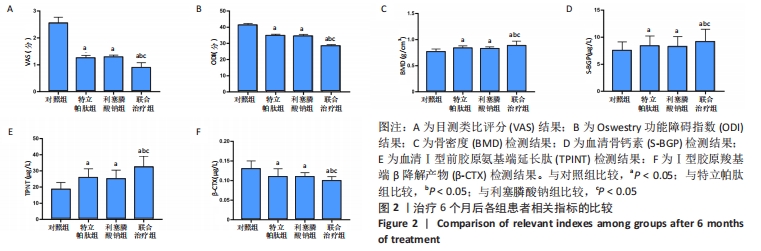
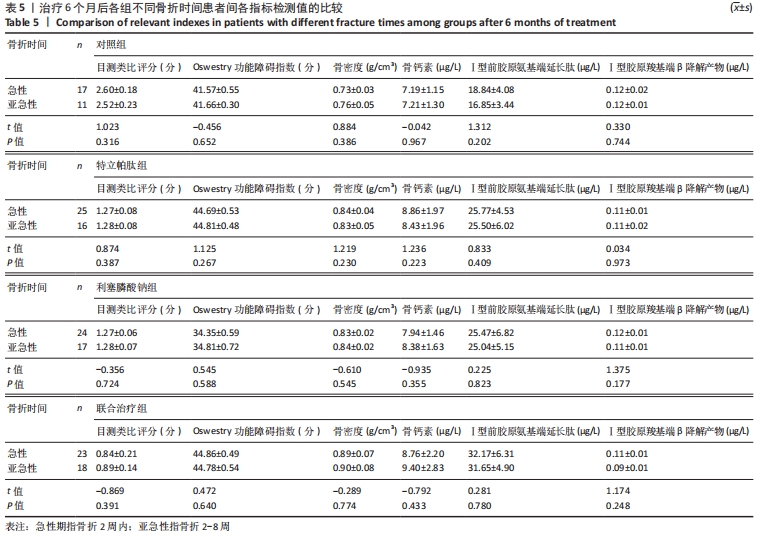
[1] YUAN F, PENG W, YANG C, et al. Teriparatide versus bisphosphonates for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis: A meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2019;66:1-11.
[2] KENDLER DL, MARIN F, ZERBINI CAF, et al. Effects of teriparatide and risedronate on new fractures in post-menopausal women with severe osteoporosis (VERO): a multicentre, double-blind, double-dummy, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10117):230-240.
[3] ANAGNOSTIS P, GKEKAS NK, POTOUPNIS M, et al. New therapeutic targets for osteoporosis. Maturitas. 2019;120:1-6.
[4] COSMAN F, MCMAHON D, DEMPSTER D, et al. Standard Versus Cyclic Teriparatide and Denosumab Treatment for Osteoporosis: A Randomized Trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(2):219-225.
[5] KOCIJAN R, WEIGL M, SKALICKY S, et al. MicroRNA levels in bone and blood change during bisphosphonate and teriparatide therapy in an animal model of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bone. 2020;131: 115104.
[6] LANGDAHL BL, LIBANATI C, CRITTENDEN DB, et al. Romosozumab (sclerostin monoclonal antibody) versus teriparatide in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis transitioning from oral bisphosphonate therapy: a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017; 390(10102):1585-1594.
[7] FUJIEDA Y, HORITA T, NISHIMOTO N, et al. Efficacy and safety of sodium RISedronate for glucocorticoid-induced OsTeoporosis with rheumaTOid arthritis (RISOTTO study): A multicentre, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Mod Rheumatol. 2021;31(3):593-599.
[8] SONGPATANASILP T, ROJANASTHIEN S, SUGKRAROEK P, et al. Open-label study of treatment with alendronate sodium plus vitamin D in men and women with osteoporosis in Thailand. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):392.
[9] SEQUETTO PL, GONÇALVES RV, PINTO AS, et al. Low Doses of Simvastatin Potentiate the Effect of Sodium Alendronate in Inhibiting Bone Resorption and Restore Microstructural and Mechanical Bone Properties in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis. Microsc Microanal. 2017;23(5):989-1001.
[10] FAZIL M, HASSAN MQ, BABOOTA S, et al. Biodegradable intranasal nanoparticulate drug delivery system of risedronate sodium for osteoporosis. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(7):2428-2438.
[11] DENG Y, LI L, LI C, et al. Efficacy of combined medication of risedronate sodium and selective estrogen receptor modulator on the postmenopausal osteoporosis. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2020;33(1(Special)): 495-498.
[12] NASOMYONT N, KEEFE C, TIAN C, et al. Safety and efficacy of teriparatide treatment for severe osteoporosis in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Osteoporos Int. 2020;31(12):2449-2459.
[13] SIMPSON EL, MARTYN-ST JAMES M, HAMILTON J, et al. Clinical effectiveness of denosumab, raloxifene, romosozumab, and teriparatide for the prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Bone. 2020;130:115081.
[14] DÍEZ-PÉREZ A, MARIN F, ERIKSEN EF, et al. Effects of teriparatide on hip and upper limb fractures in patients with osteoporosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Bone. 2019;120:1-8.
[15] LYU H, ZHAO SS, YOSHIDA K, et al. Comparison of Teriparatide and Denosumab in Patients Switching From Long-Term Bisphosphonate Use. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104(11):5611-5620.
