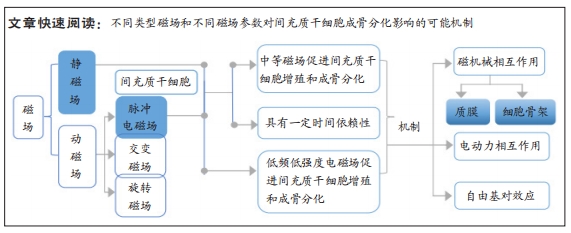
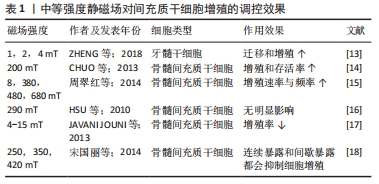
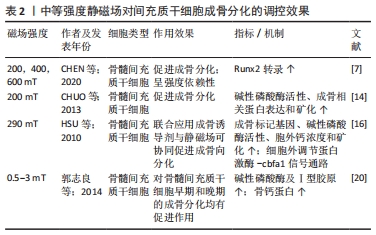
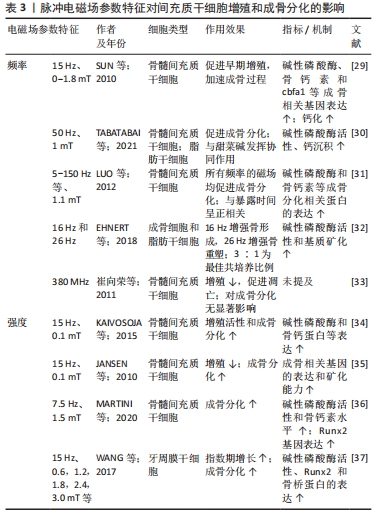
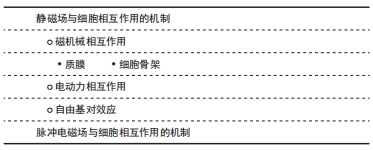
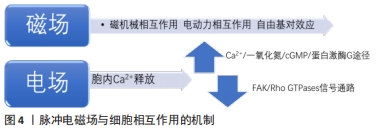
[1] ZHANG S, LI X, QI Y, et al. Comparison of Autogenous Tooth Materials and Other Bone Grafts. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18(3):327-341.
[2] ARTHUR A, GRONTHOS S. Clinical Application of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells to Repair Skeletal Tissue. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9759.
[3] SI Z, WANG X, SUN C, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells: Sources, potency, and implications for regenerative therapies. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;114:108765.
[4] GUGLIANDOLO A, FONTICOLI L, TRUBIANI O, et al. Oral Bone Tissue Regeneration: Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Secretome, and Biomaterials. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):5236.
[5] SUI BD, HU CH, LIU AQ, et al. Stem cell-based bone regeneration in diseased microenvironments: Challenges and solutions. Biomaterials. 2019;196:18-30.
[6] PARATE D, KADIR ND, CELIK C, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields potentiate the paracrine function of mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):46.
[7] CHEN G, ZHUO Y, TAO B, et al. Moderate SMFs attenuate bone loss in mice by promoting directional osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):487.
[8] MARYCZ K, KORNICKA K, RÖCKEN M. Static Magnetic Field (SMF) as a Regulator of Stem Cell Fate - New Perspectives in Regenerative Medicine Arising from an Underestimated Tool. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2018;14(6):785-792.
[9] 张灵玉,江静怡,樊瑜波,等.磁场在骨生物学领域:研究与应用中明确和未明确问题[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(4):584-590.
[10] LEAL-JUNIOR ECP, DE OLIVEIRA MFD, JOENSEN J, et al. What is the optimal time-response window for the use of photobiomodulation therapy combined with static magnetic field (PBMT-sMF) for the improvement of exercise performance and recovery, and for how long the effects last? A randomized, triple-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2020;12:64.
[11] ZHANG Y, LI W, LIU C, et al. Electromagnetic field treatment increases purinergic receptor P2X7 expression and activates its downstream Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin axis in mesenchymal stem cells under osteogenic induction. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):407.
[12] 王彦蒽,汪沛,王晟磊,等.低频脉冲电磁场增强骨形态发生蛋白9诱导牙周膜干细胞成骨分化作用[J].第二军医大学学报,2020, 41(8):855-863.
