[1] YILGOR C, SOGUNMEZ N, BOISSIERE L, et al. Global Alignment and Proportion (GAP) Score Development and Validation of a New Method of Analyzing Spinopelvic Alignment to Predict Mechanical Complications After Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(19):1661-1672.
[2] JUN HS, KIM JH, AHN JH, et al. The Effect of Lumbar Spinal Muscle on Spinal Sagittal Alignment: Evaluating Muscle Quantity and Quality. Neurosurgery. 2016;79(6):847-855.
[3] ZHANG Y, MANDELLI F, MÜNDERMANN A, et al. Association between fatty infiltration of paraspinal muscle, sagittal spinopelvic alignment and stenosis grade in patients with degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. N Am Spine Soc J. 2021;5:100054.
[4] LOWE T, BERVEN SH, SCHWAB FJ, et al. The SRS classification for Adult Spinal Deformity - Building on the King/Moe and Lenke Classification Systems. Spine. 2006;31(19):S119-S125.
[5] SCHWAB F, FARCY JP, BRIDWELL K, et al. A clinical impact classification of scoliosis in the adult. Spine. 2006;31(18):2109-2114.
[6] BESS S, SCHWAB F, LAFAGE V, et al. Classifications for Adult Spinal Deformity and Use of the Scoliosis Research Society-Schwab Adult Spinal Deformity Classification. Neurosurg Clin North Am. 2013;24(2):185-193.
[7] KALICHMAN L, CARMELI E, BEEN E. The Association between Imaging Parameters of the Paraspinal Muscles, Spinal Degeneration, and Low Back Pain. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:2562957.
[8] ASAI Y, TSUTSUI S, OKA H, et al. Sagittal spino-pelvic alignment in adults: The Wakayama Spine Study. Plos One. 2017;12(6):e0178697.
[9] HE K, HEAD J, MOUCHTOURIS N, et al. The Implications of Paraspinal Muscle Atrophy in Low Back Pain, Thoracolumbar Pathology, and Clinical Outcomes After Spine Surgery: A Review of the Literature. Global Spine J. 2020;10(5):657-666.
[10] CHO Y. Evaluation of Global Sagittal Balance in Koreans Adults. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2017;60(5):560-566.
[11] MCDOWELL MM, TEMPEL ZJ, GANDHOKE GS, et al. Evolution of Sagittal Imbalance Following Corrective Surgery for Sagittal Plane Deformity. Neurosurgery. 2017;81(1):129-134.
[12] 丁浚哲, 鲁世保, 孔超, 等. 退变性腰椎侧凸椎旁肌群不对称退变临床意义[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2019,39(18):1133-1141.
[13] XU Z, RAO H, ZHANG L, et al. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Versus Hybrid Decompression and Fusion for the Treatment of 3-Level Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: A Comparative Analysis of Cervical Sagittal Balance and Outcomes. World Neurosurg. 2019;132:e752-e758.
[14] JIN C, XIE N, REN Y, et al. How Does Cervical Sagittal Balance Change After Hangman Fracture Treated with Anterior or Posterior Approach Surgery? World Neurosurg. 2020;138:E767-E777.
[15] ZAIDMAN N, DE WITTE O. Cervical sagittal balance: a predictor of neck pain after anterior cervical spine surgery? Br J Neurosurg. 2020:1-5. doi: 10.1080/02688697.2020.1850643.
[16] HAN G, ZHOU S, WANG W, et al. Correlations between paraspinal extensor muscle endurance and clinical outcomes in preoperative LSS patients and clinical value of an endurance classification. J Orthop Translat. 2022;35:81-86.
[17] HIYAMA A, KATOH H, SAKAI D, et al. The correlation analysis between sagittal alignment and cross-sectional area of paraspinal muscle in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis and degenerative spondylolisthesis. Bmc Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):352.
[18] OZCAN-EKSI EE, EKSI MS, TURGUT VU, et al. Reciprocal relationship between multifidus and psoas at L4-L5 level in women with low back pain. Br J Neurosurg. 2021;35(2):220-228.
