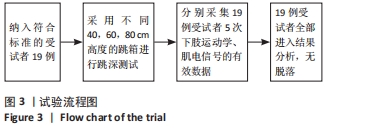
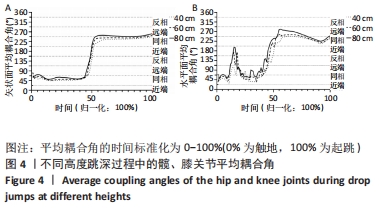
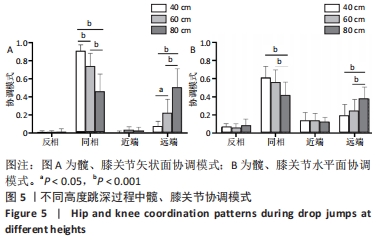
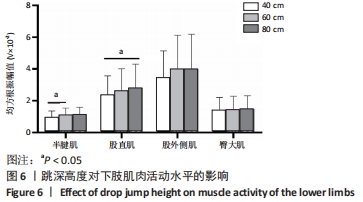
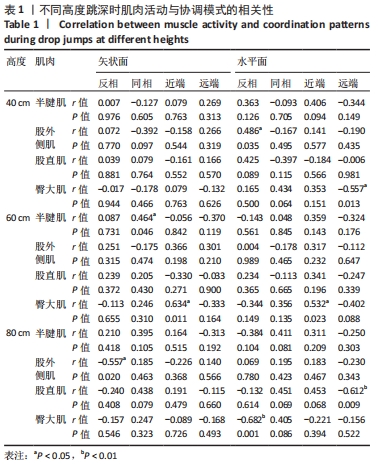
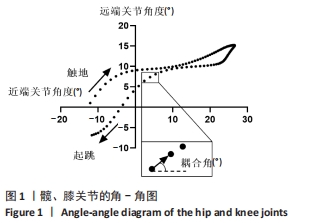
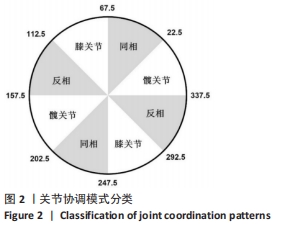
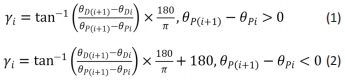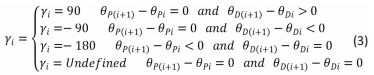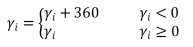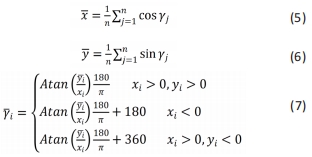[1] MAH CD, SPARKS AJ, SAMAAN MA, et al. Sleep restriction impairs maximal jump performance and joint coordination in elite athletes. J Sports Sci. 2019;37(17):1981-1988.
[2] KIRKENDALL DT, GARRETT WE JR. The anterior cruciate ligament enigma. Injury mechanisms and prevention. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;37(2):64-68.
[3] HOOTMAN JM, DICK R, AGEL J. Epidemiology of Collegiate Injuries for 15 Sports: Summary and Recommendations for Injury Prevention Initiatives. J Athl Train. 2007;42(2):311-319.
[4] DEVITA P, SKELLY WA. Effect of landing stiffness on joint kinetics and energetics in the lower extremity. / Effet de la raideur de la reception sur la cinetique et l’ energetique des membres inferieurs. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1992;24(1):108-115.
[5] YU B, GARRETT WE. Mechanisms of non-contact ACL injuries. Br J Sports Med. 2007;41 Suppl 1:i47-51.
[6] DICESARE CA, MONTALVO A, FOSS KDB, et al. Sport Specialization and Coordination Differences in Multisport Adolescent Female Basketball, Soccer, and Volleyball Athletes. J Athl Train. 2019;54(10):1105-1114.
[7] SINSURIN K, VACHALATHITI R, SRISANGBORIBOON S, et al. Knee joint coordination during single-leg landing in different directions. Sports Biomech. 2020;19(5):652-664.
[8] SCHOLZ JP. Dynamic pattern theory--some implications for therapeutics. Phys Ther. 1990;70(12):827-843.
[9] CHANG R, VAN EMMERIK R, HAMILL J. Quantifying rearfoot-forefoot coordination in human walking. J Biomech. 2008;41(14):3101-3105.
[10] NEEDHAM R, NAEMI R, CHOCKALINGAM N. Quantifying lumbar-pelvis coordination during gait using a modified vector coding technique. J Biomech. 2014;47(5):1020-1026.
[11] AKUZAWA H, IMAI A, IIZUKA S, et al. Contribution of the tibialis posterior and peroneus longus to inter-segment coordination of the foot during single-leg drop jump. Sports Biomech. 2020;1-14. doi: 10.1080/14763141.2020.1806347.
[12] 井兰香, 刘宇. 不同高度跳深动力学及下肢肌肉预激活调节[J]. 体育科学,2012,32(11):64-69.
