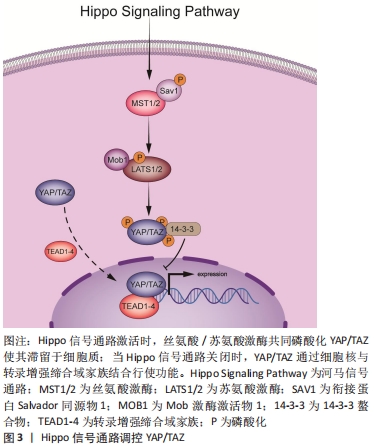
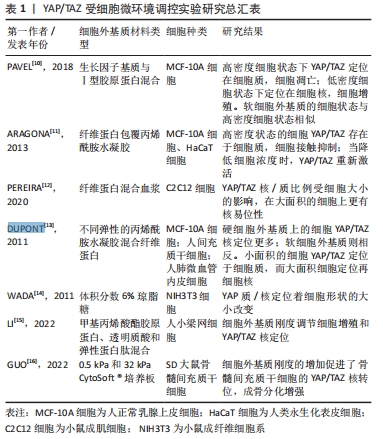
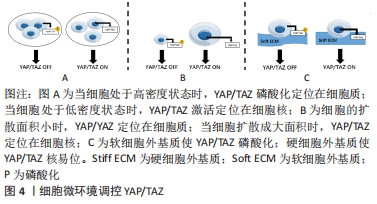
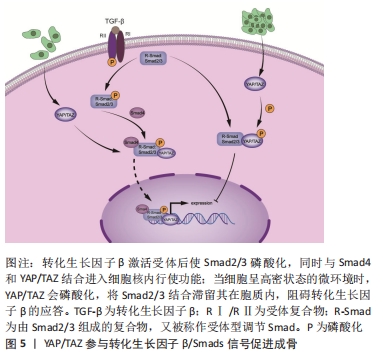
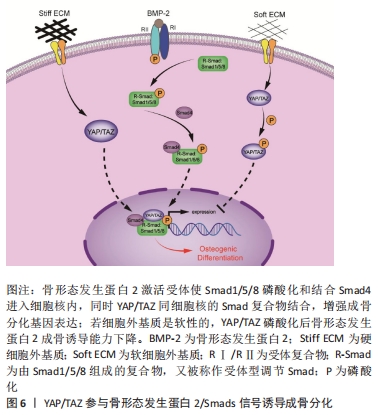
[1] QIN L, LIU W, CAO H, et al. Molecular mechanosensors in osteocytes. Bone Res. 2020;8:23.
[2] MOYA I M, HALDER G. Hippo-YAP/TAZ signalling in organ regeneration and regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(4):211-226.
[3] KOVAR H, BIERBAUMER L, RADIC-SARIKAS B. The YAP/TAZ Pathway in Osteogenesis and Bone Sarcoma Pathogenesis. Cells. 2020;9(4):972.
[4] HARVEY KF, PFLEGER CM, HARIHARAN IK. The Drosophila mst ortholog, hippo, restricts growth and cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Cell. 2003;114(4):457-467.
[5] ZHAO B, WEI X, LI W, et al. Inactivation of YAP oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev. 2007;21(21):2747-2761.
[6] ALSAMMAN S, CHRISTENSON SA, YU A, et al. Targeting acid ceramidase inhibits YAP/TAZ signaling to reduce fibrosis in mice. Sci Transl Med. 2020;12(557):eaay8798.
[7] STEIN C, BARDET AF, ROMA G, et al. YAP1 exerts its transcriptional control via TEAD-mediated activation of enhancers. PLoS Genet. 2015; 11(8):e1005465.
[8] ZHANG H, LIU CY, ZHA ZY, et al. TEAD transcription factors mediate the function of TAZ in cell growth and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(20):13355-13362.
[9] VOLTES A, HEVIA CF, ENGEL-PIZCUETA C, et al. Yap/Taz-TEAD activity links mechanical cues to progenitor cell behavior during zebrafish hindbrain segmentation. Development. 2019;146(14):dev176735.
[10] PAVEL M, RENNA M, PARK SJ, et al. Contact inhibition controls cell survival and proliferation via YAP/TAZ-autophagy axis. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):2961.
[11] ARAGONA M, PANCIERA T, MANFRIN A, et al. A mechanical checkpoint controls multicellular growth through YAP/TAZ regulation by actin-processing factors. Cell. 2013;154(5):1047-1059.
