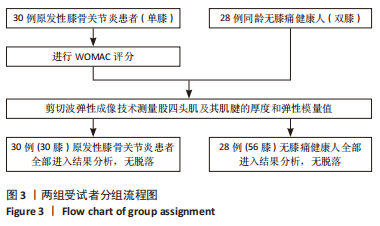
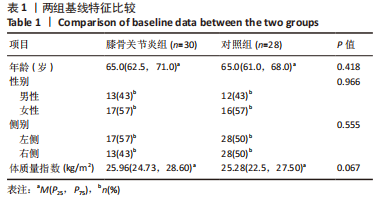
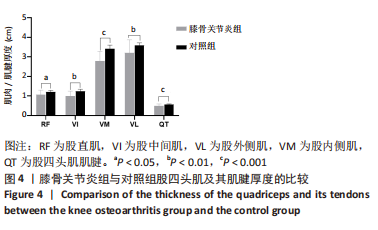
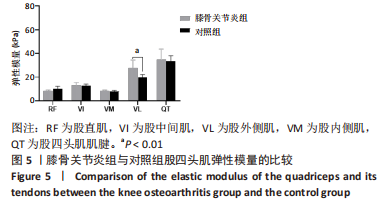
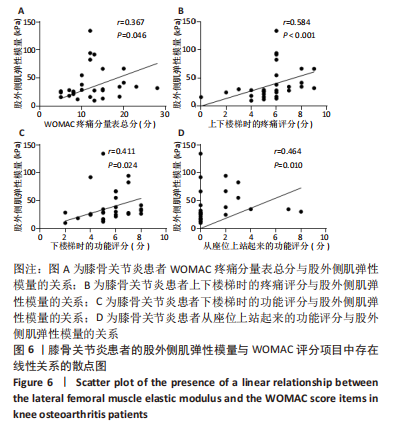
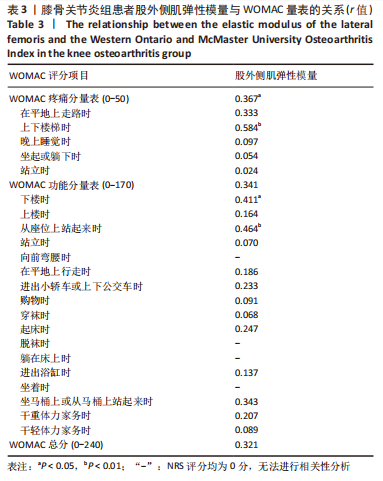
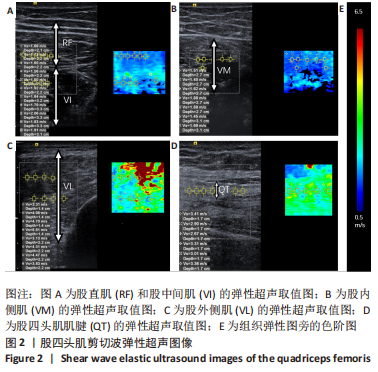
[1] BARNETT R. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2018;391(10134):1985.
[2] GOFF AJ, ELKINS MR. Knee osteoarthritis. J Physiother. 2021;67(4):240-241.
[3] HSU H, SIWIEC RM. Knee Osteoarthritis//StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2022.
[4] SEN R, HURLEY JA. Osteoarthritis//StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2022.
[5] FABBRI E, ZOLI M, GONZALEZ-FREIRE M, et al. Aging and Multimorbidity: New Tasks, Priorities, and Frontiers for Integrated Gerontological and Clinical Research. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2015;16(8):640-647.
[6] BONEWALD L. Use it or lose it to age: A review of bone and muscle communication. Bone. 2019;120:212-218.
[7] EBIHARA B, MUTSUZAKI H, FUKAYA T. Relationships between Quadriceps Tendon Elasticity and Knee Flexion Angle in Young Healthy Adults. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019;55(2):53.
[8] ALNAQEEB MA, AL ZAID NS, GOLDSPINK G. Connective tissue changes and physical properties of developing and ageing skeletal muscle. J Anat. 1984;139(Pt 4):677-689.
[9] SEGAL NA, GLASS NA. Is quadriceps muscle weakness a risk factor for incident or progressive knee osteoarthritis? Phys Sportsmed. 2011; 39(4):44-50.
[10] ØIESTAD BE, JUHL CB, EITZEN I, et al. Knee extensor muscle weakness is a risk factor for development of knee osteoarthritis. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(2):171-177.
