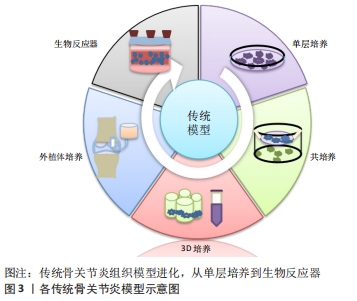
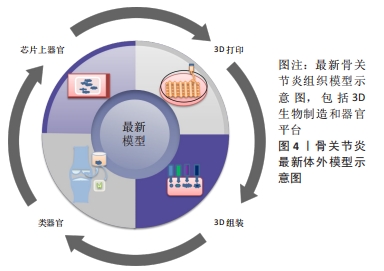
[1] GBD 2017 DISEASE AND INJURY INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789-1858.
[2] KING LK, MARCH L, Anandacoomarasamy A. Obesity & osteoarthritis. Indian J Med Res. 2013;138(2):185-193.
[3] LOESER RF, GOLDRING SR, SCANZELLO CR, et al. Osteoarthritis: a disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(6):1697-1707.
[4] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393(10182):1745-1759.
[5] THYSEN S, LUYTEN FP, LORIES RJ. Targets, models and challenges in osteoarthritis research. Dis Model Mech. 2015;8(1):17-30.
[6] CADDEO S, BOFFITO M, SARTORI S. Tissue engineering approaches in the design of healthy and pathological in vitro tissue models. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2017;5:40.
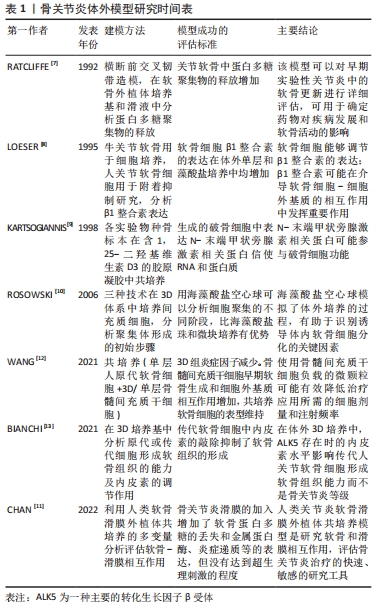
[7] RATCLIFFE A, BILLINGHAM ME, SAED-NEJAD F, et al. Increased release of matrix components from articular cartilage in experimental canine osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 1992;10(3):350-358.
[8] LOESER RF, CARLSON CS, MCGEE MP. Expression of beta 1 integrins by cultured articular chondrocytes and in osteoarthritic cartilage. Exp Cell Res. 1995;217(2): 248-257.
[9] KARTSOGIANNIS V, UDAGAWA N, NG KW, et al. Localization of parathyroid hormone-related protein in osteoclasts by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. Bone. 1998;22(3):189-194.
[10] ROSOWSKI M, FALB M, TSCHIRSCHMANN M, et al. Initiation of mesenchymal condensation in alginate hollow spheres--a useful model for understanding cartilage repair? Artif Organs. 2006;30(10):775-784.
[11] CHAN MWY, GOMEZ-ARISTIZÁBAL A, MAHOMED N, et al. A tool for evaluating novel osteoarthritis therapies using multivariate analyses of human cartilage-synovium explant co-culture. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(1):147-159.
[12] WANG B, LIU W, LI JJ, et al. A low dose cell therapy system for treating osteoarthritis: in vivo study and in vitro mechanistic investigations. Bioact Mater. 2021;7:478-490.
[13] BIANCHI VJ, PARSONS M, BACKSTEIN D, et al. Endoglin level is critical for cartilage tissue formation in vitro by passaged human chondrocytes. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(17-18):1140-1150.
[14] SALGADO C, JORDAN O, ALLÉMANN E. Osteoarthritis in vitro models: applications and implications in development of intra-articular drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(1):60.
[15] KOTHARI P, TRIPATHI AK, GIRME A. Caviunin glycoside (cafg) from dalbergia sissoo attenuates osteoarthritis by modulating chondrogenic and matrix regulating proteins. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;282:114315.
[16] LEE SA, MOON SM, HAN SH. Chondroprotective effects of aqueous extract of anthriscus sylvestris leaves on osteoarthritis in vitro and in vivo through MAPKS And Nf-Κb signaling inhibition. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:1202-1211.
[17] DESHMUKH V, HU H, BARROGA C. A small-molecule inhibitor of the wnt pathway (sm04690) as a potential disease modifying agent for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. osteoarthritis cartilage. 2018;26(1):18-27.
[18] LIU Z, LANG Y, LI L, et al. Effect of emodin on chondrocyte viability in an in vitro model of osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(6):5384-5389.
