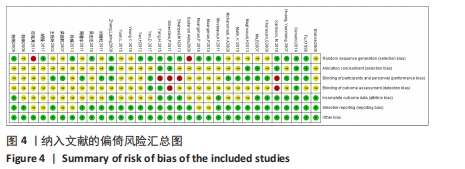
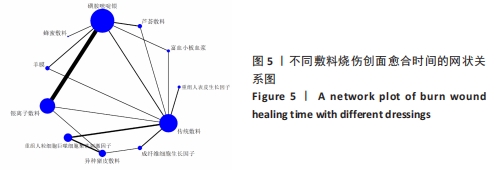
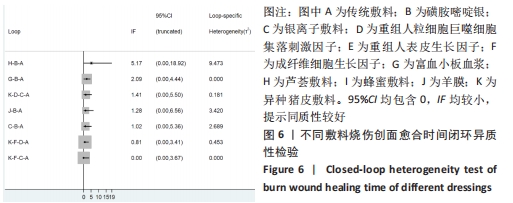
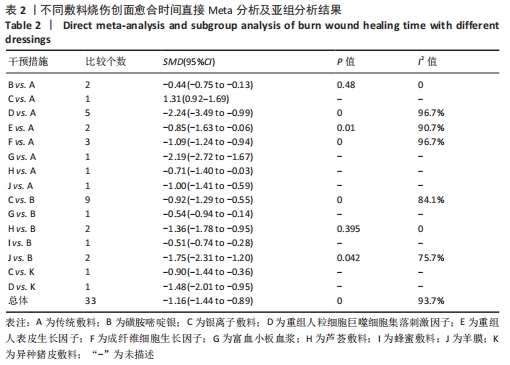
[1] 王正国.全球烧伤近况——来自世界卫生组织的报告[J].中华烧伤杂志,2001, 17(4):250-251.
[2] PECK MD. Epidemiology of burns throughout the world. Part I: Distribution and risk factors. Burns. 2011;37(7):1087-1100.
[3] WANG Y, TANG HT, XIA ZF, et al. Factors affecting survival in adult patients with massive burns. Burns. 2010;36(1):57-64.
[4] Burn Incidence Fact Sheet-American Burn Association. https://ameriburn.org/who-we-are/media/burn-incidence-fact-sheet/.
[5] 谢卫国.从中外比较看我国烧伤防治体系建设[J].中华烧伤杂志,2013,29(2):126-129.
[6] 钟淑贤,石雨晴,杨亚兰,等.软聚硅酮银离子敷料应用于烧伤创面的效果评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(22): 3602-3608.
[7] YUAN L, MINGHUA C, FEIFEI D, et al. Study of the use of recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor hydrogel externally to treat residual wounds of extensive deep partial-thickness burn. Burns. 2015;41(5):1086-1091.
[8] ROWAN MP, CANCIO LC, ELSTER EA, et al. Burn wound healing and treatment: review and advancements. Crit Care. 2015;19:243.
[9] YANG C, XIONG AB, HE XC, et al. Efficacy and feasibility of amniotic membrane for the treatment of burn wounds: a meta-analysis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2021;90(4):744-755.
[10] CHAGANTI P, GORDON I, CHAO JH, et al. A systematic review of foam dressings for partial thickness burns. Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37(6):1184-1190.
[11] PAGGIARO AO, BASTIANELLI R, CARVALHO VF, et al. Is allograft skin, the gold-standard for burn skin substitute? A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Plast Reconstruc Aesth Surg. 2019;72(8):1245-1253.
[12] CHAGANTI P, GORDON I, CHAO JH, et al. A systematic review of foam dressings for partial thickness burns. Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37(6):1184-1190.
[13] NIMIA HH, CARVALHO VF, ISAAC C, et al. Comparative study of Silver Sulfadiazine with other materials for healing and infection prevention in burns: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Burns. 2019; 45(2):282-292.
