[1] HUI S, GHERGUROVICH JM, MORSCHER RJ, et al. Glucose feeds the TCA cycle via circulating lactate. Nature. 2017;551(7678):115-118.
[2] 王杨文洁,张缨.运动与骨骼肌单羧酸转运蛋白1和4研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2020,39(10):820-824.
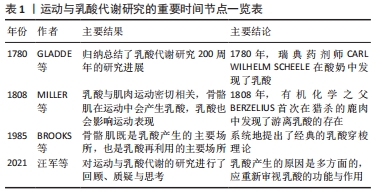
[3] GLADDEN LB. 200th anniversary of lactate research in muscle. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2008;36(3):109-115.
[4] MILLER BF, FATTOR JA, JACOBS KA, et al. Lactate and glucose interactions during rest and exercise in men: effect of exogenous lactate infusion. J Physiol. 2002;544(3):963-975.
[5] BROOKS GA. Lactate: link between glycolytic and oxidative metabolism. Sports Med. 2007;37(4-5):341-343.
[6] BROOKS GA. Glycolytic end product and oxidative substrate during sustained exercise in mammals–the “lactate shuttle”. Berlin: Springer-Verlag,1985.
[7] 汪军,周越,孙君志,等.质疑与思考:运动生理学研究的十个问题[J].成都体育学院学报,2021,47(1):118-124.
[8] BENEKE R. Anaerobic threshold, individual anaerobic threshold, and maximal lactate steady state in rowing. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1995; 27(6):863-867.
[9] PROMPHET N, RATTANAWALEEDIROJN P, SIRALERTMUKUL K, et al. Non-invasive textile based colorimetric sensor for the simultaneous detection of sweat pH and lactate. Talanta. 2019;192:424-430.
[10] JIA W, BANDODKAR AJ, VALDÉS-RAMÍREZ G, et al. Electrochemical tattoo biosensors for real-time noninvasive lactate monitoring in human perspiration. Anal Chem. 2013;85(14):6553-6560.
[11] MICHAEL G. Eat, Move, Sleep, Repeat. Meyer & Meyer Sport. 2020.
[12] 谢东山.乳酸代谢与乳酸穿梭理论发展[J].生物化工,2019,5(6): 135-141.
[13] 许豪文.运动生物化学概论[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2001:98-99.
[14] Fletcher WM. Lactic acid in amphibian muscle. J Physiol. 1907;35(4): 247-309.
[15] 苏炳添,李健良,徐慧华,等.科学训练辅助:柔性可穿戴传感器运动监测应用[J].中国科学:信息科学,2022,52(1):54-74.
[16] 杨锡让.实用运动生理学[M].北京:北京体育大学出版社,2007: 146-148.
[17] 杨锡让,傅浩坚.运动生理学进展——质疑与思考[M].北京:北京体育大学出版社,2000:315-316.
[18] 黎涌明,纪晓楠,资薇.人体运动的本质[J].体育科学,2014,34(2): 11-17.
[19] 孔凡明,米靖,马杰.能量保护模式的概念释义、作用机制与训练启示[J].北京体育大学学报,2021,44(10):90-99.
[20] 运动生物化学编写组.运动生物化学[M].北京:北京体育大学出版社,2013:65-66.
[21] JÖBSIS FF, STAINSBY WN. Oxidation of NADH during contractions of circulated mammalian skeletal muscle. Respir Physiol. 1968;4(3):292-300.
[22] CONNETT RJ, GAYESKI TE, HONIG CR. Lactate accumulation in fully aerobic, working, dog gracilis muscle. Am J Physiol. 1984;246(1 Pt 2):H120-128.
[23] 田麦久,刘大庆.运动训练学[M].北京:人民体育出版社,2012: 42-45.
[24] 翁锡全.运动训练生物化学[M].广东:广东高等教育出版社,2016: 28-30.
[25] 张爱芳.实用运动生物化学[M].北京:北京体育大学出版社,2005: 54-63.
[26] BISHOP D. Physiological predictors of flat-water kayak performance in women. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2000;82(1-2):91-97.
