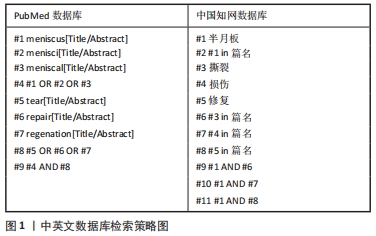
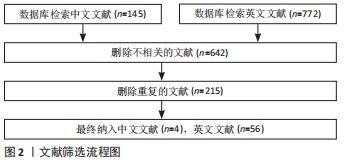
[1] RAI MF, BROPHY RH, ROSEN V. Molecular biology of meniscus pathology: lessons learned from translational studies and mouse models. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(9):1895-1904.
[2] ENGLUND M, GUERMAZI A, ROEMER FW, et al. Meniscal tear in knees without surgery and the development of radiographic osteoarthritis among middle-aged and elderly persons: the multicenter osteoarthritis study. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(3):831-839.
[3] HIRANAKA T, FURUMATSU T, OKAZAKI Y, et al. Postoperative clinical outcomes of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in patients with isolated medial compartmental osteoarthritis following medial meniscus posterior root tear. Asia Pac J Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Technol. 2021;26:15-20.
[4] Bugbee W. What Role for Chondroplasty in the Knee? Commentary on an article by Leslie J.Bisson, MD, et al. “Observation Versus Debridement of Unstable Chondral Lesions During Partial Meniscectomy. Analysis of Patient Outcomes and Degenerative Joint Disease at 5 Years in the Chondral Lesions And Meniscus Procedures (ChAMP) Randomized Controlled Trial”. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021;103(17):e70.
[5] BEDRIN MD, KARTALIAS K, YOW BG, et al. Degenerative joint disease After Meniscectomy. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2021;29(3):e44-e50.
[6] HUSSAIN ZB, CHAHLA J, MANDELBAUM BR, et al. The role of meniscal tears in spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee: a systematic review of suspected etiology and a call to revisit nomenclature. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(2):501-507.
[7] PAXTON ES, STOCK MV, BROPHY RH. Meniscal repair versus partial meniscectomy: a systematic review comparing reoperation rates and clinical outcomes. Arthroscopy. 2011;27(9):1275-1288.
[8] LUTZ C, DALMAY F, EHKIRCH FP, et al. Meniscectomy versus meniscal repair: 10 years radiological and clinical results in vertical lesions in stable knee. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(8 Suppl):S327-S331.
[9] STEIN T, MEHLING AP, WELSCH F, et al. Long-term outcome after arthroscopic meniscal repair versus arthroscopic partial meniscectomy for traumatic meniscal tears. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(8):1542-1548.
[10] WHITEHOUSE MR, HOWELLS NR, PARRY MC, et al. Repair of torn avascular meniscal cartilage using undifferentiated autologous mesenchymal stem cells: from in vitro optimization to a first-in-human study. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(4):1237-1248.
[11] RIBITSCH I, PEHAM C, ADE N, et al. Structure-Function relationships of equine menisci. PLoS One. 2018;13(3):e0194052.
[12] DANSO EK, OINAS JMT, SAARAKKALA S, et al. Structure-function relationships of human meniscus. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;67:51-60.
[13] BRINDLE T, NYLAND J, JOHNSON DL. The meniscus: review of basic principles with application to surgery and rehabilitation. J AthlTrain. 2001;36(2):160-169.
[14] 李箭,蒋欣,裴福兴,等.膝关节半月板血供的应用解剖学研究[J].临床外科杂志,2003,11(5):335-336,364.
[15] HORIBE S, SHINO K, NAKATA K, et al. Second-look arthroscopy after meniscal repair. Review of 132 menisci repaired by an arthroscopic inside-out technique. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995;77(2):245-249.
[16] MURRELL GA, MADDALI S, HOROVITZ L, et al. The effects of time course after anterior cruciate ligament injury in correlation with meniscal and cartilage loss. Am J Sports Med. 2001;29(1):9-14.
[17] Kang HJ, Chun CH, Kim KM, et al. The results of all-inside meniscus repair using the viper repair system simultaneously with anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Clin Orthop Surg. 2015;7(2):177-184.
[18] Shelbourne KD, Carr DR. Meniscal repair compared with meniscectomy for bucket-handle medial meniscal tears in anterior cruciate ligament-reconstructed knees. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31(5):718-723.
[19] Cannon WD Jr, Vittori JM. The incidence of healing in arthroscopic meniscal repairs in anterior cruciate ligament-reconstructed knees versus stable knees. Am J Sports Med. 1992;20(2):176-181.