[19] PINTER ZW, SALMONS HIT, TOWNSLEY S, et al. Semispinalis Cervicis Sarcopenia is Associated With Worsening Cervical Sagittal Balance and Junctional Alignment Following Posterior Cervical Fusion for Myelopathy. Clin Spine Surg. 2022. doi: 10.1097/BSD.0000000000001366.
[20] MUELLNER M, HAFFER H, CHIAPPARELLI E, et al. Differences in lumbar paraspinal muscle morphology in patients with sagittal malalignment undergoing posterior lumbar fusion surgery. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(11):3109-3118.
[21] FORTIN M, OMIDYEGANEH M, BATTIE MC, et al. Evaluation of an automated thresholding algorithm for the quantification of paraspinal muscle composition from MRI images. Biomed Eng Online. 2017;16(1):61.
[22] SIONS JM, COYLE PC, VELASCO TO, et al. Multifidi Muscle Characteristics and Physical Function Among Older Adults With and Without Chronic Low Back Pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017;98(1):51-57.
[23] SALIMI H, OHYAMA S, TERAI H, et al. Trunk Muscle Mass Measured by Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Reflecting the Cross-Sectional Area of the Paravertebral Muscles and Back Muscle Strength: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of a Prospective Cohort Study of Elderly Population. J Clin Med. 2021;10(6):1187.
[24] HIYAMA A, KATOH H, SAKAI D, et al. Correlation analysis of sagittal alignment and skeletal muscle mass in patients with spinal degenerative disease. Sci Reports. 2018;8(1):15492.
[25] 李佩芳, 聂涌, 陈佳丽, 等. 表面肌电及其生物反馈在下腰痛中的应用进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2017,31(4):504-507.
[26] TAKAHASHI I, KIKUCHI SI, SATO K, et al. Effects of the mechanical load on forward bending motion of the trunk - Comparison between patients with motion-induced intermittent low back pain and healthy subjects. Spine. 2007;32(2):E73-E78.
[27] MAYER TG, NEBLETT R, BREDE E, et al. The Quantified Lumbar Flexion-Relaxation Phenomenon Is a Useful Measurement of Improvement in a Functional Restoration Program. Spine. 2009;34(22):2458-2465.
[28] EBENBICHLER G, HABENICHT R, ZIEGELBECKER S, et al. Age- and sex-specific effects in paravertebral surface electromyographic back extensor muscle fatigue in chronic low back pain. Geroscience. 2020;42(1):251-269.
[29] ZYZNAWSKA J, FRANKOWSKI G, WODKA-NATKANIEC E, et al. Disbalance and fatigue of the spinal extensors as one of the causes of the overload disease of the lumbar spine. Acta of Bioeng Biomech. 2019;21(3):119-125.
[30] EGUCHI Y, TOYOGUCHI T, INAGE K, et al. Analysis of skeletal muscle mass in women over 40 with degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(7):1618-1625.
[31] MASAKI M, IKEZOE T, FUKUMOTO Y, et al. Association of sagittal spinal alignment with thickness and echo intensity of lumbar back muscles in middle-aged and elderly women. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2015;61(2):197-201.
[32] 胡宗杉, 马鸿儒, 钱至恺, 等. 基于年龄和性别的中国正常成年人脊柱-骨盆矢状位形态的多中心研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2021,41(13):844-855.
[33] 马鸿儒, 朱泽章, 史本龙, 等. 退变性脊柱侧凸矫形术后力学并发症的预测:对脊柱整体形态与平衡评分的修正与验证[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(4): 193-198.
[34] YAGI M, HOSOGANE N, WATANABE K, et al. The paravertebral muscle and psoas for the maintenance of global spinal alignment in patient with degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Spine J. 2016;16(4): 451-458.
[35] BANNO T, YAMATO Y, HASEGAWA T, et al. Assessment of the Cross-Sectional Areas of the Psoas Major and Multifidus Muscles in Patients With Adult Spinal Deformity A Case-Control Study. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(7):E968-E973.
[36] WANG X, JIA R, LI J, et al. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Lumbarmultifidus Injury and Degeneration. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2021;2021:6629037.
