中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (7): 1080-1088.doi: 10.12307/2023.028
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
海藻酸盐支架修复关节软骨
李 诚1,2,郑国爽2,蒯贤东1,2,于炜婷1,2
- 1大连大学中山临床学院,辽宁省大连市 116001;2大连大学附属中山医院骨科,辽宁省大连市 116001
-
收稿日期:2021-11-06接受日期:2022-01-18出版日期:2023-03-08发布日期:2022-07-19 -
通讯作者:于炜婷,博士,研究员,硕士生导师,大连大学中山临床学院,辽宁省大连市 116001;大连大学附属中山医院骨科,辽宁省大连市 116001 -
作者简介:李诚,男,1991年生,安徽省亳州市人,汉族,大连大学在读硕士,主要从事海藻酸盐基水凝胶在软骨损伤修复的基础研究。 -
基金资助:辽宁省重点研发计划项目(2020JH2/10300093);负责人:于炜婷;辽宁省高等学校创新人才支持计划项目(辽教函[2018]478号);负责人:于炜婷;辽宁省“百千万人才工程” 资助项目(辽人社[2019]45号);负责人:于炜婷
Alginate scaffold in articular cartilage repair
Li Cheng1, 2, Zheng Guoshuang2, Kuai Xiandong1, 2, Yu Weiting1, 2
- 1Zhongshan Clinical College of Dalian University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Zhongshan Hospital of Dalian University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2021-11-06Accepted:2022-01-18Online:2023-03-08Published:2022-07-19 -
Contact:Yu Weiting, PhD, Researcher, Master’s supervisor, Zhongshan Clinical College of Dalian University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Zhongshan Hospital of Dalian University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Li Cheng, Master candidate, Zhongshan Clinical College of Dalian University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Zhongshan Hospital of Dalian University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:Key Research and Development Program of Liaoning Province, No. 2020JH2/10300093 (to YWT); Innovative Talents Support Program for Universities of Liaoning Province, No. [2018] 478 (to YWT); “Millions of Talents Project” of Liaoning Province, No. [2019] 45 (to YWT)
摘要:
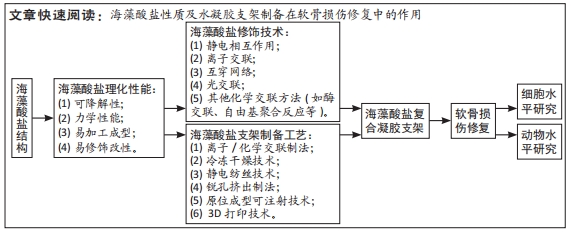
文题释义:
海藻酸盐基水凝胶:海藻酸钠由古罗糖醛酸(G单元)和甘露糖醛酸(M单元)依靠1,4-糖苷键组成的线性聚合物,遇到二价阳离子(如Ca2+、Ba2+等),会发生离子交换反应,形成“蛋壳样”结构,实现从溶液到水凝胶的转变。这种利用海藻酸钠溶胶-凝胶转变特性制备的水凝胶被称为海藻酸盐基水凝胶。
软骨组织工程:指将软骨种子细胞接种到生物支架材料中形成细胞-支架复合物。其中,支架材料可有效模拟软骨组织细胞外基质,利于软骨种子细胞在支架中生长分化,表达软骨相关功能。用于修复软骨组织缺损。
背景:由于关节软骨的解剖、生理特点,其自我修复能力有限,故而如何修复大面积的软骨缺损(直径> 4 mm)成为医学界备受瞩目的问题之一。伴随生物材料和组织工程学科的发展,通过支架技术尤其具有模拟细胞外基质微环境的水凝胶支架研究的深入发展,为软骨损伤修复提供了新的治疗思路。
目的:就海藻酸盐的性质、海藻酸盐水凝胶支架的制备以及在软骨损伤修复中的研究进展进行综述。
方法:利用计算机检索Web of Science、PubMed、万方和中国知网数据库,中文检索词为“海藻酸盐水凝胶、软骨组织工程或软骨、骨软骨、支架”,英文检索词为“alginate hydrogel,cartilage tissue engineering or chondro*,osteochondral,scaffold”,检索文献时间范围2016年1月至2020年12月。最终按入组标准筛选后纳入60篇文献进行综述分析。
结果与结论:①海藻酸盐作为带负电荷的天然亲水性多糖,可通过修饰技术赋予传统海藻酸盐水凝胶更优良的机械性能、黏附性、生物降解性以及生物相容性等。②修饰后的海藻酸盐复合水凝胶支架利于维持种子细胞的正常形态、合成相应的细胞外基质,促进成软骨相关基因的表达,表现出优良的成软骨能力。③有报道证实海藻酸盐复合水凝胶支架可在动物体内形成与周边正常软骨相似的软骨组织,有效修复缺损部位。④因此,海藻酸盐复合水凝胶支架具备良好的促软骨修复能力,为软骨组织工程提供新的治疗思路,但该材料未来还需更完善的临床前试验数据的支撑,以推进其临床转化进程。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6567-0345 (李诚) ;https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7403-1382(于炜婷)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
李 诚, 郑国爽, 蒯贤东, 于炜婷. 海藻酸盐支架修复关节软骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088.
Li Cheng, Zheng Guoshuang, Kuai Xiandong, Yu Weiting. Alginate scaffold in articular cartilage repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088.
在温和适宜的环境下,二价阳离子如Ba2+,Sr2+,Ca2+等离子通过键合反应会与海藻酸盐均聚嵌段G单元上的羧基通过静电作用形成水凝胶。在相同离子浓度下,二价阳离子与海藻酸分子交联能力的先后顺序为Pb2+>Cu2+>Cd2+>Ba2+>Sr2+>Ca2+> Zn2+,Co2+,Ni2+>Mg2+。而且不同金属离子与海藻酸钠分子中GG片段、MM片段、MG片段的交联程度不同。GG片断交联能力:Ba2+>Sr2+>Ca2+≥Mg2+;MM片断交联能力:Ba2+>Sr2+-Ca2+-Mg2+;MG片断交联能力:Ba2+-Sr2+-Ca2+-Mg2+。因此二价阳离子种类、海藻酸钠材料中G单元含量与分布等在一定程度上均可影响海藻酸盐水凝胶的稳定性和强度[12]。高G海藻酸钠与Ba2+,Sr2+反应比与Ca2+反应形成更稳定、强度更高的凝胶。但由于Ba2+是生物膜K+通道的抑制剂,在浓度大于5-10 mmol/L时即产生抑制效应,故目前以海藻酸盐凝胶制备应用于人体的生物制剂时,Ca2+是应用最多的阳离子,因为它被认为是临床使用安全、容易获得且经济的二价阳离子。且该交联技术不涉及化学交联剂的使用,对细胞和人体无毒害作用,使得海藻酸盐成为组织工程的有利材料[13]。
海藻酸钙凝胶具有一定的力学强度,可为细胞的生长、增殖提供支撑,同时具有较好的生物相容性及低免疫原性,但海藻酸钙凝胶的交联处于亚稳态,这种凝胶在遇到Ca2+螯合剂如EDTA、乳酸盐、柠檬酸盐、磷酸盐,或高浓度的Na+或Mg2+存在时,凝胶中的钙将发生离子置换,导致凝胶裂解,在一定程度上限制了海藻酸盐水凝胶的应用。由于海藻酸钠强大的亲水性能,使得细胞难以在凝胶表面黏附,甚至部分细胞(如干细胞等)难以在凝胶内部维持良好的细胞活性和功能[14]。但值得一提的是,海藻酸钠材料含有大量的羧基、羟基基团,可通过离子修饰、共价修饰等多种方式在海藻酸盐材料骨架上修饰细胞黏附配体或活性基团。比如可将生物活性肽[如精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸(arginine-glycine-aspartate,RGD)等]修饰到海藻酸盐高分子骨架上,可提高水凝胶对细胞的黏附性能,实现细胞与材料的相互作用[15]。
