骨组织工程研究的关键基础。因此,设计并制备新型的生物支架是骨组织工程研究的重要方向。
水凝胶是由亲水性均质聚合物、共聚物或大分子形成的三维交联网络凝胶,在水环境中能吸水膨胀,提供类似细胞外基质的微环境,且易于搭载药物与生物活性因子,有利于干细胞的迁移、黏附、增殖和分化,是一种广泛应用于组织工程的支架材料[7-9]。然而,传统块状水凝胶材料存在明显的缺陷,如:①较大的体积;②低的比表面积;③缺乏贯通的微孔;④降解缓慢;⑤残留有毒交联剂等,导致其有限的可注射性,以及不利于搭载细胞的存活与迁移[10]。而水凝胶微球与之相比具有一些独特的优势,如:①具有更小的可控尺寸,利于微创注射的方式取代传统的外科植入;②具有更高的比表面积和孔隙率,易于表面修饰以及能够高效搭载种子细胞或生物活性因子/药物;③能被设计成任何所需形状以适配各种不规则的损伤创面[11]。
该文详细介绍了水凝胶微球的结构特点、制备方法,重点综述了基于水凝胶微球的骨组织工程最新研究进展,凸显了水凝胶微球在骨组织工程研究中的优越性以及广阔前景,同时讨论了基于水凝胶微球的骨组织工程研究面临的关键问题和挑战,为开发新型水凝胶微球用于骨组织工程研究提供参考。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者于2022年9月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 查阅2002-2022年期间水凝胶微球应用于骨组织工程研究的相关文章。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed和中国知网数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“hydrogels,microparticles,microspheres,microcarriers,bone,bone defect,bone repair,bone healing,bone tissue engineering”,中文检索词为“水凝胶,微球,微粒,骨组织工程,骨缺损,骨修复,骨再生”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 综述、基础研究和临床研究。
1.1.6 检索策略 见图1。

1.2 入选标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①水凝胶微球作为骨组织工程研究主要材料的基础研究;②相同领域内论点、论据可靠且充分的综述。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①除水凝胶微球以外的其他材料相关研究;②除骨组织工程以外的其他应用相关研究;③Meta分析;④相似文献。
1.3 数据提取 研究内容由作者独立提取并筛选,重点记录水凝胶微球在骨组织工程中的应用。
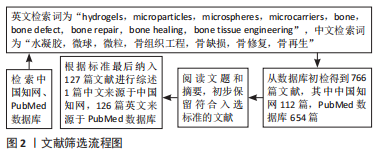
1.4 数据提取 从数据库初检得到766篇文献,其中中国知网112篇,PubMed数据库654篇。阅读文题和摘要初步筛选出部分文献,阅读全文排除与该综述相关性不大的文献,根据标准最后纳入127篇文献进行综述1篇中文来源于中国知网,126篇英文来源于PubMed数据库。文献检索流程见图2。
但目前的研究存在几个问题:①更关注于提高干细胞募集的效率或数量,但其募集和成骨分化缺乏精确的诱导,无法保证靶向招募干细胞以及发生分化的干细胞数量。因此,基于水凝胶微球的骨组织工程在提高搭载细胞存活与迁移,以及对内源干细胞的招募与分化等机制有待进一步研究。②集中于利用表面修饰、递送抗炎因子和抗炎药物等来调节炎症,而仅将水凝胶微球作为载体。因此,水凝胶微球的理化性质,如机械强度、表面亲疏水性、拓扑结构等对炎症微环境的调控,尤其是对骨损伤修复过程中免疫细胞行为与功能的调控,需要更深入的研究。③缺乏充分的体内研究探索水凝胶微球的毒性、代谢过程和潜在影响。④由于功能化水凝胶微球的大规模生产存在困难、成本高,并且基础研究中的骨缺损动物模型难以充分复刻现实中人体的骨损伤状况,缺少有效的临床前研究和临床试验结果,无法满足临床应用和工业界的需求,因此其临床转化和投入工业生产仍然存在障碍。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 该综述总结了前人关于水凝胶微球用于骨组织工程的研究进展,从搭载细胞、搭载生物活性因子、生物矿化、生物墨水、生物支架、与其他新型材料结合等方面多维度综述了水凝胶微球用于骨修复的策略和潜能,并在此基础上总结了目前基于水凝胶微球的骨组织工程策略调控骨组织再生的机制,同时讨论了未来基于水凝胶微球的骨组织工程研究面临的关键问题和挑战,以及可能的解决方法。
3.3 综述的局限性 ①该综述虽然总结了水凝胶微球的常用制备方法,但并未对其制备工艺进行全面讨论;②未对水凝胶微球的毒性、体内代谢过程和潜在影响进行全面探讨,因此无法准确评估其安全性和长期作用效果;③着重总结水凝胶微球在骨组织工程中的基础研究,未涉及其临床前研究或临床应用情况。
3.4 综述的重要意义 水凝胶微球以其独特的结构特点和优越的生物理化性质,以及随着各种生物工程技术和交叉科学的发展,新型功能性水凝胶微球在骨组织工程与再生医学研究中展现出广阔的应用前景。该文综述了水凝胶微球在骨组织工程中的最新研究进展,总结了现阶段基于水凝胶微球的骨组织工程策略调控骨再生的机制,以及未来面临的关键问题和挑战,为开发新型高效的功能性水凝胶微球用于骨组织工程研究提供了新的思路。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
水凝胶微球:由交联的亲水或两亲性聚合物组成的尺寸在1-1 000 µm的球形水凝胶。骨组织工程:用各种材料制备的搭载种子细胞或生物活性因子的具有良好生物相容性、机械性能、在体内可逐步被降解吸收的仿生支架,用于受损骨组织的修复和再生。
水凝胶微球以其独特的结构特点和优越的生物理化性质,以及随着各种生物工程技术和交叉科学的发展,新型功能性水凝胶微球在骨组织工程与再生医学研究中展现出广阔的应用前景。该文综述了水凝胶微球在骨组织工程中的最新研究进展,从搭载细胞、搭载生物活性因子、生物矿化、生物墨水、生物支架、与其他新型材料结合等方面多维度阐述了水凝胶微球用于骨修复的策略和潜能,并在此基础上探讨这些策略调控骨组织再生的机制,同时讨论了未来基于水凝胶微球的骨组织工程研究面临的关键问题和挑战,以及可能的解决方法。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||