[20] 周钢,葛兴涛,林坚平,等.关节镜下Fast-Fix联合微骨折术修复水平状半月板撕裂的临床研究[J].重庆医学,2019,48(12):2027-2030.
[21] 刘正鑫.关节镜下Fast-Fix联合微骨折术修复水平状半月板撕裂的临床效果观察[J].临床研究,2019,27(12):56-57.
[22] DEAN CS, CHAHLA J, MATHENY LM, et al. Outcomes after biologically augmented isolated meniscal repair with marrow venting are comparable with those after meniscal repair with concomitant anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(6):1341-1348.
[23] BARENIUS B, PONZER S, SHALABI A, et al. Increased risk of osteoarthritis after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a 14-year follow-up study of a randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(5):1049-1057.
[24] BOSTAN B, GEVREK F, BALTA O, et al. Effects of different bone marrow stimulation techniques on avascular zone meniscal defects. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2018;119(10):630-635.
[25] SEGAWA Y, MUNETA T, MAKINO H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from synovium, meniscus, anterior cruciate ligament, and articular chondrocytes share similar gene expression profiles. J Orthop Res. 2009; 27(4):435-441.
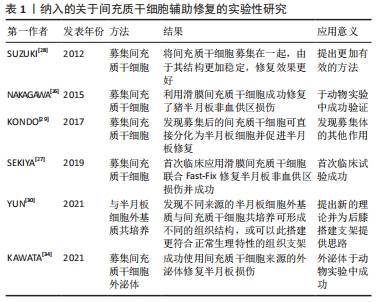
[26] NAKAGAWA Y, MUNETA T, KONDO S, et al. Synovialmesenchymal stem cells promote healing after meniscal repair in microminipigs. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(6):1007-1017.
[27] SEKIYA I, KOGA H, OTABE K, et al. Additional use of synovial mesenchymal stem cell transplantation following surgical repair of a complex degenerative tear of the medial meniscus of the knee: a case report. Cell Transplant. 2019;28(11):1445-1454.
[28] SUZUKI S, MUNETA T, TSUJI K, et al. Properties and usefulness of aggregates of synovial mesenchymal stem cells as a source for cartilage regeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(3):R136.
[29] KONDO S, MUNETA T, NAKAGAWA Y, et al. Transplantation of autologous synovial mesenchymal stem cells promotes meniscus regeneration in aged primates. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(6):1274-1282.
[30] YUN HW, SONG BR, SHIN DI, et al. Fabrication of decellularized meniscus extracellular matrix according to inner cartilaginous, middle transitional, and outer fibrous zones result in zone-specific protein expression useful for precise replication of meniscus zones. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;128:112312.
[31] IANNUCCI LE, BOYS AJ, MCCORRY MC, et al. Cellular and chemical gradients to engineer the meniscus-to-bone insertion. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(7):e1800806.
[32] DE LUNA A, OTAHAL A, NEHRER S. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles -silver linings for cartilage regeneration? Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:593386.
[33] BAO C, HE C. The role and therapeutic potential of MSC-derived exosomes in osteoarthritis. Arch BiochemBiophys. 2021;710:109002.
[34] KAWATA K, KOGA H, TSUJI K, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stromal cells mediate endogenous cell growth and migration via the CXCL5 and CXCL6/CXCR2 axes and repair menisci. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):414.
[35] ANDIA I, MAFFULLI N. Platelet-rich plasma for managing pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013;9(12):721-730.
[36] SAKATA R, REDDI AH. Platelet-rich plasma modulates actions on articular cartilage lubrication and regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2016;22(5):408-419.
[37] CAVALLO C, FILARDO G, MARIANI E, et al. Comparison of platelet-rich plasma formulations for cartilage healing: an in vitro study.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(5):423-429.
[38] ANITUA E, ANDIA I, ARDANZA B, et al. Autologous platelets as a source of proteins for healing and tissue regeneration. Thromb Haemost. 2004;91(1):4-15.
[39] BHARGAVA MM, ATTIA ET, MURRELL GA, et al. The effect of cytokines on the proliferation and migration of bovine meniscal cells. Am J Sports Med. 1999;27(5):636-643.