[37] FAUR C, PATRASCU JM, HARAGUS H, et al. Correlation between multifidus fatty atrophy and lumbar disc degeneration in low back pain. Bmc Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):414.
[38] FERRERO E, SKALLI W, LAFAGE V, et al. Relationships between radiographic parameters and spinopelvic muscles in adult spinal deformity patients. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(6):1328-1339.
[39] XIA W, FU H, ZHU Z, et al. Association between back muscle degeneration and spinal-pelvic parameters in patients with degenerative spinal kyphosis. Bmc Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):454.
[40] PARK JS, PARK YS, KIM J, et al. Sarcopenia and fatty degeneration of paraspinal muscle associated with increased sagittal vertical axis in the elderly: a cross-sectional study in 71 female patients. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(6):1353-1361.
[41] WANG XJ, HUANG KK, HE JB, et al. Fatty infiltration in cervical extensor muscle: is there a relationship with cervical sagittal alignment after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion? BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):641.
[42] MOSER M, OKANO I, ALBERTINI SANCHEZ L, et al. Preoperative Association Between Quantitative Lumbar Muscle Parameters and Spinal Sagittal Alignment in Lumbar Fusion Patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2022;47(23):1675-1686.
[43] HAN G, WANG W, ZHOU S, et al. Paraspinal Muscle Degeneration as an Independent Risk for Loss of Local Alignment in Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis Patients After Corrective Surgery. Global Spine J. 2021:21925682211022284.
[44] PENNINGTON Z, COTTRILL E, AHMED AK, et al. Paraspinal muscle size as an independent risk factor for proximal junctional kyphosis in patients undergoing thoracolumbar fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2019;31(3):380-388.
[45] HIYAMA A, KATOH H, SAKAI D, et al. The correlation analysis between sagittal alignment and cross-sectional area of paraspinal muscle in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis and degenerative spondylolisthesis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):352.
[46] ENOMOTO M, UKEGAWA D, SAKAKI K, et al. Increase in Paravertebral Muscle Activity in Lumbar Kyphosis Patients by Surface Electromyography Compared With Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis Patients and Healthy Volunteers. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(6):E167-E173.
[47] KATSU M, OHBA T, EBATA S, et al. Potential Role of Paraspinal Musculature in the Maintenance of Spinopelvic Alignment in Patients With Adult Spinal Deformities. Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33(2):E76-E80.
[48] WANG W, SUN Z, LI W, et al. Relationships between Paraspinal Muscle and Spinopelvic Sagittal Balance in Patients with Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(6):1093-1099.
[49] SHIMIZU K, MITSUHARA T, TAKEDA M, et al. Effects of Preservation of the Semispinalis Cervicis Inserted into C2 on Craniocervical Alignment After Laminoplasty. World Neurosurg. 2021;146:e1367-e1376.
[50] HYUN SJ, BAE CW, LEE SH, et al. Fatty Degeneration of the Paraspinal Muscle in Patients With Degenerative Lumbar Kyphosis: A New Evaluation Method of Quantitative Digital Analysis Using MRI and CT Scan. Clin Spine Surg. 2016; 29(10):441-447.
[51] LEE SH, PARK SW, KIM YB, et al. The fatty degeneration of lumbar paraspinal muscles on computed tomography scan according to age and disc level. Spine J. 2017;17(1):81-87.
[52] PARK MS, MOON SH, KIM TH, et al. Paraspinal Muscles of Patients with Lumbar Diseases. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2018;79(4): 323-329.
[53] FECHTENBAUM J, ETCHETO A, KOLTA S, et al. Sagittal balance of the spine in patients with osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(2):559-567.
[54] BARREY C, ROUSSOULY P, LE HUEC JC, et al. Compensatory mechanisms contributing to keep the sagittal balance of the spine. Eur Spine J. 2013;22:S834-S841.
[55] LAFAGE V, SCHWAB F, PATEL A, et al. Pelvic Tilt and Truncal Inclination Two Key Radiographic Parameters in the Setting of Adults With Spinal Deformity. Spine. 2009;34(17):E599-E606.
