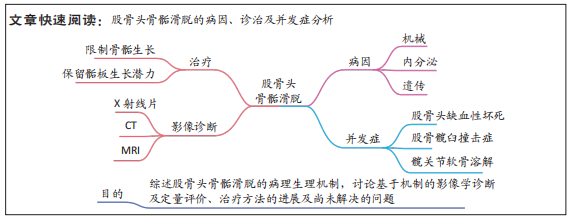
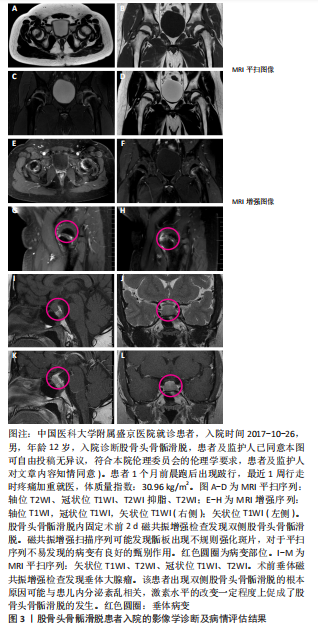
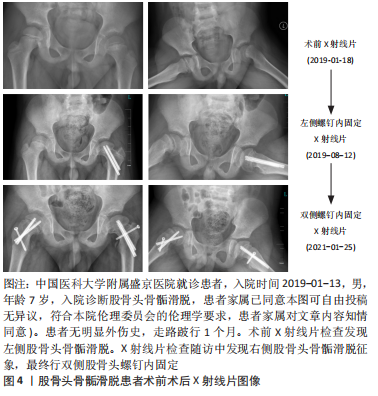
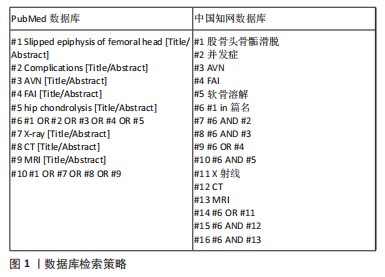
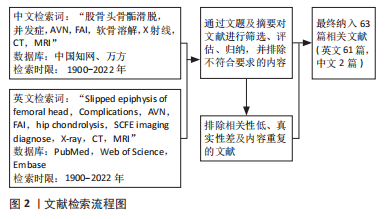
[1] SCHROEDER PB, NICHOLES MA. Schmitz MR hip injuries in the adolescent athlete. Clin Sports Med. 2021;40(2):385-398.
[2] 贾国强.儿童股骨头骨骺滑脱诊治研究进展[J].国际儿科学杂志, 2019,46(6):449-452.
[3] 李浩,张自明.股骨头骨骺滑脱的诊断与治疗相关研究进展[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2018,39(11):872-876.
[4] APRATO A, CONTI A, BERTOLO F, et al. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis: current management strategies. Orthop Res Rev. 2019;11:47-54.
[5] LEHMANN CL, ARONS RR, LODER RT, et al. The epidemiology of slipped capital femoral epiphysis: an update. J Pediatr Orthop. 2006;26(3): 286-290.
[6] ROATEN J, SPENCE DD. Complications related to the treatment of slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Orthop Clin North Am. 2016;47(2): 405-413.
[7] HELGESSON L, JOHANSSON PK, AURELL Y, et al. Early osteoarthritis after slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Acta Orthop. 2018;89(2):222-228.
[8] ORTEGREN J, PETERSON P, SVENSSON J, et al. Persisting CAM deformity is associated with early cartilage degeneration after Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: 11-year follow-up including dGEMRIC. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(4):557-563.
[9] DAVEY S, FISHER T, SCHRADER T. Controversies in the management of unstable slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Orthop Clin North Am. 2022;53(1):51-56.
[10] ZILKENS C, JAGER M, BITTERSOHL B, et al. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Orthopade. 2010;39(10):1009-1021.
[11] PARCELLS BW. Pediatric hip and pelvis. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2020; 67(1):139-152.
[12] SHAW KA, SHIVER AL, OAKES T, et al. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis associated with endocrinopathy: a narrative review. JBJS Rev. 2022; 10(2). doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.21.00188.
[13] WIRTH T, EBERHARDT O, CERKEZ D, et al. Specific cases of slipped capital femoral epiphysis: endocrinopathies, hormone therapy and other rare causes. Orthopade. 2019;48(8):685-692.
[14] SCHARSCHMIDT T, JACQUET R, WEINER D, et al. Gene expression in slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Evaluation with laser capture microdissection and quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(2):366-377.
[15] BOYER DW, MICKELSON MR, PONSETI IV. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Long-term follow-up study of one hundred and twenty-one patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981;63(1):85-95.
[16] LODER RT, RICHARDS BS, SHAPIRO PS, et al. Acute slipped capital femoral epiphysis: the importance of physeal stability. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(8):1134-1140.
[17] SWARUP I, SHAH R, GOHEL S, et al. Predicting subsequent contralateral slipped capital femoral epiphysis: an evidence-based approach. J Child Orthop. 2020;14(2):91-97.