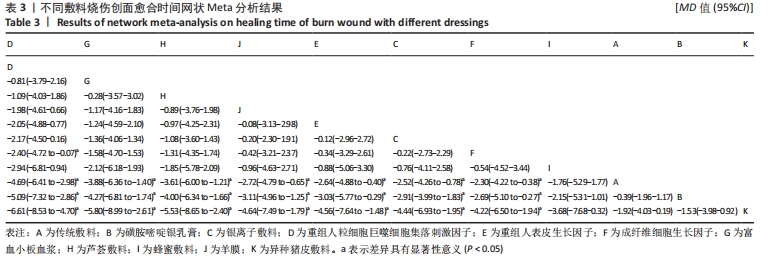
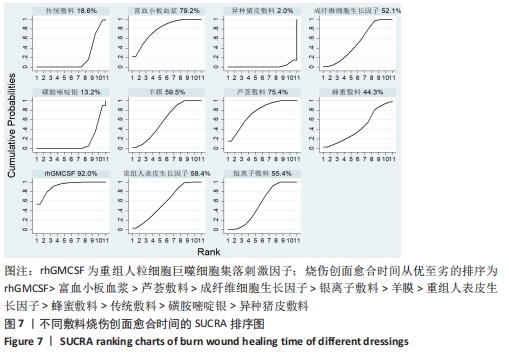
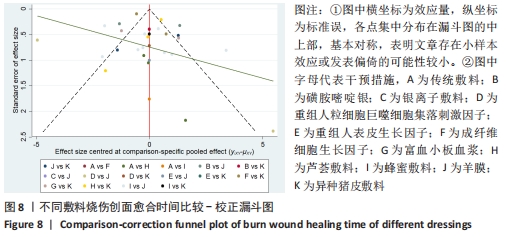
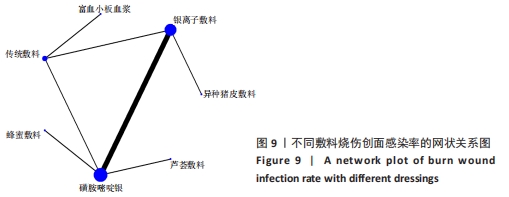
[14] 王巍巍,杨智荣,孙凤,等.网状Meta分析GRADE证据总结表的制订、解读与应用[J].中国循证医学杂志,2020,20(12): 1471-1476.
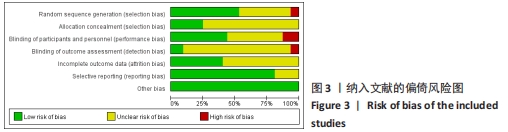
[15] HIGGINS JP, ALTMAN DG, GOTZSCHE PC, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928.
[16] KARLSSON M, ELMASRY M, STEINVALL I, et al. Superiority of silver-foam over porcine xenograft dressings for treatment of scalds in children: a prospective randomised controlled trial. Burns. 2019;45(6):1401-1409.
[17] YAN D, LIU S, ZHAO X, et al. Recombinant human granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor in deep second-degree burn wound healing. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(22):e6881.
[18] 胡强,隋爽,王国栋,等.rhGM-CSF凝胶与异种皮对深Ⅱ度烧伤创面愈合效果分析[J].医学研究杂志,2017,46(2):149-151.
[19] Muangman P, Praditsuktavorn B, Chinaroonchai K, et al. Clinical efficacy test of polyester containing herbal extract dressings in burn wound healing. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2016;15(3):203-212.
[20] TANG H, LV G, FU J, et al. An open, parallel, randomized, comparative, multicenter investigation evaluating the efficacy and tolerability of Mepilex Ag versus silver sulfadiazine in the treatment of deep partial-thickness burn injuries. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;78(5):1000-1007.
[21] 吴宏志,李晓,杨蒙,等.自体富血小板血浆凝胶对中老年电烧伤患者创面愈合的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(5): 1182-1184.
[22] GENUINO GAS, BALUYUT-ANGELES KV, ESPIRITU APT, et al. Topical petrolatum gel alone versus topical silver sulfadiazine with standard gauze dressings for the treatment of superficial partial thickness burns in adults: a randomized controlled trial. Burns. 2014;40(7):1267-1273.
[23] 邓海涛,赵耀华,徐丽红,等.亲水性纤维含银敷料治疗深Ⅱ度烧伤的疗效[J].江苏医药,2014,40(20):2460-2461.
[24] SHAHZAD MN, AHMED N. Effectiveness of Aloe Vera gel compared with 1% silver sulphadiazine cream as burn wound dressing in second degree burns. J Pak Med Assoc. 2013;63(2):225-230.
[25] MAGHSOUDI H, NEZAMI N, MIRZAJANZADEH M. Enhancement of burn wounds healing by platelet dressing. Int J Burns Trauma. 2013;3(2):96-101.
[26] 张梅,唐洪泰,马兵,等.软聚硅酮银离子泡沫敷料在患者关节部位深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的应用[J].中华烧伤杂志,2013,29(3): 315-317.
[27] YAN H, CHEN J, PENG X. Recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor hydrogel promotes healing of deep partial thickness burn wounds. Burns. 2012;38(6):877-881.
