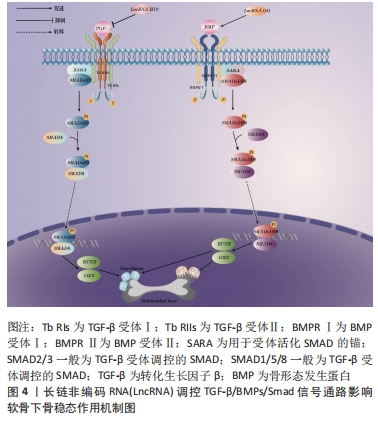
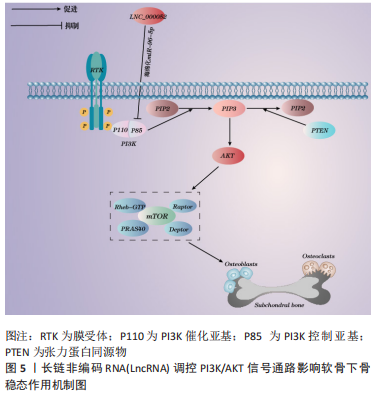
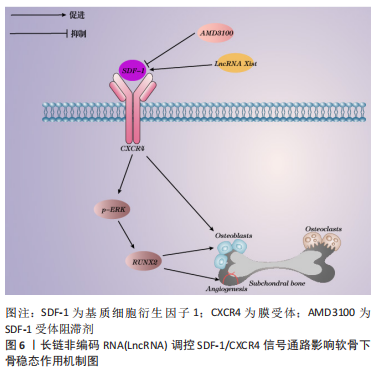
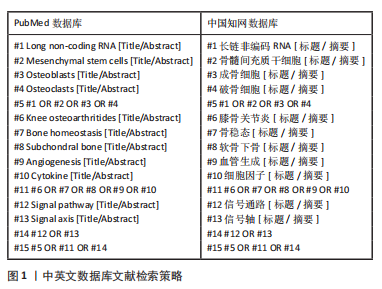
[1] ZHOU J, ZHONG P, LIAO Y, et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates subchondral bone deterioration and inhibits cartilage degeneration in ovariectomised rats. Acupunct Med. 2018;36(1):37-43.
[2] ALNAJJAR FA, SHARMA-Oates A, WIJESINGHE SN, et al. The Expression and Function of Metastases Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript-1 Long Non-Coding RNA in Subchondral Bone and Osteoblasts from Patients with Osteoarthritis. Cells. 2021;10(4):786.
[3] WANG J, SUN Y, LIU J, et al. Roles of long non coding RNA in osteoarthritis (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2021;48(1):133.
[4] GOLDRIN MB, GOLDRING SR. Articular cartilage and subchondral bone in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192: 230-237.
[5] CABAHUG-ZUCKEERMAN P, FRIKHA-BENAYDE D, MAJESKA RJ, et al. Osteocyte Apoptosis Caused by Hindlimb Unloading is Required to Trigger Osteocyte RANKL Production and Subsequent Resorption of Cortical and Trabecular Bone in Mice Femurs. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(7):1356-1365.
[6] PLOTKIN LI, GORTAZAR AR, DAVIS HM, et al. Inhibition of osteocyte apoptosis prevents the increase in osteocytic receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand (RANKL) but does not stop bone resorption or the loss of bone induced by unloading. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(31):18934-18942.
[7] JAKAITE L, SCHETININ V, HLADUVKA J, et al. Deep learning for early detection of pathological changes in X-ray bone microstructures: case of osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):2294.
[8] TUERLINGS M, VAN HOOLWERFF M, VAN BOKKUM JM, et al. Long non-coding RNA expression profiling of subchondral bone reveals AC005165.1 modifying FRZB expression during osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022;61(7):3023-3032.
[9] IKEBUCHI Y, AOKI S, HONMA M, et al. Coupling of bone resorption and formation by RANKL reverse signalling. Nature. 2018;561(7722):195-200.
[10] BERTUGLIA A, LACOURT M, GIRARD C, et al. Osteoclasts are recruited to the subchondral bone in naturally occurring post-traumatic equine carpal osteoarthritis and may contribute to cartilage degradation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(3):555-566.
