[1] SCHENK RK, BUSER D, HARDWICK WR, et al. Healing pattern of bone regeneration in membrane-protected defects: a histologic study in the canine mandible. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1994;9(1):13-29.
[2] FUNES SC, RIOS M, ESCOBAR-VERA J, et al. Implications of macrophage polarization in autoimmunity. Immunology. 2018;154(2):186-195.
[3] MURRAY PJ. Macrophage Polarization. Annu Rev Physiol. 2017;79:541-566.
[4] LASSUS J, SALO J, JIRANEK WA, et al. Macrophage activation results in bone resorption. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(352):7-15.
[5] ZHENG ZW, CHEN YH, WU DY, et al. Development of an Accurate and Proactive Immunomodulatory Strategy to Improve Bone Substitute Material-Mediated Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Theranostics. 2018; 8(19):5482-5500.
[6] GONG L, ZHAO Y, ZHANG Y, et al. The Macrophage Polarization Regulates MSC Osteoblast Differentiation in vitro. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2016;46(1):65-71.
[7] LIU YC, ZOU XB, CHAI YF, et al. Macrophage polarization in inflammatory diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 2014;10(5):520-529.
[8] WANG X, LI F, XIE L, et al. Inhibition of overactive TGF-beta attenuates progression of heterotopic ossification in mice. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):551.
[9] NIU H, MA Y, WU G, et al. Multicellularity-interweaved bone regeneration of BMP-2-loaded scaffold with orchestrated kinetics of resorption and osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2019;216:119216.
[10] LIU X, LI X, TAO Y, et al. TCDD inhibited the osteogenic differentiation of human fetal palatal mesenchymal cells through AhR and BMP-2/TGF-β/Smad signaling. Toxicology. 2020;431:152353.
[11] ZHANG J, SHI H, ZHANG N, et al. Interleukin-4-loaded hydrogel scaffold regulates macrophages polarization to promote bone mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation via TGF-beta1/Smad pathway for repair of bone defect. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(10):e12907.
[12] LI D, YANG Z, ZHAO X, et al. Osteoimmunomodulatory injectable Lithium-Heparin hydrogel with Microspheres/TGF-β1 delivery promotes M2 macrophage polarization and osteogenesis for guided bone regeneration. Chem Eng J. 2022;435:134991.
[13] WEI F, ZHOU Y, WANG J, et al. The Immunomodulatory Role of BMP-2 on Macrophages to Accelerate Osteogenesis. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24(7-8): 584-594.
[14] ZHANG X, CHEN Q, MAO X. Magnesium Enhances Osteogenesis of BMSCs by Tuning Osteoimmunomodulation. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:7908205.
[15] MAO CY, WANG YG, ZHANG X, et al. Double-edged-sword effect of IL-1β on the osteogenesis of periodontal ligament stem cells via crosstalk between the NF-κB, MAPK and BMP/Smad signaling pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2016; 7(7):e2296.
[16] KHOLODENKO BN, BIRTWISTLE MR. Four-dimensional dynamics of MAPK information processing systems. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2009; 1(1):28-44.
[17] YUE J, LóPEZ JM. Understanding MAPK Signaling Pathways in Apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21 (7):2346.
[18] 武明云 , 虞坚尔 , 薛征 , 等. 基于 MAPK 信号通路的中药治疗支气管哮喘的实验研究进展[J]. 海中医药大学学报 ,2019,33(2):86-91.
[19] HAO J, HU Y, LI Y, et al. Involvement of JNK signaling in IL4-induced M2 macrophage polarization. Exp Cell Res. 2017;357(2):155-162.
[20] LI X, HE X T, KONG DQ, et al. M2 Macrophages Enhance the Cementoblastic Differentiation of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells via the Akt and JNK Pathways. Stem Cells. 2019;37(12):1567-1580.
[21] GE C, XIAO G, JIANG D, et al. Critical role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase-MAPK pathway in osteoblast differentiation and skeletal development. J Cell Biol. 2007;176(5):709-718.
[22] XU AT, XIE YW, XU JG, et al. Effects of strontium-incorporated micro/nano rough titanium surfaces on osseointegration via modulating polarization of macrophages. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;207:111992.