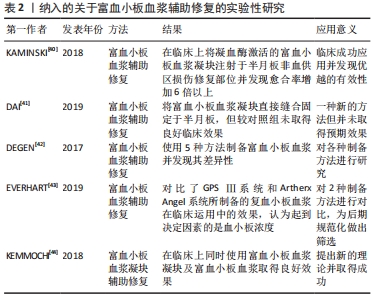
[40] KAMINSKI R, KULINSKI K, KOZAR-KAMINSKA K, et al. A prospective, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study evaluating meniscal healing, clinical outcomes, and safety in patients undergoing meniscal repair of unstable, complete vertical meniscal tears (bucket handle) augmented with platelet-rich plasma. Biomed Res Int. 2018; 2018:9315815.
[41] DAI WL, ZHANG H, LIN ZM, et al. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in arthroscopic repair for discoid lateral meniscus tears. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):113.
[42] DEGEN RM, BERNARD JA, OLIVER KS, et al. Commercial separation systems designed for preparation of platelet-rich plasma yield differences in cellular composition. HSS J. 2017;13(1):75-80.
[43] EVERHART JS, CAVENDISH PA, EIKENBERRY A, et al. Platelet-rich plasma reduces failure risk for isolated meniscal repairs but provides no benefit for meniscal repairs with anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(8):1789-1796.
[44] KEMMOCHI M, SASAKI S, TAKAHASHI M, et al. The use of platelet-rich fibrin with platelet-rich plasma support meniscal repair surgery. J Orthop. 2018;15(2):711-720.
[45] DOHANEHRENFEST DM, DE PEPPO GM, DOGLIOLI P, et al. Slow release of growth factors and thrombospondin-1 in Choukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a gold standard to achieve for all surgical platelet concentrates technologies. Growth Factors. 2009;27(1):63-69.
[46] WONG CC, KUO TF, YANG TL, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin facilitates rabbit meniscal repair by promoting meniscocytes proliferation, migration, and extracellular matrix synthesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(8):1722.
[47] KOBAYASHI E, FLÜCKIGER L, FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, et al. Comparative release of growth factors from PRP, PRF, and advanced-PRF. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(9):2353-2360.
[48] GRIFFIN JW, HADEED MM, WERNER BC, et al. Platelet-rich plasma in meniscal repair: does augmentation improve surgical outcomes? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(5):1665-1672.
[49] BURCHARD R, HUFLAGE H, SOOST C, et al. Efficiency of platelet-rich plasma therapy in knee osteoarthritis does not depend on level of cartilage damage. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):153.
[50] GUENOUN D, MAGALON J, DE TORQUEMADA I, et al. Treatment of degenerative meniscal tear with intrameniscal injection of platelets rich plasma. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2020;101(3):169-176.
[51] YANG CP, HUNG KT, WENG CJ, et al. Clinical outcomes of meniscus repair with or without multiple intra-articular injections of platelet rich plasma after surgery. J Clin Med. 2021;10(12):2546.
[52] PORT J, JACKSON DW, LEE TQ, et al. Meniscal repair supplemented with exogenous fibrin clot and autogenous cultured marrow cells in the goat model.Am J Sports Med. 1996;24(4):547-555.
[53] ARNOCZKY SP, WARREN RF, SPIVAK JM. Meniscal repair using an exogenous fibrin clot.An experimental study in dogs. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988;70(8):1209-1217.
[54] CHAHLA J, KENNEDY NI, GEESLIN AG, et al. Meniscal repair with fibrin clot augmentation. Arthrosc Tech. 2017;6(6):e2065-e2069.
[55] NAKAYAMA H, KANTO R, KAMBARA S, et al. Successful treatment of degenerative medial meniscal tears in well-aligned knees with fibrin clot implantation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(11):3466-3473.
[56] KAMIMURA T, KIMURA M. Repair of a chronic large meniscal defect with implantation of autogenous meniscal fragments using a tubular-shaped fibrin clot. Arthrosc Tech. 2018;7(3):e257-e263.
[57] PATWARI P, LIN SN, KURZ B, et al. Potent inhibition of cartilage biosynthesis by coincubation with joint capsule through an IL-1-independent pathway. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2009;19(4):528-535.
[58] VANKEMMELBEKE MN, ILIC MZ, HANDLEY CJ, et al. Coincubation of bovine synovial or capsular tissue with cartilage generates a soluble “Aggrecanase” activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;255(3):686-691.
[59] NISHIMUTA JF, BENDERNAGEL MF, LEVENSTON ME. Co-culture with infrapatellar fat pad differentially stimulates proteoglycan synthesis and accumulation in cartilage and meniscus tissues. Connect Tissue Res. 2017; 58(5):447-455.
[60] 杨君君,周益昭,黄术,等.关节镜下髁间窝微骨折术与髌下脂肪垫粉碎术在半月板损伤中的应用研究[J].中国内镜杂志,2018,24(1):22-28.
|