[12] PEREIRA D, RICHERT A, MEDJKANE S, et al. Cell geometry and the cytoskeleton impact the nucleo-cytoplasmic localisation of the SMYD3 methyltransferase. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):20598.
[13] DUPONT S, MORSUT L, ARAGONA M, et al. Role of YAP/TAZ in mechanotransduction. Nature. 2011;474(7350):179-183.
[14] WADA K, ITOGA K, OKANO T, et al. Hippo pathway regulation by cell morphology and stress fibers. Development. 2011;138(18):3907-3914.
[15] LI H, RAGHUNATHAN V, STAMER W D, et al. Extracellular matrix stiffness and TGFβ2 regulate YAP/TAZ activity in human trabecular meshwork cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:844342.
[16] GUO Y, QIAO Y, QUAN S, et al. Relationship of matrix stiffness and cell morphology in regulation of osteogenesis and adipogenesis of BMSCs. Mol Biol Rep. 2022;49(4):2677-2685.
[17] YANG X, CHEN Z, CHEN C, et al. Bleomycin induces fibrotic transformation of bone marrow stromal cells to treat height loss of intervertebral disc through the TGFβR1/Smad2/3 pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):34.
[18] KIM MS, JIN W. TrkB-induced inhibition of R-SMAD/SMAD4 activation is essential for TGF-β-mediated tumor suppressor activity. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(4):1048.
[19] STRASEN J, SARMA U, JENTSCH M, et al. Cell-specific responses to the cytokine TGFβ are determined by variability in protein levels. Mol Syst Biol. 2018;14(1):e7733.
[20] LABIBI B, BASHKUROV M, WRANA JL, et al. Modeling the control of TGF-β/Smad nuclear accumulation by the hippo pathway effectors, Taz/Yap. iScience. 2020;23(8):101416.
[21] HIEMER SE, SZYMANIAK AD, VARELAS X. The transcriptional regulators TAZ and YAP direct transforming growth factor β-induced tumorigenic phenotypes in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(19):13461-13474.
[22] VARELAS X, SAMAVARCHI-TEHRANI P, NARIMATSU M, et al. The Crumbs complex couples cell density sensing to Hippo-dependent control of the TGF-β-SMAD pathway. Dev Cell. 2010;19(6):831-844.
[23] SZETO SG, NARIMATSU M, LU M, et al. YAP/TAZ are mechanoregulators of TGF-β-Smad signaling and renal fibrogenesis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(10):3117-3128.
[24] LIU W, CUI Y, SUN J, et al. Transforming growth factor-β1 up-regulates connexin43 expression in osteocytes via canonical Smad-dependent signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(6):BSR20181678.
[25] QIN Z, XIA W, FISHER GJ, et al. YAP/TAZ regulates TGF-β/Smad3 signaling by induction of Smad7 via AP-1 in human skin dermal fibroblasts. Cell Commun Signal. 2018;16(1):18.
[26] MIRANDA MZ, BIALIK JF, SPEIGHT P, et al. TGF-β1 regulates the expression and transcriptional activity of TAZ protein via a Smad3-independent, myocardin-related transcription factor-mediated mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(36):14902-14920.
[27] UEMURA M, NAGASAWA A, TERAI K. Yap/Taz transcriptional activity in endothelial cells promotes intramembranous ossification via the BMP pathway. Sci Rep. 2016;6:27473.
[28] PARK JS, KIM M, SONG NJ, et al. A Reciprocal Role of the Smad4-Taz Axis in Osteogenesis and Adipogenesis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells. 2019;37(3):368-381.
[29] LEE E, KO JY, KIM J, et al. Osteogenesis and angiogenesis are simultaneously enhanced in BMP2-/VEGF-transfected adipose stem cells through activation of the YAP/TAZ signaling pathway. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(11):4588-602.
[30] KOPF J, PETERSEN A, DUDA GN, et al. BMP2 and mechanical loading cooperatively regulate immediate early signalling events in the BMP pathway. BMC Biol. 2012;10:37.
[31] KLOSTERHOFF BS, VANTUCCI CE, KAISER J, et al. Effects of osteogenic ambulatory mechanical stimulation on early stages of BMP-2 mediated bone repair. Connect Tissue Res. 2022;63(1):16-27.
[32] DENG M, LIU P, XIAO H, et al. Improving the osteogenic efficacy of BMP2 with mechano growth factor by regulating the signaling events in BMP pathway. Cell Tissue Res. 2015;361(3):723-731.
