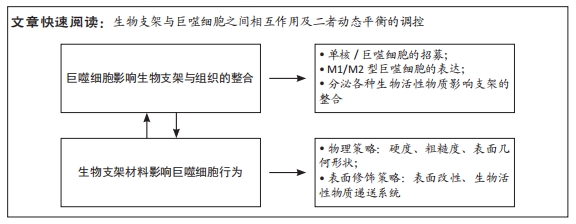
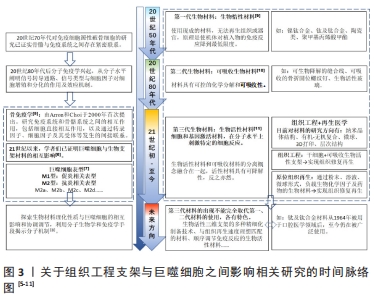
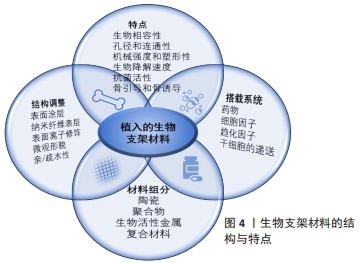
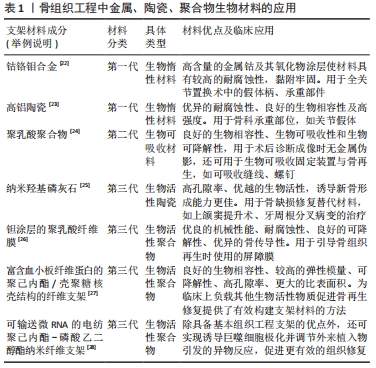
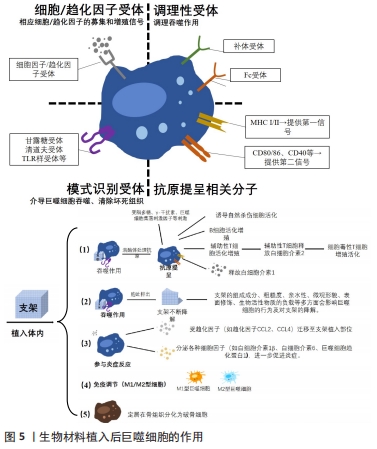
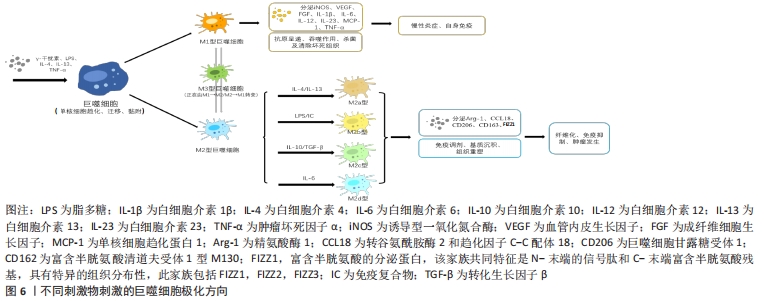
[1] YIN S, ZHANG W, ZHANG Z, et al. Recent advances in scaffold design and material for vascularized tissue-engineered bone regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(10):e1801433.
[2] VILA-PARRONDO C, GARCÍA-ASTRAIN C, LIZ-MARZÁN LM. Colloidal systems toward 3D cell culture scaffolds. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2020;283:102237.
[3] PIANTANIDA E, ALONCI G, BERTUCCI A, et al. Design of Nanocomposite Injectable Hydrogels for Minimally Invasive Surgery. Acc Chem Res. 2019;52(8):2101-2112.
[4] LI J, LI Y, GAO B, et al. Engineering mechanical microenvironment of macrophage and its biomedical applications. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2018;13(5):555-576.
[5] ARRON JR, CHOI Y. Bone versus immune system. Nature. 2000;408 (6812):535-536.
[6] YU Y, WU RX, YIN Y, et al. Directing immunomodulation using biomaterials for endogenous regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2016; 4(4):569-584.
[7] MILLS CD, KINCAID K, ALT JM, et al. M-1/M-2 macrophages and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. J Immunol. 2000;164(12):6166-6173.
[8] SHANLEY LC, MAHON OR, KELLY DJ, et al. Harnessing the innate and adaptive immune system for tissue repair and regeneration:Considering more than macrophages. Acta Biomater. 2021;133:208-221.
[9] BRÅNEMARK PI, HANSSON BO, ADELL R, et al. Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Experience from a 10-year period. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Suppl. 1977;16:1-132.
