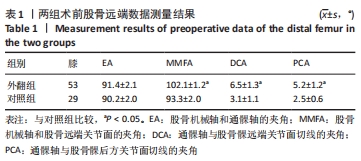
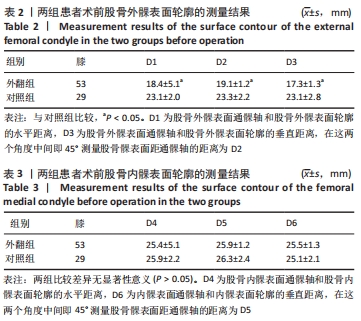
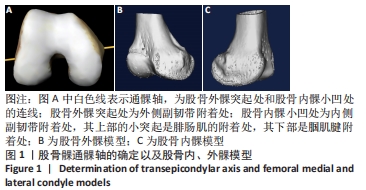
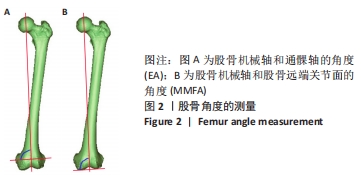
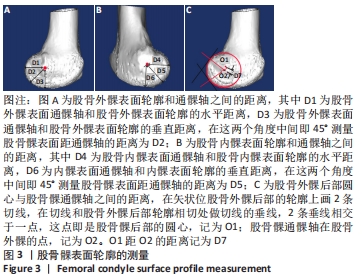
[1] TIAN F, ZANG XH, SUN YS. Impact of knee varus and valgus deformity on alignment in lower extremities after total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(1 Suppl):83-89.
[2] ZAMPOGNA B, VASTA S, PAPALIA R. Patient Evaluation and Indications for Osteotomy Around the Knee. Clin Sports Med. 2019;38(3):305-315.
[3] SANTOSO MB, WU L. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty, is it superior to high tibial osteotomy in treating unicompartmental osteoarthritis? A meta-analysis and systemic review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):50-56.
[4] SHEN Z, WANG H, DUAN Y, et al. Application of 3D printed osteotomy guide plate-assisted total knee arthroplasty in treatment of valgus knee deformity. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):327-332.
[5] MANCINO F, FALEZ F, MOCINI F, et al. Is varus-valgus constraint a reliable option in complex primary total knee arthroplasty? A systematic review. J Orthop. 2021;24:201-211.
[6] RAUT V, MATAR HE, SINGH A. Satisfactory medium-term outcomes with lateral condylar sliver osteotomy to correct valgus deformity in total knee replacements. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(5): 1394-1399.
[7] LOBENHOFFER P. The Rationale of Osteotomy around the Knee. J Knee Surg. 2017;30(5):386-392.
[8] STANNARD JT, STANNARD JP. High Tibial Osteotomy following Biologic Replacement of the Knee. J Knee Surg. 2017;30(8):764-768.
[9] MA QL, LIPMAN JD, CHENG CK, et al. A Comparison Between Chinese and Caucasian 3-Dimensional Bony Morphometry in Presimulated and Postsimulated Osteotomy for Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9):2878-2886.
[10] KIM TK, PHILLIPS M, BHANDARI M, et al. What Differences in Morphologic Features of the Knee Exist Among Patients of Various Races? A Systematic Review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(1):170-182.
[11] ALESI D, MEENA A, FRATINI S, et al. Total knee arthroplasty in valgus knee deformity: is it still a challenge in 2021? Musculoskelet Surg. 2021 Feb 15. doi: 10.1007/s12306-021-00695-x. Online ahead of print.
[12] 袁景,甄平,宋焱峰,等.膝外翻畸形全膝关节置换的假体匹配:三维模型数字化测量与分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(17): 2768-2774.
[13] HIRSCHMANN MT, MOSER LB, AMSLER F, et al. Phenotyping the knee in young non-osteoarthritic knees shows a wide distribution of femoral and tibial coronal alignment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(5):1385-1393.
[14] BONNIN M. Rotation of components in total knee arthroplasty//BONNIN M, AMENDOLA A, BELLEMANS J, et al. The Knee Joint. Paris: Springer, 2012:797-807.
[15] 高嘉翔,林剑浩,李志昌.股骨后髁偏心距在全膝关节置换术中的意义[J].中华关节外科杂志,2019,13(4):461-465.
[16] LIN YH, CHANG FS, CHEN KH, et al. Mismatch between femur and tibia coronal alignment in the knee joint: classification of five lower limb types according to femoral and tibial mechanical alignment. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):411-416.