[56] JACKSON RP, MCMANUS AC. Radiographic analysis of sagittal plane alignment and balance in standing volunteers and patients with low back pain matched for age, sex, and size. A prospective controlled clinical study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(14):1611-1618.
[57] HORI Y, HOSHINO M, INAGE K, et al. ISSLS PRIZE IN CLINICAL SCIENCE 2019: clinical importance of trunk muscle mass for low back pain, spinal balance, and quality of lifea multicenter cross-sectional study. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(5):914-921.
[58] ZHU W, WANG W, KONG C, et al. Lumbar Muscle Fat Content Has More Correlations with Living Quality than Sagittal Vertical Axis in Elderly Patients with Degenerative Lumbar Disorders. Clin Int Aging. 2020;15:1717-1726.
[59] TAKAHASHI S, HOSHINO M, OHYAMA S, et al. Relationship of back muscle and knee extensors with the compensatory mechanism of sagittal alignment in a community-dwelling elderly population. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):2179.
[60] YIN J, MA X, LIN T, et al. Characteristics and treatment of dynamic sagittal imbalance in adult spinal deformity. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(9):2340-2353.
[61] SHIBA Y, TANEICHI H, INAMI S, et al. Dynamic global sagittal alignment evaluated by three-dimensional gait analysis in patients with degenerative lumbar kyphoscoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(8):2572-2579.
[62] BASSANI T, OTTARDI C, COSTA F, et al. Semiautomated 3D Spine Reconstruction from Biplanar Radiographic Images: Prediction of Intervertebral Loading in Scoliotic Subjects. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2017;5:1.
[63] YAGI M, KING AB, BOACHIE-ADJEI O. Incidence, Risk Factors, and Natural Course of Proximal Junctional Kyphosis Surgical Outcomes Review of Adult Idiopathic Scoliosis. Minimum 5 Years of Follow-up. Spine. 2012;37(17):1479-1489.
[64] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, LANDI F, SCHNEIDER SM, et al. Prevalence of and interventions for sarcopenia in ageing adults: a systematic review. Report of the International Sarcopenia Initiative (EWGSOP and IWGS). Age Ageing. 2014;43(6):748-759.
[65] BLONDEL B, SCHWAB F, BESS S, et al. Posterior Global Malalignment After Osteotomy for Sagittal Plane Deformity It Happens and Here is Why. Spine. 2013; 38(7):E394-E401.
[66] BAE JS, JANG JS, LEE SH, et al. Radiological analysis of lumbar degenerative kyphosis in relation to pelvic incidence. Spine J. 2012;12(11):1045-1051.
[67] HONG JY, SUH SW, MODI HN, et al. Correlation of Pelvic Orientation With Adult Scoliosis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(7):461-466.
[68] LABELLE H, MAC-THIONG JM, ROUSSOULY P. Spino-pelvic sagittal balance of spondylolisthesis: a review and classification. Eur Spine J. 2011;(Suppl 5):641-646.
[69] 李方财, 陈其昕, 陈维善, 等. 腰椎退行性侧凸患者脊柱矢状位参数与骨盆参数的相关性[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2013,33(9):928-934.
[70] GOTTFRIED ON, DAUBS MD, PATEL AA, et al. Spinopelvic parameters in postfusion flatback deformity patients. Spine J. 2009;9(8):639-647.
[71] ROUSSOULY P, GOLLOGLY S, BERTHONNAUD E, et al. Sagittal alignment of the spine and pelvis in the presence of L5-S1 isthmic lysis and low-grade spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2006;31(21):2484-2490.
[72] BASSANI T, CASAROLI G, GALBUSERA F. Dependence of lumbar loads on spinopelvic sagittal alignment: An evaluation based on musculoskeletal modeling. PLoS One. 2019;14(3):e0207997.
[73] WARD SR, KIM CW, ENG CM, et al. Architectural Analysis and Intraoperative Measurements Demonstrate the Unique Design of the Multifidus Muscle for Lumbar Spine Stability. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91A(1):176-185.
