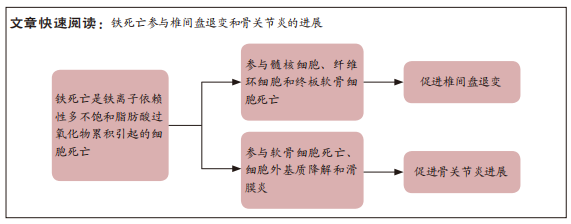
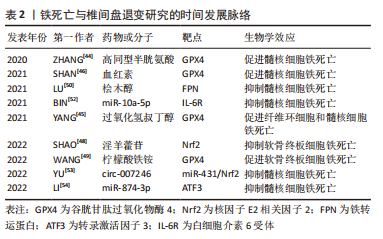
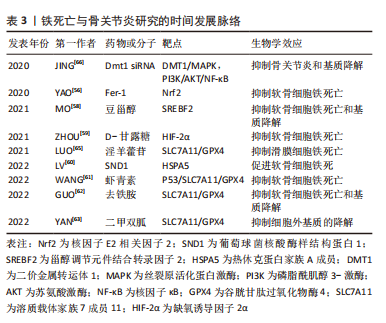
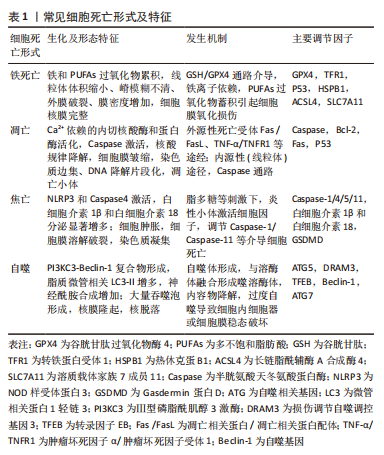
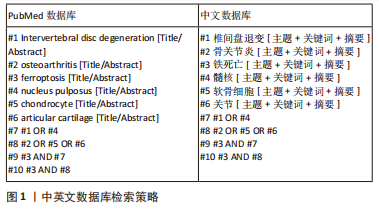
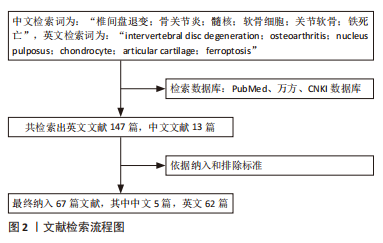
[1] CHEN HW, ZHOU JW, ZHANG GZ, et al. Emerging role and therapeutic implication of mTOR signalling in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2022:e13338.
[2] GBD 2017 DISEASE AND INJURY INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159): 1789-1858.
[3] XIN J, WANG Y, ZHENG Z, et al. Treatment of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(7):1271-1280.
[4] TAKEOKA Y, YURUBE T, NISHIDA K. Gene Therapy Approach for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: An Update. Neurospine. 2020;17(1): 3-14.
[5] LUAN L, LIANG Z. Tanshinone IIA protects murine chondrogenic ATDC5 cells from lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury by down-regulating microRNA-203a. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:628-636.
[6] LANE NE, SHIDARA K, WISE BL. Osteoarthritis year in review 2016: clinical. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(2):209-215.
[7] 金涛,刘林,朱晓燕,等.骨关节炎与线粒体异常[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(9):1452-1458.
[8] LIAO Z, KE W, LIU H, et al. Vasorin-containing small extracellular vesicles retard intervertebral disc degeneration utilizing an injectable thermoresponsive delivery system. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):420.
[9] 刘岩路,胡炜,艾克拜尔,等.抑制半乳糖凝集素3促进椎间盘软骨终板细胞凋亡诱导椎间盘退变[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(35):5599-5603.
[10] HAO X, ZHAO J, JIA L, et al. XMU-MP-1 attenuates osteoarthritis via inhibiting cartilage degradation and chondrocyte apoptosis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:998077.
[11] CHAO-YANG G, PENG C, HAI-HONG Z. Roles of NLRP3 inflammasome in intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(6): 793-801.
[12] 张皓博,赵宇楠,杨学军.细胞焦亡在椎间盘退变中的作用及治疗意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(9):1445-1451.
[13] KRITSCHIL R, SCOTT M, SOWA G, et al. Role of autophagy in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2022;237(2):1266-1284.
[14] DUAN R, XIE H, LIU ZZ. The Role of Autophagy in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:608388.
[15] MOU Y, WANG J, WU J, et al. Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: opportunities and challenges in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12(1):34.