[13] ZHENG L, ZHANG L, CHEN L, et al. Static magnetic field regulates proliferation, migration, differentiation, and YAP/TAZ activation of human dental pulp stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(10): 2029-2040.
[14] CHUO W, MA T, SAITO T, et al. A Preliminary Study of the Effect of Static Magnetic Field Acting on Rat Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells during Osteogenic Differentiation In Vitro. J Hard Tissue Biol. 2013; 22(2):227-232.
[15] 周翠红,张小云,张宇,等.不同强度静磁场间歇曝磁对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及细胞周期的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(1): 105-109.
[16] HSU SH, CHANG JC. The static magnetic field accelerates the osteogenic differentiation and mineralization of dental pulp cells. Cytotechnology. 2010;62(2):143-155.
[17] JAVANI JOUNI F, ABDOLMALEKI P, MOVAHEDIN M. Investigation on the effect of static magnetic field up to 15 mT on the viability and proliferation rate of rat bone marrow stem cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2013;49(3):212-219.
[18] 宋国丽,周翠红,张宇,等.静磁场对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及骨向分化的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2014,20(4):322-326.
[19] SADRI M, ABDOLMALEKI P, ABRUN S, et al. Static Magnetic Field Effect on Cell Alignment, Growth, and Differentiation in Human Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2017;10(3):249-262.
[20] 郭志良,滕海军,王亮,等.恒磁场对培养的骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响及机制[J].第三军医大学学报,2014,36(12):1255-1259.
[21] KIM EC, LEESUNGBOK R, LEE SW, et al. Effects of moderate intensity static magnetic fields on human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 2015;36(4):267-276.
[22] 张磊,李志元,张欣.稳态磁场对真核生物细胞骨架的影响[J].科学通报,2019,64(8):748-760.
[23] YAMAGUCHI-SEKINO S, KIRA T, SEKINO M, et al. Effects of 7 T static magnetic fields on the expression of biological markers and the formation of bone in rats. Bioelectromagnetics. 2019;40(1):16-26.
[24] 夏阳,陈慧敏,胡姝颖,等.静磁场连续曝磁对牙髓干细胞增殖和分化的影响[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2020,40(2):191-194.
[25] 刘阳,李善昌,王长振,等.静磁场对大鼠下颌骨骨折愈合的研究[J].口腔医学研究,2020,36(6):548-553.
[26] ROSS CL, ANG DC, ALMEIDA-PORADA G. Targeting Mesenchymal Stromal Cells/Pericytes (MSCs) With Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Has the Potential to Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2019;10:266.
[27] NAYAK BP, DOLKART O, SATWALEKAR P, et al. Effect of the Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) on Dental Implants Stability: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(7): 1667.
[28] ROSS CL, ZHOU Y, MCCALL CE, et al. The Use of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field to Modulate Inflammation and Improve Tissue Regeneration: A Review. Bioelectricity. 2019;1(4):247-259.
[29] SUN LY, HSIEH DK, LIN PC, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields accelerate proliferation and osteogenic gene expression in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells during osteogenic differentiation. Bioelectromagnetics. 2010;31(3):209-219.
[30] TABATABAI TS, HAJI GHASEM KASHANI M, MASKANI R, et al. Synergic effects of extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field and betaine on in vitro osteogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2021;57(4):468-476.
[31] LUO F, HOU T, ZHANG Z, et al. Effects of pulsed electromagnetic field frequencies on the osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Orthopedics. 2012;35(4):e526-e531.
[32] EHNERT S, VAN GRIENSVEN M, UNGER M, et al. Co-Culture with Human Osteoblasts and Exposure to Extremely Low Frequency Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields Improve Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(4):994.
[33] 崔向荣,苏伟,黄钊,等.高频脉冲电磁场对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和成骨分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(10):1715-1720.
[34] KAIVOSOJA E, SARIOLA V, CHEN Y, et al. The effect of pulsed electromagnetic fields and dehydroepiandrosterone on viability and osteo-induction of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(1):31-40.
[35] JANSEN JH, VAN DER JAGT OP, PUNT BJ, et al. Stimulation of osteogenic differentiation in human osteoprogenitor cells by pulsed electromagnetic fields: an in vitro study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010;11:188.
