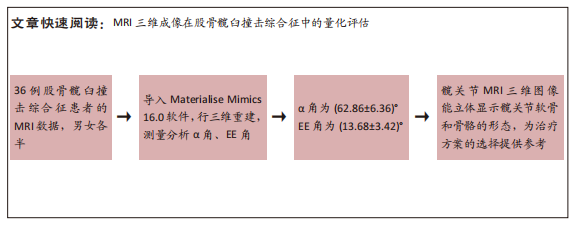
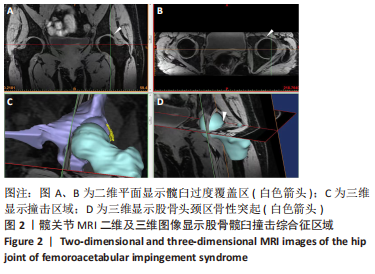
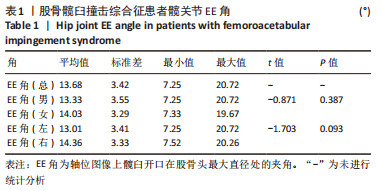
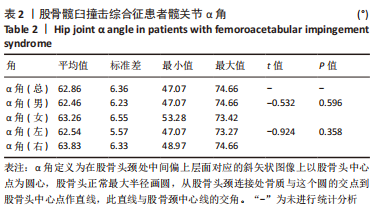
[1] 李亚超,王伟强,李韶平.髋关节撞击综合征影像学研究进展[J].安徽医学,2017,38(2):261-264.
[2] ALSHAMEERI Z, KHANDUJA V. The effect of femoro-acetabular impingement on the kinematics and kinetics of the hip joint. Int Orthop. 2014;38(8):1615-1620.
[3] JOHNSON KA. Impingement of the lesser trochanter on the ischial ramus after total hip arthroplasty. Report of three cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59(2):268-269.
[4] TOSUN O, ALGIN O, YALCIN N, et al. Ischiofemoral impingement: evaluation with new MRI parameters and assessment of their reliability. Skeletal Radiol. 2012;41(5):575-587.
[5] BREDELLA MA, AZEVEDO DC, OLIVEIRA AL, et al. Pelvic morphology in ischiofemoral impingement. Skeletal Radiol. 2015;44(2):249-253.
[6] TANNAST M, GORICKI D, BECK M, et al. Hip damage occurs at the zone of femoroacetabular impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466(2):273-280.
[7] TANNAST M, SIEBENROCK KA, ANDERSON SE. Femoroacetabular impingement: radiographic diagnosis--what the radiologist should know. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188(6):1540-1552.
[8] MASCARENHAS VV, CAETANO A, DANTAS P, et al. Advances in FAI Imaging: a Focused Review. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020;13(5): 622-640.
[9] OMAR IM, BLOUNT KJ. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Hip. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;24(4):165-181.
[10] KIM T, MIN BH, YOON SH, et al. An in vitro comparative study of T2 and T2* mappings of human articular cartilage at 3-Tesla MRI using histology as the standard of reference. Skeletal Radiol. 2014;43(7):947-954.
[11] 吴琼,高阳,牛广明,等.基于磁共振图像的膝关节软骨可视化初步研究[J].中国医药导报,2017,14(5):103-105.
[12] NÖTZLI HP, WYSS TF, STOECKLIN CH, et al. The contour of the femoral head-neck junction as a predictor for the risk of anterior impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(4):556-560.
[13] YOU T, YANG B, ZHANG XT, et al. Are “normal hips” being labeled as femoroacetabular impingement due to EE angle? Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(13):e6410.
[14] DIAZ-LEDEZMA C, NOVACK T, MARIN-PEÑA O, et al. The relevance of the radiological signs of acetabular retroversion among patients with femoroacetabular impingement. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(7):893-899.
[15] SUTTER R, DIETRICH TJ, ZINGG PO, et al. Femoral antetorsion: comparing asymptomatic volunteers and patients with femoroacetabular impingement. Radiology. 2012;263(2):475-483.
[16] WERNER CM, COPELAND CE, STROMBERG J, et al. Correlation of the cross-over ratio of the cross-over sign on conventional pelvic radiographs with computed tomography retroversion measurements. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39(7):655-660.
[17] 陈焱君,刘波,卢建烨,等. MSCT对髋关节撞击综合征的影像学研究[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2013,11(3):98-102.
[18] COOKE WR, GILL HS, MURRAY DW, et al. Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement? Br J Radiol. 2013;86(1021):20120182.
[19] SIEBENROCK KA, FERNER F, NOBLE PC, et al. The cam-type deformity of the proximal femur arises in childhood in response to vigorous sporting activity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(11):3229-3240.