2.2 海藻酸盐理化性能
2.2.1 降解性 海藻酸钠的理化特性主要取决于糖醛酸的组成及其比例分布,海藻酸盐无论在溶液中还是在有一定水分的干品中,都会有一定程度上的降解,主要表现为其黏度的降低,相对分子质量的变化。而不同比例的M/G序列对海藻酸盐的降解具有明显影响,有关研究表明G区比例的增大,有助于海藻酸盐的热稳定性。其降解主要表现为两个方面:①氧化降解:在强酸、强碱、高温、高压、物理射线环境下,或有氧化剂存在时,都会通过海藻酸盐分子中糖苷键断裂、海藻酸盐大分子解聚,使海藻酸盐分子质量明显降低。②酶降解:海藻酸盐水解酶可特异性识别GG,GM,MM片段,将海藻酸盐降解成富含M或G单元的降解产物,对制备具有特定结构和理化性质的海藻酸,特别是满足制药工业需求发挥重要作用。但由于人体内缺乏特异性降解海藻酸盐的相关酶,因此,用于支架制备的海藻酸盐,因其平均分子质量明显超过机体肾脏清除的阈值,而无法完全从机体内去除。为此,有研究者提出通过部分氧化的海藻酸盐,因其聚合物链转变为更开放的链结构,C-2和C-3之间的键断裂后,链的灵活性增加。同原海藻酸盐水凝胶相比,轻微氧化后的海藻酸盐在人体内显示出优异的降解性能。由此可见,氧化海藻酸盐材料具有开发成各种可降解组织工程支架产品的优势。
2.2.2 易加工成型 由于海藻酸钠在常温常压下即可与Ba2+、Ca2+等二价阳离子通过离子交联的方式快速形成海藻酸盐水凝胶,整个反应过程可在全生理条件下进行,且操作简便易行,易于加工成型,使得海藻酸盐材料在组织工程领域,尤其在载细胞原位成型水凝胶及可注射水凝胶的制备方面显示出独特的优势。
2.2.3 力学性能 关节软骨表面光滑,既有润滑作用,又通过扩大承重面,将力载荷在关节中均匀分布,对关节起到保护作用。因此,软骨组织工程支架的力学性能显得格外重要。有关实验研究报道,海藻酸钙凝胶压缩强度为(440.00±26.39) kPa、拉伸强度为(133.75±7.50) kPa、弯曲强度为(56.25±6.00) kPa[16]。相关文献报道成年人关节软骨的压缩强度为(3.649±0.620) MPa、拉伸强度为(33.8±9.1) MPa,可见,海藻酸钙凝胶用于软骨修复,其力学性能存在明显不足。对海藻酸盐物化性能的研究可知分子间的交联度、作用力以及分子内GG序列的含量等都会影响凝胶的力学性能。因此通过对海藻酸盐官能团的改性修饰、化学交联及互穿网络等方式,可增加复合水凝胶的交联度,提升海藻酸盐基水凝胶的力学性能。如MULLER等[17]将天然无机聚磷酸盐、天然聚合物N,O-羧甲基壳聚糖和海藻酸盐组成的的生物聚合物,通过Ca2+交联制备成复合支架,其生物力学性能接近生理骨/软骨组织所具有的特性,体内植入后能有效修复软骨缺损。
2.2.4 易修饰改性 海藻酸盐是一种聚阴离子天然高分子材料,细胞难以黏附在海藻酸盐支架上。研究者将生物活性物质修饰到海藻酸盐的羧基或羟基基团上,从而改善海藻酸盐基支架的生物学性能,有利于细胞在支架的黏附、增殖及成软骨相关基因的表达。如将RGD活性肽、YIGSR和REDV序列的小肽修饰到海藻酸盐水凝胶支架上[18],显著提升了细胞的黏附作用及增殖能力。利用RGD活性肽修饰海藻酸盐的研究报道颇多,如PARK等[19]报道利用RGD活性肽修饰海藻酸盐水凝胶对细胞的黏附能力显著增强,并在一定程度上增加了成软骨标志物基因的表达。也有研究显示RGD活性肽被引入到海藻酸链上增加了材料与细胞的特异性相互作用,特别是与软骨细胞的相互作用,为体内软骨再生提供适宜的微环境[20]。此外,有研究通过添加疏水性聚合物(如透明质酸)也可弥补海藻酸盐对细胞附着能力的不足[21]。
2.3 用于软骨组织工程的海藻酸盐材料修饰技术 海藻酸盐水凝胶支架的交联方法可概况为物理法和化学法。交联类型和交联密度对海藻酸盐水凝胶的机械性能有显著影响。其中物理交联水凝胶是通过分子链间缠结或其他作用,如氢键、静电作用、疏水作用以及结晶等作用力形成的水凝胶。常见的海藻酸盐水凝胶的物理交联包括聚阴离子海藻酸盐与聚阳离子间的静电相互作用;海藻酸盐聚合物链与二价阳离子如Ca2+,Ba2+通过配位,形成蛋盒样结构,产生的离子交联。新近发展起来的互穿网络聚合物水凝胶技术为物理交联制备海藻酸盐复合水凝胶提供了新思路。同化学交联法相比,物理交联可提供相对友好的环境、无有害物质参与,且制备方法相对更简单易行。但物理交联制得水凝胶的力学性能较差,采用化学交联可在一定程度上改善海藻酸盐凝胶的机械性能。光交联由于其本质也是通过光引发新化学键的生成,因此也定义到化学交联领域,下面就海藻酸盐复合凝胶的修饰方法做简单介绍[22-27],见表1。
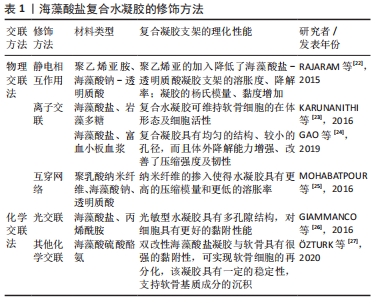
2.3.1 静电相互作用 海藻酸钠属聚阴离子高分子材料,可利用静电相互作用使海藻酸钠与聚阳离子发生离子交联制备海藻酸盐基聚合物水凝胶。由于分子链上含有较多反应位点,聚阴离子海藻酸钠和聚阳离子(如聚乙烯亚胺、壳聚糖聚合物)发生交联时,因交联密度的提高,使得水凝胶强度得到提高,同时还具有较好的韧性。如RAJARAM等[22]利用聚阳离子聚乙烯亚胺和聚阴离子海藻酸盐-透明质酸凝胶在静电相互作用力下形成聚电解质复合物,通过对机械性能、溶胀指数、降解性等物理性能及细胞活性的研究显示,聚乙烯亚胺的加入对复合凝胶支架的物理性能有显著改善,并在一定程度上提高了包被细胞的存活率,有利于聚电解质复合物在组织工程的应用。
2.3.2 离子交联 海藻酸盐与二价阳离子间的配位作用,可形成蛋盒样结构的水凝胶,是制备水凝胶最常用的方法。如KARUNANITHI等[23]通过溶液共混技术,制备的含有人间充质干细胞的海藻酸盐-岩藻多糖复合溶液,在钙液中交联形成原位载细胞的复合水凝胶,通过扫描电镜观察到软骨细胞在复合水凝胶支架中可维持在体形态,通过糖胺聚糖定量检测,显示复合水凝胶支架可促进细胞的增殖分化及相关基质的生成。另外,GAO等[24]采用溶液共混和钙离子交联的方法制备不同共混比的海藻酸钠/富血小板血浆复合水凝胶,研究显示富血小板血浆的加入降低了海藻酸盐凝胶的凝胶化速率和溶胀度,使凝胶孔径减小、结构更均匀,同时增加了凝胶表面的粗糙程度、提高了体外降解能力、改善了压缩强度和韧性。通过离子间的配位作用形成的凝胶大多存在凝胶力学强度低、稳定性差等问题,不足以为细胞提供相对持久的空间支撑和微环境,因此当前更多的是依靠互穿网络技术制备海藻酸盐基水凝胶支架。
2.3.3 互穿网络 互穿网络聚合物是由2种或2种以上的聚合物网络相互交叉渗透、机械缠结所组成的三维网络,而且这些网络在分子尺度上部分或者完全交织,但彼此之间无共价键形成。共混是制备高分子互穿网络水凝胶聚合物常用方法,在一定程度上提高了水凝胶的力学性能,同时改善高分子材料对细胞的粘附性能。如NASERI等[28]采用冷冻干燥法制备纤维素纳米晶体增强的海藻酸钠/明胶双交联互穿聚合物网络水凝胶,研究结果显示纤维素纳米晶体的加入增加了凝胶的孔隙率,形状更均匀规则,结构稳定性能得到改善。同时MOHABATPOUR等[25]制备的海藻酸钠-透明质酸-聚乳酸互穿网络复合支架,聚乳酸纳米纤维的加入使复合支架具有较好的力学性能、生物活性及细胞相容性,为细胞增殖提供适宜的微环境。通过该技术制备的互穿网络支架具备较好的孔隙率,为细胞的生长、增殖提供空间,为物质交换提供结构基础。
2.3.4 光交联 在适宜环境条件下,通过光引发剂在可见光或低强度紫外光的照射下使聚合物发生交联而形成水凝胶称为光交联。其是利用共价交联进行原位凝胶的方法,将可交联的化学键引入到聚合物链中形成力学性能更优异的聚合物,该方法具有反应温和、操作易控、创伤小及效率高等优点[29]。如JEON等[30]利用紫外光对甲基丙烯酸酯类海藻酸盐进行光交联制备光交联型水凝胶,通过对改变海藻酸盐甲基化程度控制海藻酸盐水凝胶的溶胀行为、弹性模量和降解速率。研究显示光交联水凝胶具有可调节的机械性能和降解速率。GIAMMANCO等[26]将海藻酸盐-丙烯酰胺杂化凝胶与三价铁离子配位制得光敏性水凝胶,该水凝胶在辐照后变得更软、多孔隙,同时表现出该凝胶溶胀和传输特性的变化,结构性能更接近细胞外基质。COATES等[31]在光交联制备的海藻酸盐聚合物水凝胶的研究中显示,间充质干细胞在聚合水凝胶中,早期即可检测到成软骨相关基因的表达,且可上调浅表区软骨细胞表型。另外,在YUAN等[32]的研究中,以海藻酸钠和明胶为原料,利用双交联制备海藻酸盐-明胶复合水凝胶,并通过紫外光形成水凝胶的第二网络,使双网络水凝胶具有较高的力学性能、良好的生物相容性以及可控的降解性能和溶胀率,细胞实验显示,该双网络水凝胶对细胞无明显的毒害作用,为细胞在凝胶中的增殖、黏附等提供适宜的生存环境。
2.3.5 其他化学交联方法 化学交联型水凝胶是利用各种化学交联方法,包括自由基聚合、酶介导、偶联法以及能量照射等引发聚合反应形成共价交联网络支架。同物理交联相比,化学交联是一种永久性的共价键,交联反应的过程不可逆,形成更稳定、机械强度更高的水凝胶,但是化学交联剂的加入可引起一定的毒性,使其应用受到一定的限制[33-34]。如?ZTURK等[27]通过对海藻酸盐的双重修饰制备出具有仿生性、生物相容性的酪氨酸酶促交联的海藻酸硫酸酪胺水凝胶,为软骨细胞的生长、增殖提供适宜的微环境,体内研究显示该类凝胶与周边组织具有较强的黏附性、皮下植入后表现出良好的稳定性,且成软骨相关基因,如胶原蛋白2、聚集素和Sox9的表达显著增加,软骨基质明显沉积,可见该水凝胶在软骨再生方面具有广阔的应用前景。