[16] CHENG C, WENTWORTH K, SHOBACK DM. New Frontiers in Osteoporosis Therapy. Annu Rev Med. 2020;71:277-288.
[17] YUAN L, BAI J, GENG C, et al. Comparison of targeted percutaneous vertebroplasty and traditional percutaneous vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the elderly. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):359.
[18] MCCARTHY J, DAVIS A. Diagnosis and Management of Vertebral Compression Fractures. Am Fam Physician, 2016;94(1):44-50.
[19] TAKADA J, DINAVAHI R, MIYAUCHI A, et al. Relationship between P1NP, a biochemical marker of bone turnover, and bone mineral density in patients transitioned from alendronate to romosozumab or teriparatide: a post hoc analysis of the STRUCTURE trial. J Bone Miner Metab. 2020;38(3):310-315.
[20] YOLCU Y, ALVI M, WANDERMAN N, et al. Effect of teriparatide use on bone mineral density and spinal fusion: a narrative review of animal models. Int J Neurosci. 2019;129(8):814-820.
[21] CHEN Q, GUO M, MA X, et al. Adherence to Teriparatide Treatment and Risk of Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Horm Metab Res. 2019;51(12):785-791.
[22] PASCHALIS EP, DEMPSTER DW, GAMSJAEGER S, et al. Mineral and organic matrix composition at bone forming surfaces in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis treated with either teriparatide or zoledronic acid. Bone. 2021;145:115848.
[23] SATO C, MIYAKOSHI N, KASUKAWA Y, et al. Teriparatide and exercise improve bone, skeletal muscle, and fat parameters in ovariectomized and tail-suspended rats. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(3):385-395.
[24] HUANG Y. Combined treatment of vitamin K and teriparatide on bone metabolism and biomechanics in rats with osteoporosis. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(1):315-319.
[25] GENANT HK, ENGELKE K, BOLOGNESE MA, et al. Effects of Romosozumab Compared With Teriparatide on Bone Density and Mass at the Spine and Hip in Postmenopausal Women With Low Bone Mass[J]. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32(1):181-187.
[26] CHEN CH, ELSALMAWY AH, ISH-SHALOM S, et al. The Effect of Teriparatide Treatment on the Risk of Fragility Fractures in Postmenopausal Women with Osteoporosis: Results from the Asian and Latin America Fracture Observational Study (ALAFOS). Calcif Tissue Int. 2022;110(1):74-86.
[27] WILSON LM, REBHOLZ CM, JIRRU E, et al. Benefits and Harms of Osteoporosis Medications in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166(9): 649-658.
[28] GITTOES NJ, CRISENO S, APPELMAN-DIJKSTRA NM, et al. ENDOCRINOLOGY IN THE TIME OF COVID-19: Management of calcium metabolic disorders and osteoporosis. Eur J Endocrinol. 2020;183(2): G57-g65.
[29] KITAGUCHI K, KASHII M, EBINA K, et al. The combined effects of teriparatide and anti-RANKL monoclonal antibody on bone defect regeneration in ovariectomized mice. Bone. 2020;130:115077.
[30] MERLOTTI D, FALCHETTI A, CHIODINI I, et al. Efficacy and safety of abaloparatide for the treatment of post-menopausal osteoporosis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2019;20(7):805-811.
[31] SHUAI Y, LIAO L, SU X, et al. Circulating microRNAs in serum as novel biomarkers for osteoporosis: a case-control study. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2020;12:1759720x20953331.
[32] WESKE S, VAIDYA M, REESE A, et al. Targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase as an anabolic therapy for bone loss. Nat Med. 2018;24(5):667-678.
[33] BOYACIOGLU O, ORENAY-BOYACIOGLU S, YILDIRIM H, et al. Boron intake, osteocalcin polymorphism and serum level in postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2018;48:52-56.
[34] LATEEF M, BAIG M, AZHAR A. Estimation of serum osteocalcin and telopeptide-C in postmenopausal osteoporotic females. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21(5):751-755.
[35] ATALAY S, ELCI A, KAYADIBI H, et al. Diagnostic utility of osteocalcin, undercarboxylated osteocalcin, and alkaline phosphatase for osteoporosis in premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Ann Lab Med. 2012;32(1):23-30.
[36] MCCLUNG MR, BOLOGNESE MA, BROWN JP, et al. A single dose of zoledronate preserves bone mineral density for up to 2 years after a second course of romosozumab. Osteoporos Int. 2020;31(11):2231-2241.
[37] YANG T, FENG C, QU Y, et al. Effect of teriparatide on quality of life in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis: a retrospective cohort study. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(2):300060519876744.
[38] GEUSENS P, MARIN F, KENDLER DL, et al. Effects of Teriparatide Compared with Risedronate on the Risk of Fractures in Subgroups of Postmenopausal Women with Severe Osteoporosis: The VERO Trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(5):783-794.
[39] SAAG KG, PANNACCIULLI N, GEUSENS P, et al. Denosumab Versus Risedronate in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis: Final Results of a Twenty-Four-Month Randomized, Double-Blind, Double-Dummy Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(7):1174-1184.
[40] ABOUREHAB MAS. Hyaluronic Acid Modified Risedronate and Teriparatide Co-loaded Nanocarriers for Improved Osteogenic Differentiation of Osteoblasts for the Treatment of Osteoporosis. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(27):2975-2988.
|