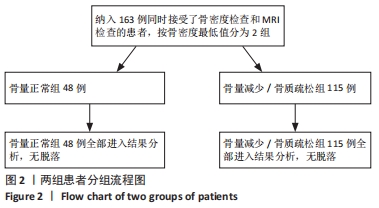
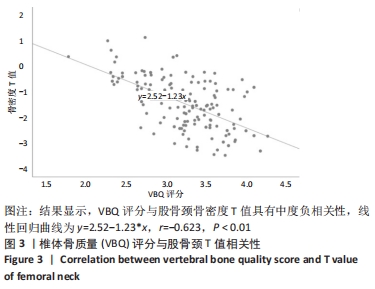
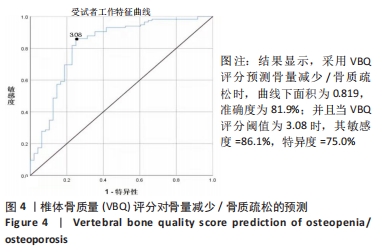
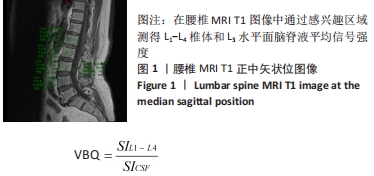
[1] 夏维波,章振林,林华,等.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2017)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(3):281-309.
[2] 智信,陈晓,苏佳灿.绝经后骨质疏松症发病机制研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(11):1510-1513+1534.
[3] COSMAN F, DE BEUR SJ, LEBOFF MS, et al. Clinician’s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Osteoporosis Int. 2014;25: 2359-2381.
[4] BERGINK AP, RIVADENEIRA F, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA SM, et al. Are bone mineral density and fractures related to the incidence and progression of radio- graphic osteoarthritis of the knee,hip,and hand in elderly men and women? The rotterdam study. Arthritis Heumatol. 2019;71(3):361-369.
[5] WATTS NB. Bone quality: getting closer to a definition. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17:1148-1150.
[6] BANDIRALI M, DI LEO G, PAPINI GD, et al. A new diagnostic score to detect osteoporosis in patients undergoing lumbar spine MRI. Eur Radiol. 2015;25(10):2951-2959.
[7] SETIAWATI R, DI CHIO F, RAHARDJO P, et al. Quantitative Assessment of Abdominal Aortic Calcifications Using Lateral Lumbar Radiograph, Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry,and Quantitative Computed Tomography of the Spine. J Clin Densitom. 2016;19:242-249.
[8] PADLINA I, GONZALEZ-RODRIGUEZ E, HANS D, et al. The lumbar spine age- related degenerative disease influences the BMD not the TBS: the Osteolaus cohort. Osteoporosis Int. 2017;28:909-915.
[9] PAIVA LC, FILARDI S, PINTO-NETO AM, et al. Impact of degenerative radiographic abnormalities and vertebral fractures on spinal bone density of women with osteoporosis. Sao Paulo Med J. 2002;120(1): 9-12.
[10] EHRESMAN J, PENNINGTON Z, SCHILLING A, et al. Novel MRI-based score for assessment of bone density in operative spine patients. Spine J. 2020;20(4):556-562.
[11] BINKLEY N, KRUEGER D, DE PAPP AE. Multiple vertebral fractures following osteoporosis treatment discontinuation:a case-report after longterm Odanacatib. Osteoporosis Int. 2018;29(4):999-1002.
[12] 刘玉林,杨国进,付文举,等.左归丸联合阿法骨化醇、替勃龙对绝经后骨质疏松症患者骨密度及内分泌激素的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2019,28(5):490-493.
[13] NEUNER JM, BINKLEY N, SPARAPANI RA, et al. Bone density testing in older women and its association with patient age. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54(3):485-489.
[14] 程晓光,袁慧书,程敬亮,等.骨质疏松的影像学与骨密度诊断专家共识[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2020,9(9):666-673.
[15] MCNAMARA LM. Perspective on post-menopausal osteoporosis: establishing an interdisciplinary understanding of the sequence of events from the molecular level to whole bone fracture. J R Soc Interface. 2010;7(44):353-372.
[16] LINK TM, LANG TF. Axial QCT:Clinical applications and new developments. J Clin Densitom. 2014;17(4):438-448.
[17] BAUM T, MÜLLER D, DOBRITZ M, et al. Converted lumbar BMD values derived from sagittal reformations of contrast-enhanced MDCT predict incidental osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Calcif Tissue Int. 2012;90:481-487.
[18] 刘梦珂,秦健,李长勤.CT及MRI对骨质疏松的定量研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(21):1972-1975.
[19] DASH AS, AGARWAL S, MCMAHON DJ, et al. Abnormal microarchitecture and stiffness in postmenopausal women with isolated osteoporosis at the 1/3 radius. Bone. 2020;132:115211.