[23] WANG L, WANG Q, WANG W, et al. Harmine Alleviates Titanium Particle-Induced Inflammatory Bone Destruction by Immunomodulatory Effect on the Macrophage Polarization and Subsequent Osteogenic Differentiation. Front Immunol. 2021;12:657687.
[24] YANG C, WANG W, ZHU K, et al. Lithium chloride with immunomodulatory function for regulating titanium nanoparticle-stimulated inflammatory response and accelerating osteogenesis through suppression of MAPK signaling pathway. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:7475-7488.
[25] ZHU K, YANG C, DAI H, et al. Crocin inhibits titanium particle-induced inflammation and promotes osteogenesis by regulating macrophage polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;76:105865.
[26] DAMERAU A, GABER T, OHRNDORF S, et al. JAK/STAT Activation: A General Mechanism for Bone Development, Homeostasis, and Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(23):9004.
[27] XIN P, XU X, DENG C, et al. The role of JAK/STAT signaling pathway and its inhibitors in diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;80:106210.
[28] KOH YC, YANG G, LAI CS, et al. Chemopreventive Effects of Phytochemicals and Medicines on M1/M2 Polarized Macrophage Role in Inflammation-Related Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(8):2208.
[29] YU Y, CUI H, ZHANG C, et al. Human nail bed extracellular matrix facilitates bone regeneration via macrophage polarization mediated by the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(18):4067-4079.
[30] HE Y, GAO Y, ZHANG Q, et al. IL-4 Switches Microglia/macrophage M1/M2 Polarization and Alleviates Neurological Damage by Modulating the JAK1/STAT6 Pathway Following ICH. Neuroscience. 2020;437:161-171.
[31] WANG N, GAO J, JIA M, et al. Exendin-4 Induces Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Migration Through Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages Polarization via PKA-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(5):1696-1714.
[32] VERGADI E, IERONYMAKI E, LYRONI K, et al. Akt Signaling Pathway in Macrophage Activation and M1/M2 Polarization. J Immunol. 2017;198(3): 1006-1014.
[33] ZHOU D, HUANG C, LIN Z, et al. Macrophage polarization and function with emphasis on the evolving roles of coordinated regulation of cellular signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 2014;26(2):192-197.
[34] LI M, GUO X, QI W, et al. Macrophage polarization plays roles in bone formation instructed by calcium phosphate ceramics. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(9):1863-1877.
[35] ZHAO SJ, KONG FQ, JIE J, et al. Macrophage MSR1 promotes BMSC osteogenic differentiation and M2-like polarization by activating PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):17-35.
[36] HOUSCHYAR KS, TAPKING C, BORRELLI MR, et al. Wnt Pathway in Bone Repair and Regeneration - What Do We Know So Far. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018;6:170.
[37] TETSU O, MCCORMICK F. Beta-catenin regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature. 1999;398(6726):422-426.
[38] 新岗,李永刚,包倪荣,等.骨代谢主要信号通路及信号分子的研究进展[J].基础医学与临床 ,2018,38(12):1799-1803.
[39] ABARICIA JO, SHAH AH, CHAUBAL M, et al. Wnt signaling modulates macrophage polarization and is regulated by biomaterial surface properties. Biomaterials. 2020;243:119920.
[40] YANG Y, YE YC, CHEN Y, et al. Crosstalk between hepatic tumor cells and macrophages via Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes M2-like macrophage polarization and reinforces tumor malignant behaviors. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(8):793.
[41] ZHENG M, WENG M, ZHANG X, et al. Beta-tricalcium phosphate promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through macrophages. Biomed Mater. 2021;16(2):025005.
[42] ZHANG J, WU Q, YIN C, et al. Sustained calcium ion release from bioceramics promotes CaSR-mediated M2 macrophage polarization for osteoinduction. J Leukoc Biol. 2021;110(3):485-496.
[43] PARIHAR A, EUBANK TD, DOSEFF AI. Monocytes and macrophages regulate immunity through dynamic networks of survival and cell death. J Innate Immun. 2010;2(3):204-215.