[18] SAMELIS PV, PAPAGRIGORAKIS E, KONSTANTINOU AL, et al. Factors affecting outcomes of slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Cureus. 2020; 12(2):e6883.
[19] LODER R What is the cause of avascular necrosis in unstable slipped capital femoral epiphysis and what can be done to lower the rate? J Pediatr Orthop. 2013;33:S88-S91.
[20] TOKMAKOVA KP, STANTON RP, MASON DE. Factors influencing the development of osteonecrosis in patients treated for slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85(5):798-801.
[21] RILEY PM, WEINER DS, GILLESPIE R, et al. Hazards of internal fixation in the treatment of slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990;72(10):1500-1509.
[22] HERRERA-SOTO JA, DUFFY MF, BIRNBAUM MA, et al. Increased intracapsular pressures after unstable slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2008;28(7):723-728.
[23] WALTON RD, MARTIN E, WRIGHT D, et al. The treatment of an unstable slipped capital femoral epiphysis by either intracapsular cuneiform osteotomy or pinning in situ: a comparative study. Bone Joint J. 2015; 97-B(3):412-419.
[24] AKIYAMA M, NAKASHIMA Y, KITANO T, et al. Remodelling of femoral head-neck junction in slipped capital femoral epiphysis: a multicentre study. Int Orthop. 2013;37(12):2331-2336.
[25] CASTANEDA P, PONCE C, VILLAREAL G, et al. The natural history of osteoarthritis after a slipped capital femoral epiphysis/the pistol grip deformity. J Pediatr Orthop. 2013;33 Suppl 1:S76-S82.
[26] ABRAHAM E, GONZALEZ MH, PRATAP S, et al. Clinical implications of anatomical wear characteristics in slipped capital femoral epiphysis and primary osteoarthritis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2007;27(7):788-795.
[27] MURGIER J, ESPIE A, BAYLE-INIGUEZ X, et al. Frequency of radiographic signs of slipped capital femoral epiphysiolysis sequelae in hip arthroplasty candidates for coxarthrosis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(7):791-797.
[28] WIRRIES N, DIENST M. Labral lesions in femoroacetabular impingement syndrome: evidence-based treatment. Orthopade. 2022;51(6):450-457.
[29] RAB GT. The geometry of slipped capital femoral epiphysis: implications for movement, impingement, and corrective osteotomy. J Pediatr Orthop. 1999;19(4):419-424.
[30] GRIFFIN DR, DICKENSON EJ, O’DONNELL J, et al. The Warwick Agreement on femoroacetabular impingement syndrome (FAI syndrome): an international consensus statement. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(19):1169-1176.
[31] SIEBENROCK KA, FERNER F, NOBLE PC, et al. The cam-type deformity of the proximal femur arises in childhood in response to vigorous sporting activity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(11):3229-3240.
[32] KEMP J, GRIMALDI A, HEEREY J, et al. Current trends in sport and exercise hip conditions: intra-articular and extra-articular hip pain, with detailed focus on femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) syndrome. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2019;33(1):66-87.
[33] LUBICKY JP. Chondrolysis and avascular necrosis: complications of slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Pediatr Orthop. 1996;5(3):162-167.
[34] ULICI A, CARP M, TEVANOV I, et al. Outcome of pinning in patients with slipped capital femoral epiphysis: risk factors associated with avascular necrosis, chondrolysis, and femoral impingement. J Int Med Res. 2018; 46(6):2120-2127.
[35] WENSAAS A, SVENNINGSEN S, TERJESEN T Long-term outcome of slipped capital femoral epiphysis: a 38-year follow-up of 66 patients. J Child Orthop. 2011;5(2):75-82.
[36] WENSAAS A, GUNDERSON RB, SVENNINGSEN S, et al. Femoroacetabular impingement after slipped upper femoral epiphysis: the radiological diagnosis and clinical outcome at long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(11):1487-1493.
[37] JOFE MH, LEHMAN W, EHRLICH MG. Chondrolysis following slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004;13(1):29-31.
[38] TUDISCO C, CATERINI R, FARSETTI P, et al. Chondrolysis of the hip complicating slipped capital femoral epiphysis: long-term follow-up of nine patients. J Pediatr Orthop. 1999;8(2):107-111.
[39] ARONSSON DD, LODER RT, BREUR GJ, et al. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis: current concepts. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2006;14(12): 666-679.
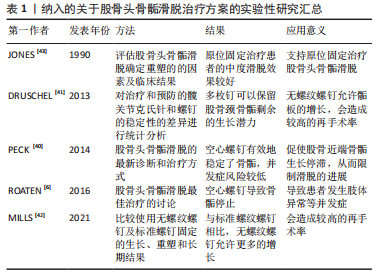
[40] PECK K, HERRERA-SOTO J. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis: what’s new? Orthop Clin North Am. 2014;45(1):77-86.
