[1] ADIPURNAMA I, YANG MC, CIACH T, et al. Surface modification and endothelialization of polyurethane for vascular tissue engineering applications: a review. Biomater Sci. 2016;5(1):22-37.
[2] 施群.移植血管的发展和应用[M].上海:复旦大学出版社,2009.
[3] SOUZA DS, DASHWOOD MR, TSUI JC, et al. Improved patency in vein grafts harvested with surrounding tissue: results of a randomized study using three harvesting techniques. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;73(4):1189-1195.
[4] JAFFER IH, FREDENBURGH JC, HIRSH J, et al. Medical device-induced thrombosis: what causes it and how can we prevent it? J Thromb Haemost. 2015;13 Suppl 1:S72-81.
[5] LABARRERE CA, DABIRI AE, KASSAB GS. Thrombogenic and Inflammatory Reactions to Biomaterials in Medical Devices. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:123.
[6] ASHCRAFT M, DOUGLASS M, CHEN Y, et al. Combination strategies for antithrombotic biomaterials: an emerging trend towards hemocompatibility. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(7):2413-2423.
[7] 田小宁,从飞,程一钊,等.血管移植三种术式修复四肢血管损伤的疗效评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(14):1282-1287.
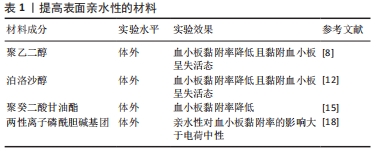
[8] DIMITRIEVSKA S, MAIRE M, DIAZ-QUIJADA GA, et al. Low thrombogenicity coating of nonwoven PET fiber structures for vascular grafts. Macromol Biosci. 2011;11(4):493-502.
[9] DAI Y, DAI S, XIE X, et al. Immobilizing argatroban and mPEG-NH2 on a polyethersulfone membrane surface to prepare an effective nonthrombogenic biointerface. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2019;30(8): 608-628.
[10] SELLATURAY P, NASSER S, EWAN P. Polyethylene Glycol-Induced Systemic Allergic Reactions (Anaphylaxis). J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9(2):670-675.
[11] AHMED F, ALEXANDRIDIS P, SHANKARAN H, et al. The ability of poloxamers to inhibit platelet aggregation depends on their physicochemical properties. Thromb Haemost. 2001;86(6):1532-1539.
[12] LE AN, TRAN NM, PHAN TB, et al. Poloxamer additive as luminal surface modification to modulate wettability and bioactivities of small-diameter polyurethane/polycaprolactone electrospun hollow tube for vascular prosthesis applications. Materials Today Communications. 2021;26: 101771.
[13] KARLETA V, ANDRLIK I, BRAUNMÜLLER S, et al. Poloxamer 188 supplemented culture medium increases the vitality of Caco-2 cells after subcultivation and freeze/thaw cycles. ALTEX. 2010;27(3):191-197.
[14] PAZHANIMALA SK, VLLASALIU D, RAIMI-ABRAHAM BT. Engineering Biomimetic Gelatin Based Nanostructures as Synthetic Substrates for Cell Culture. Applied Sciences. 2019;9(8):1583.
[15] MOTLAGH D, YANG J, LUI KY, et al. Hemocompatibility evaluation of poly(glycerol-sebacate) in vitro for vascular tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2006;27(24):4315-4324.
[16] ZARGAR KHARAZI A, ATARI M, VATANKHAH E. A nanofibrous bilayered scaffold for tissue engineering of small-diameter blood vessels. Polymers for Advanced Technologies. 2018;29(12):3151-3158.
[17] LIU P, CHEN Q, LI L, et al. Anti-biofouling ability and cytocompatibility of the zwitterionic brushes-modified cellulose membrane. J Mater Chem B. 2014;2(41):7222-7231.
[18] CHENG CH, CHEN GF, LIN JC. Studies of zwitterionic sulfobetaine functionalized polypropylene surface with or without polyethylene glycol spacer: surface characterization, antibacterial adhesion, and platelet compatibility evaluation. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2020;31(16): 2060-2077.