[10] HENCH LL, POLAK JM. Third-generation biomedical materials. Science. 2002;295(5557):1014-1017.
[11] NAVARRO M, MICHIARDI A, CASTAÑO O, et al. Biomaterials in orthopaedics. J R Soc Interface. 2008;5(27):1137-1158.
[12] PENG Z, ZHAO T, ZHOU Y, et al. Bone tissue engineering via carbon-based nanomaterials. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(5):e1901495.
[13] WEI F, XIAO Y. Modulation of the Osteoimmune Environment in the Development of Biomaterials for Osteogenesis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1077:69-86.
[14] 魏诗敏,汪媛婧,黄雯,等.异物反应中巨噬细胞调控在骨组织修复中的研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治,2019,27(9):591-597.
[15] CHOCHOLATA P, KULDA V, BABUSKA V. Fabrication of scaffolds for bone-tissue regeneration. Materials (Basel). 2019;12(4):568.
[16] BARBA A, DIEZ-ESCUDERO A, MAAZOUZ Y, et al. Osteoinduction by foamed and 3D-printed calcium phosphate scaffolds: effect of nanostructure and pore architecture. ACS Appl Mater Interface. 2017; 9(48):41722-41736.
[17] DASILVABRUM I, DECARVALHO JJ, DASILVAPIRES JL, et al. Nanosized hydroxyapatite and β-tricalcium phosphate composite: physico-chemical, cytotoxicity, morphological properties and in vivo trial. Sci Rep. 2019;9(18):77-116.
[18] MA L, CHENG S, JI X, et al. Immobilizing magnesium ions on 3D printed porous tantalum scaffolds with polydopamine for improved vascularization and osteogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;117:111303.
[19] UNAL S, ARSLAN S, YILMAZ BK, et al. Polycaprolactone/gelatin/hyaluronic acid electrospun scaffolds to mimic glioblastoma extracellular matrix. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(11):2661.
[20] LI Y, CHEN M, ZHOU W, et al. Cell-free 3D wet-electrospun PCL/silk fibroin/Sr2+ scaffold promotes successful total meniscus regeneration in a rabbit model. Acta Biomater. 2020;113(8):196-209.
[21] KIROS S, LIN S, XING M, et al. Embryonic mesenchymal multipotent cell differentiation on electrospun biodegradable poly (ester amide) scaffolds for model vascular tissue fabrication. Ann Biomed Eng. 2020; 48(3):980-991.
[22] WALKER PS, GOLD BL. The tribology (friction, lubrication and wear) of all-metal artificial hip joints. 1971. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(329 Suppl):S4-S10.
[23] CHRISTEL P, MEUNIER A, DORLOT JM, et al. Biomechanical compatibility and design of ceramic implants for orthopedic surgery. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;523:234-256.
[24] MIDDLETON JC, TIPTON AJ. Synthetic biodegradable polymers as orthopedic devices. Biomaterials. 2000;21(23):2335-2346.
[25] YANG X, LI Y, HE W, et al. Hydroxyapatite/collagen coating on PLGA electrospun fibers for osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(11):2863-2870.
[26] HWANG C, PARK S, KANG IG, et al. Tantalum-coated polylactic acid fibrous membranes for guided bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;115:111112.
[27] RASTEGAR A, MAHMOODI M, MIRJALILI M, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin-loaded PCL/chitosan core-shell fibers scaffold for enhanced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;269: 118351.
[28] LIN J, MOHAMED I, LIN PH, et al. Modulating Macrophage Phenotype by Sustained MicroRNA Delivery Improves Host-Implant Integration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(3):e1901257.
[29] DING T, KANG W, LI J, et al. An in situ tissue engineering scaffold with growth factors combining angiogenesis and osteo immunomodulatory functions for advanced periodontal bone regeneration. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19(1):247.
[30] ZHU Z, LIU Y, XUE Y, et al. Tazarotene released from aligned electrospun membrane facilitates cutaneous wound healing by promoting angiogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(39):36141-36153.
[31] QIAN J, LIN Z, LIU Y, et al. Functionalization strategies of electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. Smart Mater Med. 2021;2:260-279.
[32] ZHANG Q, BOSCH-RUÉ È, PÉREZ RA, et al. Biofabrication of tissue engineering vascular systems. APL Bioeng. 2021;5(2):021507.
[33] NOUR S, BAHEIRAEI N, IMANI R, et al. Bioactive materials: a comprehensive review on interactions with biological microenvironment based on the immune response. J Bionic Eng. 2019;16(4):563-581.
