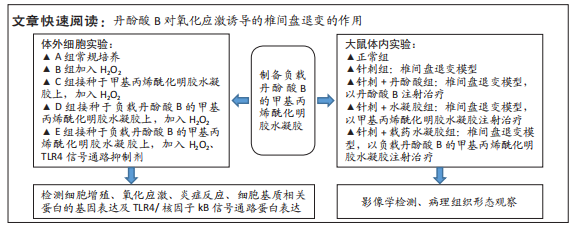
1.1 设计 体外细胞实验,体内动物实验,组间比较采用Student’s t检验或单因素方差分析(ANOVA)检验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2022年6-12月在承德医学院附属医院完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验动物 8周龄SD大鼠3只,雄性,体质量(220±15) g,用于提取原代髓核细胞;12周龄SD大鼠60只,雄性,体质量(320±20) g,用于动物体内实验。大鼠均购自河北省实验动物中心,生产许可证号:SCXK(冀)2022-001。实验已通过承德医学院附属医院伦理委员会批准(20220326)。
1.3.2 主要试剂与仪器 甲基丙烯酰化明胶购自苏州北科纳米科技有限公司;丹酚酸B购自上海诗丹德标准技术服务有限公司;光引发剂LAP购自西安瑞禧生物科技有限公司;戊巴比妥钠购自前衍化学科技(武汉)有限公司;DMEM/F-12培养基、胎牛血清购自北京缔一生物科技有限公司;丙二醛、超氧化物歧化酶检测试剂盒购自上海科艾博生物技术有限公司;白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α检测试剂盒购自上海双赢生物科技有限公司;TLR4信号通路抑制剂TAK-242购自北京百奥莱博科技有限公司;高迁移率族蛋白抗体购自武汉菲恩生物科技有限公司;TLR4、Ik Bα和核因子κB P65抗体购自济南博航生物技术有限公司;7.0-T MRI扫描仪购自上海辰光医疗科技股份有限公司。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 制备负载丹酚酸B的甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶 称量0.5 g的甲基丙烯酰化明胶,分装于包裹有锡箔纸的15 mL离心管内,置于-20 ℃冰箱备用。称量0.05 g的光引发剂LAP加入棕色瓶内,向瓶内加入20 mL的PBS,于40-50 ℃水浴加热溶解15 min,期间振荡数次,置于4 ℃冰箱备用。取出装有甲基丙烯酰化明胶的离心管,向其内加入5 mL的LAP溶液,于40-50 ℃水浴避光加热30 min,期间振荡数次,制得甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶前体溶液。趁热立即用无菌针头器进行过滤处理,将甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶前体溶液置于-20 ℃冰箱备用。
将一定量的丹酚酸B加入PBS中溶解,其中丹酚酸B浓度为1 μmol/L。在超净工作台上,将丹酚酸B溶液加入甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶前体溶液中,轻轻反复吹打均匀,其中丹酚酸B浓度为200 nmol/L;将混合溶液以波长405 nm、强度25 W/cm2的蓝光光源照射10 s成胶,即得负载丹酚酸B的甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶。扫描电子显微镜下观察水凝胶的形貌。
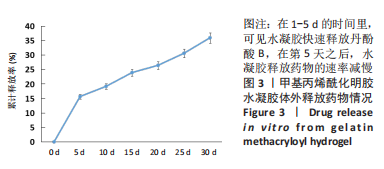
1.4.2 负载丹酚酸B的甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶的体外药物释放 将400 μL负载丹酚酸B的甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶加入24孔板内,向孔内加入2 mL的1×PBS,置于37 ℃、体积分数5%CO2培养箱内。在预定的时间下(5,10,15,20,25,30 d),分别吸取PBS至EP管内,1 000 r/min离心20 min,将上清液转移至新的EP管内备用。同时向管内补充等量的新鲜的PBS。在570 nm波长处检测上清液的吸光度值,同时根据丹酚酸B的标准曲线计算药物的释放率。每种实验重复3次。