[16] JIANG X, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(4):266-282.
[17] YAN HF, ZOU T, TUO QZ, et al. Ferroptosis: mechanisms and links with diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):49.
[18] 朱蕊,曾庆,黄国志.铁死亡与脑卒中[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(23):3734-3739.
[19] YANG J, HU S, BIAN Y, et al. Targeting Cell Death: Pyroptosis, Ferroptosis, Apoptosis and Necroptosis in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022; 9:789948.
[20] OHNISHI T, IWASAKI N, SUDO H. Causes of and Molecular Targets for the Treatment of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: A Review. Cells. 2022;11(3):394.
[21] TANG D, KANG R, BERGHE TV, et al. The molecular machinery of regulated cell death. Cell Res. 2019;29(5):347-364.
[22] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149(5):1060-1072.
[23] GAN B. Mitochondrial regulation of ferroptosis. J Cell Biol. 2021;220(9): e202105043.
[24] BOGDAN AR, MIYAZAWA M, HASHIMOTO K, et al. Regulators of Iron Homeostasis: New Players in Metabolism, Cell Death, and Disease. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016;41(3):274-286.
[25] GAO M, MONIAN P, QUADRI N, et al. Glutaminolysis and Transferrin Regulate Ferroptosis. Mol Cell. 2015;59(2):298-308.
[26] TANG D, CHEN X, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31(2):107-125.
[27] GAO M, MONIAN P, JIANG X. Metabolism and iron signaling in ferroptotic cell death. Oncotarget. 2015;6(34):35145-35146.
[28] FISCHBACHER A, VON SONNTAG C, SCHMIDT TC. Hydroxyl radical yields in the Fenton process under various pH, ligand concentrations and hydrogen peroxide/Fe(II) ratios. Chemosphere. 2017;182:738-744.
[29] YANG WS, KIM KJ, GASCHLER MM, et al. Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(34):E4966-E4975.
[30] YANG WS, SRIRAMARATNAM R, WELSCH ME, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156(1-2):317-331.
[31] FENG H, STOCKWELL BR. Unsolved mysteries: How does lipid peroxidation cause ferroptosis? PLoS Biol. 2018;16(5):e2006203.
[32] KAGAN VE, MAO G, QU F, et al. Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol. 2017;13(1):81-90.
[33] ANGELI JPF, SHAH R, PRATT DA, et al. Ferroptosis Inhibition: Mechanisms and Opportunities. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2017;38(5):489-498.
[34] PITMAN KE, ALLURI SR, KRISTIAN A, et al. Influx rate of 18F-fluoroaminosuberic acid reflects cystine/glutamate antiporter expression in tumour xenografts. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019; 46(10):2190-2198.
[35] CHEN L, LI X, LIU L, et al. Erastin sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by restraining xCT and cystathionine-γ-lyase function. Oncol Rep. 2015;33(3):1465-1474.
[36] GAO M, YI J, ZHU J, et al. Role of Mitochondria in Ferroptosis. Mol Cell. 2019;73(2):354-363.e3.
[37] XIE Y, ZHU S, SONG X, et al. The Tumor Suppressor p53 Limits Ferroptosis by Blocking DPP4 Activity. Cell Rep. 2017;20(7):1692-1704.
[38] ZHANG Y, KOPPULA P, GAN B. Regulation of H2A ubiquitination and SLC7A11 expression by BAP1 and PRC1. Cell Cycle. 2019;18(8):773-783.
[39] FAN Z, WIRTH AK, CHEN D, et al. Nrf2-Keap1 pathway promotes cell proliferation and diminishes ferroptosis. Oncogenesis. 2017;6(8):e371.
[40] BERSUKER K, HENDRICKS JM, LI Z, et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature. 2019;575(7784): 688-692.
[41] MANCIAS JD, WANG X, GYGI SP, et al. Quantitative proteomics identifies NCOA4 as the cargo receptor mediating ferritinophagy. Nature. 2014; 509(7498):105-109.
[42] BOUBRIAK OA, WATSON N, SIVAN SS, et al. Factors regulating viable cell density in the intervertebral disc: blood supply in relation to disc height. J Anat. 2013;222(3):341-348.
[43] WEI Y, LV H, SHAIKH AB, et al. Directly targeting glutathione peroxidase 4 may be more effective than disrupting glutathione on ferroptosis-based cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2020;1864(4):129539.
