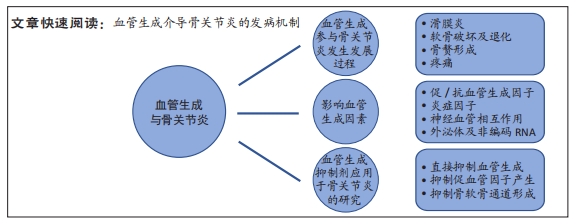
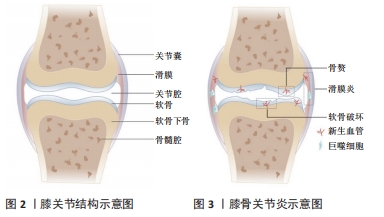
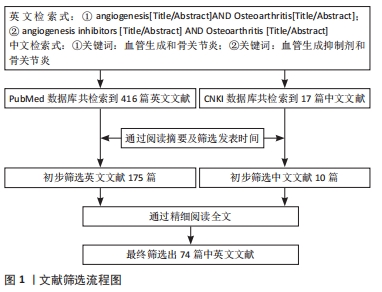
[1] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072.
[2] STAGNIC, ROCCHI M, MAZZOTTA A, et al. Randomised, double-blind comparison of a fixed co-formulation of intr a-articular polyn ucleotides and hyaluronic acid versus hyaluronic acid alone in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: two-year follow-up. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22:773.
[3] CADET C, MAHEU E, The French AGRHUM Group (Association Geriatric and RHeUMatology). Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the pharmacological management of osteoarthritis in the very old: prescribe or proscribe. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2021;13: 1759720X211022149.
[4] 陈朝蔚,陈永强.骨关节炎血管生成与炎症的关系[J].国际骨科学杂志,2007,28(1):33-35.
[5] ASHRAF S, WIBBERLEY H, MAPP PI, et al. Increased vascular penetration and nerve growth in the meniscus: a potential source of pain in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:523-529.
[6] FRANSÈS RE, MCWILLIAMS DF, MAPP PI, et al. Osteochondral angiogenesis and increased protease inhibitor expression in OA. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18:563-571.
[7] STEVENSC CR, BLAKE DR, MERRY P, et al. A comparative study by morphometry of the microvasculature in normal and rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1991;34(12):1508-1513.
[8] TOH WS, LAI RC, HUI JHP, et al. MSC Exosome as a Cell-free MSC Therapy for Cartilage Regeneration: Implications for Osteoarthritis Treatment. Semin Cel Dev Biol. 2017;67:56-64.
[9] ASHRAF S, MAPP PI, WALSH DA. Contributions of angiogenesis to inflammation, joint damage, and pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(9):2700-2710.
[10] BROWN R, WEISS J, TOMLINSON I, et al. Angiogenic factor from synovial fluid resembling that from tumours. Lancet. 1980;315(8170):682-685.
[11] HAYWOOD L, MCWILLIAMS DF, PEARSON CI, et al. Inflammation and angiogenesis in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(8):2173-2177.
[12] WALSH DA, BONNET CS, TURNER EL, et al. Angiogenesis in the synovium and at the osteochondral junction in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(7):743-751.
[13] ASHRAF S, WIBBERLEY H, MAPP PI, et al. Increased vascular penetration and nerve growth in the meniscus: a potential source of pain in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:523-529.
[14] WANG Y, XU J, ZHANG X, et al. TNF-α-induced LRG1 promotes angiogenesis and mesenchymal stem cell migration in the subchondral bone during osteoarthritis. Cell Death Disease. 2017;8(3):e2715.
[15] XIAO P, ZHU X, SUN J, et al. Cartilage tissue miR-214-3p regulates the TrkB/ShcB pathway paracrine VEGF to promote endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis. Bone. 2021;151:116034.
[16] BONDESON J, BLOM AB, WAINWRIGHT, et al. The role of synovial macrophages and macrophage‐produced mediators in driving inflammatory and destructive responses in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:647-657.