[11] TAKAYANAGI H, KIM S, KOGA T,et al. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 2002;3(6):889-901.
[12] LEE CP, HUANG YN, NITHIYANANTHAM S, et al. LncRNA-Jak3:Jak3 coexpressed pattern regulates monosodium urate crystal-induced osteoclast differentiation through Nfatc1/Ctsk expression. Environ Toxicol. 2019;34(2):179-187.
[13] BRYCE PJ, OYOSHI MK, KAWAMOTO S, et al. TRAF1 regulates Th2 differentiation, allergic inflammation and nuclear localization of the Th2 transcription factor, NIP45. Int Immunol. 2006;18(1):101-111.
[14] SHANMUGARAJAN S, HAYCRAFT CJ, REDDY SV, et al. NIP45 negatively regulates RANK ligand induced osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(4):1274-1281.
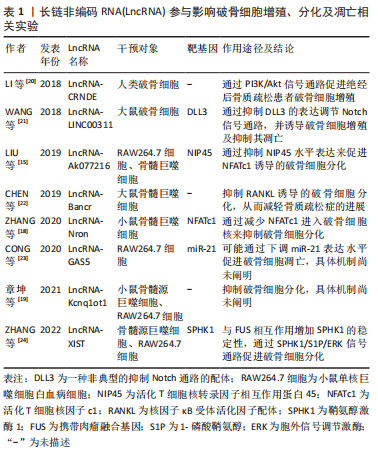
[15] LIU C, CAO Z, BAI Y, et al. LncRNA AK077216 promotes RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via NFATc1 by inhibition of NIP45. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(2):1606-1617.
[16] HANSEN TB, JENSEN TI, CLAUSEN BH, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495(7441):384-388.
[17] LING L, HU HL, LIU KY, et al. Long noncoding RNA MIRG induces osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in osteoporosis through negative regulation of miR-1897. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019; 23(23):10195-10203.
[18] ZHANG R, LI J, LI G, et al. LncRNA Nron regulates osteoclastogenesis during orthodontic bone resorption. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):14.
[19] 章坤,时哲敏,任怡,等.长链非编码RNA Kcnqlot1促进成骨细胞分化和抑制破骨细胞分化[J].南方医科大学学报,2021,41(1):31-38.
[20] LI W, ZHU HM, XU HD, et al. CRNDE impacts the proliferation of osteoclast by estrogen deficiency in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(18):5815-5821.
[21] WANG Y, LUO TB, LIU L, et al. LncRNA LINC00311 Promotes the Proliferation and Differentiation of Osteoclasts in Osteoporotic Rats Through the Notch Signaling Pathway by Targeting DLL3. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(6):2291-2306.
[22] CHEN RS, ZHANG XB, ZHU XT, et al. LncRNA Bmncr alleviates the progression of osteoporosis by inhibiting RANML-induced osteoclast differentiation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(21):9199-9206.
[23] CONG C, TIAN J, GAO T, et al. lncRNA GAS5 Is Upregulated in Osteoporosis and Downregulates miR-21 to Promote Apoptosis of Osteoclasts. Clin Interv Aging. 2020;15:1163-1169.
[24] ZHANG DW, WANG HG, ZHANG KB, et al. LncRNA XIST facilitates S1P-mediated osteoclast differentiation via interacting with FUS. J Bone Miner Metab. 2022;40(2):240-250.
[25] 路冬冬,朱天峰,张一健,等.3D生物打印甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶支架促进软骨下骨缺损的修复[J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(34):5454-5460.
[26] WANG P, DONG R, WANG B, et al. Genome-wide microRNA screening reveals miR-582-5p as a mesenchymal stem cell-specific microRNA in subchondral bone of the human knee joint. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(12):21877-21888.