[28] MOSTAQUE AK, RAHMAN KBMA. Comparisons of the effects of biological membrane (amnion) and silver sulfadiazine in the management of burn wounds in children. J Burn Care Res. 2011;32(2):200-209.
[29] SILVERSTEIN P, HEIMBACH D, MEITES H, et al. An open, parallel, randomized, comparative, multicenter study to evaluate the cost-effectiveness, performance, tolerance, and safety of a silver-containing soft silicone foam dressing (intervention) vs silver sulfadiazine cream. J Burn Care Res. 2011;32(6):617-626.
[30] 周潘宇,夏照帆,贲道锋,等.爱康肤银离子敷料在小儿浅Ⅱ度烧伤创面的临床应用[J].第二军医大学学报,2011,32(12): 1321-1323.
[31] 刘继松,方勇,姚敏,等.重组人粒细胞巨噬细胞集落刺激因子凝胶剂对深Ⅱ度烧伤创面溶痂及愈合影响的临床研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(9):1059-1062.
[32] MUANGMAN P, PUNDEE C, OPASANON S, et al. A prospective, randomized trial of silver containing hydrofiber dressing versus 1% silver sulfadiazine for the treatment of partial thickness burns. Int Wound J. 2010; 7(4):271-276.
[33] MALIK KI, MALIK MA, ASLAM A. Honey compared with silver sulphadiazine in the treatment of superficial partial-thickness burns. Int Wound J. 2010;7(5):413-417.
[34] MOHAMMADI AA, SABET B, RIAZI H, et al. Human amniotic membrane dressing: an excellent method for outpatient management of burn wounds. Iran J Med Sci. 2009;34(1):61-64.
[35] KHORASANI G, HOSSEINIMEHR SJ, AZADBAKHT M, et al. Aloe versus silver sulfadiazine creams for second-degree burns: a randomized controlled study. Surg Today. 2009;39(7):587-591.
[36] ZHANG L, CHEN J, HAN C. A multicenter clinical trial of recombinant human GM-CSF hydrogel for the treatment of deep second-degree burns. Wound Repair Regen. 2009; 17(5):685-689.
[37] 陈炯,韩春茂,张力成,等.纳米银用于Ⅱ度烧伤创面的疗效及安全性评价[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2009,25(5):451-455.
[38] AKITA S, AKINO K, IMAIZUMI T, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor accelerates and improves second‐degree burn wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2008;16(5): 635-641.
[39] BRANSKI LK, HERNDON DN, CELIS MM, et al. Amnion in the treatment of pediatric partial-thickness facial burns. Burns. 2008; 34(3):393-399.
[40] MA B, CHENG DS, XIA ZF, et al. Randomized, multicenter, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trial using topical recombinant human acidic fibroblast growth factor for deep partial-thickness burns and skin graft donor site. Wound Repair Regen. 2007;15(6):795-799.
[41] 梁自乾,黎洪棉,蒙诚跃.重组人表皮生长因子对儿童面部非Ⅲ度烧伤创面的修复[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(10):1974-1975.
[42] HUANG Y, LI X, LIAO Z, et al. A randomized comparative trial between Acticoat and SD-Ag in the treatment of residual burn wounds, including safety analysis. Burns. 2007;33(2):161-166.
[43] 陈炯,韩春茂,林小玮,等.纳米银敷料在修复Ⅱ度烧伤创面的应用研究[J].中华外科杂志,2006,44(1):50-52.
[44] 王世岭,马建丽,柴家科,等.重组人表皮生长因子软膏对烧伤创面修复的促进作用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2002, 16(3):173-176.
[45] FU X, SHEN Z, CHEN Y, et al. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of use of topical recombinant bovine basic fibroblast growth factor for second-degree burns. Lancet. 1998;352(9141):1661-1664.
[46] YEUNG C, HSIEH P, WEI L, et al. Efficacy of lyophilised platelet-rich plasma powder on healing rate in patients with deep second degree burn injury a prospective double-blind randomized clinical trial. Ann Plast Surge. 2018;801:S66-S69.
[47] YOSHINO Y, OHTSUKA M, KAWAGUCHI M, et al. The wound/burn guidelines - 6: Guidelines for the management of burns. J Dermatol. 2016;43(9):989-1010.
[48] 张烨.组织工程人工真皮替代物研究进展综述及临床应用体会[D].广州:南方医科大学,2018.
[49] ZHAO J, CHEN L, SHU B, et al. Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor influences angiogenesis by regulating the coordinated expression of VEGF and the Ang/Tie system. PLoS One. 2014;9(3): e92691.