2.4 海藻酸盐基支架的制备工艺 海藻酸盐高分子材料因其易于加工成型的特性,在软组织工程领域显示出优势[35-55]。其中,用于软骨修复的海藻酸盐支架,根据其支架形态可将其制备工艺概况为离子/化学交联制备的水凝胶支架;冷冻干燥制备的多孔海绵状支架;静电纺丝制备的纤维状支架;锐孔挤出制备微粒支架;以及根据缺损部位形状用于原位修饰的可注射支架和3D打印支架,见表2。

2.4.1 离子/化学交联制备海藻酸盐水凝胶支架 将一定浓度的海藻酸盐溶液或其与其他高分子材料的混合溶液,通过流延法,结合外部凝胶化或内部凝胶化方法,将海藻酸盐基溶液与二价钙离子通过离子交联反应,制备海藻酸盐基水凝胶支架。例如SEO等[35]对透明质酸-海藻酸钠溶液与硫酸钙浆料通过离子交联形成的水凝胶的研究显示:透明质酸和海藻酸钠的聚合度对复合水凝胶的机械强度有显著影响,而水凝胶的机械强度对ATDC5细胞在体外软骨分化具有一定的影响。此外,LUO等[36]对海藻酸钠、纳米羟基磷灰石混合物于钙液中进行离子交联制得海藻酸钠基复合水凝胶支架,研究显示纳米羟基磷灰石均匀、完整地包裹在海藻酸盐的表面,与不含纳米羟基磷灰石壳层的纯藻酸盐支架相比,表面矿化支架具有更强的力学性能,同时具有蛋白质输送能力。该类型水凝胶制备工艺相对简单,通过增加Ca2+等交联剂、海藻酸盐的浓度、添加其他类型的无机高分子材料以及使用更高分子质量的海藻酸,可进一步提高增强水凝胶的力学性能,增强其机械强度,同时可改善水凝胶体系对细胞的黏附能力,促进细胞在凝胶支架中的增殖及相关功能的表达等。
2.4.2 冷冻干燥制备海藻酸盐多孔海绵支架 冷冻干燥是将含有水分的物质,冷冻成固态使材料内部含有的水直接升华为气态,从而达到排除水分产生多孔海绵状结构的方法。该方法能有效保持溶液中蛋白等物质的生物学活性,并利于支架形态稳定等优点。如MIRALLES等[37]将含有透明质酸的海藻酸盐充分交联后,进行冷冻干燥制得多孔海绵海藻酸盐支架,研究显示含有透明质酸的海藻酸盐海绵具有大孔且相互连接的网络,但透明质酸的添加未增加海绵的孔径。此外,该海绵状支架为软骨细胞增殖及合成蛋白多糖、胶原提供有利的微环境。有关体外实验表明高度多孔的海绵支架为细胞提供充足的附着空间,能够使细胞与周边微环境充分进行物质交换,确保细胞的增殖及有关功能的表达,还需进行有关的体内动物实验进一步验证该类支架对缺损部位的修复作用。
2.4.3 静电纺丝制备海藻酸盐纤维支架 静电纺丝是一种利用静电力从聚合物中生产纤维支架的纺丝技术,其可制备具有高稳定性和渗透性、高孔隙率以及具有较好机械性能的纳米纤维支架[38]。静电纺丝支架可提供一种纤维状、高度多孔的结构,起到模拟天然细胞外基质的作用,广泛应用于生物医学领域中。如PETROVA等[39]利用静电纺丝技术制备含有脱乙酰化甲壳素纳米管的双层壳聚糖/海藻酸钠支架,甲壳素纳米管的加入提高了海藻酸钠溶液的可纺性,增加了壳聚糖-海藻酸钠/甲壳素纳米管电纺双层膜的孔隙率和生物相容性,为细胞的增殖生长提供良好的微环境。同传统表面多孔、结构紧密的电纺纤维支架相比,当前纤维支架具备高渗透、孔隙率的纳米/微米级结构,为细胞增殖、黏附提供适宜条件,有利于后期组织工程的进一步研究。
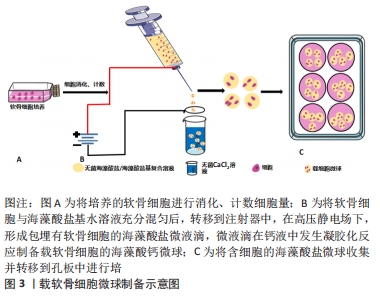
2.4.4 锐孔挤出制备海藻酸盐微粒支架 锐孔挤出法是将可溶性聚合物溶液,通过液体颗粒化技术(如气体喷雾雾化、高压静电场等)形成球状液滴,滴入到含有交联剂的溶液中,使聚合物交联固化形成微粒支架。如XU等[40]将海藻酸盐与明胶等体积混合制备海藻酸盐-明胶溶液,通过静电喷雾法在氯化钙凝固浴中制成含有人骨髓间充质干细胞的复合微球,结果显示复合微球比海藻酸钠微球具有较好的细胞相容性,同时可维持人骨髓间充质干细胞较高的细胞活性、促进干细胞的增殖以及体外软骨的形成。同时在三维打印支架上种植、组装微球并进行培养研究显示骨髓间充质干细胞可分化为软骨表型。通过对聚合物溶液的浓度、针与液面距离、电场强度等的控制可形成不同粒径的微球。细胞在微球内可避免机体免疫系统及相关应力的伤害,同时可进行物质交换等,细胞在微囊内可形成细胞聚集体,更利于软骨细胞功能活性的维持,见图3。
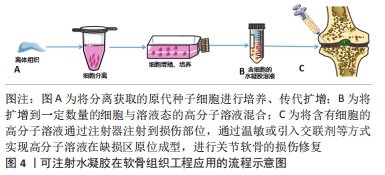
2.4.5 可注射海藻酸盐支架 可注射海藻酸盐支架是组织工程中的一类特殊水凝胶,该水凝胶可由酸碱度、温度的变化或者多价离子的存在而产生溶液-凝胶相转变,或通过共价键形成水凝胶。因具有原位成型,微创修复局部不规则缺损组织等优点,因此注入体内缺损区,可完全填充于缺损部位,形成与缺损部位相吻合的结构,进行组织损伤修复。NAGHIZADEH等[41]通过对含有氧化海藻酸钠、聚乙二醇和羧甲基壳聚糖或明胶复合材料的压缩性能及细胞活性的研究显示:氧化海藻酸钠/聚乙二醇-羧甲基壳聚糖水凝胶具备更高的机械性能、黏度以及良好的流变性能和生物降解性,更适合作为理想的可注射支架候选材料。载细胞的可注射水凝胶支架在软骨组织工程应用的流程示意图,见图4。
2.4.6 3D打印技术制备海藻酸盐支架 3D打印技术是快速成型技术中的一类,通过CT、MRI医学扫描缺损区并建立相应的模型,使得材料按照设计模型在指定部位精准堆积,制造出与计算机建模结构一致的产品。该技术可精确调控支架产品的孔径和孔隙率,还可制造复杂几何形状的多孔结构、贯穿孔结构等,以模拟活体组织的微观结构[42-43]。虽然传统制备工艺如冷冻干燥、静电纺丝、熔融成型等也可制备具有多孔结构的三维支架,但其孔隙不规则,而细胞在该类支架上造成大量细胞的损失,从而导致细胞相关性能状态的不佳[44]。而且该类支架难以实现对组织结构的仿真性,因此需要更为先进的制备方法,如3D生物打印技术,其可实现结构的规整及多孔,可为细胞的增殖及相关功能的表达提供良好的生存环境[45]。如SCHWARZ等[46]对氧化海藻酸盐和明胶水凝胶通过离子交联、酶交联构建的含有软骨细胞的三维打印支架的研究显示,通过酶交联制备的海藻酸盐-二醛-明胶水凝胶具有开放的内部结构和较高的形状保真度,可维持细胞的活力、促进软骨特异性标志物SOX9的表达,而且酶交联在一定程度上促进了软骨细胞在海藻酸盐-二醛凝胶中Ⅱ型胶原的合成,为三维培养软骨细胞提供一种可行方法。
当前利用3D打印技术可制备理想的仿生结构,但其相关材料必须具备良好的生物相容性、可降解性、无毒性、可打印以及打印后具备结构的完整性等特性[47-48]。该技术可实现上述多种方式的结合,生产出具备多种优越性能的支架材料,但还需通过相应的动物实验做进一步的研究。
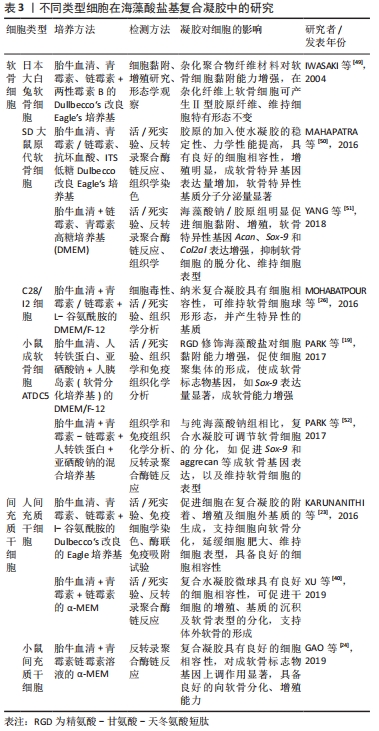
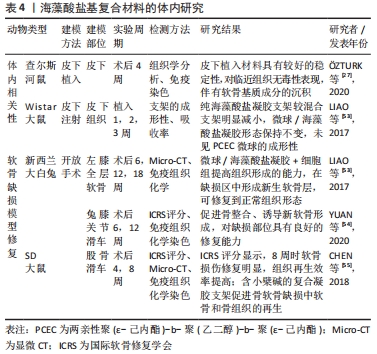
2.5 海藻酸盐基支架用于软骨修复的研究 在对海藻酸盐材料的修饰工艺及海藻酸盐基复合支架制备工艺进行总结研究的同时发现,目前针对海藻酸盐基支架用于软骨修复的报道大多局限在体外细胞水平的表征,部分研究显示了动物体内的修复效果,见表3,4。
2.5.1 软骨细胞在海藻酸盐复合凝胶中的研究 种子细胞、支架材料、细胞因子常被作为组织工程的基本要素。故在支架材料的前期研究中首先选择适宜的种子细胞开展相应的研究。如原代软骨细胞尽管受提取技术、动物二次伤害、传代数等条件的限制,但可直观地观察细胞的生命活动、形态结构、可补充体内实验的不足,而且对细胞功能及相关研究具有可操作性,如IWASAKI等[49]将兔关节软骨细胞种植在海藻酸盐/壳聚糖聚合纤维支架上,显示软骨细胞在杂化支架上具有较好的黏附性及细胞生长增殖的趋势,保持软骨细胞所特有的形态特征,并在杂化支架上有Ⅱ型胶原纤维的生成,表明该复合材料对软骨细胞具有良好的生物学反应,可促进细胞在体外的附着、增殖等。另外,MAHAPATRA等[50]将海藻酸盐-透明质酸-胶原作为软骨细胞的体外培养基质,研究显示培养7 d内凝胶中可出现部分细胞聚集体;培养21 d的结果显示,实验组软骨细胞表型保持完好、数量显著增加,并在该凝胶基质中形成的球形软骨细胞聚集体、DNA含量都明显优于海藻酸盐-透明质酸组,在基因表达的研究中显示,实验组材料促进细胞SOX9、Ⅱ型胶原及Agg等软骨相关基因的表达,成软骨特异基因的表达量明显增加,其中软骨特异性基质分子分泌量显著,进一步验证该凝胶可以为软骨细胞的体外培养提供形成软骨样基质的类机体环境。即海藻酸盐-透明质酸-胶原复合凝胶可为软骨细胞的增殖、细胞表型的维持、基因表达以及细胞外基质的形成提供良好的微环境,为后期软骨组织工程的研究提供参考。
