[1] GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789-1858.
[2] BELITSKAYA-LEVY I, CLARK JD, SHIH MC, et al. Treatment Preferences for Chronic Low Back Pain: Views of Veterans and Their Providers. J Pain Res. 2021;14:161-171.
[3] SAFIRI S, KOLAHI AA, CROSS M, et al. Prevalence, Deaths, and Disability-Adjusted Life Years Due to Musculoskeletal Disorders for 195 Countries and Territories 1990-2017. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73(4):702-714.
[4] KRUT Z, PELLED G, GAZIT D, et al. Stem Cells and Exosomes: New Therapies for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Cells. 2021;10(9):2241.
[5] YANG S, ZHANG F, MA J, et al. Intervertebral disc ageing and degeneration: The antiapoptotic effect of oestrogen. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;57:100978.
[6] THOMPSON T, DIAS S, POULTER D, et al. Efficacy and acceptability of pharmacolo gical and non-pharmacological interventions for non-specific chronic low back pain: a protocol for a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Syst Rev. 2020;9(1):130.
[7] HEINDEL P, TUCHMAN A, HSIEH PC, et al. Reoperation Rates After Single-level Lumbar Discectomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(8): E496-E501.
[8] DOWDELL J, ERWIN M, CHOMA T, et al. Intervertebral Disk Degeneration and Repair. Neurosurgery. 2017;80(3S):S46-S54.
[9] FILBIN MG, TIROSH I, HOVESTADT V, et al. Developmental and oncogenic programs in H3K27M gliomas dissected by single-cell RNA-seq. Science. 2018;360(6386):331-335.
[10] SKELLY DA, SQUIERS GT, MCLELLAN MA, et al. Single-Cell Transcriptional Profiling Reveals Cellular Diversity and Intercommunication in the Mouse Heart. Cell Rep. 2018;22(3):600-610.
[11] SHAH PT, STRATTON JA, STYKEL MG, et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomics and Fate Mapping of Ependymal Cells Reveals an Absence of Neural Stem Cell Function. Cell. 2018;173(4):1045-1057.e9.
[12] MOLLADAVOODI S, MCMORRAN J, GREGORY D. Mechanobiology of annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus cells in intervertebral discs. Cell Tissue Res. 2020;379(3):429-444.
[13] KHAN AN, JACOBSEN HE, KHAN J, et al. Inflammatory biomarkers of low back pain and disc degeneration: a review. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017;1410(1):68-84.
[14] MORRIS H, GONÇALVES CF, DUDEK M, et al. Tissue physiology revolving around the clock: circadian rhythms as exemplified by the intervertebral disc. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80(7):828-839.
[15] GHEZELBASH F, ESKANDARI AH, SHIRAZI-ADL A, et al. Modeling of human intervertebral disc annulus fibrosus with complex multi-fiber networks. Acta Biomater. 2021;123:208-221.
[16] KHAN AN, JACOBSEN HE, KHAN J, et al. Inflammatory biomarkers of low back pain and disc degeneration: a review. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017;1410(1):68-84.
[17] VADALÀ G, AMBROSIO L, RUSSO F, et al. Interaction between Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Intervertebral Disc Microenvironment: From Cell Therapy to Tissue Engineering. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019: 2376172.
[18] RISBUD MV, SHAPIRO IM. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(1): 44-56.
[19] PFIRRMANN CW, METZDORF A, ZANETTI M, et al. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(17):1873-1878.
[20] GRIFFITH JF, WANG YX, ANTONIO GE, et al. Modified Pfirrmann grading system for lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(24):E708-E712.
[21] WANG F, CAI F, SHI R, et al. Aging and age related stresses: a senescence mechanism of intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(3):398-408.
[22] HIYAMA A, SUYAMA K, SAKAI D, et al. Correlational analysis of chemokine and inflammatory cytokine expression in the intervertebral disc and blood in patients with lumbar disc disease. J Orthop Res. 2022;40(5):1213-1222.
[23] SONG Y, LU S, GENG W, et al. Mitochondrial quality control in intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(7):1124-1133.
[24] LI Z, CHEN X, XU D, et al. Circular RNAs in nucleus pulposus cell function and interver -tebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(6):e12704.
[25] WANG B, KE W, WANG K, et al. Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Piezo1 Activated by Matrix Stiffness Regulates Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence and Apoptosis in Human Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:8884922.
[26] WANG J, XIA D, LIN Y, et al. Oxidative stress-induced circKIF18A downregulation impairs MCM7-mediated anti-senescence in intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(3): 285-297.
[27] NASTO LA, ROBINSON AR, NGO K, et al. Mitochondrial-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a causal role in aging-related intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(7):1150-1157.
