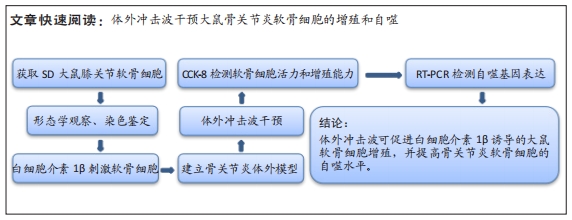
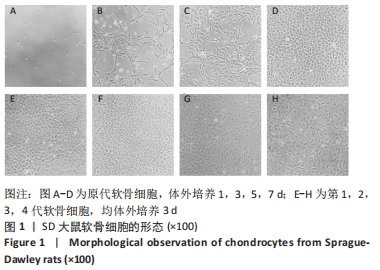
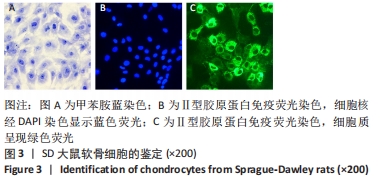
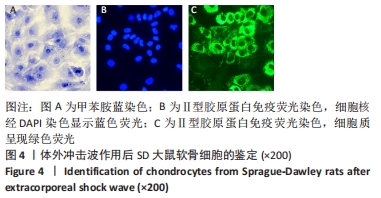
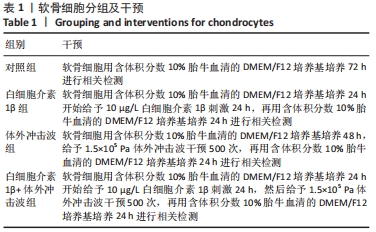
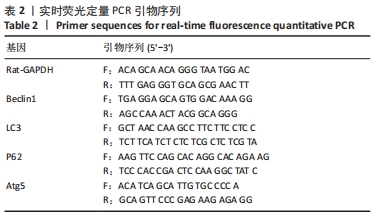
[1] SHEN J, ABU-AMER Y, O’KEEFE RJ, et al. Inflammation and epigenetic regulation in osteoarthritis. Connect Tissue Res. 2017;58(1):49-63.
[2] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072.
[3] 陈浩雄,徐启良,黄竞杰,等.牛膝总皂苷体外干预膝关节炎软骨细胞增殖与凋亡的研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2021,30(22):2400-2404.
[4] ZHOU ZB, HUANG GX, FU Q, et al. circRNA.33186 Contributes to the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis by Sponging miR-127-5p. Mol Ther. 2019; 27(3):531-541.
[5] MURATA R, NAKAGAWA K, OHTORI S, et al. The effects of radial shock waves on gene transfer in rabbit chondrocytes in vitro. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(11):1275-1282.
[6] MA F, LI G, YU Y, et al. MiR-33b-3p promotes chondrocyte proliferation and inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage ECM degradation by targeting DNMT3A in osteoarthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;519(2): 430-437.
[7] RACANELLI AC, KIKKERS SA, CHOI AMK, et al. Autophagy and inflammation in chronic respiratory disease. Autophagy. 2018;14(2):221-232.
[8] LÓPEZ DE FIGUEROA P, LOTZ MK, BLANCO FJ, et al. Autophagy activation and protection from mitochondrial dysfunction in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(4):966-976.
[9] BOUDERLIQUE T, VUPPALAPATI KK, NEWTON PT, et al. Targeted deletion of Atg5 in chondrocytes promotes age-related osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(3):627-631.
[10] LUO P, GAO F, NIU D, et al. The Role of Autophagy in Chondrocyte Metabolism and Osteoarthritis: A Comprehensive Research Review. Biomed Res Int. 2019; 2019:5171602.
[11] CARAMÉS B, TANIGUCHI N, OTSUKI S, et al. Autophagy is a protective mechanism in normal cartilage, and its aging-related loss is linked with cell death and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(3):791-801.
[12] JI Q, WANG P, HE C. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy as a novel and potential treatment for degenerative cartilage and bone disease: Osteoarthritis. A qualitative analysis of the literature. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2016;121(3):255-265.
[13] WANG CJ. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders. J Orthop Surg Res. 2012;7:11.
[14] CACCHIO A, GIORDANO L, COLAFARINA O, et al. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy compared with surgery for hypertrophic long-bone nonunions. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(11):2589-2597.
[15] WANG CJ, SUN YC, WONG T, et al. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows time-dependent chondroprotective effects in osteoarthritis of the knee in rats. J Surg Res. 2012;178(1):196-205.
[16] WANG CJ, WENG LH, KO JY, et al. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows chondroprotective effects in osteoarthritic rat knee. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(8):1153-1158.
[17] ZHAO X, LI Y, LIN X, et al. Ozone induces autophagy in rat chondrocytes stimulated with IL-1β through the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. J Pain Res. 2018;11:3003-3017.
[18] 孙盼盼,赵旭,林小雯,等.医用臭氧对大鼠骨关节炎软骨细胞中 PPARγ及自噬水平表达的影响[J].山东大学学报(医学版),2020,58(6):14-21.
[19] QI H, JIN S, YIN C, et al. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy promotes osteochondral regeneration of knee joints in rabbits. Exp Ther Med. 2018; 16(4):3478-3484.