[19] CUI L, YAO Y, YIM EKF. The effects of surface topography modification on hydrogel properties. APL Bioeng. 2021;5(3):031509.
[20] SCHMAIER AH. The contact activation and kallikrein/kinin systems: pathophysiologic and physiologic activities. J Thromb Haemost. 2016; 14(1):28-39.
[21] WANG M, BAO L, QIU X, et al. Immobilization of heparin on decellularized kidney scaffold to construct microenvironment for antithrombosis and inducing reendothelialization. Sci China Life Sci. 2018;61(10):1168-1177.
[22] SMITH RJ JR, YI T, NASIRI B, et al. Implantation of VEGF-functionalized cell-free vascular grafts: regenerative and immunological response. FASEB J. 2019;33(4):5089-5100.
[23] KONG X, XU W. Biodegradation and biocompatibility of a degradable chitosan vascular prosthesis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(3):3498-3505.
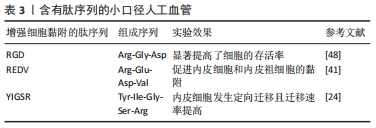
[24] ZENG Z, HU C, LIANG Q, et al. Coaxial-printed small-diameter polyelectrolyte-based tubes with an electrostatic self-assembly of heparin and YIGSR peptide for antithrombogenicity and endothelialization. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(6):1628-1638.
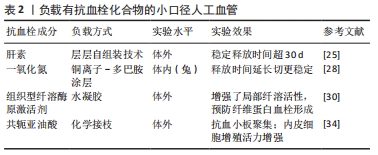
[25] WANG D, WANG X, LI X, et al. Biologically responsive, long-term release nanocoating on an electrospun scaffold for vascular endothelialization and anticoagulation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;107:110212.
[26] ELNAGGAR MA, SEO SH, GOBAA S, et al. Nitric Oxide Releasing Coronary Stent: A New Approach Using Layer-by-Layer Coating and Liposomal Encapsulation. Small. 2016;12(43):6012-6023.
[27] YANG Z, YANG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Mussel-inspired catalytic selenocystamine-dopamine coatings for long-term generation of therapeutic gas on cardiovascular stents. Biomaterials. 2018;178:1-10.
[28] ZHANG F, ZHANG Q, LI X, et al. Mussel-inspired dopamine-CuII coatings for sustained in situ generation of nitric oxide for prevention of stent thrombosis and restenosis. Biomaterials. 2019;194:117-129.
[29] LI C, DU H, YANG AZ, et al. Thrombosis-Responsive Thrombolytic Coating Based on Thrombin-Degradable Tissue Plasminogen Activator (t-PA) Nanocapsules. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017;27(45): 1703934.1-1703934.11.
[30] 黄佳磊,郁李胤,王境鸿,等.可持续抗非特异性蛋白质吸附的凝血酶响应型水凝胶涂层[J].高分子学报,2021,52(9):1118-1128.
[31] BENITO P, NELSON GJ, KELLEY DS, et al. The effect of conjugated linoleic acid on platelet function, platelet fatty acid composition, and blood coagulation in humans. Lipids. 2001;36(3):221-227.
[32] LI G, BUTZ D, DONG B, et al. Selective conjugated fatty acids inhibit guinea pig platelet aggregation. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006;545(2-3):93-99.
[33] MINH HH, HIEP NT, HAI ND, et al. Fabrication of Polycaprolactone/Polyurethane Loading Conjugated Linoleic Acid and Its Antiplatelet Adhesion. Int J Biomater. 2017;2017:5690625.
[34] TRAN N, LE A, HO M, et al. Polyurethane/polycaprolactone membrane grafted with conjugated linoleic acid for artificial vascular graft application. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2020;21(1):56-66.
[35] BREYMANN C, SCHMIDT D, HOERSTRUP SP. Umbilical cord cells as a source of cardiovascular tissue engineering. Stem Cell Rev. 2006;2(2): 87-92.
[36] WANG K, LIN RZ, MELERO-MARTIN JM. Bioengineering human vascular networks: trends and directions in endothelial and perivascular cell sources. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(3):421-439.