[28] STEFANAKIS M, AL-ABBASI M, HARDING I, et al. Annulus fissures are mechanically and chemi cally conducive to the ingrowth of nerves and blood vessels. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(22):1883-1891.
[29] KOLODZIEJCZYK AA, KIM JK, SVENSSON V, et al. The technology and biology of single-cell RNA sequencing. Mol Cell. 2015;58(4):610-620.
[30] LIU T, WU H, WU S, et al. Single-Cell Sequencing Technologies for Cardiac Stem Cell Studies. Stem Cells Dev. 2017;26(21):1540-1551.
[31] MURPHY TW, ZHANG Q, NALER LB, et al. Recent advances in the use of mic roflui dic technologies for single cell analysis. Analyst. 2017; 143(1):60-80.
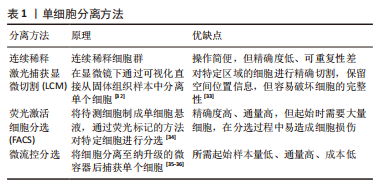
[32] AGUILAR-BRAVO B, SANCHO-BRU P. Laser capture microdissection: techniques and applications in liver diseases. Hepatol Int. 2019;13(2): 138-147.
[33] ESPINA V, WULFKUHLE JD, CALVERT VS, et al. Laser-capture microdissection. Nat Protoc. 2006;1(2):586-603.
[34] CAI Y, WANG J, ZOU K. The Progresses of Spermatogonial Stem Cells Sorting Using Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020;16(1):94-102.
[35] ZHOU WM, YAN YY, GUO QR, et al. Microfluidics applications for high-throughput single cell sequencing. Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):312.
[36] ZHANG X, LI T, LIU F, et al. Comparative Analysis of Droplet-Based Ultra-High-Throughput Single-Cell RNA-Seq Systems. Mol Cell. 2019; 73(1):130-142.e5.
[37] 孙睿男,王佐林.单细胞转录组测序技术进展及其在间充质干细胞研究中的应用[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2019,29(3):174-179.
[38] POTTER SS. Single-cell RNA sequencing for the study of development, physiology and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018;14(8):479-492.
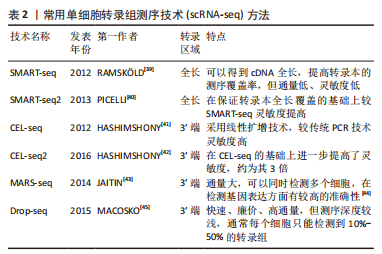
[39] RAMSKÖLD D, LUO S, WANG YC, et al. Full-length mRNA-Seq from single-cell levels of RNA and individual circulating tumor cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2012;30(8):777-782.
[40] PICELLI S, BJÖRKLUND ÅK, FARIDANI OR, et al. Smart-seq2 for sensitive full-length transcriptome profiling in single cells. Nat Methods. 2013; 10(11):1096-1098.
[41] HASHIMSHONY T, WAGNER F, SHER N, et al. CEL-Seq: single-cell RNA-Seq by multiplexed linear amplification. Cell Rep. 2012;2(3):666-673.
[42] HASHIMSHONY T, SENDEROVICH N, AVITAL G, et al. CEL-Seq2: sensitive highly-multiplexed single-cell RNA-Seq. Genome Biol. 2016;17:77.
[43] JAITIN DA, KENIGSBERG E, KEREN-SHAUL H, et al. Massively parallel single-cell RNA-seq for marker-free decomposition of tissues into cell types. Science. 2014;343(6172):776-779.
[44] SEE P, LUM J, CHEN J, et al. A Single-Cell Sequencing Guide for Immunologists. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2425.
[45] MACOSKO EZ, BASU A, SATIJA R, et al. Highly Parallel Genome-wide Expression Profiling of Individual Cells Using Nanoliter Droplets. Cell. 2015;161(5):1202-1214.
[46] HEDLUND E, DENG Q. Single-cell RNA sequencing: Technical advancements and biological applications. Mol Aspects Med. 2018;59: 36-46.
[47] 周健,张子安,赵海波,等.单细胞转录组测序技术在骨关节炎中的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(7):628-631.
[48] LUECKEN MD, THEIS FJ. Current best practices in single-cell RNA-seq analysis: a tutorial. Mol Syst Biol. 2019;15(6):e8746.
[49] STUATR T, BUTLER A, HOFFMAN P, et al. Comprehensive integration of single-cell data. Cell. 2019;177(7):1888-1902.e21.