由于3D打印技术的应用,可实现支架的空间网络结构,为细胞的增殖提供生长空间与力学支撑等优点,故细胞与3D生物打印支架结合成为研究的热点,如YANG等[51]将软骨细胞与三维打印生物墨水结合制备构建三维打印软骨组织,培养14 d细胞活死染色显示各组细胞活性良好,对含有软骨细胞的凝胶支架行苏木精-伊红染色可见海藻酸钠/胶原组活细胞量明显优于纯海藻酸钠组和海藻酸钠/琼脂糖组,而且可见到天然软骨组织中的陷窝样结构,并在周边产生丰富的细胞外基质。与单纯海藻酸组相比,海藻酸钠/胶原组明显促进细胞黏附、增殖,增强软骨特异性基因Acan,Col2al和Sox9的表达,使GAG的含量显著增加,减弱纤维软骨标志物Col1a1基因的表达,具有维持软骨细胞的表型的作用。该研究中胶原的加入改善了复合材料的机械强度和生物活性,使海藻酸钠/胶原复合凝胶支架可有效地促进软骨细胞的增殖、软骨特异性基因的表达、保持软骨细胞的表型。
2.5.2 细胞系细胞在海藻酸盐复合凝胶中的研究 同原代细胞相比,细胞系虽可能存在同原始组织不一样的遗传和表型,但其具备高纯度、性能相对稳定等优点,其中ATDC5细胞在复合凝胶支架材料的研究过程应用极为广泛。如PARK等[52]对接种ATDC5细胞的海藻酸钠-透明质酸水凝胶支架的研究显示,与其他组相比,在海藻酸钠-透明质酸0.5和1.0组可见细胞聚集体、周边细胞外基质以及正常软骨组织中的陷窝样结构,在海藻酸钠-透明质酸1.0组中的细胞聚集体、陷窝样结构等结构更明显,对含细胞的凝胶支架行染色组织学分析也证实了上述结论,而且软骨形成相关标志基因(如Sox-9和aggrecan)的定量分析显示:含透明质酸促进软骨形成相关基因的表达。由于S100蛋白是软骨细胞表型维持的典型标志蛋白,对软骨细胞的凝胶支架行免疫组织化学分析的结果显示在上述两组中可明显观察到S100蛋白阳性表达,该结果同组织学分析、基因定量表达检测结果一致,进一步证实细胞在凝胶中可维持其固有的细胞表型,在软骨损伤修复上具有一定的研究价值。另外,有研究对载ATDC5细胞的凝胶阿尔辛蓝染色结果显示,同RGD短肽未修饰的凝胶相比,在短肽修饰改性的凝胶中ATDC5细胞活性好、增殖明显、软骨形成能力更强,可见到更明显的细胞聚集体、强阳性的糖胺聚糖信号以及天然软骨组织中存在的陷窝样结构[19];对软骨形成相关基因的研究显示Sox-9和aggrecan等相关基因在短肽修饰的凝胶中表达能力增强、表达量显著。对于短肽修饰的凝胶中存在一定数量的细胞聚集体可保留N-钙黏附素介导细胞间的相互作用,增加软骨标志物基因的表达,可能有助于利用较少的细胞量促进软骨组织的形成,为后期促进软骨修复提供可能。
2.5.3 间充质干细胞在海藻酸盐复合凝胶中的研究 由于干细胞具有多项分化潜能的优点,通过诱导分化可实现干细胞向软骨细胞的分化及相关功能的表达。有关研究显示在海藻酸钠凝胶中加入富血小板血浆后所形成的复合凝胶具有更均匀的孔隙连通结构,机械性能、降解性均得到改善,使得复合凝胶对骨髓间充质干细胞表现出较好的细胞黏附性、较高的代谢活动能力。扫描电镜图像显示细胞在纯海藻酸凝胶、复合凝胶中呈无明显差异的成纤维细胞样形态,但在复合凝胶中存在更多的细胞聚集体。此外,海藻酸钠/富血小板血浆复合水凝胶具有促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖的趋势,较高量的富血小板血浆可上调软骨形成标记基因Sox-9和aggrecan的表达能力,促进干细胞的增殖和向软骨细胞分化形成软骨的能力,为软骨组织工程提供适宜的细胞载体[24]。而且KARUNANITHI等[23]通过对含有人间充质干细胞的海藻酸盐-岩藻多糖复合凝胶的研究显示复合凝胶对该细胞具有较好的附着能力,促进间充质干细胞的增殖以及相关细胞外基质的生成等,而且该复合凝胶延缓了间充质干细胞的肥大、维持细胞所特有的表型特征。由于生长因子与硫酸盐等基团之间存在的机制关系还未研究清楚,故而对于体外影响间充质干细胞分化的相关研究还需做进一步的探究,以便后期为相关临床研究提供有价值的参考。
2.5.4 海藻酸盐复合凝胶在体内相关性能的研究 海藻酸盐凝胶支架对细胞体外研究显示复合凝胶对细胞的增殖、相关软骨功能的表达具有一定的作用,为了验证不同凝胶支架的稳定性能、生物降解性等理化性能,从而需对复合凝胶支架进行相关的体内研究,如?ZTURK等[27]将双改性海藻酸盐凝胶植入实验鼠皮下,术后4周组织学分析、免疫染色结果显示植入水凝胶结构完整,被纤维薄膜包裹,在改性凝胶周边的组织未观察到坏死、水肿、充血等物质毒性的有关表现,而且免疫染色显示凝胶中沉积软骨特异性基质。该海藻酸盐水凝胶在体内可稳定存在、对机体无明显毒性反应,并且可促进相应软骨基质的产生,为软骨损伤修复提供了可能。此外LIAO等[53]为观察微球/海藻酸钠凝胶在体内成形性、降解性及生物相容性等,将混合凝胶注入大鼠皮下的结果显示在混合凝胶可形成组织丘,但结构不稳定,可发生扩散。混合支架植入1周无明显丢失,2周开始材料部分吸收、含量相对减少;同纯海藻酸盐组相比,混合支架材料组降解时间更长、性能更稳定,更有利于软骨组织工程的应用,为后期凝胶支架的研究提供基础。
2.5.5 海藻酸盐基凝胶支架修复软骨缺损 支架对软骨缺损修复的最直接证据,还要依赖于实验动物模型。目前,软骨缺损的常见动物模型以兔膝关节和大鼠股骨的关节软骨手术造模为主,在兔软骨缺损模型的构建中,YUAN等[54]采用直径4 mm,厚度4 mm的软骨缺损作为疾病模型;LIAO等[53]采用直径4 mm,厚度3 mm的全层软骨缺损作为缺损模型。通过海藻酸盐基复合支架在软骨缺损动物模型的研究结果显示,海藻酸盐基复合支架能有效促进损伤部位新生组织的生成,修复缺损部位,从而达到软骨等组织再生的目的。如YUAN等[54]将制备的牛血清白蛋白/海藻酸钠/羟基磷灰石凝胶支架植入缺损部位,植入12周时空白对照组仍有明显可见的间隙;牛血清白蛋白/海藻酸钠组缺损损伤小,新生软骨与周边组织连接良好;而牛血清白蛋白/海藻酸钠/羟基磷灰石复合组植入物与周围组织边界结合形成光滑的软骨滑面,使新生组织与天然软骨表面过度平整,同时ICRS评分显示,牛血清白蛋白/海藻酸钠/羟基磷灰石复合组明显优于其他组。样本组织学分析显示,空白对照组缺损区主要成分为纤维组织;牛血清白蛋白/海藻酸钠组纤维较少,新软骨组织形成;而牛血清白蛋白/海藻酸钠/羟基磷灰石复合凝胶支架组在软骨区形成新的软骨层,厚度相似,免疫组织化学染色显示该组胶原纤维染色强阳性,其透明质酸软骨、新骨组织含量高,染色结果的MODS评分与其一致,即牛血清白蛋白/海藻酸钠/羟基磷灰石复合凝胶支架可有效的促进骨整合以及诱导新的软骨形成,完成对损伤软骨的修复。
LIAO等[53]利用兔膝关节全层软骨缺损的模型进行研究显示,同其他组(即空白对照组、微球组、海藻酸钠水凝胶组、软骨细胞组)相比,微球/海藻酸盐复合水凝胶和微球/海藻酸盐复合水凝胶+细胞组的凝胶支架在术后18周,缺损部位被新生软骨、软骨下骨填充;半定量组织学评分显示,术后18周,微球/海藻酸盐复合水凝胶组新生骨体积89.9%,而微球/海藻酸盐复合凝胶+细胞组骨软骨组织再生率高达96.7%,显著高于其他各组。同时免疫组织化学分析显示在微球/海藻酸盐+细胞组6周后,新生软骨细胞分布均匀,其中GAG和ColⅡ表现出高表达状态,缺损部位的软骨下骨、软骨细胞为正常再生。上述研究显示海藻酸盐复合凝胶支架对于兔关节软骨缺损具有较好的修复作用,在损伤部位可形成新的软骨组织,恢复正常结构、修复缺损组织。
另外在大鼠软骨缺损模型的研究中,CHEN等[55]则是采用直径2 mm,厚度2.5 mm的全层柱状软骨缺损进行软骨缺损的研究,并将实验动物分成3组即空白对照组、海藻酸钠/透明质酸复合凝胶支架组、海藻酸钠/透明质酸复合凝胶支架+小檗碱组,8周时可观察到凝胶支架组、凝胶支架+小檗碱组缺损部位修复,表面坚固、光滑,通过ICRS评分显示支架组7.8分,其软骨修复情况明显好于空白对照组5.6分;凝胶支架+小檗碱组10.8分,该组软骨再生率明显高于支架组。另外显微CT结果显示8周时支架+小檗碱组的缺损区比对照组、支架组产生更多的钙化组织,而且缺损区的骨体积/组织体积明显高于其他两组,说明含有小檗碱的凝胶支架可促进骨软骨缺损中软骨、骨组织的再生。而且番红O染色显示对照组软骨下缺损表面为纤维组织,支架组表面充满透明软骨样组织;支架+组表面光滑,充满较厚的透明软骨样组织,该组的组织学评分为16.3分,明显高于支架组的11.8分及对照组的4.2分。上述数据进一步表明含有小檗碱的凝胶支架可促进损伤软骨的再生与修复。根据软骨损伤的类型等制备具有可控的降解性、稳定力学性能、良好生物相容性的复合海藻酸盐凝胶支架,可实现对软骨缺损组织的修复。

