2.1 腰椎融合对THA术后假体脱位率的影响 在老龄化社会中,退化性肌肉骨骼疾病的发病率不断上升,大量患者同时患有脊柱及髋关节的退行性疾病。因此,需要行腰椎融合术和THA的患者数量大幅增加。SING等[4]在811 601例行THA的患者中发现至少有3.4%的患者同时进行了腰椎融合术,其中2%的患者在THA术前进行了腰椎融合术,1.4%的患者在THA术后进行了腰椎融合术,且进一步通过病例-对照试验发现,有腰椎融合手术史的患者假体脱位与修复率(5.55%)高于对照组(3.43%),且长节段腰椎融合的患者脱位率与修复率进一步增加(7.51%)。MALKANI等[5]研究发现,在2002至2014年间,同时接受THA和腰椎融合术患者的数量增加了293%,THA术前行腰椎融合术的患者髋关节脱位发生率为7.4%,而未行腰椎融合术的患者髋关节脱位发生率为4.8%(P < 0.001)。
影响髋关节稳定性的因素有很多,但是归根到底主要为假体撞击和髋关节周围的软组织张力[6-8]。当软组织张力差时,轻微的外力与撞击即可导致脱位。影响软组织张力的因素有年龄、神经肌肉疾病、髋关节手术史、后外侧入路等;另外,由于THA术后早期麻醉的肌松作用和软组织破坏,软组织张力较差,因此合理的术后搬运、制动与功能锻炼也是非常重要的影响因素;直到术后3个月瘢痕增生,肌肉张力恢复,脱位风险才降低。撞击发生在肢体的运动过程中,当髋关节运动超过一定的范围会导致股骨假体与髋臼假体的边缘接触,发生撞击[9]。如果运动继续,由于杠杆作用,当撞击力量大于软组织张力时会导致髋关节的脱位,小于软组织张力虽然不会脱位,但是反复撞击会导致假体磨损,使用寿命缩短,翻修率增加。影响撞击的患者自身因素主要为腰椎骨盆的运动,术者因素主要包括髋臼假体的置入角度、股骨颈与股骨头假体的选择等。
LAZENNEC等[10]对这类人群的研究均排除了软组织张力差的患者,但是THA术后脱位率与翻修率依然有明显的增加。HECKMANN等[11]对20例晚期脱位的患者进行研究,发现腰椎骨盆矢状面异常是THA术后晚期脱位的唯一原因,THA术后晚期肌力恢复、瘢痕增生,软组织张力强,因此撞击被认为是导致这类人群髋关节假体脱位的重要原因。目前研究多集中于患者腰椎融合术后腰椎骨盆矢状面的变化,通过研究腰椎骨盆矢状面参数、参数的意义以及各参数与撞击之间的关系,来探究撞击风险增加的原因,并为在手术中选择合理的髋臼假体置入角度、股骨颈与股骨头假体的型号来提供理论依据,以降低撞击发生的风险,降低脱位率与翻修率。
2.2 腰椎骨盆矢状面参数及临床意义
2.2.1 腰椎前凸角 为L1上终板切线与S1终板切线所成角度。腰椎前凸角反映腰椎的凸度,Δ腰椎前凸角是站立与坐位下腰椎前凸角的差值,反映腰椎的活动度。大量研究证实了腰椎活动度的变化与骨盆运动密切相关[12-14],其中L5-S1对骨盆运动能力的影响最大。