[50] 李琳,钱四化,吕天琦,等.新一代测序技术的文库制备方法研究进展[J].应用化学,2021,38(1):11-23.
[51] SILAGI ES, SHAPIRO IM, RISBUD MV. Glycosaminoglycan synthesis in the nucleus pulposus: Dysregulation and the pathogenesis of disc degeneration. Matrix Biol. 2018;71-72:368-379.
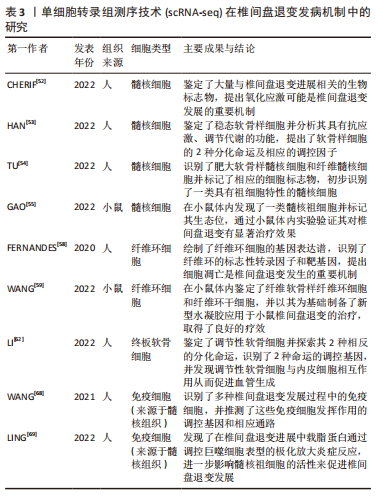
[52] CHERIF H, MANNARINO M, PACIS AS, et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Analysis of Cells from Deg enerating and Non-Degenerating Intervertebral Discs from the Same Individual Reveals New Biomarkers for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(7):3993.
[53] HAN S, ZHANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of the Nucleus Pulposus Reveals Chondrocyte Differentiation and Regulation in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:824771.
[54] TU J, LI W, YANG S, et al. Single-Cell Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Multicellular Ecosys tem of Nucleus Pulposus during Degeneration Progression. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(3):e2103631.
[55] GAO B, JIANG B, XING W, et al. Discovery and Application of Postnatal Nucleus Pulposus Progenitors Essential for Intervertebral Disc Homeostasis and Degeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(13):e2104888.
[56] TAVAKOLI J, DIWAN AD, TIPPER JL. Advanced Strategies for the Regeneration of Lumbar Disc Annulus Fibrosus. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(14):4889.
[57] CHU G, SHI C, WANG H, et al. Strategies for Annulus Fibrosus Regeneration: From Biologic al Therapies to Tissue Engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018;6:90.
[58] FERNANDES LM, KHAN NM, TROCHEZ CM, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq identifies unique transcr iptional landscapes of human nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus cells. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):15263.
[59] WANG H, WANG D, LUO B, et al. Decoding the annulus fibrosus cell atlas by scRNA-seq to develop an inducible composite hydrogel: A novel strategy for disc reconstruction. Bioact Mater. 2022;14:350-363.
[60] 张艳琳,黄国付,邹璟,等.终板软骨细胞衰老在腰椎间盘退变中的研究进展[J].医学研究杂志,2022,51(7):173-176,134.
[61] XIAO L, NI C, SHI J, et al. Analysis of Correlation Between Vertebral Endplate Change and Lumbar Disc Degeneration. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:4932-4938.
[62] LI W, ZHANG S, ZHAO Y, et al. Revealing the Key MSCs Niches and Pathogenic Genes in Influencing CEP Homeostasis: A Conjoint Analysis of Single -Cell and WGCNA. Front Immunol. 2022;13:933721.
[63] SUN Z, LIU B, LUO ZJ. The Immune Privilege of the Intervertebral Disc: Implications for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Treatment. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17(5):685-692.
[64] BRIDGEN DT, FEARING BV, JING L, et al. Regulation of human nucleus pulposus cells by peptide -coupled substrates. Acta Biomater. 2017;55: 100-108.
[65] WANG Y, CHE M, XIN J, et al. The role of IL-1β and TNF-α in intervertebral disc degenera tion. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131: 110660.
[66] LEE S, MILLECAMPS M, FOSTER DZ, et al. Long-term histological analysis of innervation and macrophage infiltration in a mouse model of intervertebral disc injury-induced low back pain. Orthop Res. 2020; 38(6):1238-1247.
[67] SILVA AJ, FERREIRA JR, CUNHA C, et al. Macrophages Down-Regulate Gene Expression of Intervertebral Disc Degenerative Markers Under a Pro-inflammatory Microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1508.
[68] WANG L, HE T, LIU J, et al. Revealing the Immune Infiltration Landscape and Identifying Diagnostic Biomarkers for Lumbar Disc Herniation. Front Immunol. 2021;12:666355.
[69] LING Z, LIU Y, WANG Z, et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Analysis Reveals Macrophage Involved in the Progression of Human Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;9:833420.
[70] DIAZ-HERNANDEZ ME, KHAN NM, TROCHEZ CM, et al. Derivation of notochordal cells from human embryonic stem cells reveals unique regulatory networks by single cell-transcriptomics. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(6):5241-5255.
|