| [1] ASHAMMAKHI N, AHADIAN S, DARABI MA, et al. Minimally invasive and regenerative therapeutics. Adv Mater. 2019;31(1):e1804041. [2] SUN W, XUE B, LI Y, et al. Polymer-supramolecular polymer double-network hydrogel. Adv Funct Mater. 2016,26(48):9044-9052. [3] YANG J, ZHANG YS, YUE K, et al. Cell-laden hydrogels for osteochondral and cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2017;57:1-25. [4] ARMIENTO AR, STODDART MJ, ALINI M, et al. Biomaterials for articular cartilage tissue engineering: learning from biology. Acta Biomater. 2018;65:1-20. [5] BONANI W, CAGOL N, MANIGLIO D. Alginate hydrogels: a tool for 3d cell encapsulation, tissue engineering, and biofabrication. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1250:49-61. [6] 王云红,刘袖洞,于炜婷,等.海藻酸盐基微囊膜的物质传递性能[J].膜科学与技术,2017,37(2):6-11,18. [7] CHOUKAIFE H, DOOLAANEA AA, ALFATAMA M. Alginate nanoformulation: influence of process and selected variables. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020;13(11):335. [8] PAWAR SN, EDGAR KJ. Alginate derivatization: a review of chemistry, properties and applications. Biomaterials. 2012;33(11):3279-3305. [9] SEVERINO P, DA SILVA CF, ANDRADE LN, et al. Alginate nanoparticles for drug delivery and targeting. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(11):1312-1334. [10] RASTOGI P, KANDASUBRAMANIAN B. Review of alginate-based hydrogel bioprinting for application in tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2019;11(4):042001. [11] MARYAM F, FARINAZ JS, ATEFEH S, et al. Alginate based scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering: a review. Int J Polym Mater Po. 2020;69(4):230-247. [12] HERNANDEZ-GONZALEZ AC, TELLEZ-JURADO L, RODRIGUEZ-LORENZO LM. Alginate hydrogels for bone tissue engineering, from injectables to bioprinting: a review. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;229:115514. [13] SARKER B, ZEHNDER T, RATH SN, et al. Oxidized alginate-gelatin hydrogel: a favorable matrix for growth and osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells in 3D. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2017;3(8):1730-1737. [14] 宋益哲,任英,娄茹云,等.胶原/海藻酸钙互穿网络水凝胶的构建及其对细胞行为的影响[J].功能材料,2016,47(11):11136-11140. [15] SARKER B, PAPAGEORGIOU DG, SILVA R, et al. Fabrication of alginate-gelatin crosslinked hydrogel microcapsules and evaluation of the microstructure and physico-chemical properties. J Mater Chem B. 2014;2(11):1470-1482. [16] 龚泰芳,方彩云,陈文,等.海藻酸盐的理化特性及其在组织工程研究和临床中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(18):3613-3616. [17] MULLER WE, NEUFURTH M, WANG S, et al. Morphogenetically active scaffold for osteochondral repair (polyphosphate/alginate/N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan). Eur Cell Mater. 2016;31:174-190. [18] YU Y, GUO L, WANG W, et al. Dual-peptide-modified alginate hydrogels for the promotion of angiogenesis. Sci China Chem. 2015;58(12):1866-1874. [19] PARK H, KIM D, LEE KY. Interaction-tailored cell aggregates in alginate hydrogels for enhanced chondrogenic differentiation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(1):42-50. [20] PARK H, LEE KY. Facile control of RGD-alginate/hyaluronate hydrogel formation for cartilage regeneration. Carbohyd Polym. 2011;86(3):1107-1112. [21] CHUAH YJ, PECK Y, LAU JE, et al. Hydrogel based cartilaginous tissue regeneration: recent insights and technologies. Biomater Sci. 2017;5(4):613-631. [22] RAJARAM A, SCHREYER DJ, CHEN DX. Use of the polycation polyethyleneimine to improve the physical properties of alginate-hyaluronic acid hydrogel during fabrication of tissue repair scaffolds. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2015;26(7):433-445. [23] KARUNANITHI P, MURALI MR, SAMUEL S, et al. Three dimensional alginate-fucoidan composite hydrogel augments the chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;147:294-303. [24] GAO X, GAO L, GROTH T, et al. Fabrication and properties of an injectable sodium alginate/PRP composite hydrogel as a potential cell carrier for cartilage repair. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(9):2076-2087. [25] MOHABATPOUR F, KARKHANEH A, SHARIFI AM. A hydrogel/fiber composite scaffold for chondrocyte encapsulation in cartilage tissue regeneration. Rsc Adv. 2016;6(86):83135-83145. [26] GIAMMANCO GE, CARRION B, COLEMAN RM, et al. Photoresponsive polysaccharide-based hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties for cartilage tissue engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(23):14423-14429. [27] ÖZTURK E, STAUBER T, LEVINSON C, et al. Tyrosinase-crosslinked, tissue adhesive and biomimetic alginate sulfate hydrogels for cartilage repair. Biomed Mater. 