2.2.2 骨盆入射角 为S1上终板的中点与股骨头中心连线和 S1 上终板垂线之间的夹角;若双侧股骨头不重叠,则取两股骨头中心连线的中点。骨盆入射角是骨盆矢状面的解剖学常数,反映骨盆、骶骨与腰椎的相对位置。有研究认为,骨盆入射角的高低代表着腰椎骨盆在矢状面平衡的适应性大小,高骨盆入射角与腰椎前凸角增大和骶骨倾斜角适应范围增加有关[15];相反,低骨盆入射角反映腰椎前凸角较小,骶骨倾斜角适应能力有限。IKE等[16]对187例(200髋)患者在初次THA前后进行了腰椎骨盆矢状位X射线片摄影,发现低骨盆入射角的患者拥有更高的撞击风险。然而,OCHI等[12]却认为骨盆入射角与骨盆活动度之间没有相关性,腰椎的功能活动对骨盆活动度的影响比骨盆入射角更大,骨盆入射角对腰椎骨盆的影响主要体现在静态平衡性,而不是活动性。
2.2.3 骨盆入射角和腰椎前凸角不匹配 -10° < 骨盆入射角-腰椎前凸角 < +10°代表腰椎平衡,骨盆入射角-腰椎前凸 角> 10°代表腰椎不平衡。HAFFER等[17]研究认为,生理腰椎前凸角的丧失及其与骨盆入射角不匹配会引起静态骨盆状态的改变,增加撞击与脱位的风险。
2.2.4 骶骨倾斜角 为S1上终板切线和水平线之间的夹角。骶骨倾斜角代表着骨盆的运动,骶骨倾斜角增加时骨盆向前倾斜,减小时骨盆向后倾斜。Δ骶骨倾斜角是站立位与坐位下骶骨倾斜角的差值,常被用来表示骨盆的活动度。STEFL等[18]研究认为,腰椎骨盆活动度正常的人群Δ骶骨倾斜角在10°-30°之间,并将骨盆运动模式异常的人群分为两类:①骨盆过度活动:Δ骶骨倾斜角> 30°;②骨盆僵硬:Δ骶骨倾斜角< 10°。
2.2.5 髋臼前倾角 为侧位X射线片上臼杯面切线与垂直于水平面的轴线之间的夹角。髋臼前倾角代表着髋臼在矢状面的方向,也是避免撞击的关键角度。Lewinnek在1978年提出“安全区”概念,认为髋臼前倾角在(15±10)°范围内脱位率最低。目前对于Lewinnek“安全区”的安全性存在较大的争议,TEZUKA等[19]研究发现,有14.2%的髋臼前倾角在Lewinnek“安全区”内依然有很大的脱位风险,并认为与腰椎融合术史、低骨盆入射角和股骨运动增加有关。MCCARTHY等[9]认为,传统Lewinnek“安全区”的测量在很大程度上来自于静态测量,活动中的“安全区”(如捡起一个物体、下蹲、低椅子上站起来等)比以前认为的要小得多。
2.2.6 骨盆股骨角 是由S1上终板中心到股骨头中心的一条线与平行于股骨骨干的第2条线所形成的夹角,Δ骨盆股骨角是站立与坐位下骨盆股骨角的差值,代表着股骨运动的范围。HECKMANN等[20]研究认为,股骨运动增加会增加THA术后假体脱位的风险,髋臼假体置入角度良好而无法解释的脱位很可能是由股骨过度运动引起的。
2.2.7 联合矢状位指数 数值上等于骨盆股骨角+髋臼前倾角,正常站立位联合矢状位指数平均为218°,正常坐位联合矢状位指数平均为180°。TEZUKA等[19]研究认为,联合矢状位指数值异常的髋关节有较高的撞击风险,异常值范围如下:站立异常值联合矢状位指数> 243°(站立位:髋臼前倾角> 45°及骨盆股骨角> 197°),有后撞击风险;坐位异常值联合矢状位指数 < 151°(坐位:髋臼前倾角< 41°及骨盆股骨角< 110°),有前撞击风险。联合矢状位指数通过髋臼与股骨运动两个指标共同预测撞击风险,具有先进性,被认为是替代Lewinnek“安全区”的首选指标,但仍需要更多的临床数据进一步证明。