[19] AL-MODAWI RN, BRINCHMANN JE, KARLSEN TA. Multi-pathway protective effects of micrornas on human chondrocytes in an in vitro model of osteoarthritis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;17:776-790.
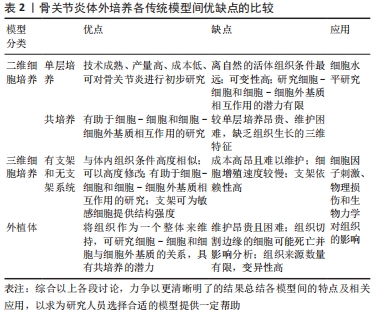
[20] SAMVELYAN HJ, HUGHES D, STEVENS C. Models of osteoarthritis: relevance and new insights. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021;109(3):243-256.
[21] BEEKHUIZEN M, BASTIAANSEN-JENNISKENS YM, KOEVOET W, et al. Osteoarthritic synovial tissue inhibition of proteoglycan production in human osteoarthritic knee cartilage: establishment and characterization of a long-term cartilage-synovium coculture. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(7):1918-1927.
[22] COPE PJ, OURRADI K, LI Y. Models of osteoarthritis: the good, the bad and the promising. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(2):230-239.
[23] BENAM KH, DAUTH S, HASSELL B, et al. Engineered in vitro disease models. Annu Rev Pathol. 2015;10:195-262.
[24] ZHENG W, FENG Z, YOU S. Fisetin inhibits il-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes through activating sirt1 and attenuates the progression of osteoarthritis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;45:135-147.
[25] JOHNSON CI, ARGYLE DJ, CLEMENTS DN. In vitro models for the study of osteoarthritis. Vet J. 2016;209:40-49.
[26] PARK H, LEE HJ, AN H, et al. Alginate hydrogels modified with low molecular weight hyaluronate for cartilage regeneration. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;162:100-107.
[27] MOHAN N, MOHANAN PV, SABAREESWARAN A. Chitosan-Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel For Cartilage Repair. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;104(Pt B):1936-1945.
[28] ZIADLOU R, BARBERO A, MARTIN I. Anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective effects of vanillic acid and epimedin c in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Biomolecules. 2020;10(6):932.
[29] HUANG S, SONG X, LI T, et al. Pellet coculture of osteoarthritic chondrocytes and infrapatellar fat pad-derived mesenchymal stem cells with chitosan/hyaluronic acid nanoparticles promotes chondrogenic differentiation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):264.
[30] ITOKAZU M, WAKITANI S, MERA H, et al. Transplantation of scaffold-free cartilage-like cell-sheets made from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage repair: a preclinical study. Cartilage. 2016;7(4):361-372.
[31] CARON MM, EMANS PJ, COOLSEN MM. Redifferentiation of dedifferentiated human articular chondrocytes: comparison of 2d and 3d cultures. osteoarthritis cartilage. 2012;20(10):1170-1178.
[32] NAKAGAWA Y, MUNETA T, OTABE K, et al. Cartilage derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells expresses lubricin in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 2016; 11(2):E0148777.
[33] DUVAL K, GROVER H, HAN LH. Modeling physiological events in 2d vs. 3d cell culture. Physiology (Bethesda). 2017;32(4):266-277.
[34] PRADAL J, ZULUAGA MF, MAUDENS P. Intra-articular bioactivity of a p38 mapk inhibitor and development of an extended-release system. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;93:110-117.
[35] GOLDRING SR, GOLDRING MB. Changes in the osteochondral unit during osteoarthritis: structure, function and cartilage-bone crosstalk. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(11):632-644.
[36] MAUDENS P, SEEMAYER CA, THAUVIN C. Nanocrystal-polymer particles: extended delivery carriers for osteoarthritis treatment. Small. 2018. doi:10.1002/Smll. 201703108.
[37] STEINMETZ NJ, AISENBREY EA, WESTBROOK KK. Mechanical loading regulates human msc differentiation in a multi-layer hydrogel for osteochondral tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2015;21:142-153.
[38] MAISANI M, PEZZOLI D, CHASSANDE O. Cellularizing hydrogel-based scaffolds to repair bone tissue: how to create a physiologically relevant micro-environment? J Tissue Eng. 2017;8:2041731417712073.
[39] DEY P, SCHNEIDER T, CHIAPPISI L. Mimicking of chondrocyte microenvironment using in situ forming dendritic polyglycerol sulfate-based synthetic polyanionic hydrogels. Macromol Biosci. 2016;16(4):580-590.
[40] STUDLE C, VALLMAJÓ-MARTÍN Q, HAUMER A. Spatially confined induction of endochondral ossification by functionalized hydrogels for ectopic engineering of osteochondral tissues. Biomaterials. 2018;171:219-229.
