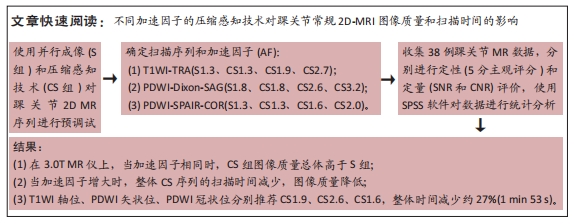
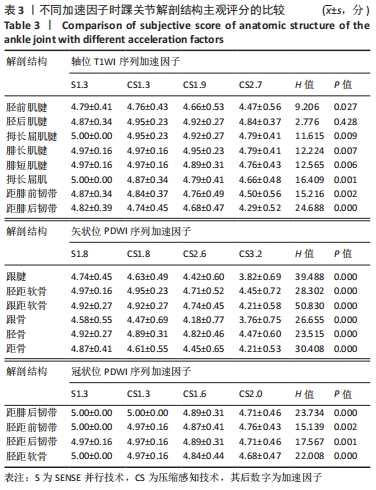
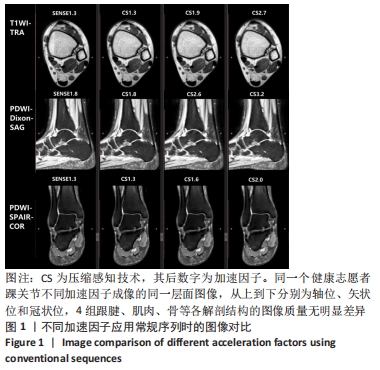
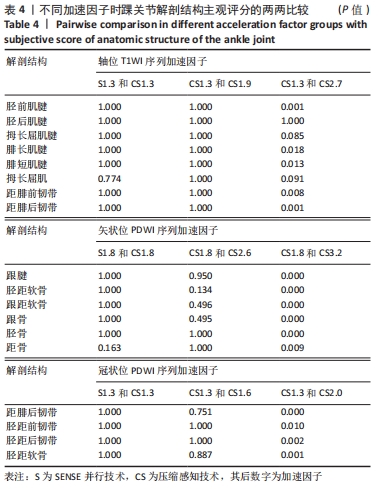
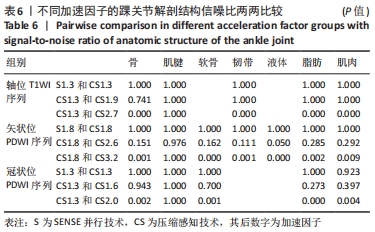
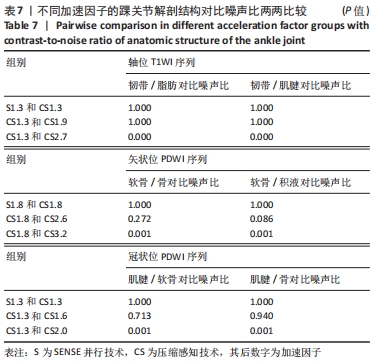
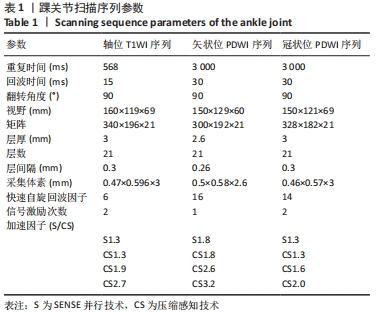
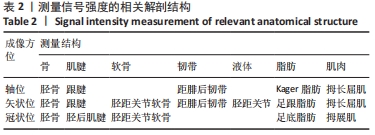
[1] CREMA MD, KRIVOKAPIC B, GUERMAZI A, et al. MRI of ankle sprain: the association between joint effusion and structural injury severity in a large cohort of athletes. Eur Radiol. 2019;29(11):6336-6344.
[2] SIRIWANARANGSUN P, BAE WC, STATUM S, et al. Advanced MRI Techniques for the Ankle. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017;209(3):511-524.