2.3 腰椎正常人群的腰椎骨盆矢状面参数变化的研究 姿势的改变需要脊柱、骨盆与髋关节的协调运动,以达到矢状面的平衡,脊柱、骨盆与髋关节是相关联的整体,一部分的运动变化必然引起另外两部分的运动变化。没有腰椎融合术手术史、无严重腰椎退行性疾病、腰椎骨盆矢状面平衡、活动良好的人群拥有较低的撞击风险,其腰椎骨盆矢状位的变化有可遵循的规律,这一规律避免了撞击,是研究此类问题的关键。撞击往往发生在姿势运动的过程中,坐位与站位是生活中最常见、最基本的活动姿势,因此探究站位与坐位下腰椎骨盆矢状面参数是研究此类问题的关键。参数的测量是通过拍摄研究对象的站立位与坐位腰椎骨盆侧位X射线片,测量范围包含全部腰椎及股骨上段。在站立姿势中,每一位患者均采取一个舒适的姿势,手指放在锁骨上;在坐位时,患者坐在一个可自由调节高度的凳子上,手放在锁骨上面,调整高度,使膝盖弯曲在90°,双脚平踩在地板上[18]。
在站立位与坐位下腰椎骨盆矢状面角度的变化有一定的规律[21]:当站位时,骨盆向前倾斜,髋关节伸展,重心向前移动,腰椎前凸增大,以平衡躯干,即骶骨倾斜角变大,腰椎前凸角增大,此时髋臼在矢状面上表现为水平,髋臼口向下,有利于髋关节的伸展,即髋臼前倾角减小;当从站立到坐姿改变时,骨盆后倾,髋关节屈曲,重心后移,腰椎扁平,以便平衡躯干,即骶骨倾斜角变小,腰椎前凸角减少,此时髋臼从矢状面上的表现是垂直的,髋臼向前张开,即髋臼前倾角增加。上述规律可以看出,在腰椎骨盆运动中腰椎前凸角与骶骨倾斜角的变化成正比,与髋臼前倾角的变化成反比。髋臼前倾角这样的变化避免了髋臼与股骨假体的撞击。腰椎正常的患者一般拥有平衡的腰椎(-10° <骨盆入射角-腰椎前凸角< +10°)以及良好的腰椎骨盆活动度(Δ骶骨倾斜角:10°-30°,平均20°)。在站立位与坐位下腰椎骨盆矢状面角度的变化量同样有一定的规律,WAN等[22]研究验证发现,骶骨倾斜角每降低1°,髋臼前倾角就会增加0.8°。HECKMANN等[11]研究了20例晚期脱位患者站立位和坐位下的腰椎脊椎矢状面X射线片,发现骨盆运动(Δ骶骨倾斜角)每减少1.0°,股骨运动(Δ骨盆股骨角)就会增加0.9°。HECKMANN等[20]紧接着根据临床数据建立了一个三角模型,发现骨盆运动(Δ骶骨倾斜角)与髋臼运动(Δ髋臼前倾角)成正比(1∶1),与股骨运动(Δ骨盆股骨角)成反比(1∶1)。无论腰椎骨盆的活动是正常还是僵硬,运动比例与运动量的变化都遵从以上模型。腰椎骨盆运动正常的人群髋臼假体可以放置在传统的“安全区”范围内,因为骨盆可以灵活地改变来避免撞击[21]。
2.4 腰椎融合人群腰椎骨盆矢状面参数变化的研究
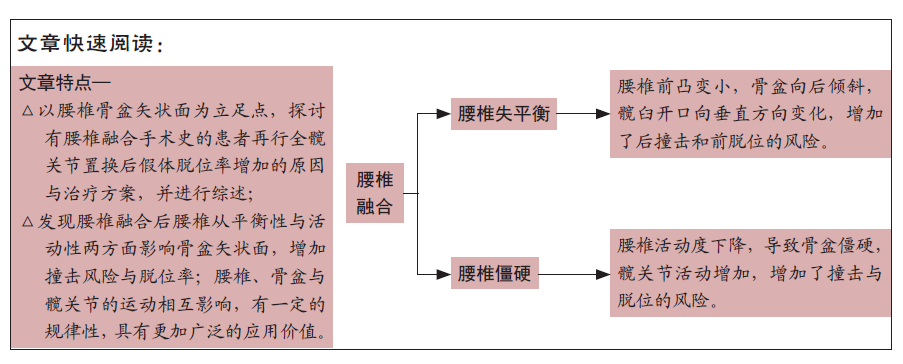
2.4.1 腰椎平衡性对骨盆的影响 骨盆入射角影响腰椎的平衡性而不是活动性,目前没有发现高、低骨盆入射角在站立位和坐位时骨盆倾斜变化有明显差异。骨盆入射角和腰椎前凸角是否匹配是判断腰椎平衡的关键,-10° <骨盆入射角-腰椎前凸角< +10°代表腰椎矢状面平衡,反之代表失衡。骨盆入射角是腰椎骨盆矢状面的解剖学常数,同一个体骨盆入射角是不变的,当腰椎前凸角越小,越有可能发生腰椎的失衡。目前多数研究认为,低骨盆入射角与高撞击风险有关,骨盆入射角越低,在相同腰椎前凸角的情况下,发生腰椎失衡的风险越大[16,18,23]。腰椎前凸角、骶骨倾斜角与髋臼前倾角相互影响,腰椎前凸角与骶骨倾斜角的变化成正比,与髋臼前倾角的变化成反比。