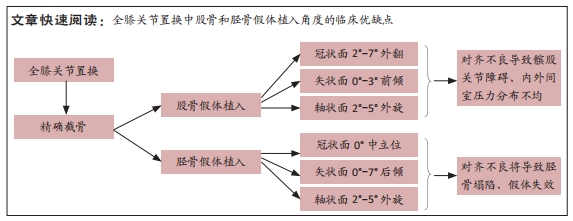
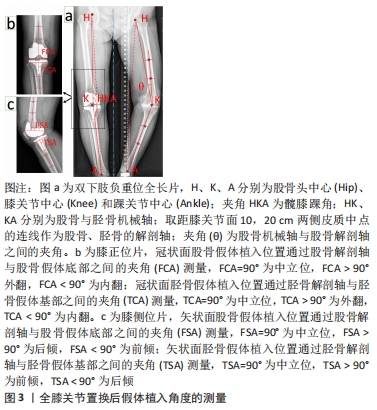
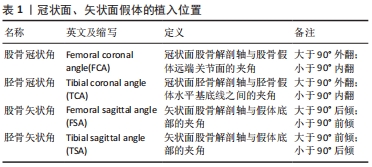
[1] 中华医学会骨科分会关节外科学组,吴阶平医学基金会骨科学专家委员会.膝骨关节炎阶梯治疗专家共识(2018年版)[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2019,13(1):124-130.
[2] ZHANG Z, HUANG C, JIANG Q, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis in China (2019 edition). Ann Transl Med. 2020; 8(19):1213.
[3] CANOVAS F, DAGNEAUX L. Quality of life after total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2018;104(1S):S41-S46.
[4] 袁伟.运动力学对线的人工膝关节有限元建模和生物力学研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2017.
[5] MATHIS DT, LOHRER L, AMSLER F, et al. Reasons for failure in primary total knee arthroplasty - An analysis of prospectively collected registry data. J Orthop. 2020;23:60-66.
[6] LUSTIG S, SAPPEY-MARINIER E, FARY C, et al. Personalized alignment in total knee arthroplasty: current concepts. SICOT J. 2021;7:19.
[7] CASTELLI CC, FALVO DA, IAPICCA ML, et al. Rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty. Ann Transl Med. 2016;4(1):4.
[8] 曲波,刘洋,马根成.术前负重位双下肢全长数字化X线测量在全膝关节置换术中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(8):843-845.
[9] 虞丁柱,王翠,张驰,等.常用股骨髓内定位杆进针点选择的CT三维重建评价[J].青岛大学学报(医学版),2020,56(5):509-512.
[10] 朱诗白,陈曦,钱文伟,等.浅谈全膝关节置换术中的冠状位下肢力线[J].中华外科杂志,2018,56(9):665-669.
[11] OU YL, LI PY, XIA H. Optimal Sagittal Insertion Depth and Direction of Femoral Intramedullary Rod in Total Knee Arthroplasty in Chinese Osteoarthritis Patients. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(4):1238-1244.
[12] XIAO J, WANG C, ZHU L, et al. Improved method for planning intramedullary guiding rod entry point in total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(5):693-698.
[13] 丁裕润,王伟力.CT三维重建在全膝关节置换中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(48):9020-9024.
[14] BONO OJ, OLCOTT CW, CARANGELO R, et al. Femoral Intramedullary Alignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Indications, Results, Pitfalls, Alternatives, and Controversies. J Knee Surg. 2020;33(1):12-14.
[15] MADERBACHER G, SCHAUMBURGER J, BAIER C, et al. Appropriate sagittal femoral component alignment cannot be ensured by intramedullary alignment rods. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(8): 2453-2460.
[16] MULLAJI AB, KHALIFA AA, SHETTY G, et al. Comparison with Navigation of a Novel Three-Step Technique for Improving Accuracy of the Distal Femoral Resection during Conventional TKA: A Case-Control Study. J Knee Surg. 2021 Jul 8. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1731458.
[17] ANDREWS SN, BEELER DM, PARKE EA, et al. Fixed Distal Femoral Cut of 6° Valgus in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Radiographic Review of 788 Consecutive Cases. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(4):755-759.
[18] ANDREWS S, WELDON E, STICKLEY C, et al. Post total knee arthroplasty alignment of 347 consecutive obese patients receiving a fixed distal femoral cut of 6° valgus. J Orthop. 2019;18:113-116.
[19] DAVIS JA, HOGAN C, DAYTON M. Postoperative Coronal Alignment After Total Knee Arthroplasty: Does Tailoring the Femoral Valgus Cut Angle Really Matter? J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(8):1444-1448.
[20] GLASSER J, MARIORENZI M, BLOOD T, et al. Distal femoral valgus cut angles unreliable in total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop. 2021;24:29-33.
[21] WERNER FW, AYERS DC, MALETSKY LP, et al. The effect of valgus/varus malalignment on load distribution in total knee replacements. J Biomech. 2005;38(2):349-355.
[22] ZHOU K, ZHOU Z, SHI X, et al. Effect of individual distal femoral valgus resection in total knee arthroplasty for patients with valgus knee: A retrospective cohort study. Int J Surg. 2018;52:309-313.