[17] 陈文昊,周一新,刘文革.外翻膝骨性结构的形态学及分型研究[J].福建医科大学学报,2013,47(1):39-45.
[18] COHEN DA, GURSEL AC, LOW AK. How coronal alignment affects distal femoral anatomy: an MRI-based comparison of varus and valgus knees. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):92-96.
[19] 张宝,许建中,李广恒,等.膝关节置换股骨髁前后径与内外径测量的临床意义[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(2):145-148.
[20] KEREMU A, MIJITI N, MIJITI S, et al. Evaluation of the application value of a three-dimensional digital model of the knee in clinical practice. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(5):300060519889742.
[21] CHANG CM, WU WT, LIU KL, et al. An anatomical study of the proximal aspect of the medial femoral condyle to define the proximal-distal condylar length. Ci Ji Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017;29(2):104-108.
[22] XIE X, ZHAN Y, DONG M, et al. Two and Three-Dimensional CT Mapping of Hoffa Fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(21):1866-1874.
[23] CONFALONIERI N, BIAZZO A. Computer-assisted surgery in total knee replacement: advantages, surgical procedure and review of the literature. Acta Biomed. 2019;90(1):16-23.
[24] TWIGGS JG, DICKISON DM, KOLOS EC, et al. Patient Variation Limits Use of Fixed References for Femoral Rotation Component Alignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(1):67-74.
[25] NG CK, CHEN JY, YEH JZY, et al. Distal Femoral Rotation Correlates With Proximal Tibial Joint Line Obliquity: A Consideration for Kinematic Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(6):1936-1944.
[26] FRANCESCHINI V, NODZO SR, GONZALEZ DELLA VALLE A. Femoral Component Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Comparison Between Transepicondylar Axis and Posterior Condylar Line Referencing. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(12):2917-2921.
[27] MANNAN A, SMITH TO. Favourable rotational alignment outcomes in PSI knee arthroplasty: A Level 1 systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee. 2016;23(2):186-190.
[28] DU Z, CHEN S, YAN M, et al. Do size, shape, and alignment parameters of the femoral condyle affect the trochlear groove tracking? A morphometric study based on 3D- computed tomography models in Chinese people. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):4-10.
[29] FITZ DW, JOHNSON DJ, HARTWELL MJ, et al. Relationship of the Posterior Condylar Line and the Transepicondylar Axis: A CT-Based Evaluation. J Knee Surg. 2020;33(7):673-677.
[30] OLMEDO-GARCIA NI, MARTÍNEZ VERGARA JL, APARICI MIRALLES TL, et al. Assessment of magnification of digital radiographs in total HIP arthroplasty. J Orthop. 2018;15(4):931-934.
[31] ZHANG Z, LIU M, WEN X, et al. The relationship between the posterior tibial slope and the sagittal femoral condylar shape: Two circles and ellipses. Clin Anat. 2020;33(7):1075-1081.
[32] WANG G, LIU M, ZHANG Z, et al. A simplified relationship between the femoral trochlea and the femoral condyle: A sagittal MRI analysis by an ellipse-fitting approach. Clin Anat. 2020;33(4):500-506.
[33] GRAMMENS J, VAN HAVER A, DANCKAERS F, et al. Small medial femoral condyle morphotype is associated with medial compartment degeneration and distinct morphological characteristics: a comparative pilot study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(6):1777-1789.
[34] EHMKE T, AGHAZADEH M, BONO OJ, et al. Anthropometric Measures of the Posterior Condyles: Gender Differences and Correlation to Implant Sizing. J Knee Surg. 2019;6(11):23-31.
[35] BONNIN MP, SAFFARINI M, NOVER L, et al. External rotation of the femoral component increases asymmetry of the posterior condyles. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(7):894-903.
[36] OU YL, LI PY, XIA H. Optimal Sagittal Insertion Depth and Direction of Femoral Intramedullary Rod in Total Knee Arthroplasty in Chinese Osteoarthritis Patients. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(4):1238-1244.
[37] LANGE J, HAAS SB. Correcting severe valgus deformity: taking out the knock. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(1 Supple A):60-64.
[38] GHOSH SK. Cadaveric dissection as an educational tool for anatomical sciences in the 21st century. Anat Sci Educ. 2017;10(3):286-299.
[39] MORO C, ŠTROMBERGA Z, RAIKOS A, et al. The effectiveness of virtual and augmented reality in health sciences and medical anatomy. Anat Sci Educ. 2017;10(6):549-559.
|