当腰椎骨盆矢状面失衡时[24-25],出现腰椎平背或后凸畸形,哪怕在站立位,腰椎前凸角依然很低,此时骶骨倾斜角代偿性减小,骨盆向后倾斜,髋臼前倾角增大,当骨盆出现极度后倾时(骶骨倾斜角< 5°),髋臼方向由向下变为向前,增加了后撞击和前脱位的风险。腰椎不平衡可能存在于活动正常的腰椎、过度活动的腰椎和僵硬的腰椎中,但无论腰椎活动度处于哪种情况,腰椎后凸畸形、骨盆极度后倾且骶骨倾斜角< 5°的患者“安全区”很小,手术难度极高。STEFL等[18]的研究中,9例患有腰椎后凸畸形的患者在行THA术后有6例依然有很高的撞击风险。
PHAN等[21]认为,这类患者可以在THA术前先行脊柱矫形术,矫正腰椎后凸畸形,恢复腰椎骨盆矢状面的平衡,二期再行THA可有效避免撞击,增加手术的成功率。
BUCKLAND等[26]研究了33例患者在进行脊柱矫形手术后髋臼前倾角的变化,发现脊柱重排后腰椎前凸角每增加3.163°,骶骨倾斜角增加1.032°,髋臼前倾角降低1°;在33例患者中有11例患者的髋臼前倾角被完全纠正,并进入安全区域。BARRY等[27]的研究得出类似的结论。脊柱矫形后要重新评估腰椎骨盆矢状面,对于不愿接受脊柱矫正术的患者,安装髋臼假体需要降低髋臼前倾角,但手术难度较高。
2.4.2 腰椎活动性对骨盆的影响 骨盆活动量的变化受到腰椎活动量变化的影响。OCHI等[12]分析了74例接受原发性THA的患者站立位与坐位的腰椎骨盆矢状面参数,发现骨盆倾斜量的变化(Δ骶骨倾斜角)与腰椎前凸的变化(Δ腰椎前凸角)有密切关系,但胸椎参数、骨盆入射角与骨盆倾斜度量变化无关。
STEFL等[18]将异常的骨盆运动模式分为两类:①过度活动(Δ骶骨倾斜角> 30°);②僵硬(Δ骶骨倾斜角< 10°):坐位僵硬、站立位僵硬。
骨盆过度活动是指从站立到坐姿时Δ骶骨倾斜角> 30°。当腰椎矢状面处于平衡状态时,过度活动的骨盆运动与正常骨盆运动类似,可以看作正常骨盆运动的变异,这种过度活动的骨盆运动往往伴随着较少的股骨运动,有较低的撞击风险,这类人群的髋臼假体安装在传统“安全区”即可。当腰椎矢状面失衡时,撞击风险较高,按照上述腰椎失平衡的治疗方法处理即可。
当腰椎僵硬时,唯一的补偿方法是改变骨盆运动。有腰椎融合手术史的患者,由于腰椎活动度下降,导致患者当从站立到坐位时Δ骶骨倾斜角< 10°,即骨盆僵硬。骨盆僵硬的患者Δ骶骨倾斜角减少,Δ髋臼前倾角减少,Δ骨盆股骨角代偿性增加,僵硬的骨盆与过度活动的股骨运动导致了潜在撞击风险的增加。
腰椎融合术后腰椎可能被固定在平衡的位置上,也可能被固定在不平衡的位置上,导致的骨盆僵硬往往有两种模式:坐位僵硬、站位僵硬。坐位僵硬的患者一般Δ骶骨倾斜角≤ 10°,且站立位与坐位骶骨倾斜角< 30°。无论是坐位还是站位,骨盆都处于坐位时的骨盆矢状面状态,此时的腰椎是僵硬且不平衡的。在坐姿时,骨盆后倾,髋关节屈曲,髋臼垂直开口向前;但在站位时,股骨伸展以保持身体平衡,而骨盆仍处于后倾状态,髋臼前倾没有明显降低,导致股骨大转子与垂直的髋臼撞击,即后撞击与前脱位的风险增加。坐位僵硬的患者可以先行脊柱矫形手术来纠正不平衡的腰椎,再评估矢状面以选用合适的髋臼前倾角,对于不愿行脊柱矫形的患者,安装髋臼假体时需要予以较低的髋臼前倾角来避免撞击。站位僵硬的患者一般Δ骶骨倾斜角≤10°,且站立位与坐位骶骨倾斜角> 30°,无论是坐位还是站位,骨盆都处于站立位的骨盆矢状面状态,此时的腰椎是僵硬且平衡的。在站位时,骨盆前倾、臀部伸展、髋臼水平、向下张开有利于髋关节的伸展;但在坐位时,髋关节屈曲,骨盆依然前倾,髋臼前倾没有明显增加,增加了股骨前转子骨与水平的髋臼撞击(前撞击与后脱位)的危险。站位僵硬的患者安装髋臼假体时需要予以较大的髋臼前倾角以避免撞击。