[17] PIROSA A, TANKUS EB, MAINARDI A, et al. Modeling In Vitro Osteoarthritis Phenotypes in a Vascularized Bone Model Based on a Bone-Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Cell Line and Endothelial Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:9581-9597.
[18] KO JY, LEE MS, LIAN WS, et al. MicroRNA-29a Counteracts Synovitis in Knee Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis by Targeting VEGF. Scientific Reports. 2017;7(1):3584.
[19] KONISTI S, KIRIAKIDIS S, PALEOLOG EM. Hypoxia--a key regulator of angiogenesis and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(3):153-162.
[20] ASHRAF S, WALSH DA. Angiogenesis in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2008;20(5):573-580.
[21] GOLDRING MB. Articular Cartilage Degradation in Osteoarthritis. Hss J. 2012;8(1):7-9.
[22] LI B, GUAN G, MEI L, et al. Pathological mechanism of chondrocytes and the surrounding environment during osteoarthritis of temporomandibular joint. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:4902-4911.
[23] HAMILTON JL, NAGAO M, LEVINE BR, et al. Targeting VEGF and Its Receptors for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis and Associated Pain. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(5):911-924.
[24] AKARAPHUTIPORN E, SUNAGA T, BWALYA EC, et al. In Insight into the Role of Apoptosis and Autophagy in Nitric Oxide-Induced Articular Chondrocyte Cell Death. Cartilage. 2021;13(2_suppl):826S-838S.
[25] HU Y, CHEN X, WANG S, et al. Subchondral bone microenvironment in osteoarthritis and pain. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):20.
[26] SURI S, GILL SE, MASSENAD CS, et al. Neurovascular invasion at the osteochondral junction and in osteophytes in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66(11):1423-1428.
[27] HE Y, SIEBUHR AS, BRANDT-HANSEN NU, et al. Type X collagen levels are elevated in serum from human osteoarthritis patients and associated with biomarkers of cartilage degradation and inflammation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:309.
[28] INTEMANN J, DE GORTER DJJ, NAYLOR AJ, et al. Importance of osteocyte-mediated regulation of bone remodelling in inflammatory bone disease. Swiss Med Wkly. 2020;150:w20187.
[29] WANG S, ZHOU C, ZHENG H, et al. Chondrogenic progenitor cells promote vascular endothelial growth factor expression through stromal-derived factor-1. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;25(5):742-749.
[30] MAPP PI, WALSH DA. Mechanisms and targets of angiogenesis and nerve growth in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8:390-398.
[31] ANDREWS S, RATTNER JB, ABUSARA Z, et al. Tie‐fibre structure and organization in the knee menisci. J Anatomy. 2014;224(5):531-537.
[32] JANSEN H, MEFFERT RH, BIRKENFELD F, et al. Detection of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in moderate osteoarthritis in a rabbit model. Ann Anat. 2012;194(5):452-456.
[33] SUGIMOTO M, KNODO M, KAMIMOTO Y, et al. Changes in VEGF-related factors are associated with presence of inflammatory factors in carbohydrate metabolism disorders during pregnancy. PloS one. 2019;14(8):e0220650.
[34] CYDZIK M, ABDUL-WAHID A, PARK S, et al. Slow binding kinetics of secreted protein, acidic, rich in cysteine-VEGF interaction limit VEGF activation of VEGF receptor 2 and attenuate angiogenesis. FASEB J. 2015;29(8):3493-3505.
[35] SU W, LIU G, LIU X, et al. Angiogenesis stimulated by elevated PDGF-BB in subchondral bone contributes to osteoarthritis development. JCI Insight. 2020;5(8):e135466.
[36] LIU SC, CHUANG SM, HSU CJ, et al. Ctgf increases vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent angiogenesis in human synovial fibroblasts by increasing mir-210 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5: e1485.