[44] HORWOOD NJ. Macrophage Polarization and Bone Formation: A review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016;51(1):79-86.
[45] QING L, FU J, WU P, et al. Metformin induces the M2 macrophage polarization to accelerate the wound healing via regulating AMPK/mTOR/NLRP3 inflammasome singling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(2):655-668.
[46] LA FONTAINE J, CHEN C, HUNT N, et al. Type 2 Diabetes and Metformin Influence on Fracture Healing in an Experimental Rat Model. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2016;55(5):955-960.
[47] YAN Z, TIAN X, ZHU J, et al. Metformin suppresses UHMWPE particle-induced osteolysis in the mouse calvaria by promoting polarization of macrophages to an anti-inflammatory phenotype. Mol Med. 2018;24(1):20.
[48] YE W, WANG J, LIN D, et al. The immunomodulatory role of irisin on osteogenesis via AMPK-mediated macrophage polarization. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;146:25-35.
[49] DRAGER J, HARVEY E J, BARRALET J. Hypoxia signalling manipulation for bone regeneration. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2015;17:e6.
[50] WAN C, SHAO J, GILBERT SR, et al. Role of HIF-1alpha in skeletal development. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192:322-326.
[51] LIU Y, YANG Z, WANG L, et al. Spatiotemporal Immunomodulation Using Biomimetic Scaffold Promotes Endochondral Ossification-Mediated Bone Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(11):e2100143.