[23] NAM D, VAJAPEY S, HAYNES JA, et al. Does Use of a Variable Distal Femur Resection Angle Improve Radiographic Alignment in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(9 Suppl):91-96.
[24] PALANISAMI D, IYYAMPILLAI G, SHANMUGAM S, et al. Individualised distal femoral cut improves femoral component placement and limb alignment during total knee replacement in knees with moderate and severe varus deformity. Int Orthop. 2016;40(10):2049-2054.
[25] SHI X, LI H, ZHOU Z, et al. Individual valgus correction angle improves accuracy of postoperative limb alignment restoration after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(1):277-283.
[26] DEAKIN AH, SARUNGI M. A comparison of variable angle versus fixed angle distal femoral resection in primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(6):1133-1137.
[27] LIU HX, SHANG P, YING XZ, et al. Shorter survival rate in varus-aligned knees after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(8):2663-2671.
[28] SCHIFFNER E, WILD M, REGENBRECHT B, et al. Neutral or Natural? Functional Impact of the Coronal Alignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2019;32(8):820-824.
[29] ZHANG X, WANG Q, XU X, et al. Is the femoral component flexion affected by the sagittal femoral shaft bowing in conventional intramedullary guided TKA? J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):701.
[30] KOH YG, LEE JA, LEE HY, et al. Effect of sagittal femoral component alignment on biomechanics after mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):400.
[31] TSUKEOKA T, TSUNEIZUMI Y, LEE TH. The effect of a sagittal cutting error of the distal femur on the flexion-extension gap difference in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(7):1099-1102.
[32] MURPHY M, JOURNEAUX S, HIDES J, et al. Does flexion of the femoral implant in total knee arthroplasty increase knee flexion: a randomised controlled trial. Knee. 2014;21(1):257-263.
[33] AMIN RM, VASAN V, ONI JK. Kneeling after Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2020;33(2):138-143.
[34] KIM YH, PARK JW, KIM JS, et al. The relationship between the survival of total knee arthroplasty and postoperative coronal, sagittal and rotational alignment of knee prosthesis. Int Orthop. 2014;38(2):379-385.
[35] BELLEMANS J, BANKS S, VICTOR J, et al. Fluoroscopic analysis of the kinematics of deep flexion in total knee arthroplasty. Influence of posterior condylar offset. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(1):50-53.
[36] ISHII Y, NOGUCHI H, TAKEDA M, et al. Posterior condylar offset does not correlate with knee flexion after TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(9): 2995-3001.
[37] STAMIRIS D, GKEKAS NK, ASTERIADIS K, et al. Anterior femoral notching ≥ 3 mm is associated with increased risk for supracondylar periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021 Apr 26. doi: 10.1007/s00590-021-02989-z.
[38] PURANIK HG, MUKARTIHAL R, PATIL SS, et al. Does Femoral Notching During Total Knee Arthroplasty Influence Periprosthetic Fracture. A Prospective Study. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(6):1244-1249.
[39] NIKI Y, NAGAI K, SASSA T, et al. Comparison between cylindrical axis-reference and articular surface-reference femoral bone cut for total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(12):3741-3746.
[40] KOH YG, NAM JH, CHUNG HS, et al. Gender difference exists in sagittal curvature of the distal femoral condyle morphology for osteoarthritic population. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(12):3740-3746.
[41] CHURCHILL DL, INCAVO SJ, JOHNSON CC, et al. The transepicondylar axis approximates the optimal flexion axis of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(356):111-118.
[42] LUSTIG S, LAVOIE F, SELMI TA, et al. Relationship between the surgical epicondylar axis and the articular surface of the distal femur: an anatomic study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2008;16(7):674-682.
[43] OLCOTT CW, SCOTT RD. A comparison of 4 intraoperative methods to determine femoral component rotation during total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15(1):22-26.
[44] COHEN DA, GURSEL AC, LOW AK. How coronal alignment affects distal femoral anatomy: an MRI-based comparison of varus and valgus knees. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):92.
[45] AKAGI M, YAMASHITA E, NAKAGAWA T, et al. Relationship between frontal knee alignment and reference axes in the distal femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(388):147-156.
[46] JANG ES, CONNORS-EHLERT R, LIARNO S, et al. Accuracy of Reference Axes for Femoral Component Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Computed Tomography-Based Study of 2,128 Femora. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019; 101(23):e125.
[47] LEE JK, LEE S, CHUN SH, et al. Rotational alignment of femoral component with different methods in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):217.
[48] DONG Y, ZHANG Z, DONG W, et al. An optimization method for implantation parameters of individualized TKA tibial prosthesis based on finite element analysis and orthogonal experimental design. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):165.
[49] FANG DM, RITTER MA, DAVIS KE. Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it? J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(6 Suppl):39-43.
[50] MEIER M, JANSSEN D, KOECK FX, et al. Variations in medial and lateral slope and medial proximal tibial angle. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(3):939-946.
[51] LASKIN RS. Instrumentation pitfalls: you just can’t go on autopilot! J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(3 Suppl 1):18-22.