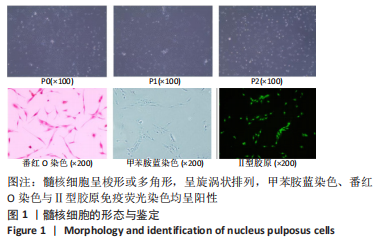
1.4.3 分离培养大鼠髓核细胞[14] 取8周龄SD大鼠3只,用于提取原代髓核细胞。腹腔注射2%戊巴比妥钠50 mg/kg麻醉大鼠,随后脱颈处死,分离腰椎,置于体积分数75%乙醇中15 min,剥皮后置于PBS中,显露椎间盘,挑出胶冻样髓核组织,置于装有PBS的培养皿中。将髓核组织转移至离心管内,1 000 r/min离心5 min,弃掉上清,加入髓核组织2倍体积的0.1%Ⅱ型胶原酶中,37 ℃水浴4 h。观察离心管内无明显絮状物时加入3 mL的DMEM/F-12培养基终止消化,1 000 r/min离心5 min,弃掉上清,以DMEM/F-12培养基(含1%青-链霉素和体积分数10%胎牛血清)重悬沉淀,将细胞转移至T25培养瓶内,置于体积分数5%CO2培养箱37 ℃恒温培养。每3 d换液一次。当细胞融合率达到85%时进行传代培养。取贴壁的细胞,分别进行甲苯胺蓝染色、番红O染色与Ⅱ型胶原免疫荧光染色,以鉴定为髓核细胞。
1.4.4 体外细胞实验
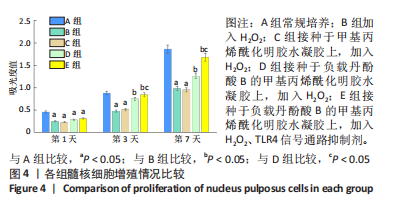
实验分组:选择第3代髓核细胞,接种于24孔板内,细胞密度为2×104/孔,分5组处理,A组置于含1%青-链霉素和体积分数10%胎牛血清的DMEM/F-12培养基(完全培养基);B组加入含100 μmol/L H2O2的完全培养基中[15];C组接种于甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶上,加入含100 μmol/L H2O2的完全培养基;D组接种于负载丹酚酸B的甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶上,加入含100 μmol/L H2O2的完全培养基;E组接种于负载丹酚酸B的甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶上,加入含100 μmol/L H2O2、10 μmol/L TLR4信号通路抑制剂TAK-242的完全培养基。孔板内水凝胶体积为400 μL,完全培养基体积为1 mL。每组设置3个平行复孔。置于体积分数5%CO2培养箱37 ℃恒温培养。
细胞增殖检测:培养1,3,7 d后,吸弃培养基,向每孔中加入10 μL CCK-8反应液,轻轻摇动混合均匀,放入恒温培养箱内孵育2 h。随后取出孔板,利用酶标仪在450 nm波长处检测吸光度值。
细胞内活性氧水平:培养5 d后,取出孔板,弃培养液,加入培养基清洗细胞,每孔加入含25 μmol/L DCFH-DA的PBS 100 μL,放入培养箱内避光孵育1 h。取出孔板,弃上清,以PBS清洗后加入适量培养基,利用酶标仪检测荧光强度值,计算实验样品的相对荧光强度。
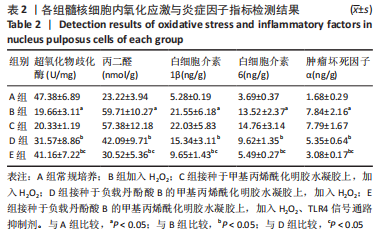
细胞内氧化应激与炎症因子指标检测:培养5 d后,取出孔板,弃掉培养基,以PBS清洗3次,每孔加入0.25%胰酶消化3 min,将消化液放入离心管内,1 000 r/min离心5 min,利用Elisa试剂盒检测超氧化物歧化酶、丙二醛、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α的含量。严格按照相关试剂盒说明书操作。
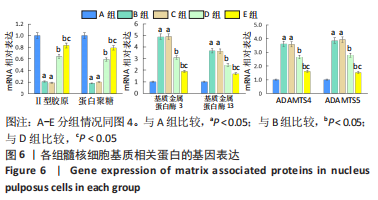
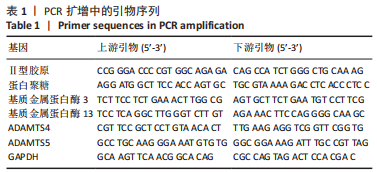