[3] FRITZ B, FRITZ J, SUTTER R. 3D MRI of the Ankle: A Concise State-of-the-Art Review. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2021;25(3):514-526.
[4] GERSING AS, BODDEN J, NEUMANN J, et al. Accelerating anatomical 2D turbo spin echo imaging of the ankle using compressed sensing. Eur J Radiol. 2019;118(9):277-284.
[5] JASPAN ON, FLEYSHER R, LIPTON ML. Compressed sensing MRI: a review of the clinical literature. Br J Radiol. 2015;88(1056):20150487.
[6] HOLLINGSWORTH KG. Reducing acquisition time in clinical MRI by data undersampling and compressed sensing reconstruction. Phys Med Biol. 2015;60(21):297-322.
[7] KLAAS PP, MARKUS W, MARKUS BS, et al. SENSE: Sensitivity Encoding for Fast MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1999;42(5):952-962.
[8] LUSTIG M, DONOHO D, PAULY JM. Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2007;58(6):1182-1195.
[9] DONOHO DL. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans Inf Theory. 2006;52(4): 1289-1306.
[10] DESHMANE A, GULANI V, GRISWOLD MA, et al. Parallel MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;36(1):55-72.
[11] NOTOHAMIPRODJO M, KUSCHEL B, HORNG A, et al. 3D-MRI of the ankle with optimized 3D-SPACE. Invest Radiol. 2012;47(4):231-239.
[12] KIM HS, YOON YC, KWON JW, et al. Qualitative and quantitative assessment of isotropic ankle magnetic resonance imaging: three-dimensional isotropic intermediate-weighted turbo spin echo versus three-dimensional isotropic fast field echo sequences. Korean J Radiol. 2012;13(4):443-449.
[13] DIETRICH O, RAYA JG, REEDER SB, et al. Measurement of signal-to-noise ratios in MR images: influence of multichannel coils, parallel imaging, and reconstruction filters. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;26(2):375-385.
[14] GOERNER FL, CLARKE GD. Measuring signal-to-noise ratio in partially parallel imaging MRI. Med Phys. 2011;38(9):5049-5057.
[15] LI X, HUANG W, ROONEY WD. Signal-to-noise ratio, contrast-to-noise ratio and pharmacokinetic modeling considerations in dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;30(9):1313-1322.
[16] FONG DT, HONG Y, CHAN LK, et al. A systematic review on ankle injury and ankle sprain in sports. Sports Med. 200;37(1):73-94.
[17] TAKATSU Y, KYOTANI K, UEYAMA T, et al. Assessment of the Quality of Breast MR Imaging Using the Modified Dixon Method and Frequency-Selective Fat Suppression: A Phantom Study. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2018;17(4):350-355.
[18] CANDES EJ, ROMBERG JK, TAO T. Stable signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements. Commun Pure Appl Math. 2006;59(8):1207-1223.
[19] CRAVEN D, MCGINLEY B, KILMARTIN L, et al. Compressed sensing for bioelectric signals: a review. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2015;19(2): 529-540.
[20] VRANIC JE, CROSS NM, WANG Y, et al. Compressed Sensing-Sensitivity Encoding (CS-SENSE) Accelerated Brain Imaging: Reduced Scan Time without Reduced Image Quality. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019;40(1): 92-98.
[21] MOLNAR U, NIKOLOV J, NIKOLIĆ O, et al. Diagnostic quality assessment of compressed SENSE accelerated magnetic resonance images in standard neuroimaging protocol: Choosing the right acceleration. Phys Medica. 2021;88:158-166.
[22] LI B, LI H, KONG H, et al. Compressed sensing based simultaneous black- and gray-blood carotid vessel wall MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;38(4):214-223.