[52] OH SM, BIN SI, LEE BS, et al. The entry point of intramedullary tibia cutting guide should vary according to the individual tibia morphology in TKA. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(3):391-400.
[53] SCHNEIDER M, HEISEL C, ALDINGER PR, et al. Use of palpable tendons for extramedullary tibial alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22(2):219-226.
[54] SUGIMURA N, IKEUCHI M, IZUMI M, et al. The dorsal pedis artery as a new distal landmark for extramedullary tibial alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(11):2618-2622.
[55] TSUKEOKA T, TSUNEIZUMI Y, LEE TH. Accuracy of the second metatarsal as a landmark for the extramedullary tibial cutting guide in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(12):2969-2974.
[56] HINO M, NAKAGAWA S, ARAI Y, et al. Extensor hallucis longus tendon is a new distal landmark for coronal tibial component alignment in total knee arthroplasty: A study of magnetic resonance imaging. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2020;28(1):2309499020912340.
[57] TSUKEOKA T, TSUNEIZUMI Y, YOSHINO K. Preoperative planned distance between the skin surface and the guide rod provides accurate posterior tibial slope in total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019; 139(8):1133-1139.
[58] TSUKEOKA T, TSUNEIZUMI Y. The distance from the extramedullary cutting guide rod to the skin surface as a reference guide for the tibial slope in total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2016;23(2):314-317.
[59] SHI W, JIANG Y, ZHAO X, et al. The influence of posterior tibial slope on the mid-term clinical effect of medial-pivot knee prosthesis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):563.
[60] KANSARA D, MARKEL DC. The effect of posterior tibial slope on range of motion after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(6):809-813.
[61] KANG KT, KWON SK, SON J, et al. The increase in posterior tibial slope provides a positive biomechanical effect in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(10):3188-3195.
[62] KANG KT, KOH YG, SON J, et al. A computational simulation study to determine the biomechanical influence of posterior condylar offset and tibial slope in cruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint Res. 2018;7(1):69-78.
[63] KANG KT, KOH YG, SON J, et al. Influence of Increased Posterior Tibial Slope in Total Knee Arthroplasty on Knee Joint Biomechanics: A Computational Simulation Study. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(2):572-579.
[64] FUJIMOTO E, SASASHIGE Y, MASUDA Y, et al. Significant effect of the posterior tibial slope and medial/lateral ligament balance on knee flexion in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013; 21(12):2704-2712.
[65] HAN HS, KANG SB. Interactive effect of femoral posterior condylar offset and tibial posterior slope on knee flexion in posterior cruciate ligament-substituting total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2018;25(2):335-340.
[66] WANG ZW, LIU YL, LIN KJ, et al. The effects of implantation of tibio-femoral components in hyperextension on kinematics of TKA. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(10):2032-2038.
[67] YOO JH, CHANG CB, SHIN KS, et al. Anatomical references to assess the posterior tibial slope in total knee arthroplasty: a comparison of 5 anatomical axes. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(4):586-592.
[68] GRASSI A, PIZZA N, LOPOMO NF, et al. No differences in knee kinematics between active and passive flexion-extension movement: an intra-operative kinematic analysis performed during total knee arthroplasty. J Exp Orthop. 2020;7(1):12.
[69] AKAGI M, OH M, NONAKA T, et al. An anteroposterior axis of the tibia for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(420):213-219.
[70] LU Y, REN X, LIU B, et al. Tibiofemoral rotation alignment in the normal knee joints among Chinese adults: a CT analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):323.
[71] KIM JI, JANG J, LEE KW, et al. Anterior tibial curved cortex is a reliable landmark for tibial rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):252.
[72] OKAZAKI Y, PUJOL N. The use of an asymmetrical tibial tray in TKA optimises tibial rotation when fitted to the posterior tibial plateau border. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(12):3821-3826.
[73] SAFFARINI M, NOVER L, TANDOGAN R, et al. The original Akagi line is the most reliable: a systematic review of landmarks for rotational alignment of the tibial component in TKA. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019; 27(4):1018-1027.
[74] MA Y, MIZU-UCHI H, USHIO T, et al. Bony landmarks with tibial cutting surface are useful to avoid rotational mismatch in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(5):1570-1579.
[75] KAWAGUCHI K, INUI H, TAKETOMI S, et al. Intraoperative Tibial Anteroposterior Axis Could Not Be Replicated After Tibial Osteotomy in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(10):2371-2375.
[76] DREXLER M, BACKSTEIN D, STUDLER U, et al. The medial border of the tibial tuberosity as an auxiliary tool for tibial component rotational alignment during total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(6):1736-1742.
[77] HOWELL SM, CHEN J, HULL ML. Variability of the location of the tibial tubercle affects the rotational alignment of the tibial component in kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(10):2288-2295.
[78] 赵旻暐,田华,曾琳,等.中国人采用胫骨结节及胫前肌腱定位的髓外截骨法术后胫骨假体冠状位力线的测量与分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2016,48(2):351-355.
[79] RITTER MA, DAVIS KE, MEDING JB, et al. The effect of alignment and BMI on failure of total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(17):1588-1596.
|