[50] KRZYSZCZYK P, SCHLOSS R, PALMER A, et al. The role of macrophages in acute and chronic wound healing and interventions to promote pro-wound healing phenotypes. Front Physiol. 2018;9:419.
[51] MANN A, BREUHAHN K, SCHIRMACHER P, et al. Keratinocyte-derived granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor accelerates wound healing: stimulation of keratinocyte proliferation, granulation tissue formation, and vascularization. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;117(6):1382-1390.
[52] FANG Y, SHEN J, YAO M, et al. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor enhances wound healing in diabetes via upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines. Br J Dermatol. 2010;162(3):478-486.
[53] KAPLAN G, WALSH G, GUIDO LS, et al. Novel responses of human skin to intradermal recombinant granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor: langerhans cell recruitment, keratinocyte growth, and enhanced wound healing. J Exp Med. 1992; 175(6):1717-1728.
[54] WU F, DAI L, GENG L, et al. Practically feasible production of sustained-release microspheres of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (rhGM-CSF). J Control Release. 2017;259:195-202.
[55] COKCETIN NN, PAPPALARDO M, CAMPBELL LT, et al. The Antibacterial Activity of Australian Leptospermum Honey Correlates with Methylglyoxal Levels. PLoS One. 2016; 11(12):e167780.
[56] ALBARIDI NA. Antibacterial potency of honey. Int J Microbiol. 2019;2019:2464507.
[57] ESCUREDO O, DOBRE I, FERNANDEZ-GONZALEZ M, et al. Contribution of botanical origin and sugar composition of honeys on the crystallization phenomenon. Food Chem. 2014;149:84-90.
[58] BRUDZYNSKI K, ABUBAKER K, ST-MARTIN L, et al. Re-examining the role of hydrogen peroxide in bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities of honey. Front Microbiol. 2011; 2:213.
[59] HUSSAIN MB. Role of honey in topical and systemic bacterial infections. J Altern Complement Med. 2018;24(1):15-24.
[60] COOKE J, DRYDEN M, PATTON T, et al. The antimicrobial activity of prototype modified honeys that generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) hydrogen peroxide. BMC Res Notes. 2015;8:20.
[61] MOLAN PC. The evidence supporting the use of honey as a wound dressing. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2006;5(1):40-54.
[62] ZHU G, WANG Q, LU S, et al. Hydrogen peroxide: a potential wound therapeutic target? Med Princ Pract. 2017;26(4):301-308.
[63] BOGDANOV S. Nature and origin of the antibacterial substances in honey. Lebensm Wissu Techol. 1997;30(7):748-753.
[64] WASIHUN AG, KASA BG. Evaluation of antibacterial activity of honey against multidrug resistant bacteria in Ayder Referral and Teaching Hospital, Northern Ethiopia. Springerplus. 2016;5(1):842.
[65] PATTAMAYUTANON P, ANGELI S, THAKEOW P, et al. Biomedical Activity and Related Volatile Compounds of Thai Honeys from 3 Different Honeybee Species. J Food Sci. 2015,80(10):M2228-M2240.
[66] POSTMES T, VANDEPUTTE J. Recombinant growth factors or honey? Burns. 1999; 25(7):676-678.
[67] KARAYIL S, DESHPANDE SD, KOPPIKAR GV. Effect of honey on multidrug resistant organisms and its synergistic action with three common antibiotics. J Postgrad Med. 1998;44(4):93-96.
[68] WANG R, STARKEY M, HAZAN R, et al. Honey’s ability to counter bacterial infections arises from both bactericidal compounds and QS inhibition. Front Microbiol. 2012;3:144.
[69] ATKINSON S, WILLIAMS P. Quorum sensing and social networking in the microbial world. J R Soc Interface. 2009;6(40):959-978.
[70] CUTTING KF, WHITE RJ. Maceration of the skin and wound bed. 1: Its nature and causes. J Wound Care. 2002;11(7):275-278.
[71] GOPAL SK, BALAJI M, SUBIKSHA G, et al. Honey based treatment strategies for infected wounds and burns: a systematic review of recent pre-clinical research. Wound Med. 2020 (prepublish).
[72] VICTORIA CN, JAMES H, JONATHAN AGC. Dissecting the antimicrobial composition of honey. Antibiotics. 2019;8(4):251.
[73] SIMON A, TRAYNOR K, SANTOS K, et al. Medical honey for wound care--still the ‘latest resort’? Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2009;6(2):165-173.
[74] EGGER M, EBRAHIM S, SMITH GD. Where now for meta-analysis? Int J Epidemiol. 2002;31(1):1-5.
|