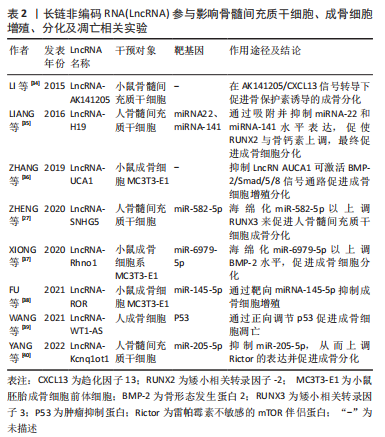
[27] ZHENG J, GUO H, QIN Y, et al. SNHG5/miR-582-5p/RUNX3 feedback loop regulates osteogenic differentiation and apoptosis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2020. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29527.
[28] HUANG G, KANG Y, HUANG Z, et al. Identification and Characterization of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(3):1037-1050.
[29] WU Y, JIANG Y, LIU Q, et al. lncRNA H19 promotes matrix mineralization through up-regulating IGF1 by sponging miR-185-5p in osteoblasts. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(1):48.
[30] ZHU J, SHIMIZU E, ZHANG X, et al. EGFR signaling suppresses osteoblast differentiation and inhibits expression of master osteoblastic transcription factors Runx2 and Osterix. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(7): 1749-1760.
[31] LIAN WS, WU RW, LEE MS, et al. Subchondral mesenchymal stem cells from osteoarthritic knees display high osteogenic differentiation capacity through microRNA-29a regulation of HDAC4. J Mol Med (Berl). 2017;95(12):1327-1340.
[32] YANG Q, YAO Y, ZHAO D, et al. LncRNA H19 secreted by umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells through microRNA-29a-3p/FOS axis for central sensitization of pain in advanced osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(3):1245-1256.
[33] XIAO X, ZHOU T, GUO S, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 sponges miR-204 to promote osteoblast differentiation of human aortic valve interstitial cells through up-regulating Smad4. Int J Cardiol. 2017;243:404-412.
[34] LI H, ZHANG Z, CHEN Z, et al. Osteogenic growth peptide promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells mediated by LncRNA AK141205-induced upregulation of CXCL13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;466(1):82-88.
[35] LIANG WC, FU WM, WANG YB, et al. H19 activates Wnt signaling and promotes osteoblast differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20121.
[36] ZHANG RF, LIU JW, YU SP, et al. LncRNA UCA1 affects osteoblast proliferation and differentiation by regulating BMP-2 expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(16):6774-6782.
[37] XIONG Y, CHEN L, YAN C, et al. The lncRNA Rhno1/miR-6979-5p/BMP2 Axis Modulates Osteoblast Differentiation. Int J Biol Sci. 2020; 16(9):1604-1615.
[38] FU Y, HU X, GAO Y, et al. LncRNA ROR/miR-145-5p axis modulates the osteoblasts proliferation and apoptosis in osteoporosis. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):7714-7723.
[39] WANG C, XIE Q, SUN W, et al. lncRNA WT1-AS is upregulated in osteoporosis and regulates the apoptosis of osteoblasts by interacting with p53. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(1):734.
[40] YANG JJ, PENG WX, ZHANG MB. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes osteogenic differentiation via miR-205-5p/RICTOR axis. Exp Cell Res. 2022;415(1):113119.
[41] BURR DB, GALLANT MA. Bone remodelling in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(11):665-673.
[42] SU W, LIU G, LIU X, et al. Angiogenesis stimulated by elevated PDGF-BB in subchondral bone contributes to osteoarthritis development. JCI Insight. 2020;5(8):e135446.
[43] XIE H, CUI Z, WANG L, et al. PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis. Nat Med. 2014;20(11):1270-1278.
[44] SUFEN G, XIANGHONG Y, YONGXIA C, et al. bFGF and PDGF-BB have a synergistic effect on the proliferation, migration and VEGF release of endothelial progenitor cells. Cell Biol Int. 2011;35(5):545-551.
[45] GERBER HP, VU TH, RYAN AM, et al. VEGF couples hypertrophic cartilage remodeling, ossification and angiogenesis during endochondral bone formation. Nat Med. 1999;5(6):623-628.
[46] SU W, XIE W, SHANG Q, et al. The Long Noncoding RNA MEG3 Is Downregulated and Inversely Associated with VEGF Levels in Osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:356893.
[47] FARHANG GHAHREMANI M, GOOSSENS S, NITTNER D, et al. p53 promotes VEGF expression and angiogenesis in the absence of an intact p21-Rb pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2013;20(7):888-897.