[74] HEBERT JJ, KOPPENHAVER SL, TEYHEN DS, et al. The evaluation of lumbar multifidus muscle function via palpation: reliability and validity of a new clinical test. Spine J. 2015;15(6):1196-1202.
[75] HOFSTE A, SOER R, HERMENS HJ, et al. Inconsistent descriptions of lumbar multifidus morphology: A scoping review. Bmc Musculoskelet Disord. 2020; 21(1):312.
[76] SHAFAQ N, SUZUKI A, MATSUMURA A, et al. Asymmetric Degeneration of Paravertebral Muscles in Patients With Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis. Spine. 2012;37(16):1398-1406.
[77] KIM H, LEE CK, YEOM JS, et al. Asymmetry of the cross-sectional area of paravertebral and psoas muscle in patients with degenerative scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(6):1332-1338.
[78] YAGI M, KANEKO S, YATO Y, et al. Drop Body Syndrome A Distinct Form of Adult Spinal Deformity. Spine. 2017;42(16):E969-E977. |
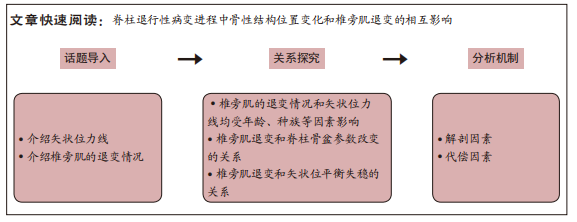
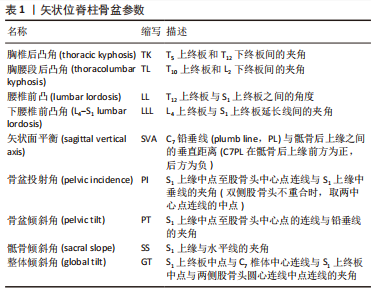
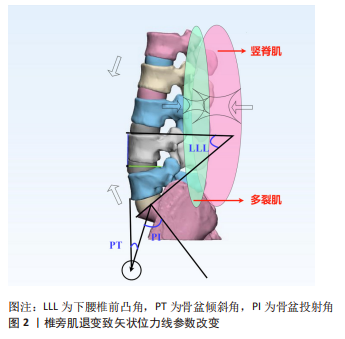

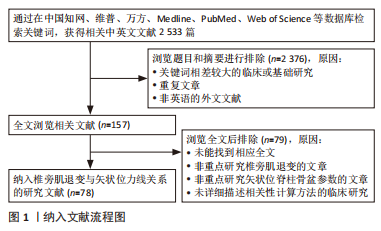
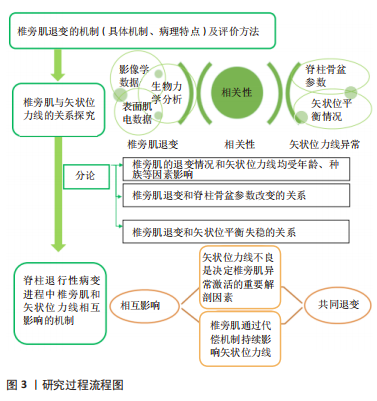 这些研究使用组织学、影像学以及表面肌电等方法帮助人们逐步加深对两者关系以及在脊柱退变性疾病中作用的认识。脊柱矢状位力线是利用多种矢状面参数,对脊柱和骨盆相对位置进行描述和评价脊柱矢状位的平衡情况,其组成和评价较为复杂,随着年龄的增长,其中部分参数逐渐发生变化,用以评估矢状面力线的正常范围也会随之改变。而矢状位平衡的失稳会对患者生活质量产生不利影响。同样在对椎旁肌的研究中,随着年龄增加,椎旁肌的前后群会发生形态学上的退变,包括萎缩和变性,即肌肉容积减少(肌纤维变细或减少)和脂肪浸润(肌肉被脂肪组织渗透代替)。而形态学上的退变会导致椎旁肌功能上的障碍,与脊柱退行性病变的进程相关联。