[36] MARTINI F, PELLATI A, MAZZONI E, et al. Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Signaling in the Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Induced by Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(6):2104.
[37] WANG T, WANG P, CAO Z, et al. Effects of BMP9 and pulsed electromagnetic fields on the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 2017;38(1):63-77.
[38] LI X, ZHANG M, BAI L, et al. Effects of 50 Hz pulsed electromagnetic fields on the growth and cell cycle arrest of mesenchymal stem cells: an in vitro study. Electromagn Biol Med. 2012;31(4):356-364.
[39] CECCARELLI G, BLOISE N, MANTELLI M, et al. A comparative analysis of the in vitro effects of pulsed electromagnetic field treatment on osteogenic differentiation of two different mesenchymal cell lineages. Biores Open Access. 2013;2(4):283-294.
[40] ZHOU W, LIN J, ZHAO K, et al. Single-Cell Profiles and Clinically Useful Properties of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells of Adipose and Bone Marrow Origin. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(7):1722-1733.
[41] HAYASHI S, KAKIKAWA M. Exposure to 60 Hz magnetic field can affect membrane proteins and membrane potential in human cancer cells. Electromagn Biol Med. 2021;40(4):459-466.
[42] LEW WZ, HUANG YC, HUANG KY, et al. Static magnetic fields enhance dental pulp stem cell proliferation by activating the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway as its putative mechanism. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(1):19-29.
[43] LIU Y, QI H, SUN RG, et al. An investigation into the combined effect of static magnetic fields and different anticancer drugs on K562 cell membranes. Tumori. 2011;97(3):386-392.
[44] ZABLOTSKII V, POLYAKOVA T, DEJNEKA A. Modulation of the Cell Membrane Potential and Intracellular Protein Transport by High Magnetic Fields. Bioelectromagnetics. 2021;42(1):27-36.
[45] GE S, LI J, HUANG D, et al. Strong static magnetic field delayed the early development of zebrafish. Open Biol. 2019;9(10):190137.
[46] LEW WZ, FENG SW, LIN CT, et al. Use of 0.4-Tesla static magnetic field to promote reparative dentine formation of dental pulp stem cells through activation of p38 MAPK signalling pathway. Int Endod J. 2019;52(1):28-43.
[47] INABA H, YAMADA M, RASHID MR, et al. Magnetic Force-Induced Alignment of Microtubules by Encapsulation of CoPt Nanoparticles Using a Tau-Derived Peptide. Nano Lett. 2020;20(7):5251-5258.
[48] WOSIK J, CHEN W, QIN K, et al. Magnetic Field Changes Macrophage Phenotype. Biophys J. 2018;114(8):2001-2013.
[49] ZHANG J, DING C, REN L, et al. The effects of static magnetic fields on bone. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2014;114(3):146-152.
[50] ZHENG Y, DOU JR, GAO Y, et al. Effects of 15 Hz square wave magnetic fields on the voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels in prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons. Int J Radiat Biol. 2017;93(4):449-455.
[51] EHNERT S, FENTZ AK, SCHREINER A, et al. Extremely low frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields cause antioxidative defense mechanisms in human osteoblasts via induction of •O2- and H2O2. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):14544.
[52] SONG K, IM SH, YOON YJ, et al. A 60 Hz uniform electromagnetic field promotes human cell proliferation by decreasing intracellular reactive oxygen species levels. PLoS One. 2018;13(7):e0199753.
[53] VAN HUIZEN AV, MORTON JM, KINSEY LJ, et al. Weak magnetic fields alter stem cell-mediated growth. Sci Adv. 2019;5(1):eaau7201.
[54] ZHANG J, DING C, MENG X, et al. Nitric oxide modulates the responses of osteoclast formation to static magnetic fields. Electromagn Biol Med. 2018;37(1):23-34.
[55] KIM YM, LIM HM, LEE EC, et al. Synergistic effect of electromagnetic fields and nanomagnetic particles on osteogenesis through calcium channels and p-ERK signaling. J Orthop Res. 2021; 39(8):1633-1646.
[56] ZHANG Y, YAN J, XU H, et al. Extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields promote mesenchymal stem cell migration by increasing intracellular Ca2+ and activating the FAK/Rho GTPases signaling pathways in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):143.
|