[37] LIN YM, HUANG YL, FONG YC, et al. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Increases Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A Production in Human Synovial Fibroblasts through c-Met Receptor Pathway. PLOS ONE. 2012; 7(11):es50924.
[38] ZHAO H, LIU S, MA C, et al. Estrogen-related receptor γ induces angio- genesis and extracellular matrix degradation of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis in rats. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1290.
[39] PESESSE L, SANCHEZ C, HENROTIN Y. Osteochondral plate angio- genesis: a new treatment target in osteoarthritis. Joint bone spine. 2011;78(2):144-149.
[40] HUANG EJ, REICHARDT LF. Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:677e736.
[41] MONTAGNOLI C, TIRIBUZI R, CRISPOLTONI L, et al. beta-NGF and beta-NGF receptor upregulation in blood and synovial fluid in osteoarthritis. Biol Chem. 2017;398:1045e54.
[42] WALSH DA, MCWILLIAMS DF, TURLEY MJ, et al. Angiogenesis and nerve growth factor at the osteochondral junction in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49:1852e61.
[43] XINNING, YIYING, TENGFEI, et al. NGF Increases FGF2 Expression and Promotes Endothelial Cell Migration and Tube Formation Through PI3K/Akt and ERK/MAPK Pathways in Human Chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis and cartilage,2018.
[44] KUO MH, LEE HF, TU YF, et al. Astaxanthin Ameliorates Ischemic-Hypoxic-Induced Neurotrophin Receptor p75 Upregulation in the Endothelial Cells of Neonatal Mouse Brains. Int J Mol Scie. 2019;20(24):6168.
[45] KALAMVOKI M, DU T, ROIZMAN B. Cells Infected with Herpes Simplex Virus 1 export to Uninfected Cells Exosomes Containing STING, Viral mRNAs, and microRNAs. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA. 2014; 111(46):E4991-E4996.
[46] KOWAL J, TKACH M, THÉRY C. Biogenesis and Secretion of Exosomes. Curr Opin Cel Biol. 2014;29:116-125.
[47] GUPTA SK, THUM T. Non-coding RNAs as Orchestrators of Autophagic Processes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016;95:26-30.
[48] KNOWLING S, MORRIS KV. Non-coding RNA and Antisense RNA. Nature’s Trash or Treasure? Biochimie. 2011;93(11):1922-1927.
[49] XIE W, SU W, XIA H, et al. Synovial Fluid MicroRNA-210 as a Potential Biomarker for Early Prediction of Osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2019; 2019:1-4.
[50] WEI S, XIE W, SHANG Q, et al. The Long Noncoding RNA MEG3 Is Downregulated and Inversely Associated with VEGF Levels in Osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:356893.
[51] KIM HA, SEO KH, KANG YR, et al. Mechanisms of platelet-activating factor-induced enhancement of VEGF expression. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;27(1):55-62.
[52] ZHANG Y, WU J, JING H, et al. Long noncoding RNA MEG3 inhibits breast cancer growth via upregulating endoplasmic reticulum stress and activating NF‐κB and p53. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(4):6789-6797.
[53] HE P, ZHANG Z, HUANG G, et al. miR-141 modulates osteoblastic cell proliferation by regulating the tar-get gene of lncRNA H19 and lncRNA H19-derived miR-675. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8:1780.
[54] ZHOU L, WAN Y, CHENG Q, et al. The Expression and Diagnostic Value of LncRNA H19 in the Blood of Patients with Osteoarthritis. Iran J Public Health. 2020;49(8):1494-1501.
[55] BEHERA J, KUMAR A, VOOR MJ, et al. Exosomal lncRNA-H19 Promotes Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis through Mediating Angpt1/Tie2-NO Signaling in CBS-Heterozygous Mice. Theranostics. 2021;11(16): 7715-7734.
[56] BORNSTEIN P. Thrombospondins function as regulators of angiogenesis. J Cell Commun Signal. 2009;3(3-4):189-200.