[44] ZHANG X, HUANG Z, XIE Z, et al. Homocysteine induces oxidative stress and ferroptosis of nucleus pulposus via enhancing methylation of GPX4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;160:552-565.
[45] YANG RZ, XU WN, ZHENG HL, et al. Involvement of oxidative stress-induced annulus fibrosus cell and nucleus pulposus cell ferroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration pathogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2021; 236(4):2725-2739.
[46] SHAN L, XU X, ZHANG J, et al. Increased hemoglobin and heme in MALDI-TOF MS analysis induce ferroptosis and promote degeneration of herniated human nucleus pulposus. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):103.
[47] 张艳琳,黄国付,邹璟,等.终板软骨细胞衰老在腰椎间盘退变中的研究进展[J].医学研究杂志,2022,51(7):173-176.
[48] SHAO Y, SUN L, YANG G, et al. Icariin protects vertebral endplate chondrocytes against apoptosis and degeneration via activating Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:937502.
[49] WANG W, JING X, DU T, et al. Iron overload promotes intervertebral disc degeneration via inducing oxidative stress and ferroptosis in endplate chondrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;190:234-246.
[50] LU S, SONG Y, LUO R, et al. Ferroportin-Dependent Iron Homeostasis Protects against Oxidative Stress-Induced Nucleus Pulposus Cell Ferroptosis and Ameliorates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration In Vivo. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6670497.
[51] ZHANG Y, HAN S, KONG M, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis identifies unique chondrocyte subsets and reveals involvement of ferroptosis in human intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(9):1324-1334.
[52] BIN S, XIN L, LIN Z, et al. Targeting miR-10a-5p/IL-6R axis for reducing IL-6-induced cartilage cell ferroptosis. Exp Mol Pathol. 2021;118:104570.
[53] YU X, XU H, LIU Q, et al. circ_0072464 Shuttled by Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Secreted Extracellular Vesicles Inhibits Nucleus Pulposus Cell Ferroptosis to Relieve Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:2948090.
[54] LI Y, PAN D, WANG X, et al. Silencing ATF3 Might Delay TBHP-Induced Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Repressing NPC Ferroptosis, Apoptosis, and ECM Degradation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022: 4235126.
[55] FINDLAY DM, ATKINS GJ. Osteoblast-chondrocyte interactions in osteoarthritis. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2014;12(1):127-134.
[56] YAO X, SUN K, YU S, et al. Chondrocyte ferroptosis contribute to the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2020;27:33-43.
[57] MIAO Y, CHEN Y, XUE F, et al. Contribution of ferroptosis and GPX4’s dual functions to osteoarthritis progression. EBioMedicine. 2022;76: 103847.
[58] MO Z, XU P, LI H. Stigmasterol alleviates interleukin-1beta-induced chondrocyte injury by down-regulatingsterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 2 to regulateferroptosis. Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):9332-9340.
[59] ZHOU X, ZHENG Y, SUN W, et al. D-mannose alleviates osteoarthritis progression by inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis in a HIF-2alpha-dependent manner. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(11):e13134.
[60] LV M, CAI Y, HOU W, et al. The RNA-binding protein SND1 promotes the degradation of GPX4 by destabilizing the HSPA5 mRNA and suppressing HSPA5 expression, promoting ferroptosis in osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Inflamm Res. 2022;71(4):461-472.
[61] WANG X, LIU Z, PENG P, et al. Astaxanthin attenuates osteoarthritis progression via inhibiting ferroptosis and regulating mitochondrial function in chondrocytes. Chem Biol Interact. 2022;366:110148.
[62] GUO Z, LIN J, SUN K, et al. Deferoxamine Alleviates Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Chondrocyte Ferroptosis and Activating the Nrf2 Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:791376.
[63] YAN J, FENG G, MA L, et al. Metformin alleviates osteoarthritis in mice by inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis and improving subchondral osteosclerosis and angiogenesis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):333.
[64] SCANZELLO CR, GOLDRING SR. The role of synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 2012;51(2):249-257.
[65] LUO H, ZHANG R. Icariin enhances cell survival in lipopolysaccharide-induced synoviocytes by suppressing ferroptosis via the Xc-/GPX4 axis. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21(1):72.
[66] JING X, LIN J, DU T, et al. Iron Overload Is Associated With Accelerated Progression of Osteoarthritis: The Role of DMT1 Mediated Iron Homeostasis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:594509.
[67] XIA L, GONG N. Identification and verification of ferroptosis-related genes in the synovial tissue of osteoarthritis using bioinformatics analysis. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:992044. |