[33] WEI Q, HOLLE A, LI J, et al. BMP-2 Signaling and mechanotransduction synergize to drive osteogenic differentiation via YAP/TAZ. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(15):1902931.
[34] MATSUMOTO Y, LA ROSE J, KENT OA, et al. Reciprocal stabilization of ABL and TAZ regulates osteoblastogenesis through transcription factor RUNX2. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(12):4482-4496.
[35] YANG JH, KIM SC, KIM KM, et al. Isorhamnetin attenuates liver fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β/Smad signaling and relieving oxidative stress. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;783:92-102.
[36] KOMATSU N, KAJIYA M, MOTOIKE S, et al. Type I collagen deposition via osteoinduction ameliorates YAP/TAZ activity in 3D floating culture clumps of mesenchymal stem cell/extracellular matrix complexes. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):342.
[37] LORTHONGPANICH C, THUMANU K, TANGKIETTRAKUL K, et al. YAP as a key regulator of adipo-osteogenic differentiation in human MSCs. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):402.
[38] KEGELMAN CD, COULOMBE JC, JORDAN KM, et al. YAP and TAZ mediate osteocyte perilacunar/canalicular remodeling. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(1):196-210.
[39] ZHAO G, HUANG B L, RIGUEUR D, et al. CYR61/CCN1 regulates sclerostin levels and bone maintenance. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(6): 1076-1089.
[40] ZARKA M, ETIENNE F, BOURMAUD M, et al. Mechanical loading activates the YAP/TAZ pathway and chemokine expression in the MLO-Y4 osteocyte-like cell line. Lab Invest. 2021;101(12):1597-1604.
[41] SCHLUNDT C, EL KHASSAWNA T, SERRA A, et al. Macrophages in bone fracture healing: Their essential role in endochondral ossification. Bone. 2018;106:78-89.
[42] ZHANG F, HUAN L, XU T, et al. Inflammatory macrophages facilitate mechanical stress-induced osteogenesis. Aging (Albany NY). 2020; 12(4):3617-3625.
[43] ATCHA H, MELI VS, DAVIS CT, et al. Crosstalk between CD11b and Piezo1 mediates macrophage responses to mechanical cues. Front Immunol. 2021;12:689397.
[44] ATCHA H, JAIRAMAN A, HOLT JR, et al. Mechanically activated ion channel Piezo1 modulates macrophage polarization and stiffness sensing. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):3256.
[45] DONG L, SONG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Mechanical stretch induces osteogenesis through the alternative activation of macrophages. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(9):6376-6390.
[46] MCDONALD MM, KHOO WH, NG PY, et al. Osteoclasts recycle via osteomorphs during RANKL-stimulated bone resorption. Cell. 2021; 184(5):1330-1347.
[47] ZHAO L, GUAN H, SONG C, et al. YAP1 is essential for osteoclastogenesis through a TEADs-dependent mechanism. Bone. 2018;110:177-186.
[48] YANG W, LU X, ZHANG T, et al. TAZ inhibits osteoclastogenesis by attenuating TAK1/NF-kappaB signaling. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):33.
[49] KEGELMAN CD, MASON DE, DAWAHARE JH, et al. Skeletal cell YAP and TAZ combinatorially promote bone development. FASEB J. 2018; 32(5):2706-2721.
[50] XIONG J, ALMEIDA M, O’BRIEN CA. The YAP/TAZ transcriptional co-activators have opposing effects at different stages of osteoblast differentiation. Bone. 2018;112:1-9.
[51] VANYAI HK, PRIN F, GUILLERMIN O, et al. Control of skeletal morphogenesis by the Hippo-YAP/TAZ pathway. Development. 2020; 147(21):dev187187.
[52] LI Y, YANG S, QIN L, et al. TAZ is required for chondrogenesis and skeletal development. Cell Discov. 2021;7(1):26.
[53] WANG L, MISHINA Y, LIU F. Osterix-Cre transgene causes craniofacial bone development defect. Calcif Tissue Int. 2015;96(2):129-137.
[54] WANG J, XIAO Y, HSU CW, et al. Yap and Taz play a crucial role in neural crest-derived craniofacial development. Development. 2016; 143(3):504-515.
[55] WILLIAMSON KA, RAINGER J, FLOYD JA, et al. Heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in YAP1 cause both isolated and syndromic optic fissure closure defects. Am J Hum Genet. 2014;94(2):295-302.
[56] GOODWIN AF, CHEN CP, VO NT, et al. YAP/TAZ regulate elevation and bone formation of the mouse secondary palate. J Dent Res. 2020; 99(12):1387-1396.
|