[11] VÅRBAKKEN K, LORÅS H, NILSSON KG, et al. Relative difference in muscle strength between patients with knee osteoarthritis and healthy controls when tested bilaterally and joint-inclusive: an exploratory cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):593.
[12] KEMNITZ J, WIRTH W, ECKSTEIN F, et al. The role of thigh muscle and adipose tissue in knee osteoarthritis progression in women: data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(9):1190-1195.
[13] YAMAUCHI K, SUZUKI S, KATO C, et al. Atrophy of individual thigh muscles measured by MRI in older adults with knee osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional study. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2020;63(1):38-45.
[14] NOEHREN B, KOSMAC K, WALTON RG, et al. Alterations in quadriceps muscle cellular and molecular properties in adults with moderate knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(10):1359-1368.
[15] FINK B, EGL M, SINGER J, et al. Morphologic changes in the vastus medialis muscle in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(11):3626-3633.
[16] RYU J, JEONG WK. Current status of musculoskeletal application of shear wave elastography. Ultrasonography. 2017;36(3):185-197.
[17] 卞东林,王学梅,黄崑.实时剪切波弹性成像对跟腱生物力学的评估及其临床应用[J].中华超声影像学杂志,2014,23(6):545-546.
[18] PEDERSEN M, FREDBERG U, LANGBERG H. Sonoelastography as a diagnostic tool in the assessment of musculoskeletal alterations: a systematic review. Ultraschall Med. 2012;33(5):441-446.
[19] 林晓君,李振洲,王慧芳.剪切波弹性成像在肌肉骨骼系统检测中的应用进展[J].临床超声医学杂志,2018,20(12):835-837.
[20] 郑乙,陈国材,邹玉婵,等.剪切波弹性成像评价女性膝骨关节炎患者股四头肌弹性模量变化[J].河北医学,2019,25(10):1634-1638.
[21] Recommendations for the medical management of osteoarthritis of the hip and knee: 2000 update. American College of Rheumatology Subcommittee on Osteoarthritis Guidelines. Arthritis Rheum. 2000; 43(9):1905-1915.
[22] MENKES CJ. Radiographic criteria for classification of osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1991;27:13-15.
[23] SIGRIST RMS, LIAU J, KAFFAS AE, et al. Ultrasound Elastography: Review of Techniques and Clinical Applications. Theranostics. 2017;7(5):1303-1329.
[24] HOCHBERG MC, ALTMAN RD, BRANDT KD, et al. Guidelines for the medical management of osteoarthritis. Part II. Osteoarthritis of the knee. American College of Rheumatology. Arthritis Rheum. 1995; 38(11):1541-1546.
[25] WEN J, WANG Y, JIANG W, et al. Quantitative Evaluation of Denervated Muscle Atrophy with Shear Wave Ultrasound Elastography and a Comparison with the Histopathologic Parameters in an Animal Model. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2018;44(2):458-466.
[26] SMITH SL, WOODBURN J, STEULTJENS MPM. Sex- and osteoarthritis-related differences in muscle co-activation during weight-bearing tasks. Gait Posture. 2020;79:117-125.
[27] SMITH SL, ALLAN R, MARREIROS SP, et al. Muscle Co-Activation Across Activities of Daily Living in Individuals With Knee Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2019;71(5):651-660.
[28] LI F, WANG ZY, ZHANG ZJ et al. In Hamstring Muscles of Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis an Increased Ultrasound Shear Modulus Indicates a Permanently Elevated Muscle Tonus. Front Physiol. 2022;12:752455.
[29] VÅRBAKKEN K, LORÅS H, NILSSON KG, et al. Relative difference in muscle strength between patients with knee osteoarthritis and healthy controls when tested bilaterally and joint-inclusive: an exploratory cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):593.
[30] FUKAYA T, MUTSUZAKI H, NAKANO W, et al. Characteristics of frontal plane lower limb movement during walking in patients with knee osteoarthritis of varying severity. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019;27(2):2309499019848085.
[31] EBIHARA B, MUTSUZAKI H, FUKAYA T, et al. Influence of the Amount of Change in Quadriceps Tendon Young’s Modulus on Amount of Change in Walking Speed before and after Total Knee Arthroplasty. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(12):1329.
[32] EBIHARA B, MUTSUZAKI H, FUKAYA T, et al. Interpretation of causal relationship between quadriceps tendon Young’s modulus and gait speed by structural equation modeling in patients with severe knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2021;29(2): 23094990211034003. |