[20] 綦惠,杰永生,郑蕊,等.放散式体外冲击波对软骨细胞生物学行为的影响[J].北京生物医学工程,2020,39(3):278-284.
[21] LIU Q, WANG S, LIN J, et al. The burden for knee osteoarthritis among Chinese elderly: estimates from a nationally representative study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(12):1636-1642.
[22] NEOGI T. The epidemiology and impact of pain in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(9):1145-1153.
[23] JOHNSON VL, HUNTER DJ. The epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2014;28(1):5-15.
[24] MOBASHERI A, RAYMAN MP, GUALILLO O, et al. The role of metabolism in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(5):302-311.
[25] WU CW, TCHETINA EV, MWALE F, et al. Proteolysis involving matrix metalloproteinase 13 (collagenase-3) is required for chondrocyte differentiation that is associated with matrix mineralization. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(4):639-651.
[26] MA Y, WU Y, CHEN J, et al. miR-10a-5p Promotes Chondrocyte Apoptosis in Osteoarthritis by Targeting HOXA1. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;14:398-409.
[27] GAO GC, CHENG XG, WEI QQ, et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 inhibits apoptosis and matrix metabolism disorder in interleukin-1β-induced inflammation in articular chondrocytes via the JNK signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(10):17167-17179.
[28] ROMEO P, LAVANGA V, PAGANI D, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders: a review. Med Princ Pract. 2014;23(1):7-13.
[29] SCHMITZ C, CSÁSZÁR NB, MILZ S, et al. Efficacy and safety of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for orthopedic conditions: a systematic review on studies listed in the PEDro database. Br Med Bull. 2015;116(1):115-138.
[30] 高宏梁,周新华,吴猛,等.低能量体外冲击波对膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国现代医生,2018,56(1):32-35.
[31] KIM YH, BANG JI, SON HJ, et al. Protective effects of extracorporeal shockwave on rat chondrocytes and temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis; preclinical evaluation with in vivo99mTc-HDP SPECT and ex vivo micro-CT. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(11):1692-1701.
[32] NOTARNICOLA A, IANNONE F, MACCAGNANO G, et al. Chondrocytes treated with different shock wave devices. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2017;7(1):152-156.
[33] VETRANO M, RANIERI D, NANNI M, et al. Hyaluronic Acid (HA), Platelet-Rich Plasm and Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) promote human chondrocyte regeneration in vitro and ESWT-mediated increase of CD44 expression enhances their susceptibility to HA treatment. PLoS One. 2019;14(6):e0218740.
[34] CHENG NT, MENG H, MA LF, et al. Role of autophagy in the progression of osteoarthritis: The autophagy inhibitor, 3-methyladenine, aggravates the severity of experimental osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med. 2017;39(5):1224-1232.
[35] CARAMÉS B, HASEGAWA A, TANIGUCHI N, et al. Autophagy activation by rapamycin reduces severity of experimental osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(4):575-581.
[36] SALMINEN A, KAARNIRANTA K, KAUPPINEN A. Beclin 1 interactome controls the crosstalk between apoptosis, autophagy and inflammasome activation: impact on the aging process. Ageing Res Rev. 2013;12(2):520-534.
[37] LONG M, LI X, LI L, et al. Multifunctional p62 Effects Underlie Diverse Metabolic Diseases. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017;28(11):818-830.
[38] LAHUERTA M, AGUADO C, SÁNCHEZ-MARTÍN P, et al. Degradation of altered mitochondria by autophagy is impaired in Lafora disease. FEBS J. 2018;285(11):2071-2090.
[39] SCHAAF MB, KEULERS TG, VOOIJS MA, et al. LC3/GABARAP family proteins: autophagy-(un)related functions. FASEB J. 2016;30(12):3961-3978.
[40] 孙明帅,范重山,李凯杰,等.骨关节炎中软骨细胞自噬的作用及其靶向治疗[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(35):5688-5693.
[41] 杜汉承.雷诺嗪联合血栓通胶囊对糖尿病大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤过程中细胞自噬及心肌核因子-κB、人磷酸化Akt蛋白、IP7水平的影响[J].中国药物经济学,2020,15(9):39-43.
[42] 唐琴,朱海鹏,郭卫中,等.锌对THP-1细胞自噬、NF-κB通路活化及产生白细胞介素23的影响[J].免疫学杂志,2018,34(4):319-325.
[43] DU L, SHEN T, LIU B, et al. Shock Wave Therapy Promotes Cardiomyocyte Autophagy and Survival during Hypoxia. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(2):673-684.
[44] QIU Q, SHEN T, YU X, et al. Cardiac Shock Wave Therapy Alleviates Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Myocardial Necroptosis by Modulating Autophagy. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:8880179.
[45] LONG Q, LI X, HE H, et al. Autophagy activation protects shock wave induced renal tubular epithelial cell apoptosis may through modulation of Akt/ GSK-3β pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12(12):1461-1471.
[46] ZHU GQ, JEON SH, BAE WJ, et al. Efficient Promotion of Autophagy and Angiogenesis Using Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy Enhanced by the Low-Energy Shock Waves in the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:1302672.
|