[34] CORSI F, CAROTENUTO F, DI NARDO P, et al. Harnessing inorganic nanoparticles to direct macrophage polarization for skeletal muscle regeneration. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(10):1963.
[35] NIU Y, WANG Z, SHI Y, et al. Modulating macrophage activities to promote endogenous bone regeneration: biological mechanisms and engineering approaches. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(1):244-261.
[36] GOODMAN SB, PAJARINEN J, YAO Z,et al. Inflammation and bone repair: from particle disease to tissue regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:230.
[37] LAVIN Y, WINTER D, Blecher-Gonen R, et al. Tissue-resident macrophage enhancer landscapes are shaped by the local microenvironment. Cell. 2014;159(6):1312-1326.
[38] 张艺,张晓梦,史俊宇,等.巨噬细胞极化在种植体周围组织愈合的作用及研究进展[J].口腔医学,2020,40(7):644-647.
[39] 梁蓓蕾,王佐林.巨噬细胞极化与骨组织再生关系的研究进展[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2020,30(3):187-190.
[40] GAO X, WANG YS, LI XQ, et al. Macrophages promote vasculogenesis of retinal neo vascularization in an oxygen-induced retinopathy model in mice. Cell Tissue Res. 2016;364(3):599-610.
[41] TANG H, HUSCH JFA, ZHANG Y, et al. Coculture with monocytes/macrophages modulates osteogenic differentiation of adipose‐derived mesenchymal stromal cells on poly (lactic‐co‐glycolic) acid/polycaprolactone scaffolds. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(5):785-798.
[42] 单宇华,应惜裕,张晓宇,等.巨噬细胞在β-TCP支架修复牙槽突裂中成骨作用的探讨[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2021,19(4):315-319.
[43] ZHANG YQ, YU W, BA ZY, et al. 3D-printed scaffolds of mesoporous bioglass/gliadin/polycaprolactone ternary composite for enhancement of compressive strength, degradability, cell responses and new bone tissue ingrowth. Int J Nanomed. 2018;13:5433-5447.
[44] 焦鑫,王栋梁,干耀恺.骨生物材料通过细胞途径降解的研究进展[J].生物工程学报,2020,36(2):201-209.
[45] ZHONG QW, LI WH, SU XP, et al. Degradation pattern of porous CaCO3 and hydroxyapatite microspheres in vitro and in vivo for potential application in bone tissue engineering. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016;143:56–63.
[46] GUO C, LI C, KAPLAN DL. Enzymatic degradation of bombyx mori silk materials: a review. Biomacromolecules. 2020;21(5):1678-1686.
[47] 陈泽涛,林义雄,杨杰婷,等.基于“免疫微环境调控”的屏障膜研发理念[J].口腔疾病防治,2021,29(8):505-514.
[48] KO Y, LEE G, KIM B, et al. Modification of the RANKL-RANK-binding site for the immunotherapeutic treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2020;31(5):983–993.
[49] LOU ZK, PENG Z, WANG B. et al. miR-142-5p promotes the osteoclast differentiation of bone marrow-derived macrophages via PTEN/PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 pathway. J Bone Miner Metab. 2019;37(5):815-824.
[50] 陈慧子,郭萌萌,赵娟娟,等.miR-7基因敲减对LPS诱导巨噬细胞炎症反应的影响[J].现代免疫学,2019,39(3):195-200, 216.
[51] ZHOU P, XIA D, NI Z, et al. Calcium silicate bioactive ceramics induce osteogenesis through oncostatin M. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(3):810-822.
[52] LAMICHHANE S, ANDERSON JA, VIERHOUT T, et al. Polytetrafluoroethylene topographies determine the adhesion, activation, and foreign body giant cell formation of macrophages. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(9):2441-2450.
[53] WANG YL, ZHANG YF, SCULEAN AS, et al. Macrophage behavior and interplay with gingival fibroblasts cultured on six commercially available titanium, zirconium, and titanium-zirconium dental implants. Clin Oral Investig. 2019;23(8):3219-3227.
[54] ZHENG X, XIN L, LUO Y, et al. Near-infrared-triggered dynamic surface topography for sequential modulation of macrophage phenotypes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(46):43689-43697.
[55] LI J, ZHANG YJ, LV ZY, et al. The observed difference of macrophage phenotype on different surface roughness of mineralized collagen. Regen Biomater. 2020;7(2):203-211.
[56] 张吉昊,白云洋,皇文进.电活性P(VDF-TrFE)取向纳米纤维调控巨噬细胞功能促进软组织愈合[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2021,37(8):451-455.