现阶段研究者们注意到椎旁肌在维持矢状位力线的稳定中具有相应作用,保护和改善椎旁肌功能可以延缓脊柱退行性变,因此首先探究矢状位力线与椎旁肌的具体联系,目前有很多研究均表明椎旁肌的退变和脊柱骨盆参数异常有关。研究之间结果类似,即脊柱骨盆参数异常的患者椎旁肌脂肪浸润程度值升高,CSA(包括rmCSA)减低,呈退变性改变。经过总结,明确发现两者具有相关性,同时相关性受年龄、种族等因素影响。接着作者在探究椎旁肌退变和矢状位平衡失稳的关系时着重分析了椎旁肌在脊柱退行性病变进程中的代偿作用。即在脊柱发生退行性改变的时候,为了维持脊柱矢状位的平衡,机体可以通过控制肌肉进行体态改变的代偿,如通过椎旁肌等全身肌肉进行胸椎后凸减少、骨盆后倾或旋转、髋部伸展甚至膝关节屈曲等姿势变化。但这种代偿机制存在弊端,如骨盆后倾增加会影响行走的效率,产生疼痛。且椎旁肌的代偿有一定限度,SVA没有被代偿机制改善,受试者会产生背痛。而随着椎旁肌的退变加重,椎旁肌的代偿能力下降,会导致矢状位平衡的失稳。上文所述许多研究也证实了这种相关性的存在。最后作者在两者相关性明确的基础上对两者可能出现的相互影响的机制进行了分析,考虑矢状位力线的不良是决定椎旁肌退变重要的解剖因素,以及椎旁肌通过代偿机制动态且持续影响着矢状位力线。
这些研究使用组织学、影像学以及表面肌电等方法帮助人们逐步加深对两者关系以及在脊柱退变性疾病中作用的认识。脊柱矢状位力线是利用多种矢状面参数,对脊柱和骨盆相对位置进行描述和评价脊柱矢状位的平衡情况,其组成和评价较为复杂,随着年龄的增长,其中部分参数逐渐发生变化,用以评估矢状面力线的正常范围也会随之改变。而矢状位平衡的失稳会对患者生活质量产生不利影响。同样在对椎旁肌的研究中,随着年龄增加,椎旁肌的前后群会发生形态学上的退变,包括萎缩和变性,即肌肉容积减少(肌纤维变细或减少)和脂肪浸润(肌肉被脂肪组织渗透代替)。而形态学上的退变会导致椎旁肌功能上的障碍,与脊柱退行性病变的进程相关联。现阶段研究者们注意到椎旁肌在维持矢状位力线的稳定中具有相应作用,保护和改善椎旁肌功能可以延缓脊柱退行性变,因此首先探究矢状位力线与椎旁肌的具体联系,目前有很多研究均表明椎旁肌的退变和脊柱骨盆参数异常有关。研究之间结果类似,即脊柱骨盆参数异常的患者椎旁肌脂肪浸润程度值升高,CSA(包括rmCSA)减低,呈退变性改变。经过总结,明确发现两者具有相关性,同时相关性受年龄、种族等因素影响。接着作者在探究椎旁肌退变和矢状位平衡失稳的关系时着重分析了椎旁肌在脊柱退行性病变进程中的代偿作用。即在脊柱发生退行性改变的时候,为了维持脊柱矢状位的平衡,机体可以通过控制肌肉进行体态改变的代偿,如通过椎旁肌等全身肌肉进行胸椎后凸减少、骨盆后倾或旋转、髋部伸展甚至膝关节屈曲等姿势变化。但这种代偿机制存在弊端,如骨盆后倾增加会影响行走的效率,产生疼痛。且椎旁肌的代偿有一定限度,SVA没有被代偿机制改善,受试者会产生背痛。而随着椎旁肌的退变加重,椎旁肌的代偿能力下降,会导致矢状位平衡的失稳。上文所述许多研究也证实了这种相关性的存在。最后作者在两者相关性明确的基础上对两者可能出现的相互影响的机制进行了分析,考虑矢状位力线的不良是决定椎旁肌退变重要的解剖因素,以及椎旁肌通过代偿机制动态且持续影响着矢状位力线。