[23] PARK CJ, CHA J, AHN SS, et al. Contrast-Enhanced High-Resolution Intracranial Vessel Wall MRI with Compressed Sensing: Comparison with Conventional T1 Volumetric Isotropic Turbo Spin Echo Acquisition Sequence. Korean J Radiol. 2020;21(12):1334-1344.
[24] YOON JK, KIM MJ, LEE S. Compressed Sensing and Parallel Imaging for Double Hepatic Arterial Phase Acquisition in Gadoxetate-Enhanced Dynamic Liver Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Invest Radiol. 2019;54(6): 374-382.
[25] ZIBETTI MVW, SHARAFI A, OTAZO R, et al. Compressed sensing acceleration of biexponential 3D-T(1ρ) relaxation mapping of knee cartilage. Magn Reson Med. 2019;81(2):863-880.
[26] ZIBETTI MVW, JOHNSON PM, SHARAFI A, et al. Rapid mono and biexponential 3D-T(1ρ) mapping of knee cartilage using variational networks. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):19144.
[27] ZIBETTI MVW, SHARAFI A, OTAZO R, et al. Accelerated mono- and biexponential 3D-T1ρ relaxation mapping of knee cartilage using golden angle radial acquisitions and compressed sensing. Magn Reson Med. 2020;83(4):1291-1309.
[28] ZEILINGER MG, WIESMüLLER M, FORMAN C, et al. 3D Dixon water-fat LGE imaging with image navigator and compressed sensing in cardiac MRI. Eur Radiol. 2021;31(6):3951-3961.
[29] 魏强,王家正,伊东娜,等.结合压缩感知技术与敏感度编码的3D mDixon序列以及3D Vane序列对肝脏成像的影响的对比研究[J].磁共振成像,2020,11(9):781-785.
[30] 李爽,陆敏杰,赵世华.压缩感知技术及其在心脏磁共振中的应用进展[J].磁共振成像,2018,9(4):299-302.
[31] WORTERS PW, SUNG K, STEVENS KJ, et al. Compressed-sensing multispectral imaging of the postoperative spine. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;37(1):243-248.
[32] TAKATO Y, HATA H, INOUE Y, et al. Evaluation of a novel reconstruction method based on the compressed sensing technique: Application to cervical spine MR imaging. Clin Imaging. 2019;56:140-145.
[33] MORITA K, NAKAURA T, MARUYAMA N, et al. Hybrid of Compressed Sensing and Parallel Imaging Applied to Three-dimensional Isotropic T(2)-weighted Turbo Spin-echo MR Imaging of the Lumbar Spine . Magn Reson Med Sci. 2020;19(1):48-55.
[34] VASANAWALA SS, ALLEY MT, HARGREAVES BA, et al. Improved pediatric MR imaging with compressed sensing. Radiology. 2010;256(2):607-616.
[35] IUGA AI, ABDULLAYEV N, WEISS K, et al. Accelerated MRI of the knee. Quality and efficiency of compressed sensing. Eur J Radiol. 2020;132: 109273.
[36] KIJOWSKI R, ROSAS H, SAMSONOV A, et al. Knee imaging: Rapid three-dimensional fast spin-echo using compressed sensing. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;45(6):1712-1722.
[37] BAUR OL, DEN HARDER JM, HEMKE R, et al. The road to optimal acceleration of Dixon imaging and quantitative T2-mapping in the ankle using compressed sensing and parallel imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2020;132: 109295.
[38] MATCUK GR, GROSS JS, FIELDS BKK, et al. Compressed Sensing MR Imaging (CS-MRI) of the Knee: Assessment of Quality, Inter-reader Agreement, and Acquisition Time. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2020;19(3):254-258.
[39] DELATTRE BMA, BOUDABBOUS S, HANSEN C, et al. Compressed sensing MRI of different organs: ready for clinical daily practice? Eur Radiol. 2020;30(1):308-319.
[40] SARTORETTI T, REISCHAUER C, SARTORETTI E, et al. Common artefacts encountered on images acquired with combined compressed sensing and SENSE. Insights Imaging. 2018;9(6):1107-1115.
|