[41] GALUZZI M, PERTEGHELLA S, ANTONIOLI B. Human engineered cartilage and decellularized matrix as an alternative to animal osteoarthritis model. Polymers (Basel). 2018;10(7):738.
[42] KATOH S, YOSHIOKA H, SENTHILKUMAR R. Enhanced expression of hyaluronic acid in osteoarthritis-affected knee-cartilage chondrocytes during three-dimensional in vitro culture in a hyaluronic-acid-retaining polymer scaffold. Knee. 2021;29:365-373.
[43] KANG LJ, YOON J, RHO JG, et al. Self-assembled hyaluronic acid nanoparticles for osteoarthritis treatment. Biomaterials. 2021;275:120967.
[44] SINGH YP, MOSES JC, BHUNIA BK, et al. Hierarchically structured seamless silk scaffolds for osteochondral interface tissue engineering. J Mater Chem B. 2018; 6(36):5671-5688.
[45] GUVENDIREN M, BURDICK JA. Stiffening hydrogels to probe short- and long-term cellular responses to dynamic mechanics. Nat Commun. 2012;3:792.
[46] CAI Z, ZHANG H, WEI Y. Shear-thinning hyaluronan-based fluid hydrogels to modulate viscoelastic properties of osteoarthritis synovial fluids. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(8):3143-3157.
[47] MALIKMAMMADOV E, TANIR TE, KIZILTAY A, et al. Pcl and pcl-based materials in biomedical applications. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018;29(7-9):863-893.
[48] GEURTS J, JURIĆ D, MULLER M. Novel ex vivo human osteochondral explant model of knee and spine osteoarthritis enables assessment of inflammatory and drug treatment responses. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(5):1314.
[49] BYRON CR, TRAHAN RA. Comparison of the effects of interleukin-1 on equine articular cartilage explants and cocultures of osteochondral and synovial explants. Front Vet Sci. 2017;4:152.
[50] SCHWAB A, MEEUWSEN A, EHLICKE F, et al. Ex vivo culture platform for assessment of cartilage repair treatment strategies. Altex. 2017;34(2):267-277.
[51] BICHO D, PINA S, OLIVEIRA JM. In vitro mimetic models for the bone-cartilage interface regeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1059:373-394.
[52] AHMED S, CHAUHAN VM, GHAEMMAGHAMI AM, et al. New generation of bioreactors that advance extracellular matrix modelling and tissue engineering. Biotechnol Lett. 2019;41(1):1-25.
[53] LIN H, LOZITO TP, ALEXANDER PG, et al. Stem cell-based microphysiological osteochondral system to model tissue response to interleukin-1β. Mol Pharm. 2014;11(7):2203-2212.
[54] NICHOLS DA, SONDH IS, LITTLE SR, et al. Design and validation of an osteochondral bioreactor for the screening of treatments for osteoarthritis. Biomed Microdevices. 2018;20(1):18.
[55] LDE MELO BAG, JODAT YA, MEHROTRA S, et al. 3D printed cartilage-like tissue constructs with spatially controlled mechanical properties. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(51):1906330.
[56] NOWICKI MA, CASTRO NJ, PLESNIAK MW, et al. 3d printing of novel osteochondral scaffolds with graded microstructure. Nanotechnology. 2016;27(41):414001.
[57] MORONI L, BURDICK JA, HIGHLEY C, et al. Biofabrication strategies for 3d in vitro models and regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Mater. 2018;3(5):21-37.
[58] MEKHILERI NV, LIM KS, BROWN GCJ, et al. Automated 3d bioassembly of micro-tissues for biofabrication of hybrid tissue engineered constructs. Biofabrication. 2018;10(2):024103.
[59] FATEHULLAH A, TAN SH, BARKER N. Organoids as an in vitro model of human development and disease. Nat Cell Biol. 2016;18(3):246-254.
[60] NILSSON HALL G, MENDES LF, GKLAVA C, et al. Developmentally engineered callus organoid bioassemblies exhibit predictive in vivo long bone healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019;7(2):1902295.
[61] MOSIG AS. Organ-on-chip models: new opportunities for biomedical research. Future Sci Oa. 2016;3(2):FSO130.
[62] OCCHETTA P, MAINARDI A, VOTTA E, et al. Hyperphysiological compression of articular cartilage induces an osteoarthritic phenotype in a cartilage-on-a-chip model. Nat Biomed Eng. 2019;3(7):545-557.
[63] LIN Z, LI Z, LI EN, et al. Osteochondral tissue chip derived from ipscs: modeling oa pathologies and testing drugs. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:411.
|