[41] DRUSCHEL C, PLACZEK R, FUNK JF. Growth and deformity after in situ fixation of slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Z Orthop Unfall. 2013; 151(4):371-379.
[42] MILLS H, FLOWERS MJ, AGRAWAL Y, et al. Outcomes of distally un-threaded screw fixation of slipped capital femoral epiphysis at skeletal maturity: a matched cohort study. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2021;30(6): 540-548.
[43] JONES JR, PATERSON DC, HILLIER TM, et al. Remodelling after pinning for slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990;72(4): 568-573.
[44] WÖLFLE-ROOS J, URLAUB S, REICHEL H, et al. Significantly lower femoral neck growth in screw fixation of the asymptomatic contralateral hip in unilateral slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2016;25(3):197-201.
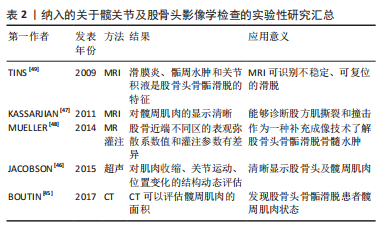
[45] BOUTIN RD, BAMRUNGCHART S, BATENI CP, et al. CT of patients with hip fracture: muscle size and attenuation help predict mortality. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017;208(6):W208-W215.
[46] JACOBSON JA, KHOURY V, BRANDON CJ. Ultrasound of the groin: techniques, pathology, and pitfalls. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015;205(3): 513-523.
[47] KASSARJIAN A, TOMAS X, CEREZAL L, et al. MRI of the quadratus femoris muscle: anatomic considerations and pathologic lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197(1):170-174.
[48] MUELLER D, SCHAEFFELER C, BAUM T, et al. Magnetic resonance perfusion and diffusion imaging characteristics of transient bone marrow edema, avascular necrosis and subchondral insufficiency fractures of the proximal femur. Eur J Radiol. 2014;83(10):1862-1869.
[49] TINS B, CASSAR-PULLICINO V, MCCALL I. The role of pre-treatment MRI in established cases of slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Eur J Radiol. 2009;70(3):570-578.
[50] ZILKENS C, MIESE F, BITTERSOHL B, et al. Delayed gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of cartilage (dGEMRIC), after slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Eur J Radiol. 2011;79(3):400-406.
[51] JONES CE, COOPER AP, DOUCETTE J, et al. Southwick angle measurements and SCFE slip severity classifications are affected by frog-lateral positioning. Skeletal Radiol. 2018;47(1):79-84.
[52] JARRETT DY, MATHENEY T, KLEINMAN PK. Imaging SCFE: diagnosis, treatment and complications. Pediatr Radiol. 2013;43 Suppl 1:S71-S82.
[53] GALLETTA C, APRATO A, GIACHINO M, et al. Hip morphology in slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2021;30(6):535-539.
[54] FISCHER-COLBRIE ME, LOUER CR, BOMAR JD, et al. Predicting epiphyseal stability of slipped capital femoral epiphysis with preoperative CT imaging. J Child Orthop. 2020;14(1):68-75.
[55] SUBBURAJ K, VALENTINITSCH A, DILLON AB, et al. Regional variations in MR relaxation of hip joint cartilage in subjects with and without femoralacetabular impingement. Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;31(7): 1129-1136.
[56] SAMAAN MA, PEDOIA V, ZHANG AL, et al. A novel mr-based method for detection of cartilage delamination in femoroacetabular impingement patients. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(3):971-978.
[57] GAO Y, LYU X, LIU Q, et al. Quantitative evaluation of hip muscle atrophy in patients with unilateral slipped capital femoral epiphysis based on magnetic resonance imaging. Acad Radiol. 2020;28(8):1125-1132.
[58] ROBBEN SG, MERADJI M, DIEPSTRATEN AF, et al. US of the painful hip in childhood: diagnostic value of cartilage thickening and muscle atrophy in the detection of Perthes disease. Radiology, 1998;208(1):35-42.
[59] ZUO B, ZHU JF, WANG XY, et al. Outcome of the modified Dunn procedure in severe slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):506.
[60] HANSEN CH, BOMAR JD, BADRINATH R, et al. Telescoping screw fixation compared to traditional in situ screw fixation for slipped capital femoral epiphysis: clinical, radiographic and patient-reported outcomes. J Pediatr Orthop. 2022;31(3):224-231.
[61] RAHM S, JUD L, JUNGWIRTH-WEINBERGER A, et al. Mid-term results after in situ pinning and hip arthroscopy for mild slipped capital femoral epiphysis: a minimum five-year follow-up. J Child Orthop. 2020;14(6): 521-528.
[62] SWARUP I, GOODBODY C, GOTO R, et al. Risk factors for contralateral slipped capital femoral epiphysis: a meta-analysis of cohort and case-control studies. J Pediatr Orthop. 2020;40(6):e446-e453.
[63] BOYLE MJ, LIROLA JF, HOGUE GD, et al. The alpha angle as a predictor of contralateral slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Child Orthop. 2016;10(3):201-207. |