2020;15(4):045019. [28] NASERI N, DEEPA B, MATHEW AP, et al. Nanocellulose-Based Interpenetrating Polymer Network (IPN) Hydrogels for Cartilage Applications. Biomacromolecules. 2016;17(11):3714-3723. [29] HU Y, REN G, DENG L, et al. Degradable UV-crosslinked hydrogel for the controlled release of triclosan with reduced cytotoxicity. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;67:151-158. [30] JEON O, BOUHADIR KH, MANSOUR JM, et al. Photocrosslinked alginate hydrogels with tunable biodegradation rates and mechanical properties. Biomaterials. 2009; 30(14):2724-2734. [31] COATES EE, RIGGIN CN, FISHER JP. Photocrosslinked alginate with hyaluronic acid hydrogels as vehicles for mesenchymal stem cell encapsulation and chondrogenesis. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(7):1962-1970. [32] YUAN L, WU Y, GU QS, et al. Injectable photo crosslinked enhanced double-network hydrogels from modified sodium alginate and gelatin. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;96:569-577. [33] ESLAHI N, ABDORAHIM M, SIMCHI A. Smart polymeric hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering: a review on the chemistry and biological functions. Biomacromolecules. 2016;17(11):3441-3463. [34] SHAMEKHI MA, RABIEE A, MIRZADEH H, et al. Fabrication and characterization of hydrothermal cross-linked chitosan porous scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;80:532-542. [35] SEO Y, LEE H, LEE JW, et al. Hyaluronate-alginate hybrid hydrogels prepared with various linkers for chondrocyte encapsulation. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;218:1-7. [36] LUO Y, LODE A, WU C, et al. Alginate/nanohydroxyapatite scaffolds with designed core/shell structures fabricated by 3D plotting and in situ mineralization for bone tissue engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(12):6541-6549. [37] MIRALLES G, BAUDOIN R, DUMAS D, et al. Sodium alginate sponges with or without sodium hyaluronate: in vitro engineering of cartilage. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;57(2):268-278. [38] JUN I, HAN HS, EDWARDS JR, et al. Electrospun fibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering: viewpoints on architecture and fabrication. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):745. [39] PETROVA VA, GOLOVKIN AS, MISHANIN AI, et al. Cytocompatibility of bilayer scaffolds electrospun from chitosan/alginate-chitin nanowhiskers. Biomedicines. 2020;8(9):305. [40] XU Y, PENG J, RICHARDS G, et al. Optimization of electrospray fabrication of stem cell-embedded alginate-gelatin microspheres and their assembly in 3D-printed poly(ε-caprolactone) scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering. J Orthop Translat. 2019;18:128-141. [41] NAGHIZADEH Z, KARKHANEH A, KHOJASTEH A. Self-crosslinking effect of chitosan and gelatin on alginate based hydrogels: injectable in situ forming scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;89:256-264. [42] YANG S, LEONG KF, DU Z, et al. The design of scaffolds for use in tissue engineering. Part II. Rapid prototyping techniques. Tissue Eng. 2002;8(1):1-11. [43] NAGHIEH S, KARAMOOZ-RAVARI MR, SARKER MD, et al. Influence of crosslinking on the mechanical behavior of 3D printed alginate scaffolds: experimental and numerical approaches. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;80:111-118. [44] PARK JY, CHOI YJ, SHIM JH, et al. Development of a 3D cell printed structure as an alternative to autologs cartilage for auricular reconstruction. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(5):1016-1028. [45] YU J, PARK SA, KIM WD, et al. Current Advances in 3D Bioprinting Technology and Its Applications for Tissue Engineering. Polymers (Basel). 