[20] SUTTER R, DIETRICH TJ, ZINGG PO, et al. How useful is the alpha angle for discriminating between symptomatic patients with cam-type femoroacetabular impingement and asymptomatic volunteers? Radiology. 2012;264(2):514-521.
[21] 孙钢,李敏,姜庆军,等.凸轮型髋臼撞击综合征影像学表现[J].实用放射学杂志,2010,26(5):695-698.
[22] PANZER S, AUGAT P, ESCH U. CT assessment of herniation pits: prevalence, characteristics, and potential association with morphological predictors of femoroacetabular impingement. Eur Radiol. 2008;18(9): 1869-1875.
[23] APRATO A, MASSÈ A, FALETTI C, et al. Magnetic resonance arthrography for femoroacetabular impingement surgery: is it reliable? J Orthop Traumatol. 2013;14(3):201-206.
[24] SMITH TO, HILTON G, TOMS AP, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of acetabular labral tears using magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance arthrography: a meta-analysis. Eur Radiol. 2011; 21(4):863-874.
[25] LATTANZI R, PETCHPRAPA C, ASCANI D, et al. Detection of cartilage damage in femoroacetabular impingement with standardized dGEMRIC at 3 T. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(3):447-456.
[26] ELLERMANN J, ZIEGLER C, NISSI MJ, et al. Acetabular cartilage assessment in patients with femoroacetabular impingement by using T2* mapping with arthroscopic verification. Radiology. 2014;271(2): 512-523.
[27] ROBINSON P. Conventional 3-T MRI and 1.5-T MR arthrography of femoroacetabular impingement. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;199(3): 509-515.
[28] CRESPO-RODRÍGUEZ AM, DE LUCAS-VILLARRUBIA JC, PASTRANA-LEDESMA M, et al. The diagnostic performance of non-contrast 3-Tesla magnetic resonance imaging (3-T MRI) versus 1.5-Tesla magnetic resonance arthrography (1.5-T MRA) in femoro-acetabular impingement. Eur J Radiol. 2017;88:109-116.
[29] 庞智晖,魏秋实,周广全,等.个体股骨头坏死三维有限元模型的建立与应用[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2012,29(4):251-255.
[30] STEPHEN JM, CALDER JD, WILLIAMS A, et al. Comparative accuracy of lower limb bone geometry determined using MRI, CT, and direct bone 3D models. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(9):1870-1876.
[31] LERCH TD, SCHMARANZER F, HANKE MS, et al. Torsional deformities of the femur in patients with femoroacetabular impingement : Dynamic 3D impingement simulation can be helpful for the planning of surgical hip dislocation and hip arthroscopy. Orthopade. 2020;49(6):471-481.
[32] YAN K, XI Y, SASIPONGANAN C, et al. Does 3DMR provide equivalent information as 3DCT for the pre-operative evaluation of adult Hip pain conditions of femoroacetabular impingement and Hip dysplasia? Br J Radiol. 2018;91(1092):20180474.
[33] LI W, ABRAM F, BEAUDOIN G, et al. Human hip joint cartilage: MRI quantitative thickness and volume measurements discriminating acetabulum and femoral head. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2008;55(12): 2731-2740.
[34] NARDI C, DE FALCO L, CARACCHINI G, et al. A three-dimensional measurement method on MR arthrography of the hip to classify femoro-acetabular impingement. Jpn J Radiol. 2021;39(12):1175-1185.
[35] SCHAUWECKER N, XI Y, SLEPICKA C, et al. Quantifying differences in femoral head and neck asphericity in CAM type femoroacetabular impingement and hip dysplasia versus controls using radial 3DCT imaging and volumetric segmentation. Br J Radiol. 2020;93(1110):20190039.
[36] SCHMARANZER F, HELFENSTEIN R, ZENG G, et al. Automatic MRI-based Three-dimensional Models of Hip Cartilage Provide Improved Morphologic and Biochemical Analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019; 477(5):1036-1052.
[37] DENIZ CM, XIANG S, HALLYBURTON RS, et al. Segmentation of the Proximal Femur from MR Images using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):16485.
[38] CHENG CT, HO TY, LEE TY, et al. Application of a deep learning algorithm for detection and visualization of hip fractures on plain pelvic radiographs. Eur Radiol. 2019;29(10):5469-5477.
[39] ZENG G, SCHMARANZER F, DEGONDA C, et al. MRI-based 3D models of the hip joint enables radiation-free computer-assisted planning of periacetabular osteotomy for treatment of hip dysplasia using deep learning for automatic segmentation. Eur J Radiol Open. 2020;8: 100303.
[40] GUIRGUIS A, POLSTER J, KARIM W, et al. Interchangeability of CT and 3D “pseudo-CT” MRI for preoperative planning in patients with femoroacetabular impingement. Skeletal Radiol. 2020;49(7):1073-1080. |