骨盆运动量越少撞击风险越大,当患者骨盆运动(Δ骶骨倾斜角)< 5°时,称为病理性僵硬或融合髋,常由手术(腰椎融合术手术史)和生物性原因(腰椎退行性变、强直性脊柱炎)导致。STEFL等[18]对160例患者进行了THA,并分析了手术前后撞击风险大小的变化,发现大部分Δ骶骨倾斜
角≤10°的患者可以通过调整合理的髋臼安装角度来降低撞击风险,但Δ骶骨倾斜角< 5°与骶骨倾斜角< 5°的患者在行THA术后依然有较多的患者处于高撞击风险中,得到了广泛的关注。这类患者除了选择合适的髋臼前倾角外,使用双动杯装置也是必要的。DAGNEAUX等[28]研究认为,对于腰椎骨盆矢状面异常的老年患者使用双动杯装置是合理的,可增加髋关节稳定性,降低撞击脱位的风险。双动杯装置的主要好处有两方面:首先,拥有更大的股骨头尺寸,提高了头颈
比,降低脱位的风险;其次,双动杯装置使得髋关节拥有更大的活动度,可以满足基本的生活活动需求。
BERNSTEIN等[13]进一步研究了腰椎对骨盆活动度的影响,认为L5-S1节段融合对骨盆活动能力的影响最大,L5-S1以上节段的融合与骨盆活动能力减少无关。SALIB等[14]也认为累积骶骨的腰椎融合术对脱位率的影响更大。依据BERNSTEIN等[13]与SALIB等[14]的研究,长节段腰椎融合与短节段腰椎融合的脱位率应该是接近的,但大量研究显示,长节段腰椎融合患者较短节段腰椎融合患者行THA的脱位率增 加[4,29]。BUCKLAND等[29]通过Medicare数据库对1年间有腰椎融合手术史再行THA的患者进行随访,研究其脱位率,并根据融合级别分为3个队列:1-2节段,3-7节段和8节段,发现脱位风险的增加与融合水平的增加存在相关性。融合1-2节段的患者(2.96%)和融合3-7节段的患者(4.12%)的脱位风险明显不同,3-7节段融合组的脱位率明显高于1-2节段融合组(OR=1.60,P < 0.000 1)。BUCKLAND等[29]的研究与上述两个研究的结果冲突,有两点原因:一方面,该研究并没有将涉及骶骨融合组列为单独亚组,与短节段腰椎融合组相比,长节段腰椎融合组可能拥有更多涉及骶骨的腰椎融合患者;另一方面,L5-S1以上节段的融合对脱位的影响可能与腰椎平衡性有关,需要进一步研究证明。
有趣的是,KATAKAM等[30]在一项回顾性研究中,对比了患有强直性脊柱炎(142例)与有腰椎融合手术史(135例)的患者,发现腰椎融合手术史组的平均腰椎前凸角(34.18°)大于强直性脊柱炎组(21°);并得出结论:腰椎前凸角每增加1°,强直性脊柱炎和腰椎融合手术史患者发生脱位的概率增加13%。这与此次研究的结论相反,实际上有腰椎融合手术史的患者可能被固定在平衡的腰椎上,也可能被固定在不平衡的腰椎上,而强直性脊柱炎患者的特征则是低腰椎前凸角,因此有腰椎融合手术史患者的平均腰椎前凸角较高,忽略了脱位率是腰椎活动性与平衡性共同作用的结果。