[37] TAKAHASHI K, YAMANAKA S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126(4):663-676.
[38] FREIMAN A, SHANDALOV Y, ROZENFELD D, et al. Adipose-derived endothelial and mesenchymal stem cells enhance vascular network formation on three-dimensional constructs in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:5.
[39] LIN RZ, MORENO-LUNA R, LI D, et al. Human endothelial colony-forming cells serve as trophic mediators for mesenchymal stem cell engraftment via paracrine signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(28):10137-10142.
[40] CHEN W, ZENG W, SUN J, et al. Construction of an Aptamer-SiRNA Chimera-Modified Tissue-Engineered Blood Vessel for Cell-Type-Specific Capture and Delivery. ACS Nano. 2015;9(6):6069-6076.
[41] DUAN Y, YU S, XU P, et al. Co-immobilization of CD133 antibodies, vascular endothelial growth factors, and REDV peptide promotes capture, proliferation, and differentiation of endothelial progenitor cells. Acta Biomater. 2019;96:137-148.
[42] HAO D, FAN Y, XIAO W, et al. Rapid endothelialization of small diameter vascular grafts by a bioactive integrin-binding ligand specifically targeting endothelial progenitor cells and endothelial cells. Acta Biomater. 2020;108:178-193.
[43] INGRAM DA, MEAD LE, TANAKA H, et al. Identification of a novel hierarchy of endothelial progenitor cells using human peripheral and umbilical cord blood. Blood. 2004;104(9):2752-2760.
[44] LUO J, SHI X, LIN Y, et al. Efficient Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells into Endothelial Cells under Xenogeneic-free Conditions for Vascular Tissue Engineering. Acta Biomater. 2021;119: 184-196.
[45] GENERALI M, CASANOVA EA, KEHL D, et al. Autologous endothelialized small-caliber vascular grafts engineered from blood-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2019;97:333-343.
[46] STEVENS KR, MURRY CE. Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Engineered Tissues: Clinical Considerations. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(3): 294-297.
[47] XING Y, GU Y, GUO L, et al. Gelatin coating promotes in situ endothelialization of electrospun polycaprolactone vascular grafts. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2021;32(9):1161-1181.
[48] ANTONOVA LV, SILNIKOV VN, SEVOSTYANOVA VV, et al. Biocompatibility of Small-Diameter Vascular Grafts in Different Modes of RGD Modification. Polymers (Basel). 2019;11(1):174.
[49] 明华伟,何芸,夏德林,等.VEGF165基因转染HUVEC促进大鼠血管生成的实验研究[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2017,27(3):161-165.
[50] 刘仕琪,慈红波,雷鹏,等.磁压榨吻合技术实现犬腹主动脉人工血管置换快速无缝线吻合[J].器官移植,2021,12(2):191-196.
[51] 李飞,贾国良,张荣庆,等.弱恒磁场对人脐静脉及兔主动脉内皮细胞增殖的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2003,19(6):772,777.
[52] 李春梅,杨佐森,解学魁,等.钕铁硼磁片对小鼠微循环影响的观察实验[J].中国公共卫生,2001,17(10):913.
[53] 王泽,刘佩,杨志凯,等.下肢动脉人工血管旁路移植术后闭塞的治疗效果研究[J].影像研究与医学应用,2017,1(1):138-139.
[54] MINGA LOWAMPA E, HOLEMANS C, STIENNON L, et al. Late Fate of Cryopreserved Arterial Allografts. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2016; 52(5):696-702.
[55] 任章勇,吕少诚,贺强.同种异体血管在肝胆胰手术中的应用现状[J].解放军医学院学报,2020,41(7):724-727.
[56] JASHARI R, VAN HOECK B, NGAKAM R, et al. Banking of cryopreserved arterial allografts in Europe: 20 years of operation in the European Homograft Bank (EHB) in Brussels. Cell Tissue Bank. 2013;14(4):589-599.
[57] DIMITRIEVSKA S, NIKLASON LE. Historical Perspective and Future Direction of Blood Vessel Developments. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018;8(2):a025742.
|