qRT-PCR检测细胞基质相关蛋白的基因表达:培养5 d后,取出孔板,加入细胞裂解液,提取总RNA,检测RNA纯度。按照反转录试剂盒说明书操作进行反转录反应,将得到的cDNA产物置于-20 ℃冰箱备用。设计引物序列(表1),配制10 μL反应体系,进行实时荧光定量PCR反应,PCR程序为:变性阶段95 ℃,30 s;变性阶段95 ℃,5 s,退火延伸阶段60 ℃,30 s,共40个循环。熔解曲线阶段:95 ℃,15 s;60 ℃,1 min;95 ℃,30 s;60 ℃,15 s。分析扩增曲线和熔解曲线,各个基因的相对表达水平以Ct值表示,得到的数据通过通用的公式2-ΔΔCt计算目的基因的相对表达量。
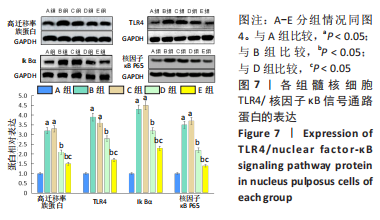
Western blot检测TLR4/核因子κB 信号通路蛋白的表达:培养5 d后,取出孔板,加入细胞裂解液,提取总蛋白,采用BCA法检测蛋白浓度。加入适量Loading buffer,并上样,利用120 V凝胶电泳在10%聚丙烯酰胺凝胶中分离蛋白。用聚偏二氟乙烯转膜,湿式转运和转膜的电压控制在100 mV,持续1 h。而后将膜密封于5%的脱脂奶粉TBST溶液中,摇床充分混摇1 h。取出牛奶TBST溶液,洗涤3次后,再向其中加入按1∶1 000稀释的一抗(高迁移率族蛋白、TLR4、Ik Bα和核因子κB P65抗体)4 ℃过夜孵育;加入二抗(稀释比为1∶5 000),室温封闭1 h。TBST洗膜3次后,加入ECL化学发光液,利用凝胶成像系统中采集图像,同时采用Image J软件对蛋白条带进行定量分析。
1.4.5 动物体内实验
实验动物分组:选取12周龄SD大鼠60只,按照随机数字表法分成5组,分别为正常组、针刺组、针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组、针刺+载药水凝胶组,每组12只。
建立椎间盘退变模型[16]:除正常组外,其余4组大鼠均建立椎间盘退变模型。腹腔注射2%戊巴比妥钠50 mg/kg麻醉大鼠,通过触诊找到Co7/8、Co8/9椎体,应用20 G针头从椎间盘正上方垂直刺入髓核中心部位并旋转360°,维持30 s,刺入深度约5 mm。造模后,随即进行对应的干预,针刺组向退变椎间盘内注射2 μL的生理盐水,针刺+丹酚酸组注射2 μL的丹酚酸B溶液(200 nmol/L),针刺+水凝胶组注射2 μL的甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶,载药水凝胶组注射2 μL负载丹酚酸B的甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶。
X射线检查:术后0,4周,腹腔注射戊巴比妥钠麻醉大鼠后,将其以仰卧位固定于检测平台,保持尾巴静止伸直,调整X射线光源对准目标节段(Co7/8、Co8/9),拍摄并获取射线照片,计算椎间盘高度指数。椎间盘高度指数越大,退变椎间盘高度恢复越好。
MRI检查:术后0周与4周,腹腔注射戊巴比妥钠麻醉大鼠后,置于检测平台,并检测目标椎间盘,T2加权7.0-T MRI扫描仪用于显示椎间盘的结构。获得目标MRI图像后,使用Radiant dicomviwer软件测量髓核面积和 T2信号强度,计算髓核组织的 MRI 指数(髓核面积×平均T2信号强度)评估髓核改变。
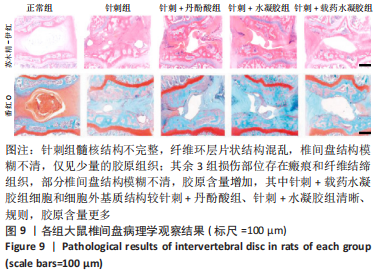
椎间盘病理观察:术后4周影像学检查结束后,过量麻醉处死大鼠,在Co7和Co8椎体中央用咬骨钳剪断,在剪骨时避免过度牵拉或挤压对椎间盘结构产生影响。浸泡于40 g/L多聚甲醛中固定7 d,随后进行、脱钙、脱水、透明、浸蜡、包埋、切片(片厚4 μm)处理,进行苏木精-伊红染色与番红O染色。采用改良的组织学评分进行组织学评价[17],该评分系统为0-15分,评分越高椎间盘退变越严重。
1.5 主要观察指标 体外细胞实验与体内动物实验结果。
1.6 统计学分析 通过统计学软件SPSS 25.0处理实验数据,数据以x±s的格式表达,组间比较采用Student’s t检验或单因素方差分析(ANOVA)检验。文章统计学方法已通过承德医学院附属医院生物统计学专家审核。