[52] DAI X, HENG BC, BAI Y, et al. Restoration of electrical microenvironment enhances bone regeneration under diabetic conditions by modulating macrophage polarization. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(7):2029-2038.
[53] HALL A. Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science. 1998;279(5350): 509-514.
[54] XU Y, CUI K, LI J, et al. Melatonin attenuates choroidal neovascularization by regulating macrophage/microglia polarization via inhibition of RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. J Pineal Res. 2020;69(1):e12660.
[55] ZHU Y, LIANG H, LIU X, et al. Regulation of macrophage polarization through surface topography design to facilitate implant-to-bone osteointegration. Sci Adv. 2021;7(14):eabf6654.
|
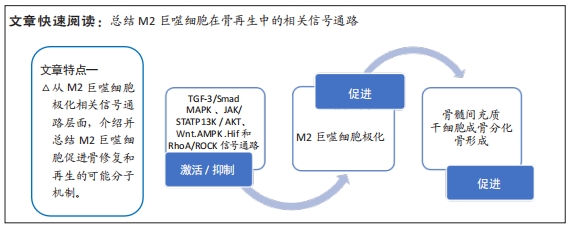
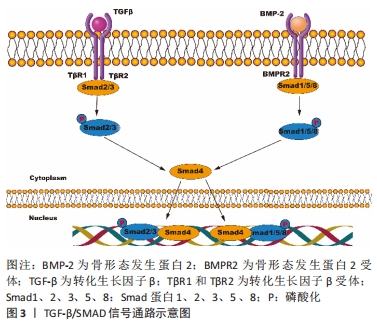
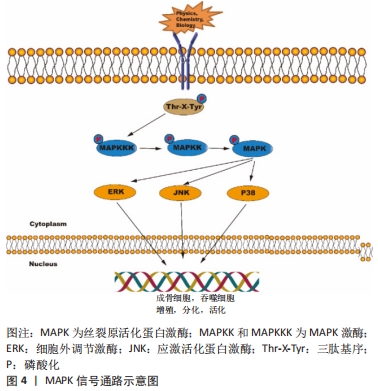
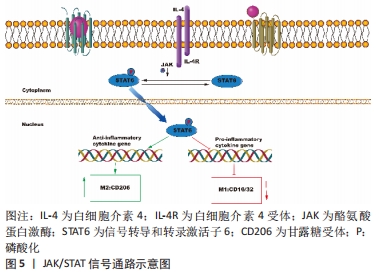
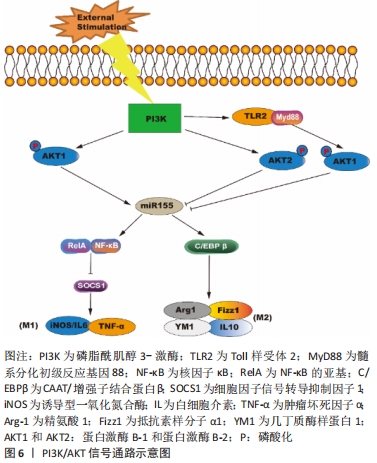
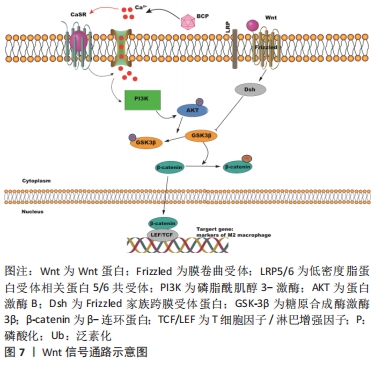
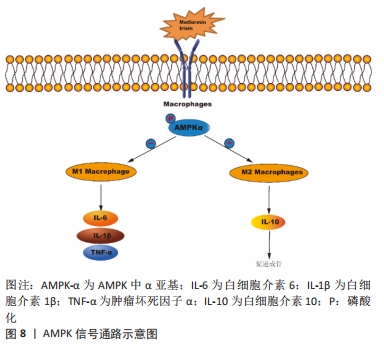


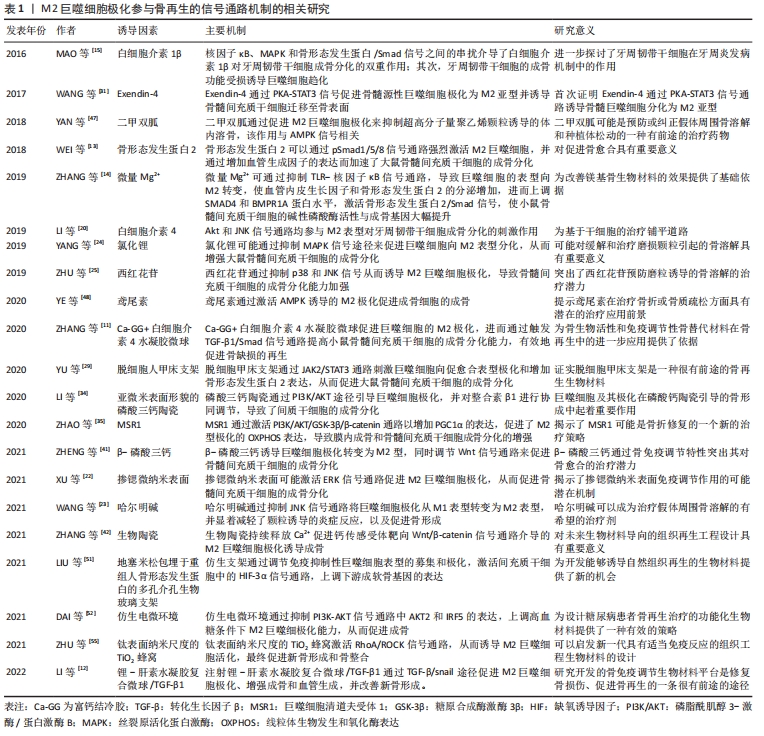 3.2 综述的创新性 以往此类综述都是对成骨信号通路在骨相关疾病中的作用进行总结分析,或者是总结M1/M2巨噬细胞在肿瘤/炎症性疾病/骨组织工程的作用,很少有综述对巨噬细胞极化促进骨再生的相关信号通路进行总结。该文总结了近年来M2巨噬细胞促进骨缺损修复或成骨分化所关联的信号通路,并讨论分析其可能的分子机制。
3.2 综述的创新性 以往此类综述都是对成骨信号通路在骨相关疾病中的作用进行总结分析,或者是总结M1/M2巨噬细胞在肿瘤/炎症性疾病/骨组织工程的作用,很少有综述对巨噬细胞极化促进骨再生的相关信号通路进行总结。该文总结了近年来M2巨噬细胞促进骨缺损修复或成骨分化所关联的信号通路,并讨论分析其可能的分子机制。