[27] BRAND K, AICHINGER S, FORSTER S, et al. Cell-cycle-related metabolic and enzymatic events in proliferating rat thymocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1988;172(3):695-702.
[28] FERGUSON B. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription 9th Ed.J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2014;58(3):328.
[29] 运动医学名词审定分委员会.运动医学名词[M].北京:科学出版社,2019:40-41.
[30] MADER A. Zur Beurteilung der sportartspezifischen Ausdauerleistungsfähigkeit im Labor. Sportarzt und Sportmedizin. 1976;27(4): S80-88.
[31] 冯连世,冯美云,冯炜权,等.优秀运动员身体机能评定方法[M].北京:人民体育出版社,2003:104-117.
[32] 张恒.应用生物化学[M].江苏:南京大学出版社,2017:203-207.
[33] BROOKS GA. The tortuous path of lactate shuttle discovery: From cinders and boards to the lab and ICU. J Sport Health Sci. 2020;9(5): 446-460.
[34] HODGETTS V, COPPACK SW, FRAYN KN, et al. Factors controlling fat mobilization from human subcutaneous adipose tissue during exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1991;71(2):445-451.
[35] BROOKS GA. The Science and Translation of Lactate Shuttle Theory. Cell Metab. 2018;27(4):757-785.
[36] GLANCY B, KANE DA, KAVAZIS AN, et al. Mitochondrial lactate metabolism: history and implications for exercise and disease. J Physiol. 2021;599(3):863-888.
[37] 严亨秀,盘强文.整合应用生理学[M].北京:科学出版社,2021: 164-168.
[38] STEFFENS L, PETTINATO E, STEINER TM, et al. High CO2 levels drive the TCA cycle backwards towards autotrophy. Nature. 2021;592(7856): 784-788.
[39] 查锡良,周春燕.生物化学[M].7版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2011: 224-226.
[40] BONEN A, BELCASTRO AN. Comparison of self-selected recovery methods on lactic acid removal rates. Med Sci Sports. 1976;8(3):176-178.
[41] DE LA CRUZ-LÓPEZ KG, CASTRO-MUÑOZ LJ, REYES-HERNÁNDEZ DO, et al. Lactate in the Regulation of Tumor Microenvironment and Therapeutic Approaches. Front Oncol. 2019;9:1143.
[42] WANG J, CUI Y, YU Z, et al. Brain Endothelial Cells Maintain Lactate Homeostasis and Control Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Cell Stem Cell. 2019;25(6):754-767.e9.
[43] XU K, YIN N, PENG M, et al. Glycolysis fuels phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling to bolster T cell immunity. Science. 2021;371(6527):405-410.
[44] 魏文哲,孙科,赵之光,等.模拟全程马拉松跑过程中能量代谢的变化[J].中国体育科技,2020,56(6):3-8.
[45] THOMAS C, BISHOP DJ, LAMBERT K, et al. Effects of acute and chronic exercise on sarcolemmal MCT1 and MCT4 contents in human skeletal muscles: current status. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012; 302(1):R1-14.
[46] BENTON CR, YOSHIDA Y, LALLY J, et al. PGC-1alpha increases skeletal muscle lactate uptake by increasing the expression of MCT1 but not MCT2 or MCT4. Physiol Genomics. 2008;35(1):45-54.
[47] SCHEIMAN J, LUBER JM, CHAVKIN TA, et al. Meta-omics analysis of elite athletes identifies a performance-enhancing microbe that functions via lactate metabolism. Nat Med. 2019;25(7):1104-1109.
[48] 孙景权,严翊,叶建平,等.乳酸/GPR81信号通路调节脂肪酸利用的研究进展[J].北京体育大学学报,2016,39(10):71-75.
[49] FERGUSON BS, ROGATZKI MJ, GOODWIN ML, et al. Lactate metabolism: historical context, prior misinterpretations, and current understanding. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018;118(4):691-728.
[50] OLIVER SG, WINSON MK, KELL DB, et al. Systematic functional analysis of the yeast genome. Trends Biotechnol. 1998;16(9):373-378.
|