2020;12(12):2958. [46] SCHWARZ S, KUTH S, DISTLER T, et al. 3D printing and characterization of human nasoseptal chondrocytes laden dual crosslinked oxidized alginate-gelatin hydrogels for cartilage repair approaches. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020; 116:111189. [47] GUVENDIREN M, MOLDE J, SOARES RM, et al. Designing biomaterials for 3D printing. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2016;2(10):1679-1693. [48] JI S, GUVENDIREN M. Recent advances in bioink design for 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2017;5:23. [49] IWASAKI N, YAMANE ST, MAJIMA T, et al. Feasibility of polysaccharide hybrid materials for scaffolds in cartilage tissue engineering: evaluation of chondrocyte adhesion to polyion complex fibers prepared from alginate and chitosan. Biomacromolecules. 2004;5(3):828-833. [50] MAHAPATRA C, JIN GZ, KIM HW. Alginate-hyaluronic acid-collagen composite hydrogel favorable for the culture of chondrocytes and their phenotype maintenance. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;13(5):538-546. [51] YANG X, LU Z, WU H, et al. Collagen-alginate as bioink for three-dimensional (3D) cell printing based cartilage tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;83:195-201. [52] PARK H, LEE HJ, AN H, et al. Alginate hydrogels modified with low molecular weight hyaluronate for cartilage regeneration. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;162:100-107. [53] LIAO J, WANG B, HUANG Y, et al. Injectable alginate hydrogel cross-linked by calcium gluconate-loaded porous microspheres for cartilage tissue engineering. ACS Omega. 2017;2(2):443-454. [54] YUAN H, ZHENG X, LIU W, et al. A novel bovine serum albumin and sodium alginate hydrogel scaffold doped with hydroxyapatite nanowires for cartilage defects repair. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;192:111041. [55] CHEN P, XIA C, MO J, et al. Interpenetrating polymer network scaffold of sodium hyaluronate and sodium alginate combined with berberine for osteochondral defect regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;91:190-200. [56] MORGAN FLC, MORONI L, BAKER MB. Dynamic Bioinks to Advance Bioprinting. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(15):e1901798. [57] WAN Z, ZHANG P, LIU Y, et al. Four-dimensional bioprinting: current developments and applications in bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2020;101:26-42. [58] VIDAL L, KAMPLEITNER C, BRENNAN MA, et al. Reconstruction of large skeletal defects: current clinical therapeutic strategies and future directions using 3D printing. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:61. [59] DE MELO BAG, JODAT YA, MEHROTRA S, et al. 3D Printed Cartilage-Like Tissue Constructs with Spatially Controlled Mechanical Properties. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(51):1906330. [60] SCHIPANI R, SCHEURER S, FLORENTIN R, et al. Reinforcing interpenetrating network hydrogels with 3D printed polymer networks to engineer cartilage mimetic composites. Biofabrication. 2020;12(3):035011. |
| [1] | 孙可欣, 曾今实, 李佳, 蒋海越, 刘霞. 力学刺激提高生物3D打印软骨构建物基质的形成[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | 潘钟杰, 秦志鸿, 郑铁军, 丁晓飞, 廖世杰. 股骨头坏死发病机制中非编码RNA的靶标性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [3] | 蔡志浩, 谢召勇. 股骨颈前倾角测量评估:如何建立统一的方法和标准[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [4] | 党 祎, 杜成砚, 姚红林, 袁能华, 曹 金, 熊 山, 张顶梅, 王 信. 激素型骨坏死与氧化应激[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [5] | 柳晓琳, 穆新月, 马子雨, 刘树泰, 王文龙, 韩晓谦, 董志恒. 水凝胶复合载辛伐他汀蛋白微球对成骨细胞增殖分化的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [6] | 徐星星, 文超举, 孟茂花, 王勤英, 陈镜桥, 董 强. 口腔种植中的碳纳米材料[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [7] | 杨怡天, 王 璐, 姚 蔚, 赵 彬. 生物支架与巨噬细胞在骨再生中的相互影响及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1071-1079. |
| [8] | 陈世崧, 刘晓红, 徐志云. 人工生物瓣膜的研究现状及展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1096-1102. |
