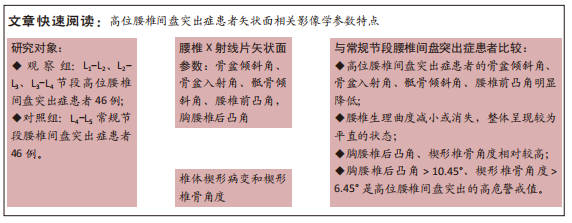
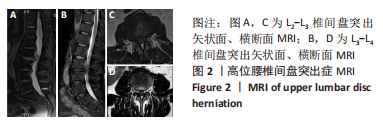
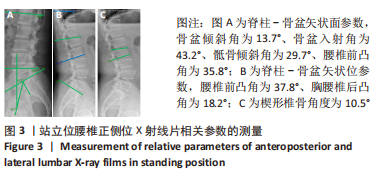
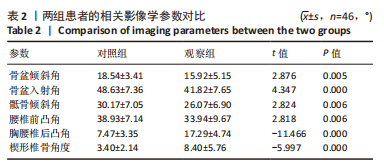
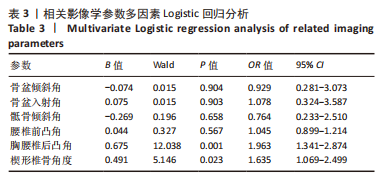
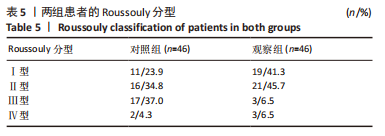
[1] LIU C, XUE J, LIU J, et al. Is there a correlation between upper lumbar disc herniation and multifidus muscle degeneration? A retrospective study of MRI morphology. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):92.
[2] LI Z, ZHANG C, CHEN W, et al. Percutaneous Endoscopic Transforaminal Discectomy versus Conventional Open Lumbar Discectomy for Upper Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Comparative Cohort Study. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:1852070.
[3] SHIN MH, BAE JS, CHO HL, et al. Extradiscal Epiduroscopic Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy for Upper Lumbar Disc Herniation A Technical Note. Clin Spine Surg. 2019;32(3):98-103.
[4] LIN TY, WANG YC, CHANG CW, et al. Surgical Outcomes for Upper Lumbar Disc Herniation: Decompression Alone versus Fusion Surgery. J Clin Med. 2019;8(9):1435.
[5] SANDERSON SP, HOUTEN J, ERRICO T, et al. The unique characteristics of “upper” lumbar disc herniations. Neurosurgery. 2004;55(2):385-389; discussion 389.
[6] BAE J, LEE SH, SHIN SH, et al. Radiological analysis of upper lumbar disc herniation and spinopelvic sagittal alignment. Eur Spine J. 2016; 25(5):1382-1388.
[7] XIAO L, NI C, SHI J, et al. Analysis of Correlation Between Vertebral Endplate Change and Lumbar Disc Degeneration. Med Sci Monit. 2017; 23:4932-4938.
[8] ROUSSOULY P, GOLLOGLY S, BERTHONNAUD E, et al. Classification of the normal variation in the sagittal alignment of the human lumbar spine and pelvis in the standing position. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(3):346-353.
[9] WANG F, DONG Z, LI YP, et al. Wedge-shaped vertebrae is a risk factor for symptomatic upper lumbar disc herniation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):265.
[10] FEI H, LI WS, SUN ZR, et al. Analysis of Spino-pelvic Sagittal Alignment in Young Chinese Patients with Lumbar Disc Herniation. Orthop Surg. 2017;9(3):271-276.
[11] ASAI Y, TSUTSUI S, OKA H, et al. Sagittal spino-pelvic alignment in adults: The Wakayama Spine Study. PLoS One. 2017;12(6):e0178697.
[12] 汪凌骏,顾勇,冯煜,等.脊柱-骨盆矢状面形态变化与椎间盘摘除及后路椎体间植骨融合的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(29):4598-4602.