[57] TYLEK T, BLUM C, HRYNEVICH A, et al. Precisely defined fiber scaffolds with 40μm porosity induce elongation driven M2-like polarization of human macrophages. Biofabrication. 2020;12(2):025007.
[58] KIM YK, CHEN EY, LIU WF. Biomolecular strategies to modulate the macrophage response to implanted materials. J Mater Chem B. 2016; 4(9):1600-1609.
[59] BARATI D, WATKINS K, WANG Z, et al. Injectable and crosslinkable PLGA‐based microribbons as 3D macroporous stem cell niche. Small. 2020;16(22):1905820.
[60] TANG Y, TONG X, CONRAD B, et al. Injectable and in situ crosslinkable gelatin microribbon hydrogels for stem cell delivery and bone regenerationin vivo. Theranostics. 2020;10(13):6035-6047.
[61] TOYAMA N, TSUCHIYA S, KAMIO H, et al. The effect of macrophages on an atmospheric pressure plasma-treated titanium membrane with bone marrow stem cells in a model of guided bone regeneration. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020;31(8):70.
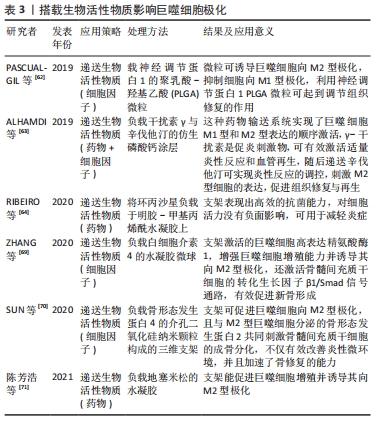
[62] PASCUAL-GIL S, ABIZANDA G, IGLESIAS E, et al. NRG1 PLGA MP locally induce macrophage polarisation toward a regenerative phenotype in the heart after acute myocardial infarction. J Drug Target. 2019; 27(5/6):573-581.
[63] ALHAMDI JR, PENG T, AL-NAGGAR IM, et al. Controlled M1-to-M2 transition of aged macrophages by calcium phosphate coatings. Biomaterials. 2019;196:90-99.
[64] RIBEIRO JS, DAGHRERY A, DUBEY N, et al. Hybrid antimicrobial hydrogel as injectable therapeutics for oral infection ablation. Biomacromolecules. 2020;21(9):3945-3956.
[65] INOUE M, MATSUMOTO C, NAKAJIMA K, et al. Alendronate/dexamethasone combination therapy worsens soft and hard tissue wound healing around implants in rat maxillae. Bone. 2021;148:115942.
[66] 李莉,卓瑾,郑玲,等.不同诱导极化方式对大鼠骨髓来源巨噬细胞增殖、凋亡及吞噬能力的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(25):4032-4037.
[67] VAGHASIYA K, ERAM A, SHARMA A, et al. Alginate microspheres elicit innate M1-inflammatory response in macrophages leading to bacillary killing. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2019;20(6):241.
[68] MORAIS AÍS, VIEIRA EG, AFEWERKI S, et al. Fabrication of polymeric microparticles by electrospray: the impact of experimental parameters. J Funct Biomater. 2020;11(1):4.
[69] ZHANG J, SHI H, ZHANG N, et al. Interleukin-4-loaded hydrogel scaffold regulates macrophages polarization to promote bone mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation via TGF-β1/Smad pathway for repair of bone defect. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(10):e12907.
[70] SUN X, MA Z, ZHAO X, et al. Three-dimensional bioprinting of multicell-laden scaffolds containing bone morphogenic protein-4 for promoting M2 macrophage polarization and accelerating bone defect repair in diabetes mellitus. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(3):757-769.
[71] 陈芳浩,何奕德,李哲,等.钛种植体表面新型DNA水凝胶递送地塞米松诱导巨噬细胞M2极化的研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2021, 37(2):192-196.
[72] MURRAY PJ. Macrophage polarization. Annu Rev Physiol. 2017;79:541-566.
[73] QIU P, LI M, CHEN K, et al. Periosteal matrix-derived hydrogel promotes bone repair through an early immune regulation coupled with enhanced angio- and osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2020;227:119552.
[74] WANG Y, YAO D, LI L, et al. Effect of electrospun silk fibroin–silk sericin films on macrophage polarization and vascularization. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(6):3502-3512.
[75] MOORE EM, WEST JL. Harnessing macrophages for vascularization in tissue engineering. Ann Biomed Eng. 2019;47(2):354-365.
[76] JULIER Z, PARK AJ, BRIQUEZ PS, et al. Promoting tissue regeneration by modulating the immune system. Acta Biomater. 2017;53:13-28.
|