[57] GELSE K, KLINGER P, KOCH M, et al. Thrombospondin-1 prevents excessive ossification in cartilage repair tissue induced by osteogenic protein-1. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(15-16):2101-2112.
[58] ARICO-MUENDEL CC, BELANGER B, BENJAMIN D, et al. Metabolites of PPI-2458, a Selective, Irreversible Inhibitor of Methionine Aminopeptidase-2: Structure Determination and In Vivo Activity. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013;41(4):814-826.
[59] LI B, CHEN KC, QIAN ND, et al. Baicalein alleviates osteoarthritis by protecting subchondral bone, inhibiting angiogenesis and synovial proliferation. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(11):5283-5294.
[60] XIONG G, YANG Y, GUO M. Effect of resveratrol on abnormal bone remodeling and angiogenesis of subchondral bone in osteoarthritis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2021;14(4):417-425.
[61] VADALA G, AMBROSIO L, CATTANI C, et al. Bevacizumab Arrests Osteoarthritis Progression in a Rabbit Model: A Dose-Escalation Study. J Clin Med. 2021;10(13):2825.
[62] NAGAI T, SATO M, KOBAYASHI M, et al. Bevacizumab, an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody, inhibits osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(5):427.
[63] LI W, LIN J, WANG Z, et al. Bevacizumab tested for treatment of knee osteoarthritis via inhibition of synovial vascular hyperplasia in rabbits. J Orthop Translat. 2019;19:38-46.
[64] REMON J, GAZZAH A, BESSE B, et al. Crizotinib improves osteoarthritis symptoms in a ROS1-fusion advanced non-small cell lung cancer patient. J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10(8):e72-e73.
[65] MIFUNE Y, MATSUMOTO T, TAKAYAMA K, et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on the regenerative therapy of muscle derived stem cells for articular cartilage repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):175-185.
[66] LI MY, NIE Y, ZENG Y, et al. Does Bisphosphonate Increase the Sclerosis of Tibial Subchondral Bone in the Progression of Knee Osteoarthritis-A Propensity Score Matching Cohort Study Based on Osteoarthritis Initiative. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:781219.
[67] FERNÁNDEZ-MARTÍN S, LÓPEZ-PEÑA M, MUÑOZ F, et al. Bisphosphonates as disease-modifying drugs in osteoarthritis preclinical studies: a systematic review from 2000 to 2020. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23:60.
[68] MOBASHERI A, HENROTIN Y, BIESALSKI HK, et al. Scientific Evidence and Rationale for the Development of Curcumin and Resveratrol as Nutraceutricals for Joint Health. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(4):4202-4232.
[69] LI Y, MU W, XU B, et al. Artesunate, an Anti-Malaria Agent, Attenuates Experimental Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Bone Resorption and CD31hiEmcnhi Vessel Formation in Subchondral Bone. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:685.
[70] WANG YJ, CUI J, GU ZG, et al. Betaine Attenuates Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Osteoclastogenesis and Angiogenesis in Subchondral Bone. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12.
[71] BINGÜL İ, BAŞARAN-KÜÇÜKGERGIN C, AYDIN AF, et al. Betaine Treatment Decreased Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Stellate Cell Activation in Rats with Alcoholic Liver Fibrosis. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016;45:170-178.
[72] GE CX, YU R, XU MX, et al. Betaine Prevented Fructose-Induced NAFLD by Regulating LXRα/PPARα Pathway and Alleviating ER Stress in Rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;770:154-164.
[73] XIA Y, CHEN S, ZHU G, et al. Betaine Inhibits Interleukin-1β Production and Release: Potential Mechanisms. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2670.
[74] PRASADAM I, AKUIEN A, FRIIS TE, et al. Mixed cell therapy of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and articular cartilage chondrocytes ameliorates osteoarthritis development. Lab Invest. 2018;98:106-116.
|