[20] ENGELKE K, STAMPA B, TIMM W, et al. Short-term in vivo precision of BMD and parameters of trabecular architecture at the distal forearm and tibia. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23:2151-2158.
[21] 弓健,程晓光,徐浩. 非骨密度DXA测量对骨折风险的预测骨小梁评分(TBS):ISCD 2015官方共识(第四部分)[J].中国骨质疏杂志, 2018,24(11):1401-1404.
[22] 韩晓清,金晖,王春雷,等.TBS在监测及诊断骨质疏松方面的应用价值[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(6):749-751+756.
[23] BOUSSON V,BERGOT C,SUTTER B, et al. Trabecular bone score (TBS): available knowledge, clinical relevance, and future prospects. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23:1489-1501.
[24] 黄淑纾,林华,朱秀芬,等.骨质量与骨质疏松性骨折[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2012,5(4):285-291.
[25] SHEN W, SCHERZER R, GANTZ M, et al.Relationship between MRI- measured bone marrow adipose tissue and hip and spine bone mineral density in African-American and Caucasian participants:the CARDIA study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(4):1337-1346.
[26] 施丹,史晓,王晶晶,等.绝经后女性骨髓脂肪含量与骨密度的相关性[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2016,9(1):32-36.
[27] 唐睿,汤光宇,诸静其.骨质疏松症骨髓脂肪的影像学研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(2):284-288.
[28] CHANG G, BOONE S, MARTEL D, et al. MRI assessment of bone structure and microarchitecture. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;46(2): 323-337.
[29] SHAH LM, HANRAHAN CJ. MRI of spinal bone marrow: part I,techniques and normal age-related appearances. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 197(6):1298-1308.
[30] SHAYGANFAR A, KHODAYI M, EBRAHIMIAN S, et al. Quantitative diagnosis of osteoporosis using lumbar spine signal intensity in magnetic resonance imaging. Br J Radiol. 2019;(1097):20180774.
[31] WANG L, YU W, YIN X, et al. Prevalence of Osteoporosis and Fracture in China:The China Osteoporosis Prevalence Study. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(8):e2121106.
[32] EHRESMAN J, SCHILLING A, YANG X, et al. Vertebral bone quality score predicts fragility fractures independently of bone mineral density. Spine J. 2021; 21(1):20-27.
[33] EHRESMAN J,AHMED AK,LUBELSKI D, et al. Vertebral Bone Quality Score and Postoperative Lumbar Lordosis Associated with Need for Reoperation After Lumbar Fusion. World Neurosurg. 2020;140:e247 -e252.
[34] EHRESMAN J,SCHILLING A,PENNINGTON Z, et al. A novel MRI-based score assessing trabecular bone quality to predict vertebral compression fractures in patients with spinal metastasis. Neurosurg. Spine. 2019;20:1-8.
[35] PENNINGTON Z, EHRESMAN J, LUBELSKI D, et al. Assessing underlying bone quality in spine surgery patients:a narrative review of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry(DXA)and alternatives. Spine J. 2021;21(2): 321-331.
[36] SCHILLING AT,EHRESMAN J,PENNINGTON Z, et al. Interater and Intrarater Reliability of the Vertebral Bone Quality Score. World Neurosurg. 2021;154:e277-e282.
[37] REICHENBACH JR,SCHWESER F,SERRES B, et al. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping:Concepts and Applications. Clin Neuroradiol. 2015;25:225 -230.
[38] WU HZ, ZHANG XF, HAN SM, et al. Correlation of bone mineral density with MRI T2* values in quantitative analysis of lumbar osteoporosis. Arch Osteoporos. 2020;15(1):18.
[39] HE L, LIU Z, LIU C, et al. Radiomics Based on Lumbar Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Detect Osteoporosis. Acad Radiol. 2021;28(6): e165-e171.
[40] ZHU HL, DING JP, QI YJ. Quantitative evaluation of lumbar spine osteoporosis by apparent diffusion coefficient and signal intensity ratio of magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2021;34(8):743-749.
[41] KADRI A, BINKLEY N, HERNANDO D, et al. Opportunistic Use of Lumbar Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Osteoporosis Screening. Osteoporos Int. 2021. doi: 10.1007/s00198-021-06129-5.
[42] MU S, WANG J, GONG S. Application of Medical Imaging Based on Deep Learning in the Treatment of Lumbar Degenerative Diseases and Osteoporosis with Bone Cement Screws. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021;2021:2638495.
[43] OMAR PACHA T, GHASEMI A, OMAR M, et al. Possible Correlation Between Kyphosis of Lumbar Osteoporosis Fractures and the Spinal Signal Intensity Ratio (SSIR). Int J Spine Surg. 2021;15(3):478-484.
|