| [9] | 芦 笛, 张 成, 段荣泉, 刘宗响. 磷酸钙陶瓷骨修复材料的骨诱导性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1103-1109. |
| [10] | 史业弘, 王 成, 陈世玖. 小口径人工血管的早期血栓形成与预防[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1110-1116. |
| [11] | 唐昊天, 廖荣东, 田 京. 压电材料修复骨缺损的应用及设计思路[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [12] | 许 言, 李 平, 赖春花, 朱培君, 杨 烁, 徐淑兰. 血管化骨再生中压电生物材料的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1126-1132. |
| [13] | 郭颖奇, 宫先旭, 张 岩, 肖 寒, 王 野, 谷文光. 半月板外突与髌股关节软骨损伤及骨髓病变:MRI半定量评分的评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| [14] | 陶 新, 徐 逸, 宋志文, 刘锦波. Hippo信号通路参与脊髓损伤的调控[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(4): 619-625. |
| [15] | 李世浩, 李 奇, 李 震, 张媛媛, 刘苗苗, 欧阳懿, 徐卫国. 前交叉韧带损伤与重建术后患者的足底压力及步态分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(4): 626-631. |
关节软骨是覆盖在关节骨骺表面的结缔组织,组织中含有大量的水分(占关节软骨总量65%-80%),起到润滑关节及减少关节腔损伤的作用。软骨组织中不含血管、淋巴管等结构,基质中的细胞需要通过渗透作用摄取所需的营养物质、排出代谢物,其代谢活性较低,因此损伤后的软骨组织的自我修复能力较差。软骨损伤可发生在不同的年龄段,会严重影响患者的生活质量,其中创伤、疾病以及年龄等都可造成关节软骨病变。当前软骨损伤大多采用保守或手术治疗,但并不能取得很好疗效。而其修复技术如骨髓刺激和同种异体/自体移植都具有一定的局限性,如增加有关疾病传播的风险、造成继发性创伤等问题[1-2]。伴随生物材料和组织工程学科的快速发展,构建软骨组织工程支架为软骨损伤修复提供了新的治疗思路。
水凝胶支架具有类似于软骨细胞外基质结构并能呈现与天然关节软骨相似的力学和生物学环境,可维持软骨细胞形态和软骨细胞功能相关蛋白的表达[3],因此,水凝胶作为软骨修复的支架材料备受关注。其可概括为天然高分子水凝胶支架和合成高分子水凝胶支架两大类,同合成高分子材料相比,天然高分子材料如海藻酸盐(alginate,ALG)、壳聚糖(chitosan,CS)、透明质酸(hyaluronic acid,HA)、胶原(collagen,COL)、明胶(gelatin, GEL)及琼脂糖(agarose,AG)等因其良好的生物相容性、无毒性以及生物降解性等而备受关注[4-5]。
海藻酸盐由于具有良好的生物相容性,可塑性强及生物降解性等优势,成为软骨组织工程中理想的支架材料,为软骨损伤修复提供了新的治疗方法。尤其伴随国家药品监督管理局发布的中华人民共和国医药行业标准:组织工程医疗器械产品海藻酸钠(YY/T 1654-2019,原YY/T 0606.8-2008)的颁布实施,实现了海藻酸钠(sodium alginate,SA)产品的临床准入,推进了海藻酸盐基软骨组织工程修复产品走向临床的进程,为后期利用海藻酸盐基复合凝胶支架修复软骨缺损提供便利条件。文章就海藻酸盐的性质、海藻酸盐水凝胶支架的制备以及在软骨损伤修复中的研究进展进行综述。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2021年2月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 主要是2016年1月至2020年12月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 Web of Science、PubMed、中国知网、万方数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词:“海藻酸盐水凝胶、软骨组织工程或软骨、骨软骨、支架”;英文检索词:“alginate hydrogel,cartilage tissue engineering or chondro*,osteochondral,scaffold”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 与该综述目的相关的研究原著和综述。
1.1.6 文献检索策略 以Web of Science数据库检索策略为例,见图1。

1.1.7 检索文献量 各数据库共检索得到764篇文献。
1.2 入组标准
纳入标准:与海藻酸盐及其改性修饰的海藻酸盐衍生物与海藻酸盐基复合材料等相关的软骨组织研究文献;以及与海藻酸盐复合支架制备技术有关的研究。
排除标准:排除与该综述主题不相关以及重复的研究文献。
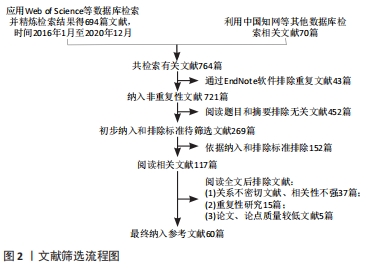
1.3 文献数据提取和质量评价 输入检索词检索并精炼检索结果共得764篇文献,通过EndNote软件排除重复文献、阅读文献摘要后按照纳入与排除标准的相关文献117篇,对剩余文献阅读总结后最终纳入相关文献60篇进行综述。具体检索过程见图2。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 文章重点对海藻酸盐基支架在关节软骨修复的研究进展进行综述。全面总结了用于软骨组织工程的海藻酸盐材料的修饰技术和海藻酸盐基支架的制备工艺,重点对软骨细胞、间充质干细胞等细胞在海藻酸盐复合水凝胶支架中的增殖、表达和成软骨作用,以及海藻酸盐基支架在动物体内的研究进展进行较为全面的综述,较好地总结了支架材料当前的研究进展并为后期相关研究提供指导。
3.3 综述的局限性 就目前对于海藻酸盐复合凝胶支架在软骨组织工程的研究显示,该类研究大部分是体外实验,动物实验大都集中在中小型动物模型上,缺少大型实验动物及临床研究相关的研究结果。另外,各实验室动物造模方法、支架修复效果的表征方法以及制备支架所需原材料的质控等均缺乏相关标准,导致不同实验室的研究成果难以相互比较。这些都是制约海藻酸盐基支架应用于临床软骨组织缺损修复的重要因素。
3.4 综述的重要意义 文章汇总了近些年来海藻酸盐复合凝胶支架在软骨组织工程的实验研究,较为系统地描述了海藻酸盐复合凝胶支架促进软骨损伤修复的研究及其进展,可为后续的实验提供参考,让更多的研究人员关注该天然材料。
3.5 总结与展望 随着新材料、新技术的不断涌现,如微流控技术、3D甚至4D打印等技术,可将修饰的海藻酸盐材料制备成动态水凝胶、刺激响应性材料、具有特性化的生物医学设备或移植物装置等[56-58],有研究报道利用3D生物打印技术将聚乙二醇-海藻酸钠双重交联的水凝胶与互穿网络聚合物结合制得力学性能在MPa范围内的仿生生物材料,能够承受关节软骨通常所承载的机械负荷[59]。此外,将海藻酸钠-甲基丙烯酰明胶互穿网络凝胶与3D打印的聚己酸内酯网络结合,可制备出具有模拟正常关节软骨力学性能的复合材料,并为细胞提供有利的软骨形成环境[60]。因此制备结构相对复杂的支架,在一定程度上有望解决海藻酸盐自身较差的力学性能、黏附性及降解性等问题。但支架可能使植入部位存在软骨细胞肥大,形成软骨内成骨,阻碍损伤部位功能性软骨结构的形成,甚至导致有创性手术的发生。因此如何结合多种材料优势,又不影响材料生物相容性,结构、力学及降解性能可控的水凝胶,或将成为目前所面临的重难点。同时加快软骨组织工程支架在体内微环境的远期效果研究,以及支架对所携带细胞、周边局部组织甚至整个机体的影响也至关重要,是海藻酸盐基水凝胶支架用于临床软骨修复的重要前提和保障。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程

文题释义:
海藻酸盐基水凝胶:海藻酸钠由古罗糖醛酸(G单元)和甘露糖醛酸(M单元)依靠1,4-糖苷键组成的线性聚合物,遇到二价阳离子(如Ca2+、Ba2+等),会发生离子交换反应,形成“蛋壳样”结构,实现从溶液到水凝胶的转变。这种利用海藻酸钠溶胶-凝胶转变特性制备的水凝胶被称为海藻酸盐基水凝胶。
软骨组织工程:指将软骨种子细胞接种到生物支架材料中形成细胞-支架复合物。其中,支架材料可有效模拟软骨组织细胞外基质,利于软骨种子细胞在支架中生长分化,表达软骨相关功能。用于修复软骨组织缺损。
文章全面总结了用于软骨组织工程的海藻酸盐材料的修饰技术和海藻酸盐基复合支架的制备工艺,重点阐述了软骨细胞、间充质干细胞等细胞在海藻酸盐复合水凝胶支架中的增殖、表达和成软骨作用,并概述了海藻酸盐基复合支架在动物体内实验的研究进展。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||