[13] 李松,孙旭,陈曦,等.高位腰椎间盘突出症患者脊柱-骨盆矢状面形态的影像学分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017,27(6):532-538.
[14] SUN D, LIU P, CHENG J, et al. Correlation between intervertebral disc degeneration, paraspinal muscle atrophy, and lumbar facet joints degeneration in patients with lumbar disc herniation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):167.
[15] 施皆乐,史金辉.高位腰椎间盘突出症与椎体楔形变的关系[J].颈腰痛杂志,2021,42(2):263-265.
[16] XU JX, YANG SD, WANG BL, et al. Correlative analyses of isolated upper lumbar disc herniation and adjacent wedge-shaped vertebrae. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(1):1150-1155.
[17] CHEN RQ, HOSOGANE N, WATANABE K, et al. Reliability Analysis of Spino-Pelvic Parameters in Adult Spinal Deformity: A Comparison of Whole Spine and Pelvic Radiographs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016; 41(4):320-327.
[18] LEGAYE J, DUVAL-BEAUPÈRE G, HECQUET J, et al. Pelvic incidence: a fundamental pelvic parameter for three-dimensional regulation of spinal sagittal curves. Eur Spine J. 1998;7(2):99-103.
[19] 江龙,朱泽章,邱勇,等.青少年腰椎间盘突出症患者脊柱-骨盆矢状面形态的影像学研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(2):140-144.
[20] WANG Q, SUN CT. Characteristics and correlation analysis of spino-pelvic sagittal parameters in elderly patients with lumbar degenerative disease. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):127.
[21] WANG W, PEI B, WU S, et al. Biomechanical responses of human lumbar spine and pelvis according to the Roussouly classification. PLoS One. 2022;17(7):e0266954.
[22] ROUSSOULY P, PINHEIRO-FRANCO JL. Biomechanical analysis of the spino-pelvic organization and adaptation in pathology. Eur Spine J. 2011;20 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):609-618.
[23] JOHNSON RD, VALORE A, VILLAMINAR A, et al. Pelvic parameters of sagittal balance in extreme lateral interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disc disease. J Clin Neurosci. 2013;20(4):576-581.
[24] ROUSSOULY P, PINHEIRO-FRANCO JL. Sagittal parameters of the spine: biomechanical approach. Eur Spine J. 2011;20 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):578-585.
[25] 唐烨,卢圆圆,贾真.脊柱-骨盆矢状面参数对腰椎间盘手术临床疗效的预测价值[J].中国现代医学杂志,2020,30(13):80-83.
[26] 宋继彭,鲁世保,朱卫国,等.我国高龄腰椎间盘突出症人群脊柱-骨盆矢状面影像学特点[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2021,10(9):688-694.
[27] SCHMIDT H, KETTLER A, HEUER F, et al. Intradiscal pressure, shear strain, and fiber strain in the intervertebral disc under combined loading. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(7):748-755.
[28] CHUNG SK, KIM YE, WANG KC. Biomechanical effect of constraint in lumbar total disc replacement: a study with finite element analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(12):1281-1286.
[29] GAO A, WANG Y, YU M, et al. Analysis of sagittal profile and radiographic parameters in symptomatic thoracolumbar disc herniation patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):177.
[30] DOLAN P, LUO J, POLLINTINE P, et al. Intervertebral disc decompression following endplate damage: implications for disc degeneration depend on spinal level and age. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(17):1473-1481.
[31] LOUIE PK, ESPINOZA ORÍAS AA, FOGG LF, et al. Changes in Lumbar Endplate Area and Concavity Associated With Disc Degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(19):E1127-E1134.
[32] KIM J, PARK HJ, KIM MS, et al. Wedging of vertebral bodies at the thoracolumbar spine in healthy individuals on whole body MRI screening: correlation with disc degeneration and disc herniation. Acta Radiol. 2022;63(7):958-963. |