2.5 腰椎骨盆矢状面参数关系在其他领域应用的研究
2.5.1 腰椎退行性疾病 患有腰椎退行性疾病的患者腰椎骨盆矢状面的改变与腰椎融合术有相似之处[31]。GU等[32]将138例单侧股骨头坏死的患者分为腰椎退变组与腰椎正常组,发现腰椎退变组的患者比对照组平均腰椎前凸角低5°,骨盆后倾5°,腰椎运动减少16°,骨盆运动减少8°,髋关节屈曲增加7°。ESPOSITO等[33]发现,THA术后发生脱位的多节段腰椎退行性变患者比未发生脱位的多节段腰椎退行性变患者拥有更多的骨盆后倾、髋关节屈曲和更低的骨盆运动。腰椎退行性疾病的患者腰椎间隙变窄,导致腰椎前凸角减少与腰椎活动度降低,从而进一步影响骨盆的运动状态。腰椎退行性疾病患者的腰椎骨盆运动模式与坐位僵硬类似,有后撞击与前脱位的风险。
2.5.2 强直性脊柱炎 强直性脊柱炎的患者腰椎骨盆矢状面运动有类似机制。强直性脊柱炎的特征性脊柱畸形为腰椎后凸畸形,并伴有髋关节伸展和骨盆后倾及较大的髋臼前倾,随着病情的发展,出现脊柱与关节强直,影响腰椎骨盆的活动度,类似坐位僵硬的腰椎骨盆运动,有后撞击与前脱位的风险[34]。
2.5.3 髋关节撞击综合征 髋关节撞击综合征与腰椎的平衡性、活动性有很强的相关性。FADER等[35]对比了有症状与无症状的髋臼撞击患者,发现有症状的髋臼撞击患者有更小的腰椎前凸及矢状位活动度,更多的骨盆后倾及髋关节屈曲,增加了骨撞击风险,可降低生活质量,长期撞击可能发展为髋关节骨性关节炎。
2.6 THA与腰椎融合手术顺序的优势 已知腰椎融合术后再行THA脱位率增加,那么对于同时患有髋关节退行性疾病和腰椎疾患的患者手术顺序的选择则十分重要,目前也存在较大争议。
2.6.1 先行THA STEFL等[18]的研究证明,多数腰椎骨盆矢状面失衡与僵硬的患者可以通过选择合适的髋臼前倾角来降低撞击风险。大量研究发现,与先行腰椎融合术的患者相比,先行THA的患者假体脱位率更低[4,36]。这可能因为对于先行THA的患者已经在僵硬和失衡的腰椎中置入了一个稳定、位置良好的髋臼植入物,而再行腰椎融合术对腰椎前凸矫治不足以使髋臼前倾有明显改变,脱位的风险不会明显增加。另一方面,如果患者行THA术后髋关节假体出现不稳定的情况,为了避免脱位的发生,则不再进一步行腰椎融合术。需要注意的是,先行THA术后再行腰椎手术如果明显改变腰椎平衡性,则原本稳定的假体可能会变得不稳定,使得重新翻修的概率增加。
髋关节疾病也会影响腰椎骨盆矢状面参数,髋关节屈曲挛缩或因疼痛而限制了髋关节的运动,会导致骨盆与腰椎的活动性代偿性增大,影响腰椎的精确评估,因此这类患者尤其是患有髋关节屈曲挛缩的患者禁止进行任何腰椎手术,需先行THA矫正髋关节活动度后再重新评估腰椎骨盆矢状面,使腰椎手术方案更加精确[37]。
2.6.2 先行腰椎融合 对于腰椎失平衡,尤其是骶骨倾斜
角< 5°的患者,虽然先行THA可以将髋臼放置在安全的区域内,但是手术难度较大。因此,先行腰椎融合术与脊柱矫形术将腰椎恢复到平衡的位置,二期再行THA是更为稳妥的选择[38]。
除了髋关节屈曲挛缩与腰椎严重失衡的情况之外,两者手术顺序的选择取决于患者两部位症状的轻重,优先治疗患者疼痛严重的部位也是一个重要的原则。