[48] ZHOU Y, ZHONG Y, WANG Y, et al. Activation of p53 by MEG3 non-coding RNA. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(34):24731-24742.
[49] KASPIRIS A, MIKELIS C, HEROULT M, et al. Expression of the growth factor pleiotrophin and its receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta in the serum, cartilage and subchondral bone of patients with osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2013;80(4):407-413.
[50] SIN A, TANG W, WEN CY, et al. The emerging role of endothelin-1 in the pathogenesis of subchondral bone disturbance and osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;3(4):516-524.
[51] PAN L, LIU D, ZHAO L, et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury by upregulating microRNA-19b in murine chondrogenic ATDC5 cells. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(12):10165-10175.
[52] JIN L, GAO F, ZHANG L, et al. Pleiotropin enhances the osteo/dentinogenic differentiation potential of dental pulp stem cells. Connect Tissue Res. 2021;62(5):495-507.
[53] ZHUO X, WU Y, YANG Y, et al. LncRNA AK094457 promotes AngII-mediated hypertension and endothelial dysfunction through suppressing of activation of PPARγ. Life Sci. 2019;233:116745.
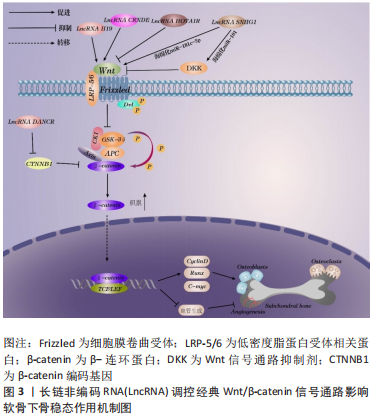
[54] WANG CG, HU YH, SU SL, et al. LncRNA DANCR and miR-320a suppressed osteogenic differentiation in osteoporosis by directly inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Exp Mol Med. 2020; 52(8):1310-1325.
[55] XIANG J, FU HQ, XU Z, et al. lncRNA SNHG1 attenuates osteogenic differentiation via the miR 101/DKK1 axis in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(5):3715-3722.
[56] YU X, RONG PZ, SONG MS, et al. lncRNA SNHG1 induced by SP1 regulates bone remodeling and angiogenesis via sponging miR-181c-5p and modulating SFRP1/Wnt signaling pathway. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):141.
[57] SHEN JJ, ZHANG CH, CHEN ZW, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR inhibited osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(17):7232-7246.
[58] DING Q, MO F, CAI X, et al. LncRNA CRNDE is activated by SP1 and promotes osteosarcoma proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(5-6):3358-3371.
[59] HUANG Y, ZHENG Y, JIA L, et al. Long Noncoding RNA H19 Promotes Osteoblast Differentiation Via TGF-β1/Smad3/HDAC Signaling Pathway by Deriving miR-675. Stem Cells. 2015;33(12):3481-3492.
[60] SHEN H. LncRNA-OG Promotes the Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Under the Regulation of hnRNPK. Stem Cells. 2019;37(2):270-283.
[61] LIN C, SHAO Y, ZENG C, et al. Blocking PI3K/AKT signaling inhibits bone sclerosis in subchondral bone and attenuates post-traumatic osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(8):6135-6147.
[62] 林创鑫. 软骨下骨PI3K/AKT/mTORC1信号通路活性在骨关炎发病中的作用及机制研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2018.
[63] LI M, CONG R, YANG L, et al. A novel lncRNA LNC_000052 leads to the dysfunction of osteoporotic BMSCs via the miR-96-5p-PIK3R1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(9):795.
[64] QIN H, ZHAO X, HU YJ, et al. Inhibition of SDF-1/CXCR4 Axis to Alleviate Abnormal Bone Formation and Angiogenesis Could Improve the Subchondral Bone Microenvironment in Osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:8852574.
[65] 段亚妮,木拉提·阿比来列提,朱雁秋,等.LncRNA Xist通过调控SDF-1/CXCR4轴促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖与迁移[J].中山大学学报(医学版),2020,41(1):37-43. |