[13] SCHUSTER RW, PATERNOSTER FK, SEIBERL W. High-density electromyographic assessment of stretch reflex activity during drop jumps from varying drop heights. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2020;50: 102375.
[14] RAGHAVA NEELAPALA YV, BHAGAT M, SHAH P. Hip Muscle Strengthening for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review of Literature. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2020;43(2):89-98.
[15] ARNOLD AS, DELP SL. Rotational moment arms of the medial hamstrings and adductors vary with femoral geometry and limb position: implications for the treatment of internally rotated gait. J Biomech. 2001;34(4):437-447.
[16] 田进, 周家颖. 跳深着地阶段下肢所测肌肉的表面肌电活动特征研究[J]. 西安体育学院学报,2009,26(3):341-346.
[17] 臧宇, 许贻林, 殷飞, 等. 落地高度对高水平短跑运动员跳深动作下肢生物力学和反应性力量的影响[J]. 体育与科学,2019,40(6): 101-110.
[18] PENG HT. Changes in biomechanical properties during drop jumps of incremental height. J Strength Cond Res. 2011;25(9):2510-2518.
[19] HAMILL J, HADDAD JM, MCDERMOTT WJ. Issues in quantifying Variability From a Dynamical Systems Perspective. J App Biomech. 2000;16(4):407-418.
[20] BUTTON C, WHEAT J, LAMB P. Why coordination dynamics is relevant for studying sport performance. Complex Syst Sport. 2014:44-61.
[21] YEOW CH, LEE PV, GOH JC. Sagittal knee joint kinematics and energetics in response to different landing heights and techniques. Knee. 2010; 17(2):127-131.
[22] DI GIMINIANI R, GIOVANNELLI A, CAPUANO L, et al. Neuromuscular Strategies in Stretch-Shortening Exercises with Increasing Drop Heights: The Role of Muscle Coactivation in Leg Stiffness and Power Propulsion. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(22):8647.
[23] TAUBE W, LEUKEL C, LAUBER B, et al. The drop height determines neuromuscular adaptations and changes in jump performance in stretch-shortening cycle training. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2012;22(5): 671-683.
[24] RUIZ-CARDENAS JD, RODRIGUEZ-JUAN JJ, RIOS-DIAZ J. Relationship between jumping abilities and skeletal muscle architecture of lower limbs in humans: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Mov Sci. 2018;58:10-20.
[25] PENG HT, KERNOZEK TW, SONG CY. Quadricep and hamstring activation during drop jumps with changes in drop height. Phys Ther Sport. 2011; 12(3):127-132.
[26] MRDAKOVIC V, ILIC DB, JANKOVIC N, et al. Pre-activity modulation of lower extremity muscles within different types and heights of deep jump. J Sports Sci Med. 2008;7(2):269-278.
[27] KOULOURIS G, CONNELL D. Hamstring muscle complex: an imaging review. Radiographics. 2005;25(3):571-586.
[28] BOURNE MN, TIMMINS RG, OPAR DA, et al. An Evidence-Based Framework for Strengthening Exercises to Prevent Hamstring Injury. Sports Med. 2018;48(2):251-267.
[29] ARNER JW, MCCLINCY MP, BRADLEY JP. Hamstring Injuries in Athletes: Evidence-based Treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27(23):868-877.
[30] THELEN DG, CHUMANOV ES, HOERTH DM, et al. Hamstring muscle kinematics during treadmill sprinting. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005;37(1): 108-114.
[31] LLOYD DG, BUCHANAN TS. Strategies of muscular support of varus and valgus isometric loads at the human knee. J Biomech. 2001;34(10): 1257-1267.
[32] KARLSSON E, JONSSON B. Function of the Gluteus Maximus Muscle. An Electromyographic Study. Acta Morphol Neerl Scand. 1965;6:161-169.
[33] WALSH M, BOLING MC, MCGRATH M, et al. Lower extremity muscle activation and knee flexion during a jump-landing task. J Athl Train. 2012;47(4):406-413.
[34] STEARNS KM, KEIM RG, POWERS CM. Influence of relative hip and knee extensor muscle strength on landing biomechanics. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2013;45(5):935-941.
[35] TOUMI H, POUMARAT G, BENJAMIN M, et al. New insights into the function of the vastus medialis with clinical implications. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39(7):1153-1159.
[36] HERB CC, CHINN L, HERTEL J. Altering Shank-Rear-Foot Joint Coupling During Gait With Ankle Taping in Patients With Chronic Ankle Instability and Healthy Controls. J Sport Rehabil. 2016;25(1):13-22.
[37] 杨文燕. 基于矢量编码技术对不同步行速度下肢协调模式的量化分析[D]. 太原:中北大学,2019.
[38] 马玉丹, 温朝晖, 具中山, 等. 基于惯性测量单元的女子速度滑冰运动员下肢运动协调特征研究 [J]. 北京体育大学学报,2021,44(12): 98-109.
|